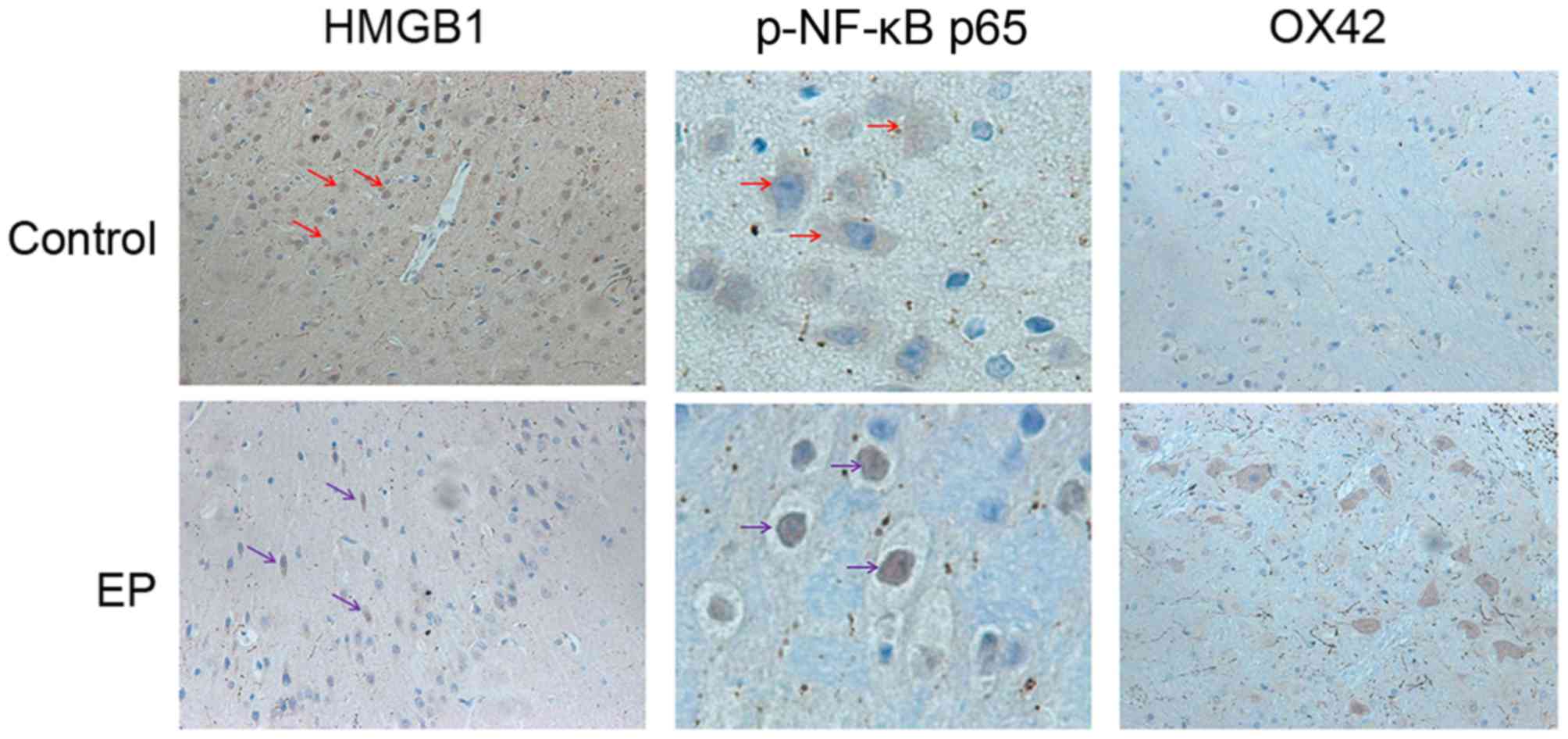
|
1
|
Snoeijen-Schouwenaars FM, van Ool JS, Tan
IY, Schelhaas HJ and Majoie MH: Evaluation of perampanel in
patients with intellectual disability and epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav.
66:64–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gavvala JR and Schuele SU: New-onset
seizure in adults and adolescents: A review. JAMA. 316:2657–2668.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pohlmann-Eden B, Aldenkamp A, Baker GA,
Brandt C, Cendes F, Coras R, Crocker CE, Helmstaedter C,
Jones-Gotman M, Kanner AM, et al: The relevance of neuropsychiatric
symptoms and cognitive problems in new-onset epilepsy-Current
knowledge and understanding. Epilepsy Behav. 51:199–209. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Singh T and Goel RK: Managing
epilepsy-associated depression: Serotonin enhancers or serotonin
producers? Epilepsy Behav. 66:93–99. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jehi LE, Palmini A, Aryal U, Coras R and
Paglioli E: Cerebral cavernous malformations in the setting of
focal epilepsies: Pathological findings, clinical characteristics
and surgical treatment principles. Acta Neuropathol. 128:55–65.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zubkov S and Friedman D: Epilepsy
treatment and creativity. Epilepsy Behav. 57:230–233. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Prontera P, Sarchielli P, Caproni S,
Bedetti C, Cupini LM, Calabresi P and Costa C: Epilepsy in
hemiplegic migraine: Genetic mutations and clinical implications.
Cephalalgia. 2017.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang C, Ding H, Tang X, Li Z and Gan L:
Liuweibuqi capsules suppress inflammation by affecting T cell
polarization and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Med Chem Res. 26:2816–2823. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Okuneva O, Li Z, Körber I, Tegelberg S,
Joensuu T, Tian L and Lehesjoki AE: Brain inflammation is
accompanied by peripheral inflammation in Cstb-/-mice, a model for
progressive myoclonus epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation. 13:2982016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Benson MJ, Thomas NK, Talwar S, Hodson MP,
Lynch JW, Woodruff TM and Borges K: A novel anticonvulsant
mechanism via inhibition of complement receptor C5ar1 in murine
epilepsy models. Neurobiol Dis. 76:87–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alyu F and Dikmen M: Inflammatory aspects
of epileptogenesis: Contribution of molecular inflammatory
mechanisms. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 29:1–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dambach H, Hinkerohe D, Prochnow N,
Stienen MN, Moinfar Z, Haase CG, Hufnagel A and Faustmann PM: Glia
and epilepsy: Experimental investigation of antiepileptic drugs in
an astroglia/microglia co-culture model of inflammation. Epilepsia.
55:184–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patterson KP, Brennan GP, Curran M,
Kinney-Lang E, Dubé C, Rashid F, Ly C, Obenaus A and Baram TZ:
Rapid, coordinate inflammatory responses after experimental febrile
status epilepticus: Implications for epileptogenesis. eNeuro.
2:2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
von Bernhardi R, Eugenín-von Bernhardi J,
Flores B and Eugenín León J: Glial cells and integrity of the
nervous system. Adv Exp Med Biol. 949:1–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Papageorgiou IE, Fetani AF, Lewen A,
Heinemann U and Kann O: Widespread activation of microglial cells
in the hippocampus of chronic epileptic rats correlates only
partially with neurodegeneration. Brain Struct Funct.
220:2423–2439. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo C, Ikegaya Y and Koyama R: Microglia
and neurogenesis in the epileptic dentate gyrus. Neurogenesis
(Austin). 3:e12355252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Najjar S, Pearlman D, Miller DC and
Devinsky O: Refractory epilepsy associated with microglial
activation. Neurologist. 17:249–254. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mazarati A, Maroso M, Iori V, Vezzani A
and Carli M: High-mobility group box-1 impairs memory in mice
through both toll-like receptor 4 and receptor for advanced
glycation end products. Exp Neurol. 232:143–148. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Xia J, Zhang Y, Xiao F, Wang J,
Gao H, Liu Y, Rong S, Yao Y, Xu G and Li J: HMGB1-TLR4 signaling
participates in renal ischemia reperfusion injury and could be
attenuated by dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of the ERK/NF-κB
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:4054–4067. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Jin Q, Yao Q, Xu B, Li Z and Tu C:
Quercetin attenuates the activation of hepatic stellate cells and
liver fibrosis in mice through modulation of HMGB1-TLR2/4-NF-κB
signaling pathways. Toxicol Lett. 261:1–12. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zurolo E, Iyer A, Maroso M, Carbonell C,
Anink JJ, Ravizza T, Fluiter K, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Vezzani A
and Aronica E: Activation of Toll-like receptor, RAGE and HMGB1
signalling in malformations of cortical development. Brain.
134:1015–1032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maroso M, Balosso S, Ravizza T, Liu J,
Bianchi ME and Vezzani A: Interleukin-1 type 1 receptor/Toll-like
receptor signalling in epilepsy: The importance of IL-1beta and
high-mobility group box 1. J Intern Med. 270:319–326. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Huang XJ, Yu N, Xie Y, Zhang K,
Wen F, Liu H and Di Q: HMGB1 contributes to the expression of
P-glycoprotein in mouse epileptic brain through toll-like receptor
4 and receptor for advanced glycation end products. PLoS One.
10:e01409182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ratovitski T, Chaerkady R, Kammers K,
Stewart JC, Zavala A, Pletnikova O, Troncoso JC, Rudnicki DD,
Margolis RL, Cole RN and Ross CA: Quantitative proteomic analysis
reveals similarities between huntington's disease (HD) and
huntington's disease-like 2 (HDL2) human brains. J Proteome Res.
15:3266–3283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smith AM, Gibbons HM, Oldfield RL, Bergin
PM, Mee EW, Curtis MA, Faull RL and Dragunow M: M-CSF increases
proliferation and phagocytosis while modulating receptor and
transcription factor expression in adult human microglia. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Delahaye-Duriez A, Srivastava P, Shkura K,
Langley SR, Laaniste L, Moreno-Moral A, Danis B, Mazzuferi M,
Foerch P, Gazina EV, et al: Rare and common epilepsies converge on
a shared gene regulatory network providing opportunities for novel
antiepileptic drug discovery. Genome Biol. 17:2452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mameniskiene R and Wolf P: Epilepsia
partialis continua: A review. Seizure. 44:74–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ertürk Çetin Ö, İşler C, Uzan M and Özkara
Ç: Epilepsy-related brain tumors. Seizure. 44:93–97. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Falco-Walter J, Owen C, Sharma M, Reggi C,
Yu M, Stoub TR and Stein MA: Magnetoencephalography and new imaging
modalities in epilepsy. Neurotherapeutics. 14:4–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Loscher W, Hirsch LJ and Schmidt D: The
enigma of the latent period in the development of symptomatic
acquired epilepsy-Traditional view versus new concepts. Epilepsy
Behav. 52:78–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang I, Alizadeh D, Liang J, Zhang L, Gao
H, Song Y, Ren H, Ouyang M, Wu X, D'Apuzzo M and Badie B:
Characterization of arginase expression in glioma-associated
microglia and macrophages. PLoS One. 11:e01651182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Eyo UB, Murugan M and Wu LJ:
Microglia-neuron communication in epilepsy. Glia. 65:5–18. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luan G, Gao Q, Zhai F, Chen Y and Li T:
Upregulation of HMGB1, toll-like receptor and RAGE in human
Rasmussen's encephalitis. Epilepsy Res. 123:36–49. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iori V, Maroso M, Rizzi M, Iyer AM,
Vertemara R, Carli M, Agresti A, Antonelli A, Bianchi ME, Aronica
E, et al: Receptor for advanced glycation endproducts is
upregulated in temporal lobe epilepsy and contributes to
experimental seizures. Neurobiol Dis. 58:102–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Beijnum JR, Buurman WA and Griffioen
AW: Convergence and amplification of toll-like receptor (TLR) and
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) signaling
pathways via high mobility group B1 (HMGB1). Angiogenesis.
11:91–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang Z, Zhong Z, Zhang L, Wang X, Xu R,
Zhu L, Wang Z, Hu S and Zhao X: Down-regulation of HMGB1 expression
by shRNA constructs inhibits the bioactivity of urothelial
carcinoma cell lines via the NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 5:128072015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|