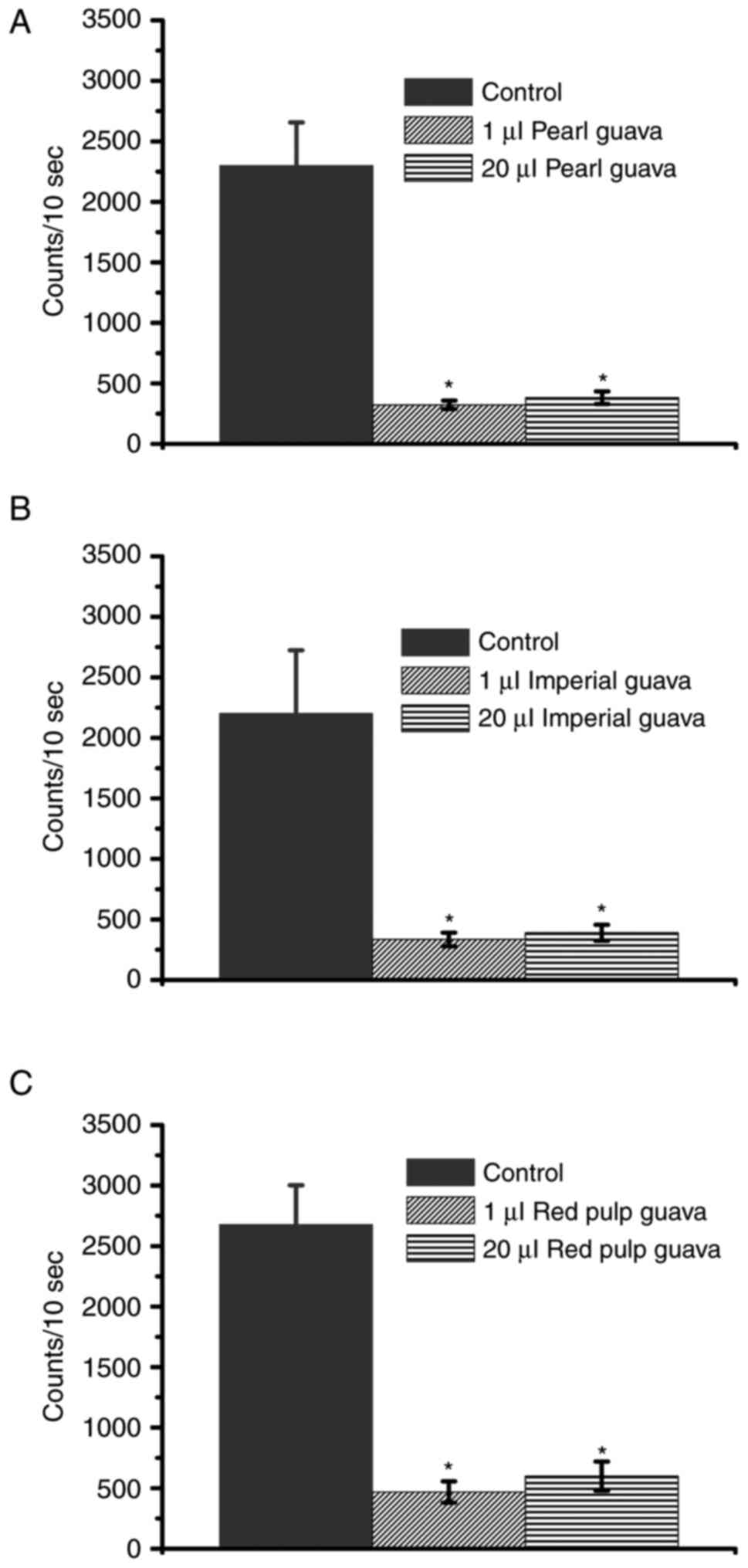
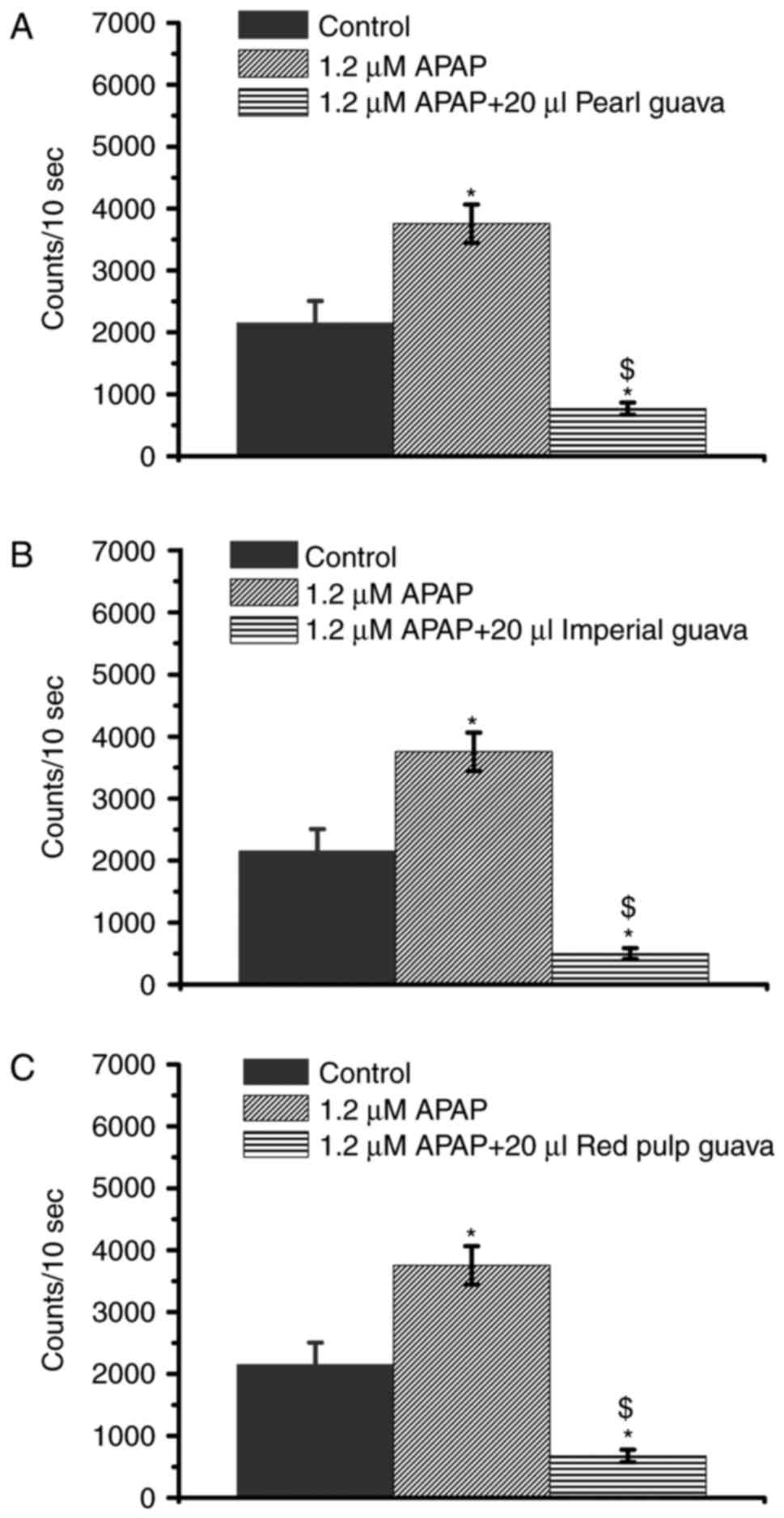
|
1
|
Bertolini A, Ferrari A, Ottani A, Guerzoni
S, Tacchi R and Leone S: Paracetamol: New vistas of an old drug.
CNS Drug Rev. 12:250–275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klotz U: Paracetamol (acetaminophen) - a
popular and widely used nonopioid analgesic. Arzneimittelforschung.
62:355–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yiang GT, Yu YL, Lin KT, Chen JN, Chang WJ
and Wei CW: Acetaminophen induces JNK/p38 signaling and activates
the caspase-9-3-dependent cell death pathway in human mesenchymal
stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 36:485–492. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bauer M, Babel B, Giesen H and Patzelt D:
Fulminant liver failure in a young child following repeated
acetaminophen overdosing. J Forensic Sci. 44:1299–1303. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Young RJ: Dextropropoxyphene overdosage.
Pharmacological considerations and clinical management. Drugs.
26:70–79. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu YL, Yiang GT, Chou PL, Tseng HH, Wu TK,
Hung YT, Lin PS, Lin SY, Liu HC, Chang WJ and Wei CW: Dual role of
acetaminophen in promoting hepatoma cell apoptosis and kidney
fibroblast proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 9:2077–2084. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hawton K, Bergen H, Simkin S, Arensman E,
Corcoran P, Cooper J, Waters K, Gunnell D and Kapur N: Impact of
different pack sizes of paracetamol in the United Kingdom and
Ireland on intentional overdoses: A comparative study. BMC Public
Health. 11:4602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hawton K, Townsend E, Deeks J, Appleby L,
Gunnell D, Bennewith O and Cooper J: Effects of legislation
restricting pack sizes of paracetamol and salicylate on self
poisoning in the United Kingdom: Before and after study. BMJ.
322:1203–1207. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Daly FF, Fountain JS, Murray L, Graudins A
and Buckley NA; Panel of Australian and New Zealand clinical
toxicologists, : Guidelines for the management of paracetamol
poisoning in Australia and New Zealand-explanation and elaboration.
A consensus statement from clinical toxicologists consulting to the
Australasian poisons information centres. Med J Aust. 188:296–301.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo C, Xie G, Su M, Wu X, Lu X, Wu K and
Wei C: Characterization of acetaminophen-induced cytotoxicity in
target tissues. Am J Transl Res. 8:4440–4445. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murad HA, Habib H, Kamel Y, Alsayed S,
Shakweer M and Elshal M: Thearubigins protect against
acetaminophen-induced hepatic and renal injury in mice:
Biochemical, histopathological, immunohistochemical, and flow
cytometry study. Drug Chem Toxicol. 39:190–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ramachandran A, McGill MR, Xie Y, Ni HM,
Ding WX and Jaeschke H: Receptor interacting protein kinase 3 is a
critical early mediator of acetaminophen-induced hepatocyte
necrosis in mice. Hepatology. 58:2099–2108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inkielewicz-Stępniak I and Knap N: Effect
of exposure to fluoride and acetaminophen on oxidative/nitrosative
status of liver and kidney in male and female rats. Pharmacol Rep.
64:902–911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Slitt AM, Dominick PK, Roberts JC and
Cohen SD: Effect of ribose cysteine pretreatment on hepatic and
renal acetaminophen metabolite formation and glutathione depletion.
Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 96:487–494. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McGill MR, Kennon-McGill S, Durham D and
Jaeschke H: Hearing, reactive metabolite formation, and oxidative
stress in cochleae after a single acute overdose of acetaminophen:
An in vivo study. Toxicol Mech Methods. 26:104–111. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Galal RM, Zaki HF, Seif El-Nasr MM and
Agha AM: Potential protective effect of honey against
paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Iran Med. 15:674–680.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wołonciej M, Milewska E and
Roszkowska-Jakimiec W: Trace elements as an activator of
antioxidant enzymes. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 70:1483–1498.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kefer JC, Agarwal A and Sabanegh E: Role
of antioxidants in the treatment of male infertility. Int J Urol.
16:449–457. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lores Arnaiz S, Llesuy S, Cutrín JC and
Boveris A: Oxidative stress by acute acetaminophen administration
in mouse liver. Free Radic Biol Med. 19:303–310. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji L, Jiang P, Lu B, Sheng Y, Wang X and
Wang Z: Chlorogenic acid, a dietary polyphenol, protects
acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its mechanism. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:1911–1919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang AY, Lian LH, Jiang YZ, Wu YL and Nan
JX: Gentiana manshurica Kitagawa prevents acetaminophen-induced
acute hepatic injury in mice via inhibiting JNK/ERK MAPK pathway.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:384–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ravi K and Divyashree P: Psidium guajava:
A review on its potential as an adjunct in treating periodontal
disease. Pharmacogn Rev. 8:96–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morais-Braga MFB, Sales DL, Carneiro JNP,
Machado AJT, Dos Santos ATL, de Freitas MA, Martins GMAB, Leite NF,
de Matos YMLS, Tintino SR, et al: Psidium guajava L. and Psidium
brownianum Mart ex DC.: Chemical composition and anti-Candida
effect in association with fluconazole. Microb Pathog. 95:200–207.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shao M, Wang Y, Huang XJ, Fan CL, Zhang
QW, Zhang XQ and Ye WC: Four new triterpenoids from the leaves of
Psidium guajava. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 14:348–354. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin HC and Lin JY: Immune cell-conditioned
media suppress prostate cancer PC-3 cell growth correlating with
decreased proinflammatory/anti-inflammatory cytokine ratios in the
media using 5 selected crude polysaccharides. Integr Cancer Ther.
15:NP13–NP25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ashraf A, Sarfraz RA, Rashid MA, Mahmood
A, Shahid M and Noor N: Chemical composition, antioxidant,
antitumor, anticancer and cytotoxic effects of Psidium guajava leaf
extracts. Pharm Biol. 54:1971–1981. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin J, Puckree T and Mvelase TP:
Anti-diarrhoeal evaluation of some medicinal plants used by Zulu
traditional healers. J Ethnopharmacol. 79:53–56. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Obode O, Okafor O, Erukainure O, Ajayi A,
Suberu Y, Ogunji A, Okporua T, Oluwole O, Ozumba A and Elemo G:
Protective effect of some selected fruit blends on testicular
toxicity in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Complement Integr Med.
12:137–142. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tandon N, Roy M, Roy S and Gupta N:
Protective effect of Psidium guajava in arsenic-induced oxidative
stress and cytological damage in rats. Toxicol Int. 19:245–249.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang CS, Yin MC and Chiu LC:
Antihyperglycemic and antioxidative potential of Psidium guajava
fruit in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
49:2189–2195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Soman S, Rauf AA, Indira M and
Rajamanickam C: Antioxidant and antiglycative potential of ethyl
acetate fraction of Psidium guajava leaf extract in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Plant Foods Hum Nutr.
65:386–391. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin CF, Kuo YT, Chen TY and Chien CT:
Quercetin-rich guava (Psidium guajava) juice in combination with
trehalose reduces autophagy, apoptosis and pyroptosis formation in
the kidney and pancreas of type II diabetic rats. Molecules.
21:3342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baek HJ, Lee YM, Kim TH, Kim JY, Park EJ,
Iwabuchi K, Mishra L and Kim SS: Caspase-3/7-mediated cleavage of
β2-spectrin is required for acetaminophen-induced liver damage. Int
J Biol Sci. 12:172–183. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Posadas I, Santos P and Ceña V:
Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB
activation. PLoS One. 7:e501602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fu L, Lu W and Zhou X: Phenolic compounds
and in vitro antibacterial and antioxidant activities of three
tropic fruits: Persimmon, Guava, and Sweetsop. Biomed Res Int.
2016:42874612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cuadrado-Silva CT, Pozo-Bayón MÁ and
Osorio C: Targeted metabolomic analysis of polyphenols with
antioxidant activity in sour guava (Psidium friedrichsthalianum
Nied.) fruit. Molecules. 22:E112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Flores G, Wu SB, Negrin A and Kennelly EJ:
Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of seven cultivars of
guava (Psidium guajava) fruits. Food Chem. 170:327–335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Araújo HM, Rodrigues FF, Costa WD, Nonato
Cde F, Rodrigues FF, Boligon AA, Athayde ML and Costa JG: Chemical
profile and antioxidant capacity verification of Psidium guajava
(Myrtaceae) fruits at different stages of maturation. EXCLI J.
14:1020–1030. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arrey Tarkang P, Nwachiban Atchan AP,
Kuiate JR, Okalebo FA, Guantai AN and Agbor GA: Antioxidant
potential of a polyherbal antimalarial as an indicator of its
therapeutic value. Adv Pharmacol Sci. 2013:6784582013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin CY and Yin MC: Renal protective
effects of extracts from guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.) in
diabetic mice. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 67:303–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mondal K, Malhotra SP, Jain V and Singh R:
Oxidative stress and antioxidant systems in Guava (Psidium guajava
L.) fruits during ripening. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 15:327–334.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yiang GT, Chen JN, Lin PS, Liu HC, Chen SY
and Wei CW: Combined treatment with vitamin E and gefitinib has
synergistic effects to inhibit TGF-β1-induced renal fibroblast
proliferation. Mol Med Rep. 13:5372–5378. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kwon YJ, Baek HS, Ye DJ, Shin S, Kim D and
Chun YJ: CYP1B1 enhances cell proliferation and metastasis through
induction of EMT and activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling via Sp1
upregulation. PLoS One. 11:e01515982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Imig JD and Khan MA: Cytochrome P450 and
lipoxygenase metabolites on renal function. Compr Physiol.
6:423–441. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Johnson BP, Walisser JA, Liu Y, Shen AL,
McDearmon EL, Moran SM, McIntosh BE, Vollrath AL, Schook AC,
Takahashi JS and Bradfield CA: Hepatocyte circadian clock controls
acetaminophen bioactivation through NADPH-cytochrome P450
oxidoreductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:pp. 18757–18762. 2014;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang Y, Wong SE and Lightstone FC:
Understanding a substrate's product regioselectivity in a family of
enzymes: A case study of acetaminophen binding in cytochrome P450s.
PLoS One. 9:e870582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miyakawa K, Albee R, Letzig LG, Lehner AF,
Scott MA, Buchweitz JP, James LP, Ganey PE and Roth RA: A
cytochrome P450-independent mechanism of acetaminophen-induced
injury in cultured mouse hepatocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
354:230–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
McGill MR and Jaeschke H: Metabolism and
disposition of acetaminophen: Recent advances in relation to
hepatotoxicity and diagnosis. Pharm Res. 30:2174–2187. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chatuphonprasert W and Jarukamjorn K:
Impact of six fruits-banana, guava, mangosteen, pineapple, ripe
mango and ripe papaya-on murine hepatic cytochrome P450 activities.
J Appl Toxicol. 32:994–1001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
James LP, Letzig L, Simpson PM, Capparelli
E, Roberts DW, Hinson JA, Davern TJ and Lee WM: Pharmacokinetics of
acetaminophen-protein adducts in adults with acetaminophen overdose
and acute liver failure. Drug Metab Dispos. 37:1779–1784. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Vargha R, Mostafa G, Burda G, Hermon M,
Trittenwein G and Gole J: Treatment with N-acetylcystein and total
plasma exchange for extracorporeal liver support in children with
paracetamol intoxication. Klin Padiatr. 226:84–85. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Prescott LF, Park J, Ballantyne A,
Adriaenssens P and Proudfoot AT: Treatment of paracetamol
(acetaminophen) poisoning with N-acetylcysteine. Lancet. 2:432–434.
1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang Y, Fan X, Wang Y, Chen P, Zeng H,
Tan H, Gonzalez FJ, Huang M and Bi H: Schisandrol B protects
against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibition of
CYP-mediated bioactivation and regulation of liver regeneration.
Toxicol Sci. 143:107–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yi BR, Kim SU and Choi KC: Synergistic
effect of therapeutic stem cells expressing cytosine deaminase and
interferon-beta via apoptotic pathway in the metastatic mouse model
of breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:5985–5999. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tang J, Yan Y, Zhao TC, Gong R, Bayliss G,
Yan H and Zhuang S: Class I HDAC activity is required for renal
protection and regeneration after acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 307:F303–F316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|