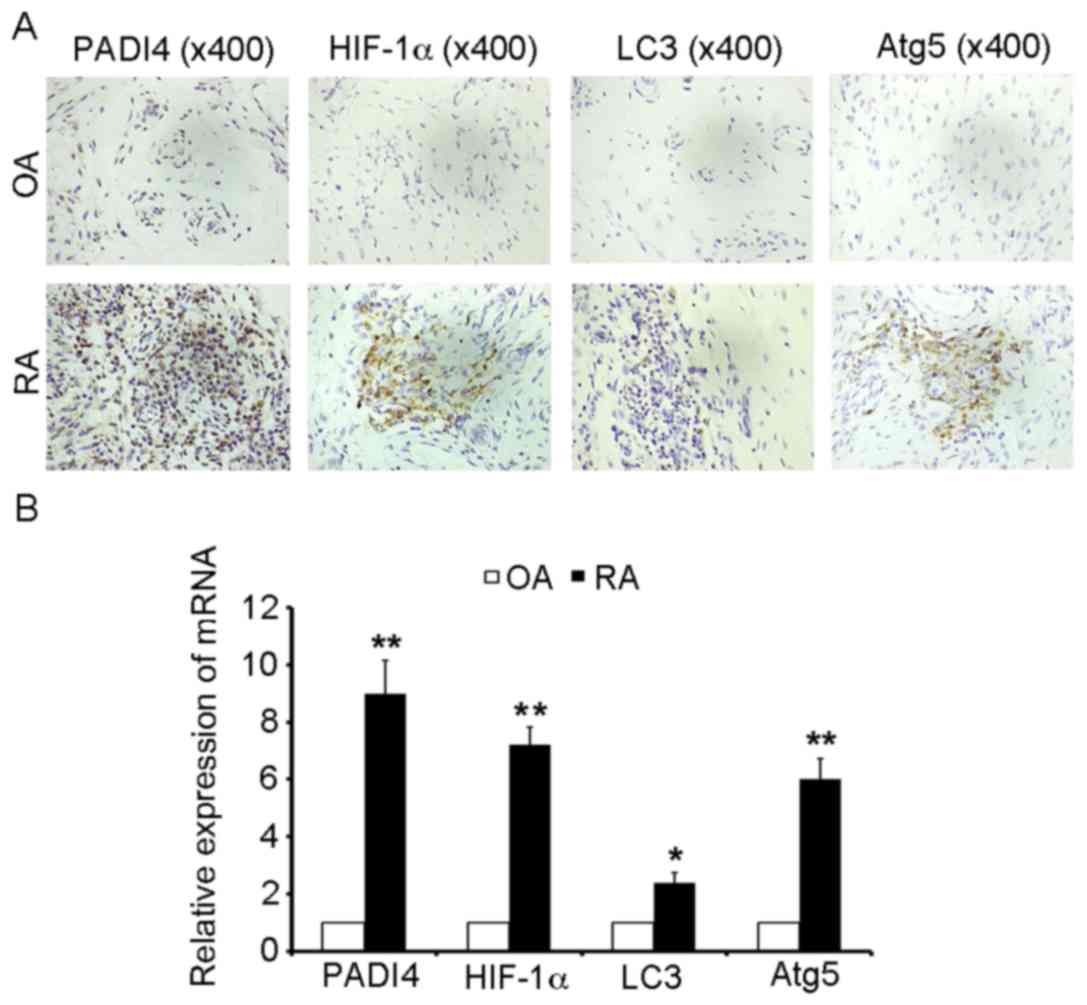
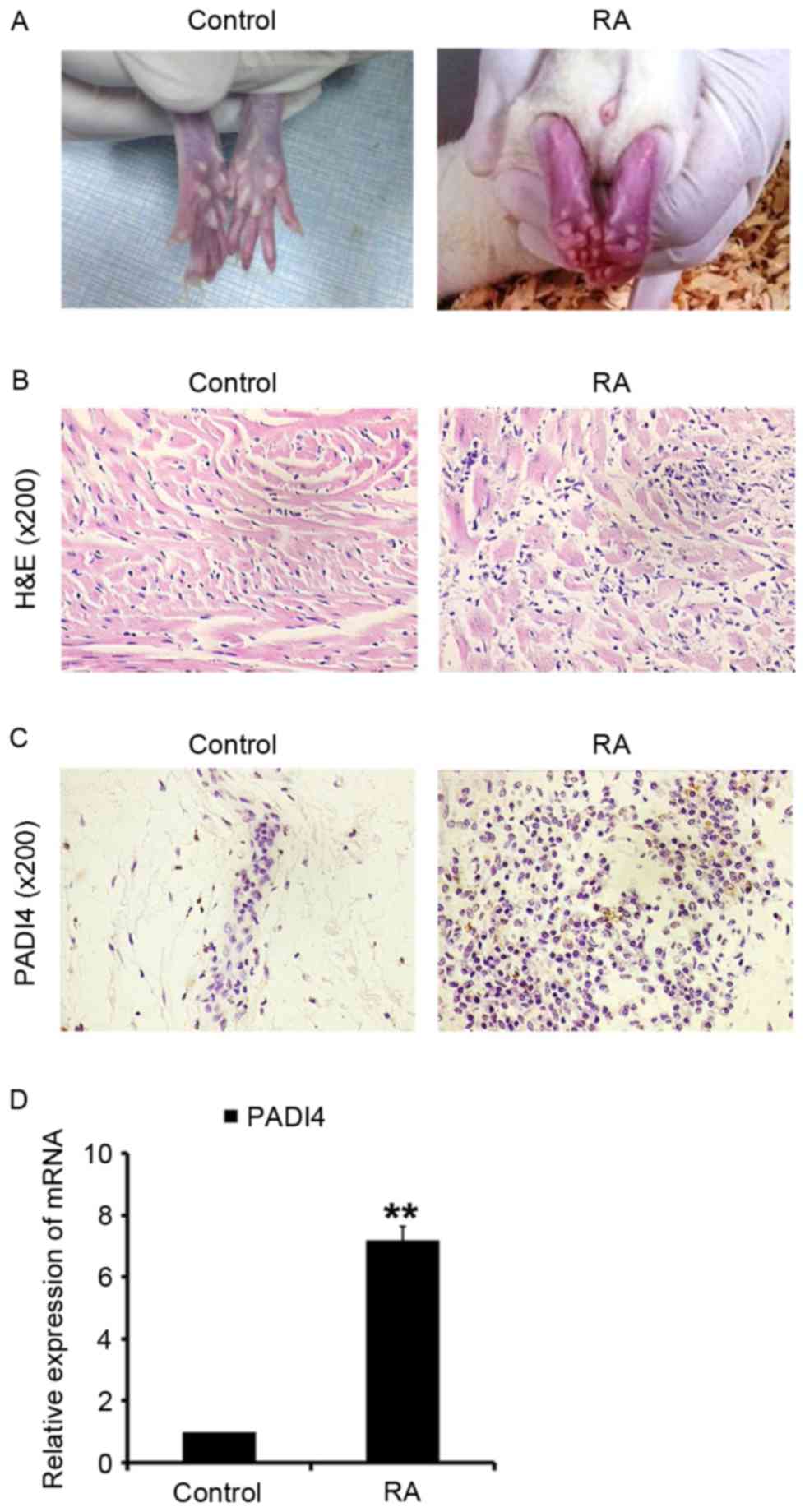
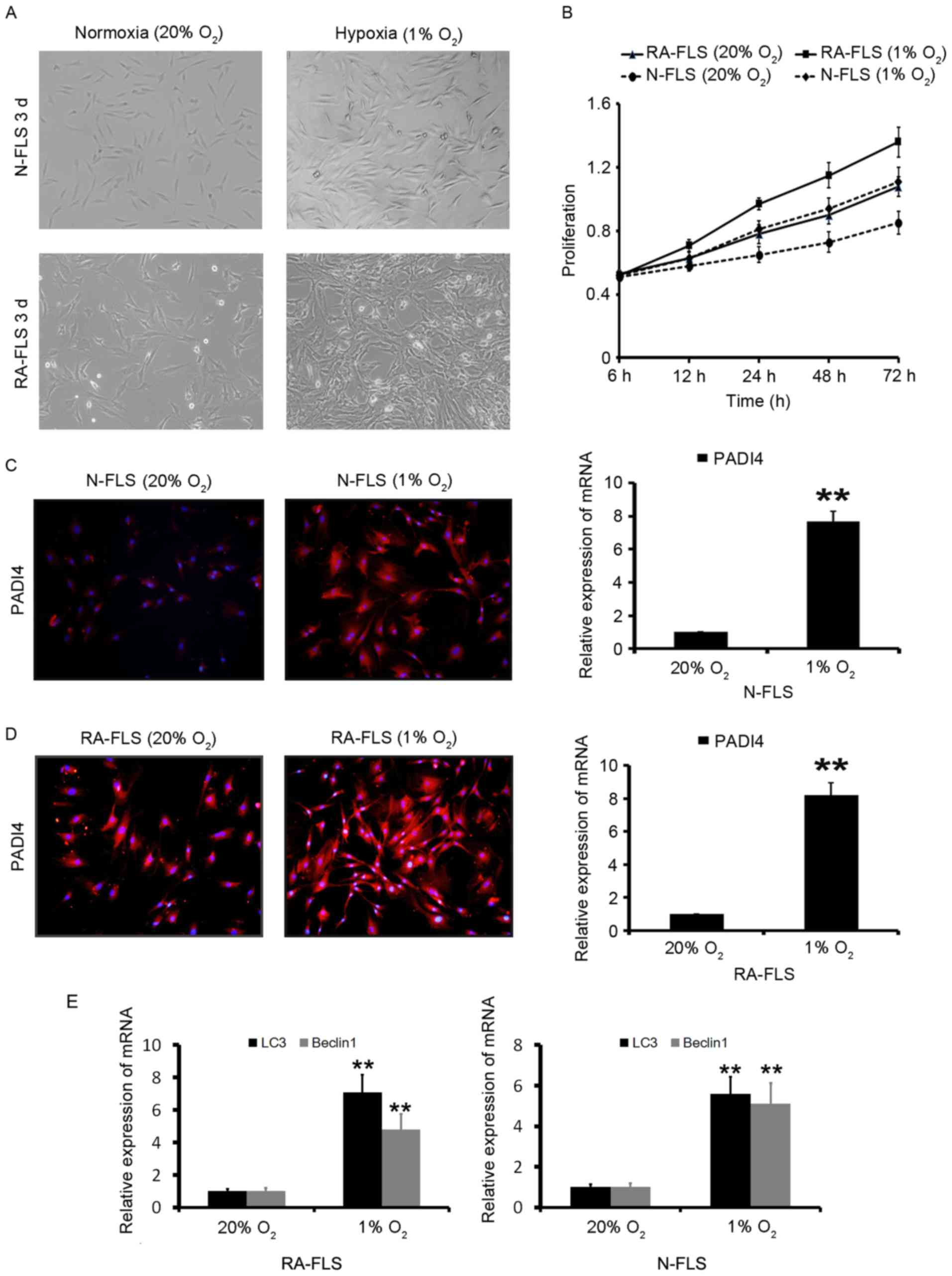
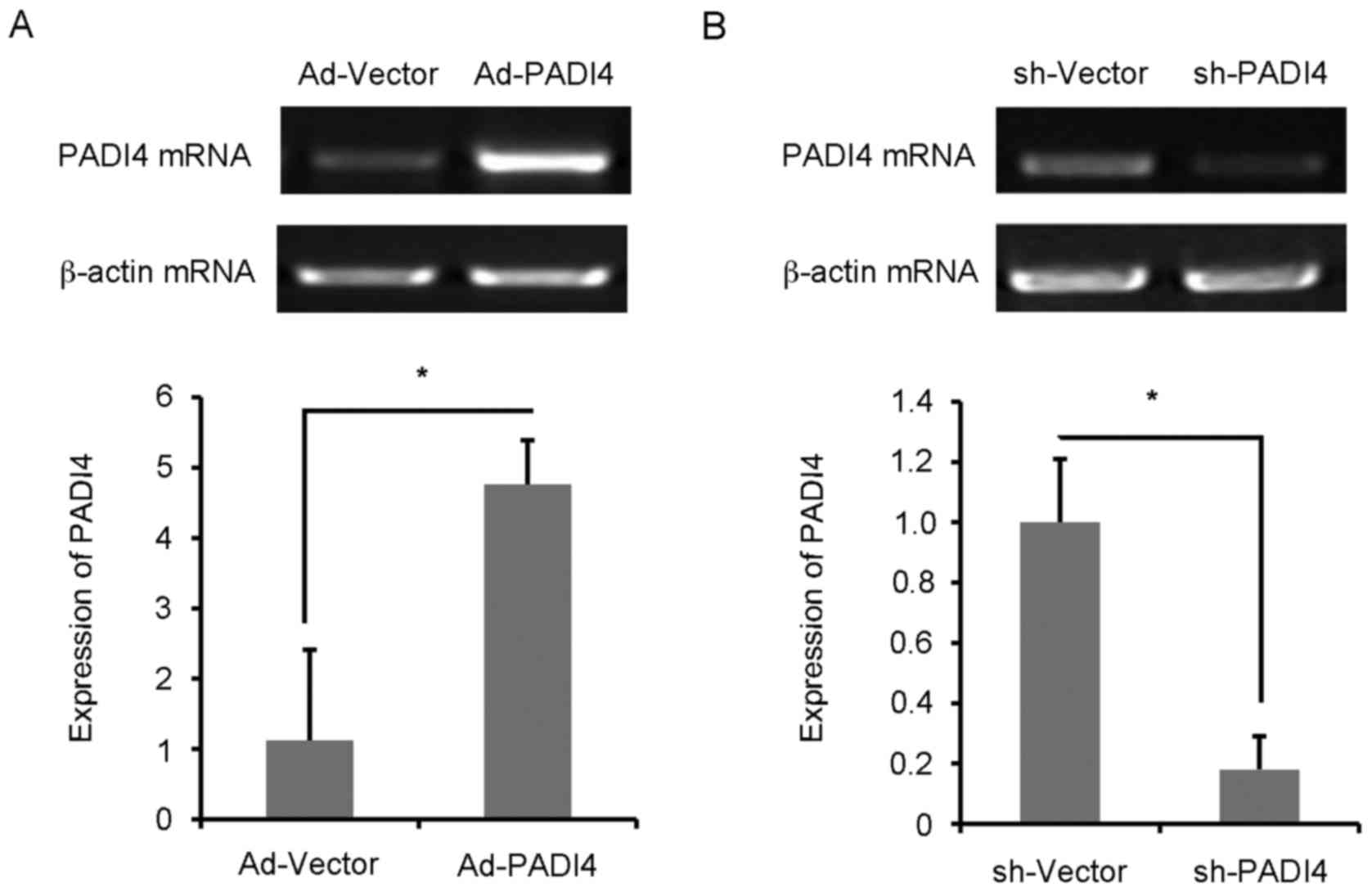
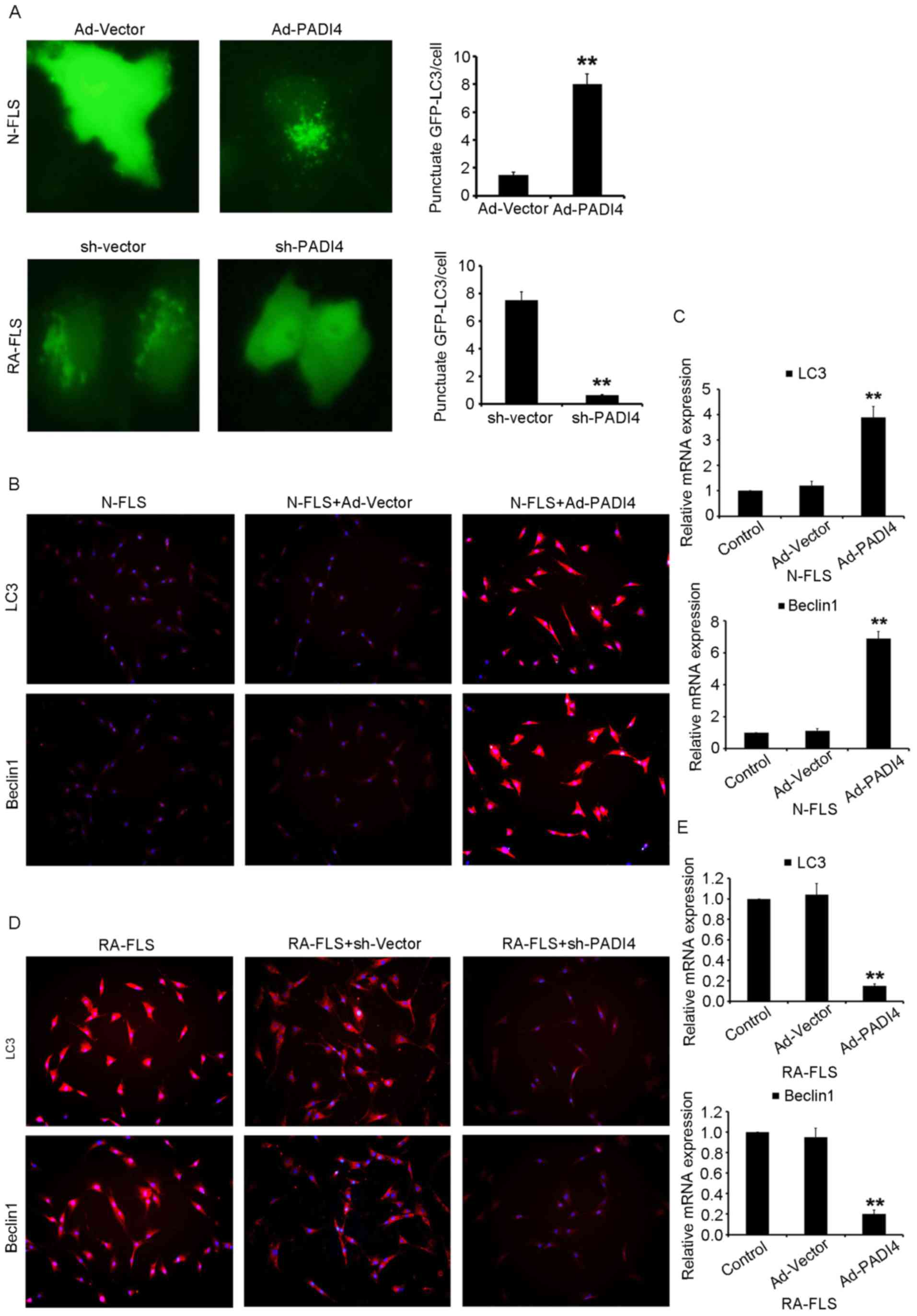
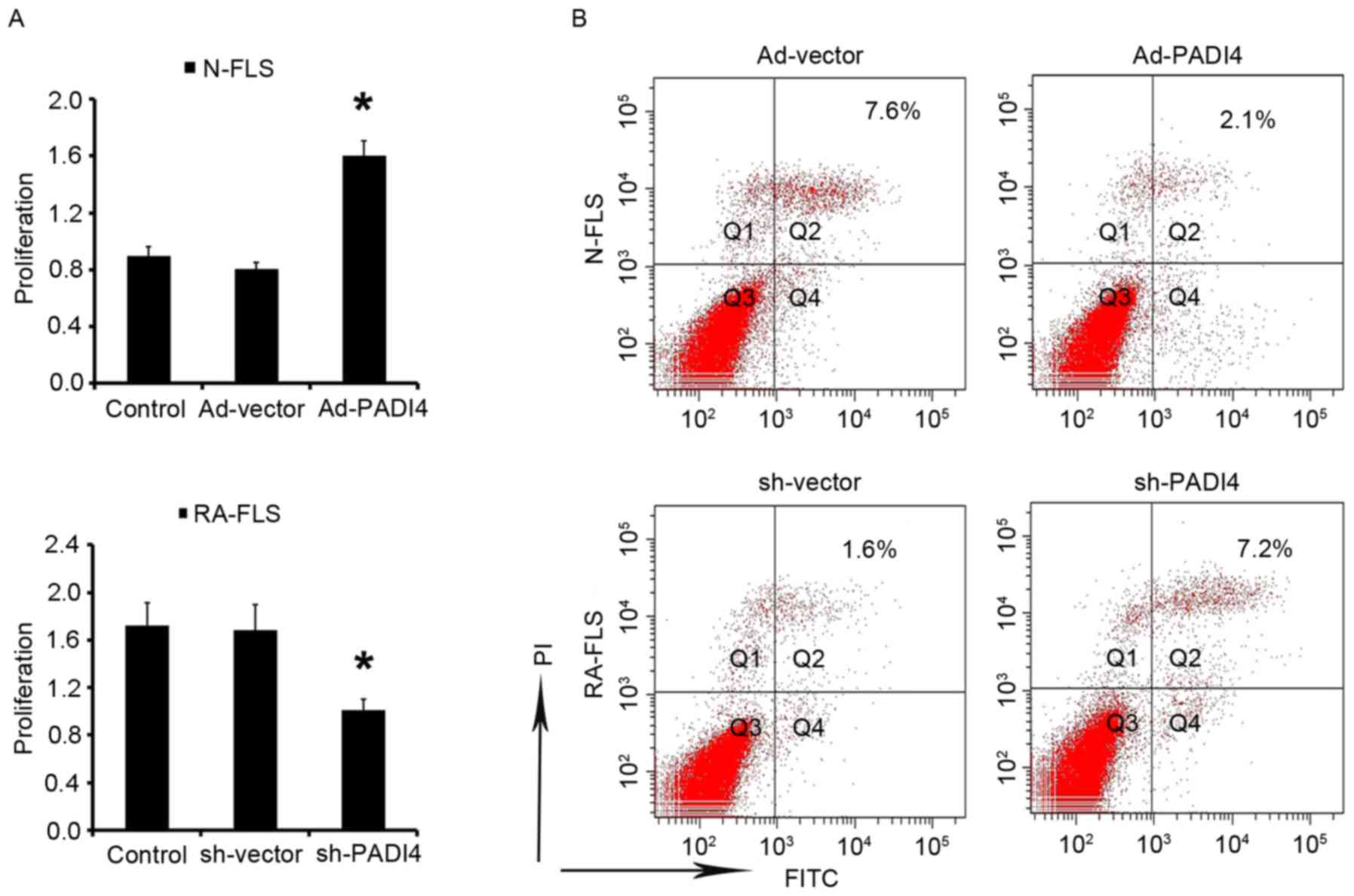
|
1
|
Ikari K, Yano K, Yoshida S, Taniguchi A,
Yamanaka H and Momohara S: Response to ‘Peptidyl arginine deiminase
type IV (PADI4) haplotypes interact with shared epitope regardless
of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody or erosive joint
status in rheumatoid arthritis: A case control study’. Arthritis
Res Ther. 16:4222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong S, Zhang Z and Takahara H:
Estrogen-enhanced peptidylarginine deiminase type IV gene (PADI4)
expression in MCF-7 cells is mediated by estrogen
receptor-alpha-promoted transfactors activator protein-1, nuclear
factor-Y, and Sp1. Mol Endocrinol. 21:1617–1629. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamada R, Suzuki A, Chang X and Yamamoto
K: Citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Biosci.
10:54–64. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S,
Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, Ono
M, et al: Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating
enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid
arthritis. Nat Genet. 34:395–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zavala-Cerna MG, Gonzalez-Montoya NG, Nava
A, Gamez-Nava JI, Moran-Moguel MC, Rosales-Gomez RC,
Gutierrez-Rubio SA, Sanchez-Corona J, Gonzalez-Lopez L,
Davalos-Rodriguez IP and Salazar-Paramo M: PADI4 haplotypes in
association with RA Mexican patients, a new prospect for antigen
modulation. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:3836812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bang SY, Han TU, Choi CB, Sung YK, Bae SC
and Kang C: Peptidyl arginine deiminase type IV (PADI4) haplotypes
interact with shared epitope regardless of anti-cyclic
citrullinated peptide antibody or erosive joint status in
rheumatoid arthritis: A case control study. Arthritis Res Ther.
12:R1152010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki T, Ikari K, Yano K, Inoue E, Toyama
Y, Taniguchi A, Yamanaka H and Momohara S: PADI4 and HLA-DRB1 are
genetic risks for radiographic progression in RA patients,
independent of ACPA status: Results from the IORRA cohort study.
PLoS One. 8:e610452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bottini N and Firestein GS: Duality of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and
imprinted aggressors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 9:24–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H and Wan A: Apoptosis of rheumatoid
arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Possible roles of nitric
oxide and the thioredoxin 1. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:9534622013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gu X, Gu B, Lv X, Yu Z, Wang R, Zhou X,
Qiao W, Mao Z, Zuo G, Li Q, et al: 1, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 with
tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against rheumatoid arthritis
by promoting p53 acetylation-mediated apoptosis via Sirt1 in
synoviocytes. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang L, Zhang HY, Gao B, Shi J, Huang Q,
Han YH, Hu YQ, Lu WG, Zhao ZJ, Liu BH, et al: Tetramethylpyrazine
protects against glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by promoting
autophagy in mesenchymal stem cells and improves bone mass in
glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis rats. Stem Cells Dev.
26:419–430. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan L, Wang Q, Liu R, Zong M, He D, Zhang
H, Ding Y and Ma J: Citrullinated fibronectin inhibits apoptosis
and promotes the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines in
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 14:R2662012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin TN, He YY, Wu G, Khan M and Hsu CY:
Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral
ischemia model in rats. Stroke. 24:117–121. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsunaga K, Saitoh T, Tabata K, Omori H,
Satoh T, Kurotori N, Maejima I, Shirahama-Noda K, Ichimura T, Isobe
T, et al: Two Beclin 1-binding proteins, Atg14L and Rubicon,
reciprocally regulate autophagy at different stages. Nat Cell Biol.
11:385–396. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kremer JM: Rheumatoid arthritis: New EULAR
guidelines for RA: A job well done. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 10:6–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hou S, Gao GP, Zhang XJ, Sun L, Peng WJ,
Wang HF, Ge XJ, Huang W and Sun YH: Erratum to: PADI4 polymorphisms
and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Mod
Rheumatol. 23:612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwamoto T, Ikari K, Nakamura T, Kuwahara
M, Toyama Y, Tomatsu T, Momohara S and Kamatani N: Association
between PADI4 and rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 45:804–807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang X, Zhao Y, Sun S, Zhang Y and Zhu Y:
The expression of PADI4 in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatol Int. 29:1411–1416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reyes-Castillo Z, Palafox-Sánchez CA,
Parra-Rojas I, Martínez-Bonilla GE, del Toro-Arreola S,
Ramírez-Dueñas MG, Ocampo-Bermudes G and Muñoz-Valle JF:
Comparative analysis of autoantibodies targeting peptidylarginine
deiminase type 4, mutated citrullinated vimentin and cyclic
citrullinated peptides in rheumatoid arthritis: Associations with
cytokine profiles, clinical and genetic features. Clin Exp Immunol.
182:119–131. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Konisti S, Kiriakidis S and Paleolog EM:
Hypoxia-a key regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:153–162. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brouwer E, Gouw AS, Posthumus MD, van
Leeuwen MA, Boerboom AL, Bijzet J, Bos R, Limburg PC, Kallenberg CG
and Westra J: Hypoxia inducible factor-1-alpha (HIF-1alpha) is
related to both angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid
arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 27:945–951. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Muz B, Khan MN, Kiriakidis S and Paleolog
EM: Hypoxia. The role of hypoxia and HIF-dependent signalling
events in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:2012009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Marin JJG, Lozano E and Perez MJ: Lack of
mitochondrial DNA impairs chemical hypoxia-induced autophagy in
liver tumor cells through ROS-AMPK-ULK1 signaling dysregulation
independently of HIF-1α. Free Radic Biol Med. 101:71–84. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Z, Yang M, Wang Y, Wang L, Jin Z,
Ding L, Zhang L, Zhang L, Jiang W, Gao G, et al: Autophagy
regulates the apoptosis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells under hypoxic condition via AMP-activated protein
kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cell Biol Int.
40:671–685. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park SY, Jang WJ, Yi EY, Jang JY, Jung Y,
Jeong JW and Kim YJ: Melatonin suppresses tumor angiogenesis by
inhibiting HIF-1alpha stabilization under hypoxia. J Pineal Res.
48:178–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng LX, Sun P, Mi T, Liu M, Liu W, Yao S,
Cao YM, Yu XL, Wu WY, Jiang BH, et al: Agglutinin isolated from
Arisema heterophyllum Blume induces apoptosis and autophagy in A549
cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt pathway and inducing ER stress.
Chin J Nat Med. 14:856–864. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kato M, Ospelt C, Gay RE, Gay S and Klein
K: Dual role of autophagy in stress-induced cell death in
rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheumatol.
66:40–48. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|