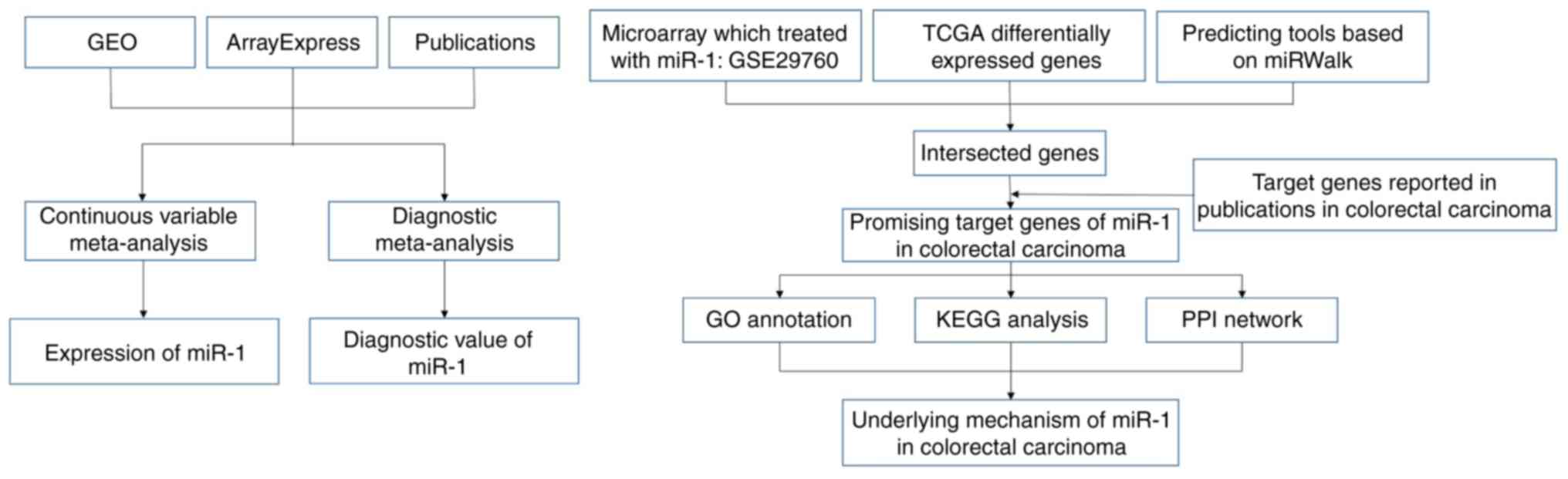
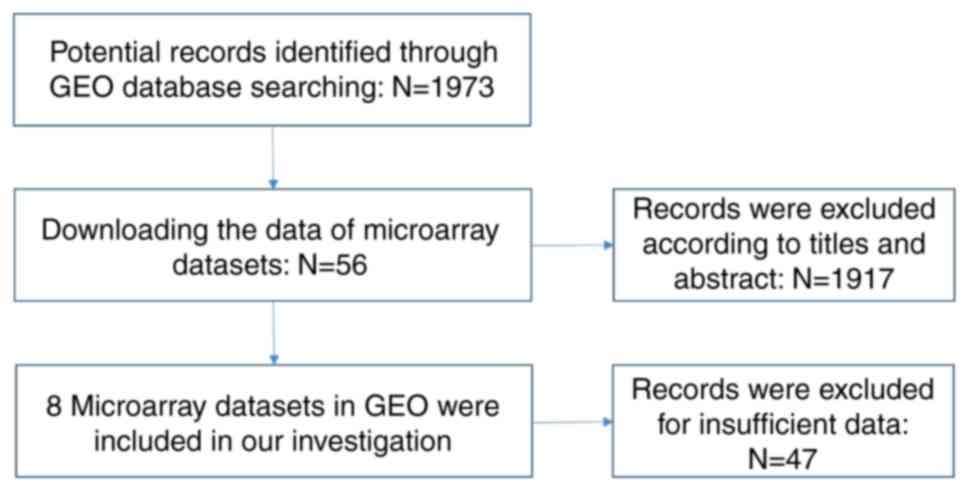
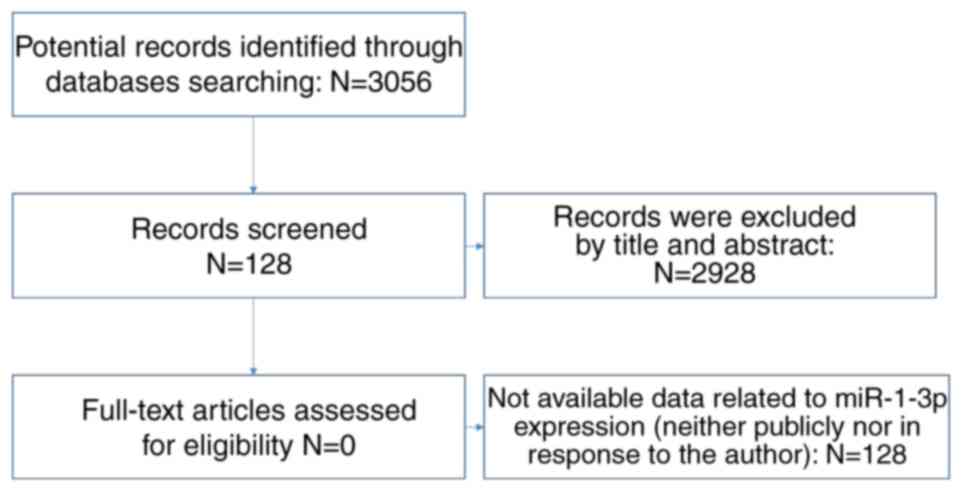
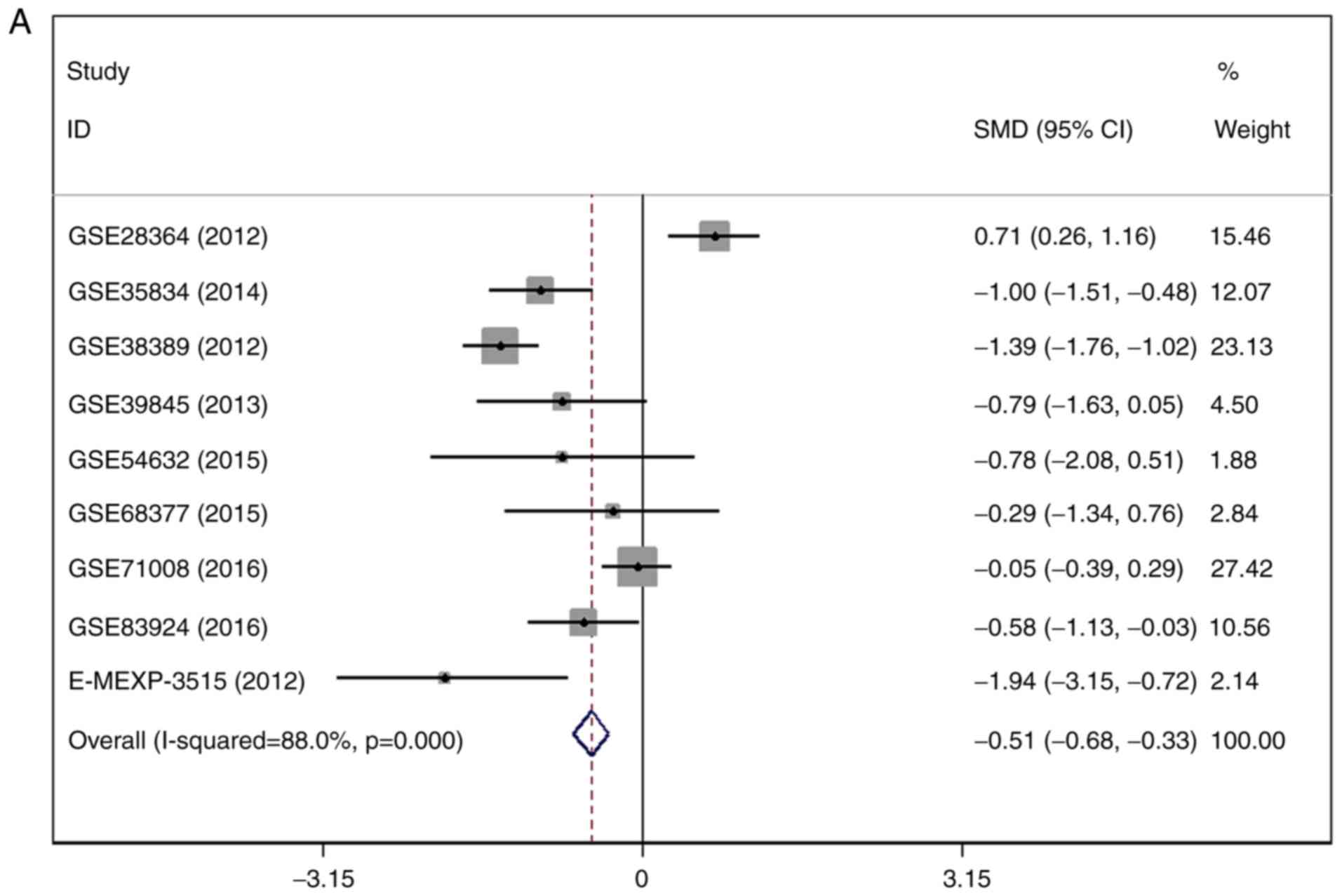
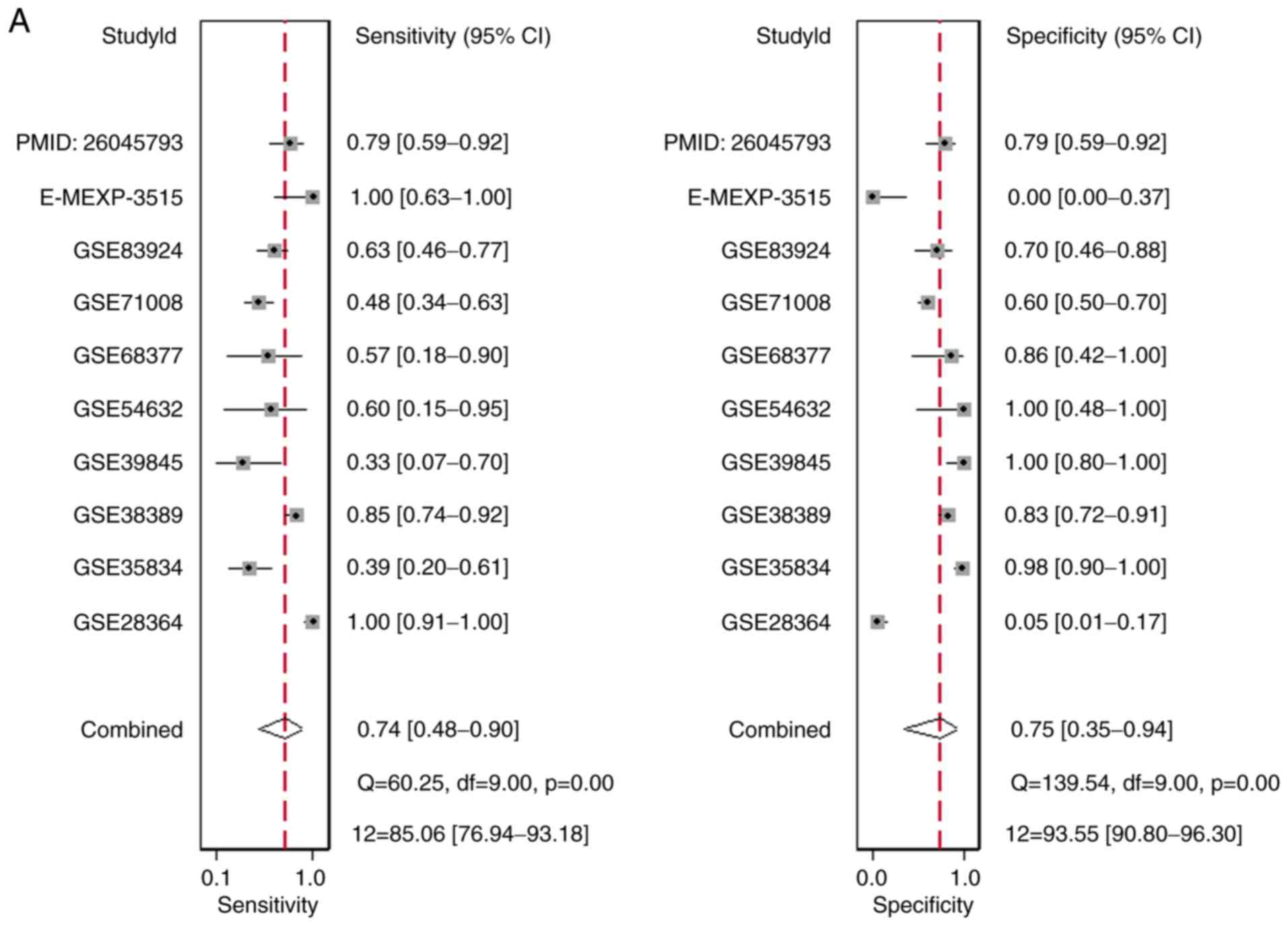
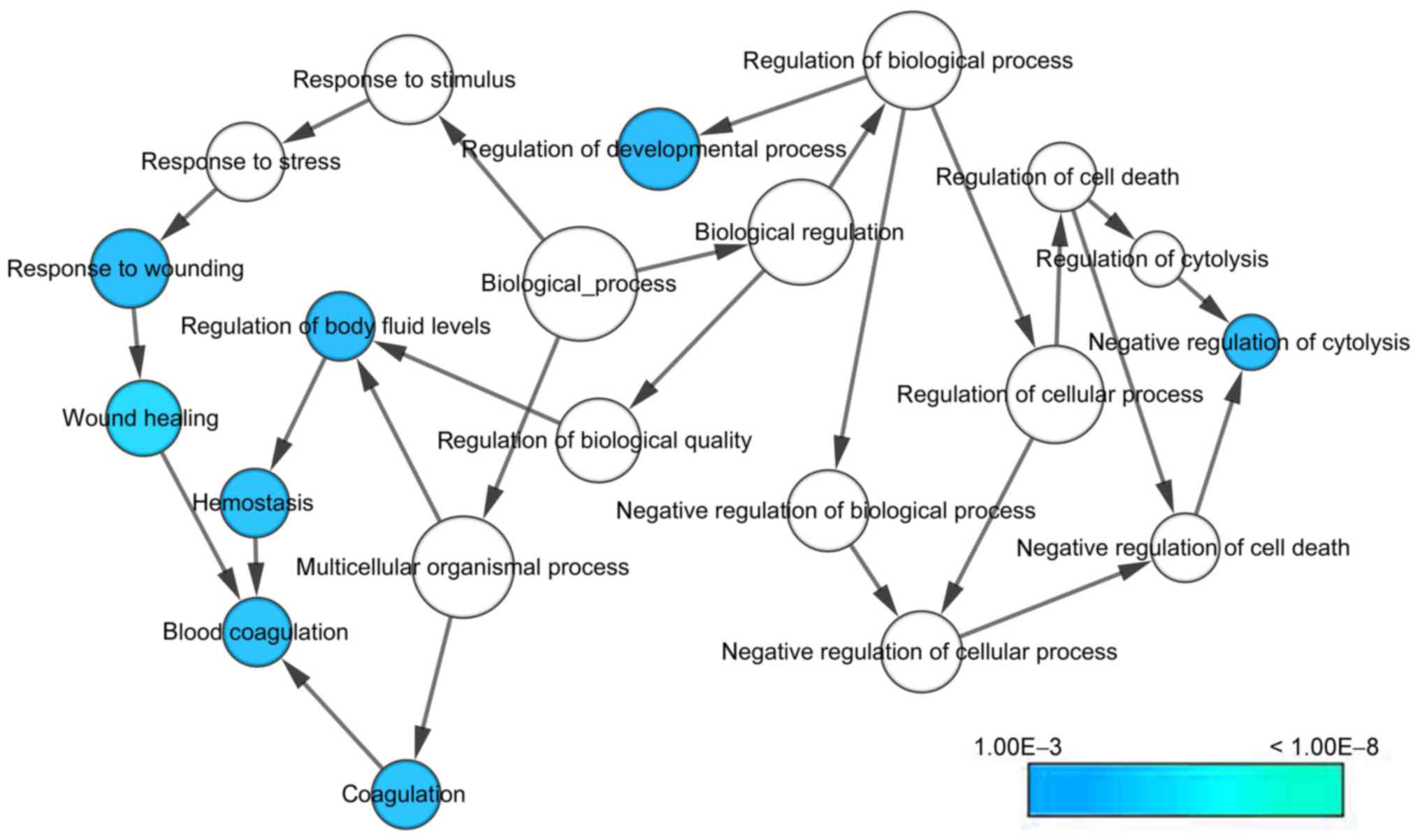
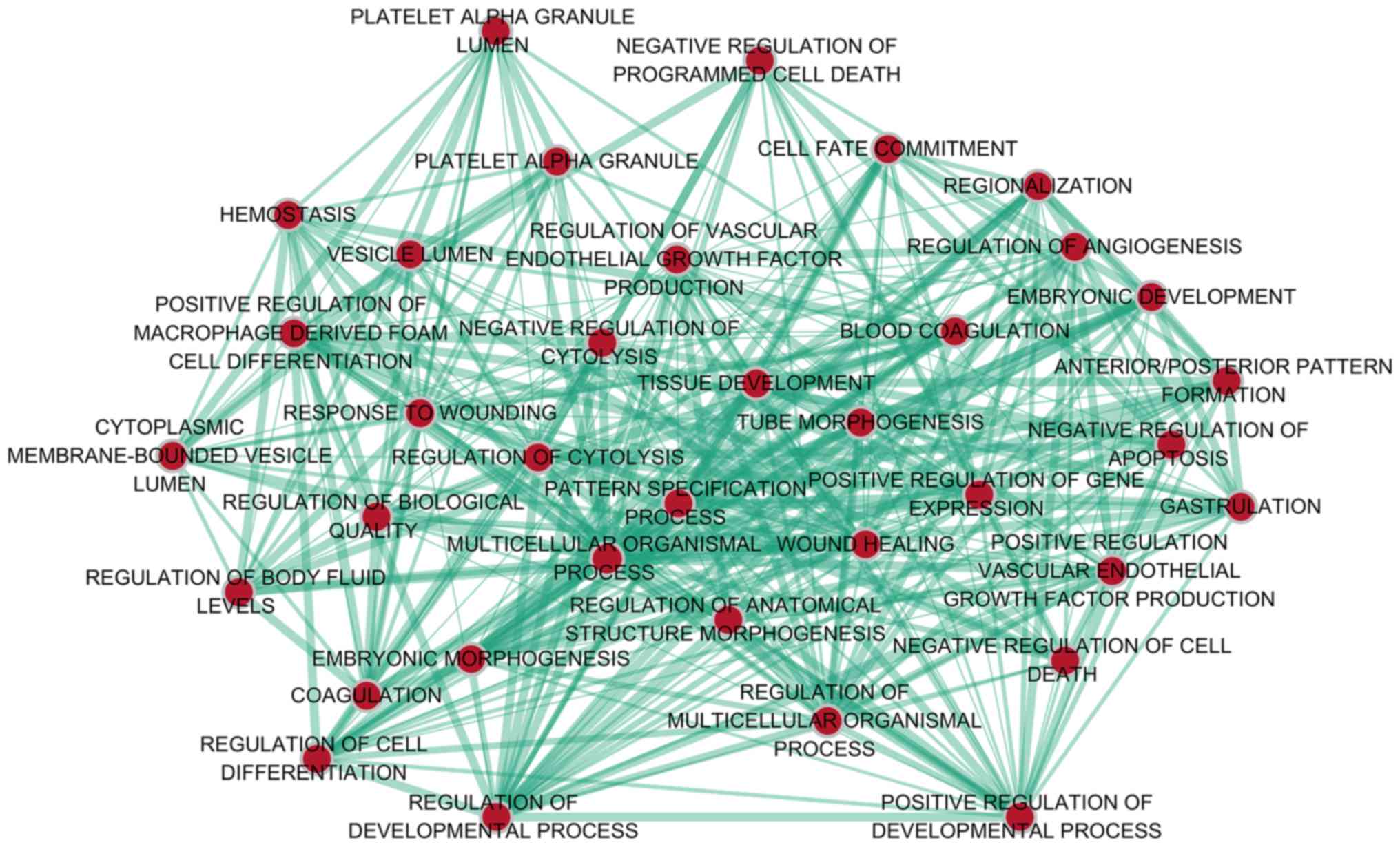
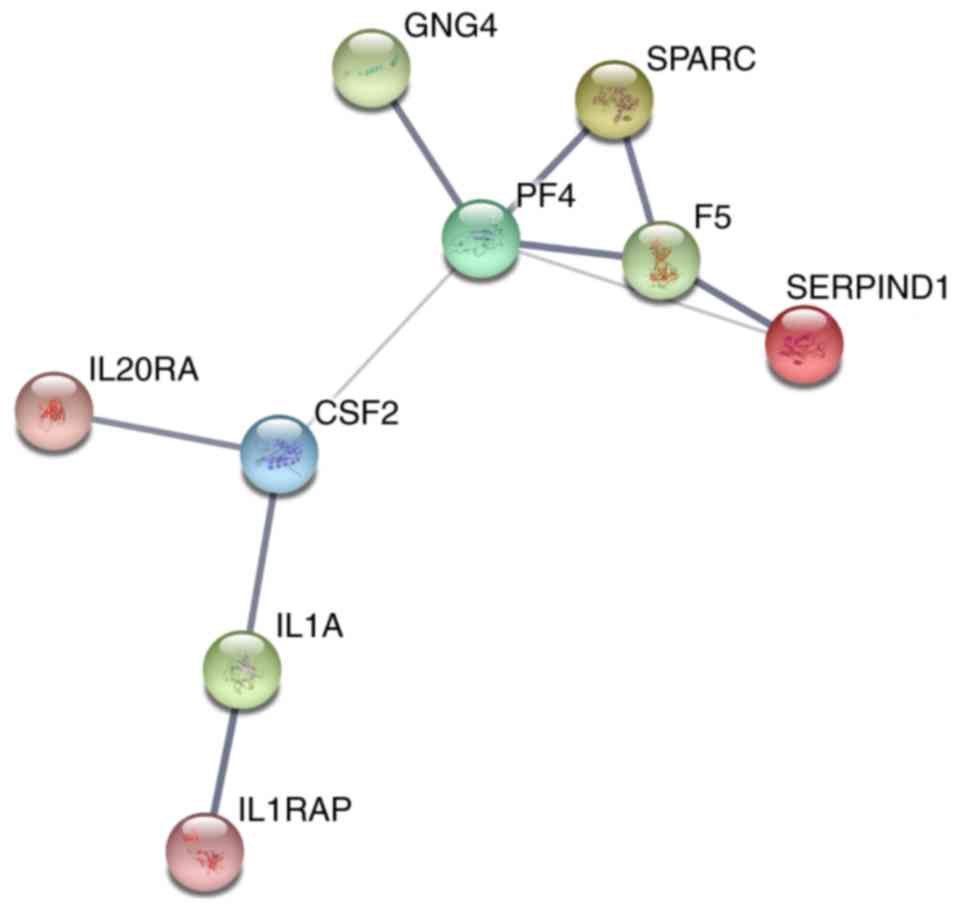
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stewart BW and Wild C; International
Agency for Research on Cancer, : World cancer report 2014. IARC
Nonserial Publication; 2014
|
|
3
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hesse M and Arenz C: MicroRNA maturation
and human disease. Methods Mol Biol. 1095:11–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qu YL, Wang HF, Sun ZQ, Tang Y, Han XN, Yu
XB and Liu K: Up-regulated miR-155-5p promotes cell proliferation,
invasion and metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6988–6994. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhong M, Bian Z and Wu Z: miR-30a
suppresses cell migration and invasion through downregulation of
PIK3CD in colorectal carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:209–218.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang XH: MicroRNA in myogenesis and muscle
atrophy. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 16:258–266. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karatas OF, Guzel E, Suer I, Ekici ID,
Caskurlu T, Creighton CJ, Ittmann M and Ozen M: miR-1 and miR-133b
are differentially expressed in patients with recurrent prostate
cancer. PLoS One. 9:e986752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li D, Yang P, Li H, Cheng P, Zhang L, Wei
D, Su X, Peng J, Gao H, Tan Y, et al: MicroRNA-1 inhibits
proliferation of hepatocarcinoma cells by targeting endothelin-1.
Life Sci. 91:440–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Letelier P, Garcia P, Leal P, Álvarez H,
Ili C, López J, Castillo J, Brebi P and Roa JC: miR-1 and miR-145
act as tumor suppressor microRNAs in gallbladder cancer. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:1849–1867. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Q, Zhang B, Shao Y, Chen L, Wang X,
Zhang Z, Shu Y and Guo R: Correlation between the expression levels
of miR-1 and PIK3CA in non-small-cell lung cancer and their
relationship with clinical characteristics and prognosis. Future
Oncol. 10:49–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han C, Zhou Y, An Q, Li F, Li D, Zhang X,
Yu Z, Zheng L, Duan Z and Kan Q: MicroRNA-1 (miR-1) inhibits
gastric cancer cell proliferation and migration by targeting MET.
Tumour Biol. 36:6715–6723. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh A, Happel C, Manna SK,
Acquaah-Mensah G, Carrerero J, Kumar S, Nasipuri P, Krausz KW,
Wakabayashi N, Dewi R, et al: Transcription factor NRF2 regulates
miR-1 and miR-206 to drive tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest.
123:2921–2934. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chang YS, Chen WY, Yin JJ,
Sheppard-Tillman H, Huang J and Liu YN: EGF receptor promotes
prostate cancer bone metastasis by downregulating miR-1 and
activating TWIST1. Cancer Res. 75:3077–3086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin C, Yan B, Lu Q, Lin Y and Ma L:
Reciprocal regulation of Hsa-miR-1 and long noncoding RNA MALAT1
promotes triple-negative breast cancer development. Tumour Biol.
37:7383–7394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Gu X, Fang Y, Xiang J and Chen Z:
microRNA expression profiles in human colorectal cancers with brain
metastases. Oncol Lett. 3:346–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Li S, Xu X, Wu S, Chen R, Jiang Q,
Li Y and Xu Y: The potential value of miR-1 and miR-374b as
biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:2840–2851. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Furukawa S, Kawasaki Y, Miyamoto M,
Hiyoshi M, Kitayama J and Akiyama T: The miR-1-NOTCH3-Asef pathway
is important for colorectal tumor cell migration. PLoS One.
8:e806092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Manzo SG, Zhou ZL, Wang YQ, Marinello J,
He JX, Li YC, Ding J, Capranico G and Miao ZH: Natural product
triptolide mediates cancer cell death by triggering CDK7-dependent
degradation of RNA polymerase II. Cancer Res. 72:5363–5373. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oh HR, An CH, Yoo NJ and Lee SH:
Frameshift mutations of TAF7L gene, a core component for
transcription by RNA polymerase II, in colorectal cancers. Pathol
Oncol Res. 21:849–850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harrison DA: The Jak/STAT pathway. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4(pii): a0112052012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
O'Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV,
Gadina M, McInnes IB and Laurence A: The JAK-STAT pathway: Impact
on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med.
66:311–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Kadlubar SA,
Bondurant KL and Wolff RK: JAK/STAT/SOCS-signaling pathway and
colon and rectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 52:155–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang SW, Hu J, Guo QH, Zhao Y, Cheng JJ,
Zhang DS, Fei Q, Li J and Sun YM: AZD1480, a JAK inhibitor,
inhibits cell growth and survival of colorectal cancer via
modulating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
32:1991–1998. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Witte S and Muljo SA: Integrating
non-coding RNAs in JAK-STAT regulatory networks. JAKSTAT.
3:e280552014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Aghaee-Bakhtiari SH, Arefian E, Naderi M,
Noorbakhsh F, Nodouzi V, Asgari M, Fard-Esfahani P, Mahdian R and
Soleimani M: MAPK and JAK/STAT pathways targeted by miR-23a and
miR-23b in prostate cancer: Computational and in vitro approaches.
Tumour Biol. 36:4203–4212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eisman R, Surrey S, Ramachandran B,
Schwartz E and Poncz M: Structural and functional comparison of the
genes for human platelet factor 4 and PF4alt. Blood. 76:336–344.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Al-Astani Tengku Din TA, Shamsuddin SH,
Idris FM, Ariffin Wan Mansor WN, Abdul Jalal MI and Jaafar H:
Rapamycin and PF4 induce apoptosis by upregulating Bax and
down-regulating survivin in MNU-induced breast cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3939–3944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pucci F, Rickelt S, Newton AP, Garris C,
Nunes E, Evavold C, Pfirschke C, Engblom C, Mino-Kenudson M, Hynes
RO, et al: PF4 promotes platelet production and lung cancer growth.
Cell Rep. 17:1764–1772. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jian J, Pang Y, Yan HH, Min Y, Achyut BR,
Hollander MC, Lin PC, Liang X and Yang L: Platelet factor 4 is
produced by subsets of myeloid cells in premetastatic lung and
inhibits tumor metastasis. Oncotarget. 8:27725–27739. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abbasciano V, Bianchi MP, Trevisani L,
Sartori S, Gilli G and Zavagli G: Platelet activation and
fibrinolysis in large bowel cancer. Oncology. 52:381–384. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peterson JE, Zurakowski D, Italiano JE Jr,
Michel LV, Connors S, Oenick M, D'Amato RJ, Klement GL and Folkman
J: VEGF, PF4 and PDGF are elevated in platelets of colorectal
cancer patients. Angiogenesis. 15:265–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Maione TE, Gray GS, Hunt AJ and Sharpe RJ:
Inhibition of tumor growth in mice by an analogue of platelet
factor 4 that lacks affinity for heparin and retains potent
angiostatic activity. Cancer Res. 51:2077–2083. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|