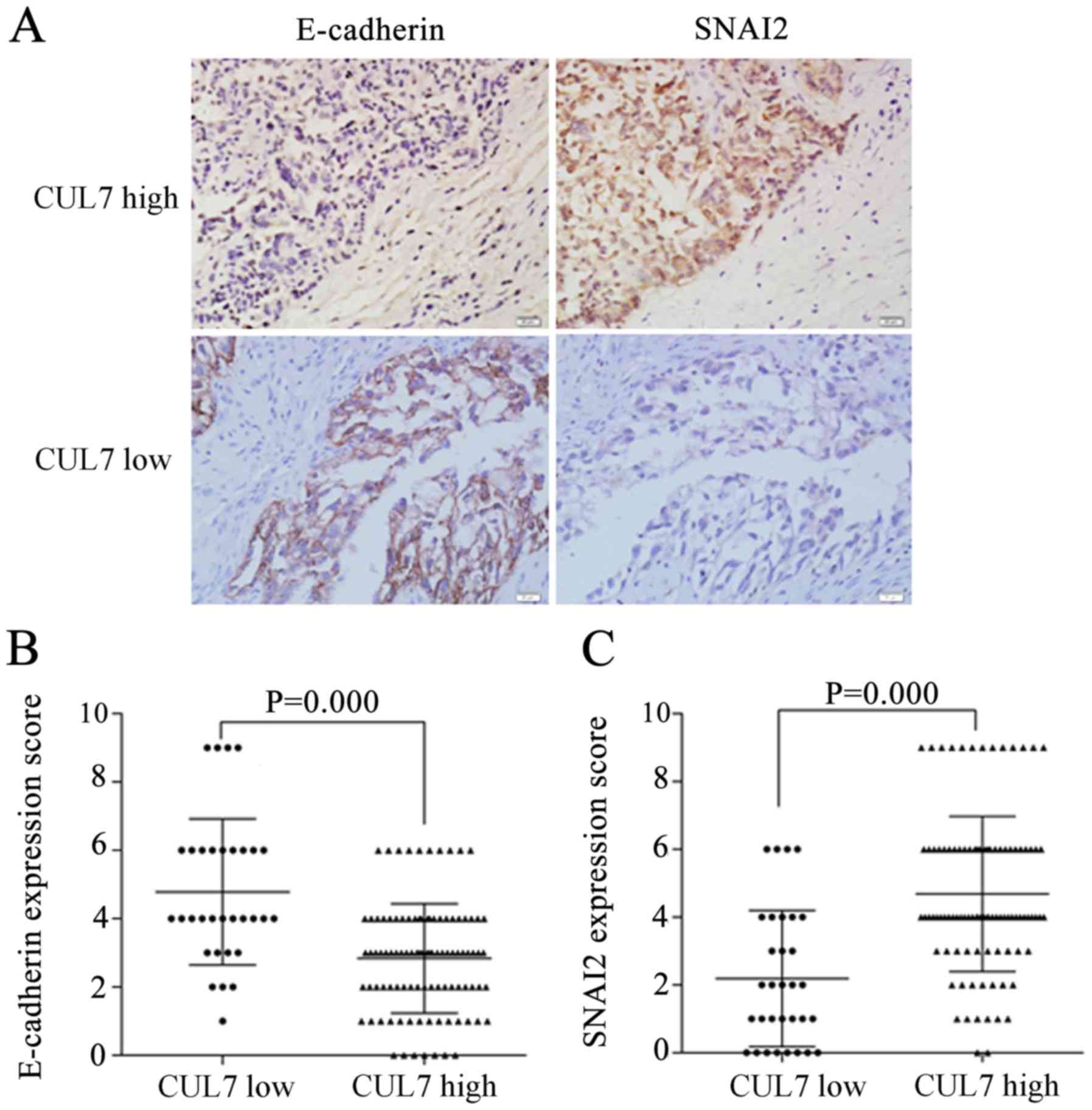
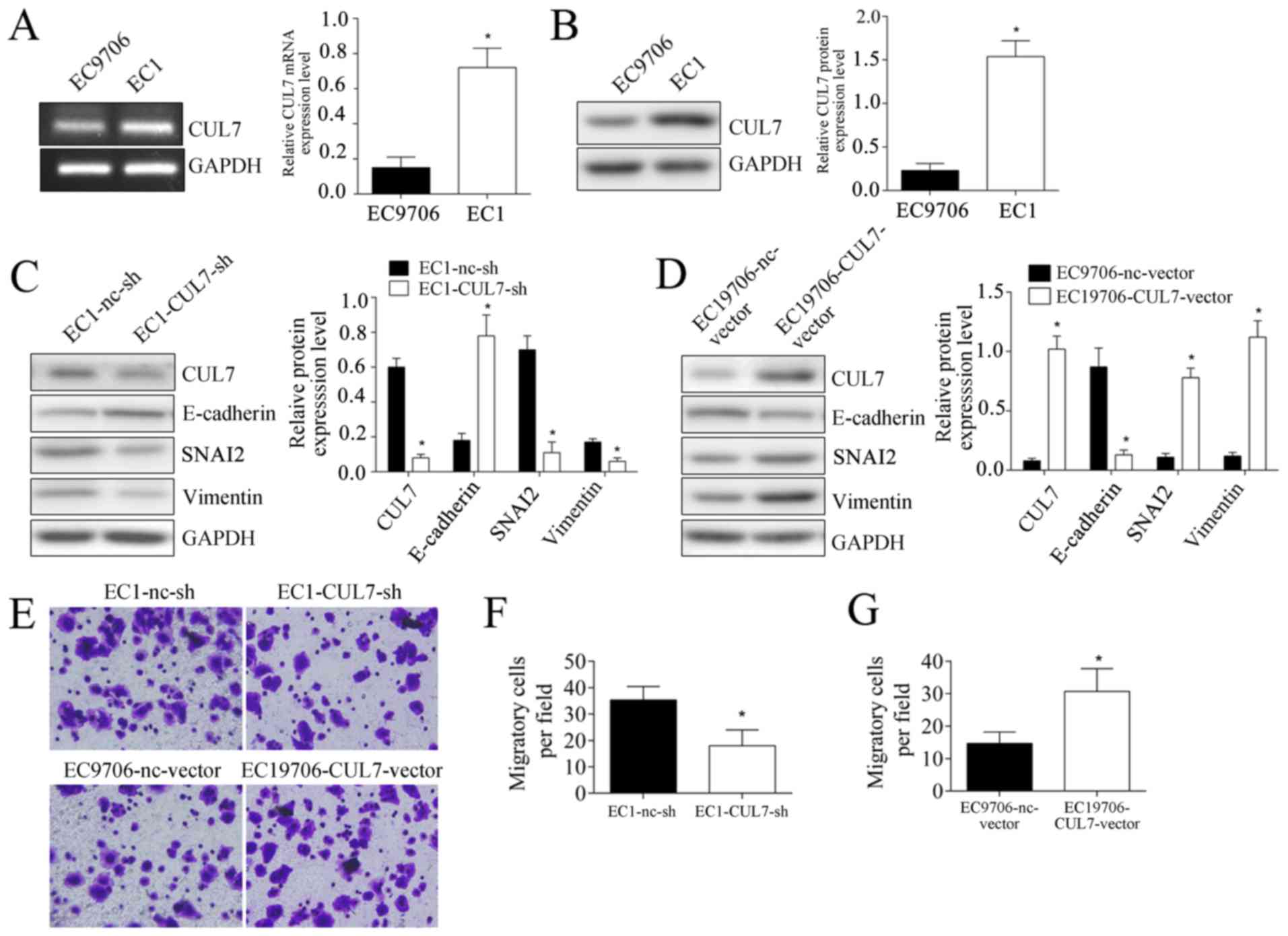
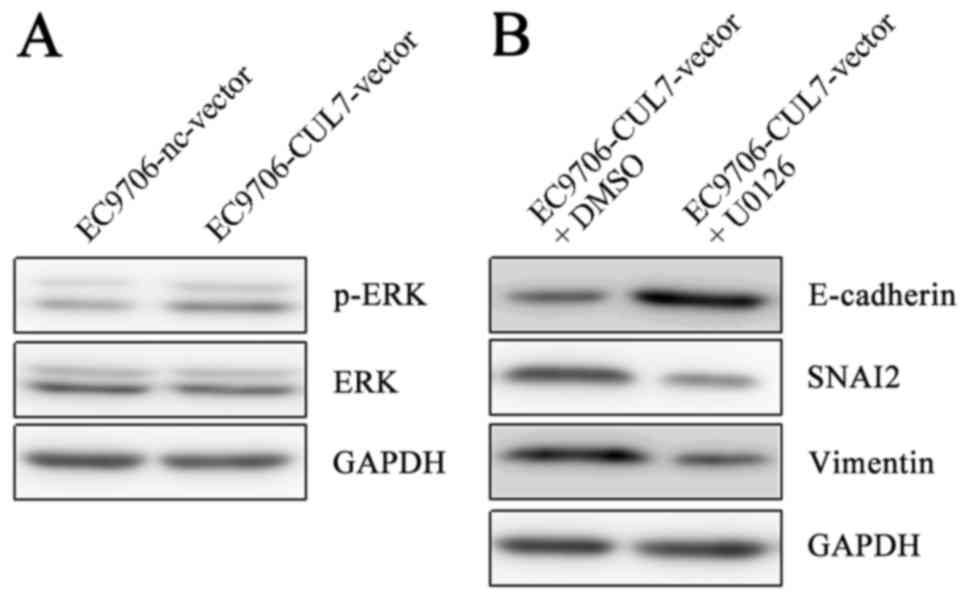
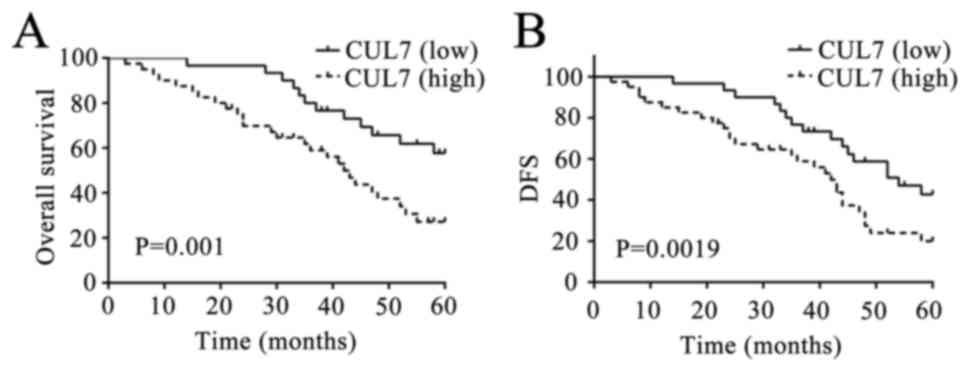
|
1
|
Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrandez Arenas A and
Lanas Arbeloa A: Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and
endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7933–7943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Na MK, Kim CH, Kim JM, Cheong JW, Ryu JI
and Kim HW: Multiple meningocerebral metastasis and extensive skull
metastasis from squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus: A case report
and review of literature. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 4:142–144. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ni PZ, Yang YS, Hu WP, Wang WP, Yuan Y and
Chen LQ: Primary adenosquamous carcinoma of the esophagus: an
analysis of 39 cases. J Thorac Dis. 8:2689–2696. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yazbeck R, Jaenisch SE and Watson DI: From
blood to breath: New horizons for esophageal cancer biomarkers.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:10077–10083. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rhim AD, Mirek ET, Aiello NM, Maitra A,
Bailey JM, McAllister F, Reichert M, Beatty GL, Rustgi AK,
Vonderheide RH, et al: EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic
tumor formation. Cell. 148:349–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nieto MA, Huang RY, Jackson RA and Thiery
JP: EMT: 2016. Cell. 166:21–45. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao C, Su L, Shan J, Zhu C, Liu L, Liu C,
Xu Y, Yang Z, Bian X, Shao J, et al: IGF/STAT3/NANOG/Slug signaling
axis simultaneously controls epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
stemness maintenance in colorectal cancer. Stem Cells. 34:820–831.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen Z, Che Q, He X, Wang F, Wang H, Zhu
M, Sun J and Wan X: Stem cell protein Piwil1 endowed endometrial
cancer cells with stem-like properties via inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. BMC Cancer. 15:8112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dias DC, Dolios G, Wang R and Pan ZQ:
CUL7: A DOC domain-containing cullin selectively binds Skp1. Fbx29
to form an SCF-like complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 99:pp.
16601–16606. 2002; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arai T, Kasper JS, Skaar JR, Ali SH,
Takahashi C and DeCaprio JA: Targeted disruption of p185/Cul7 gene
results in abnormal vascular morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S
A. 100:pp. 9855–9860. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim SS, Shago M, Kaustov L, Boutros PC,
Clendening JW, Sheng Y, Trentin GA, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Mao DY, Kay
R, et al: CUL7 is a novel antiapoptotic oncogene. Cancer Res.
67:9616–9622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Men X, Wang L, Yu W and Ju Y: Cullin7 is
required for lung cancer cell proliferation and is overexpressed in
lung cancer. Oncol Res. 22:123–128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Skaar JR, Florens L, Tsutsumi T, Arai T,
Tron A, Swanson SK, Washburn MP and DeCaprio JA: PARC and CUL7 form
atypical cullin RING ligase complexes. Cancer Res. 67:2006–2014.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Paradis V, Albuquerque M, Mebarki M,
Hernandez L, Zalinski S, Quentin S, Belghiti J, Soulier J and
Bedossa P: Cullin7: a new gene involved in liver carcinogenesis
related to metabolic syndrome. Gut. 62:911–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang D, Yang G, Li X, Xu C and Ge H:
Inhibition of liver carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by
knockdown of cullin7 in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Res. 23:171–181.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xi J, Zeng ST, Guo L and Feng J: High
expression of cullin7 correlates with unfavorable prognosis in
epithelial ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Invest. 34:130–136.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li XL, Liu L, Li DD, He YP, Guo LH, Sun
LP, Liu LN, Xu HX and Zhang XP: Integrin β4 promotes cell invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through the modulation of
Slug expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:404642017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumari R, Chouhan S, Singh S, Chhipa RR,
Ajay AK and Bhat MK: Constitutively activated ERK sensitizes cancer
cells to doxorubicin: Involvement of p53-EGFR-ERK pathway. J
Biosci. 42:31–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Semaan J, Pinon A, Rioux B, Hassan L,
Limami Y, Pouget C, Fagnere C, Sol V, Diab-Assaf M, Simon A and
Liagre B: Resistance to 3-HTMC-induced apoptosis through activation
of PI3K/Akt, MEK/ERK, and p38/COX-2/PGE2 pathways in human HT-29
and HCT116 colorectal cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 117:2875–2885.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kokcu A, Kurtoglu E, Celik H, Kefeli M,
Tosun M and Onal M: Is surgical staging necessary for patients with
low-risk endometrial cancer? A retrospective clinical analysis.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 16:5331–5335. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ando M, Yamauchi H, Aogi K, Shimizu S,
Iwata H, Masuda N, Yamamoto N, Inoue K, Ohono S, Kuroi K, et al:
Randomized phase II study of weekly paclitaxel with and without
carboplatin followed by cyclophosphamide/epirubicin/5-fluorouracil
as neoadjuvant chemotherapy for stage II/IIIA breast cancer without
HER2 overexpression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 145:401–409. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|