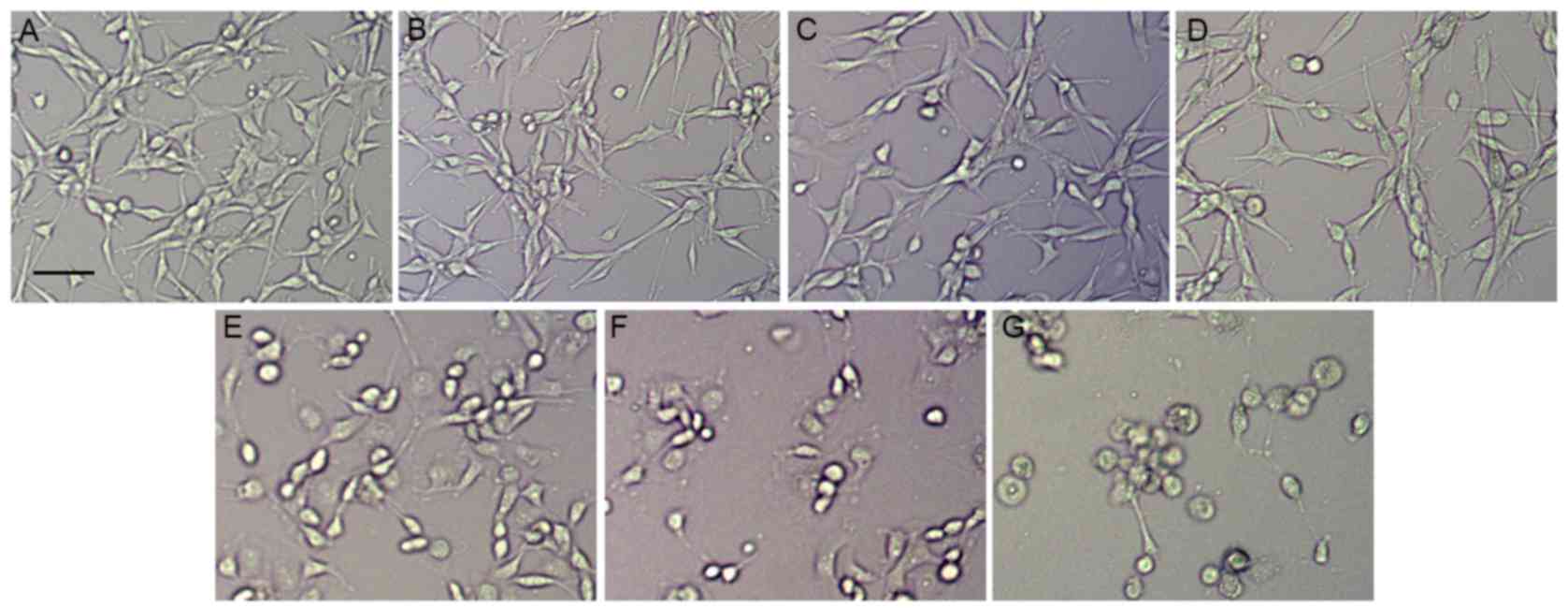
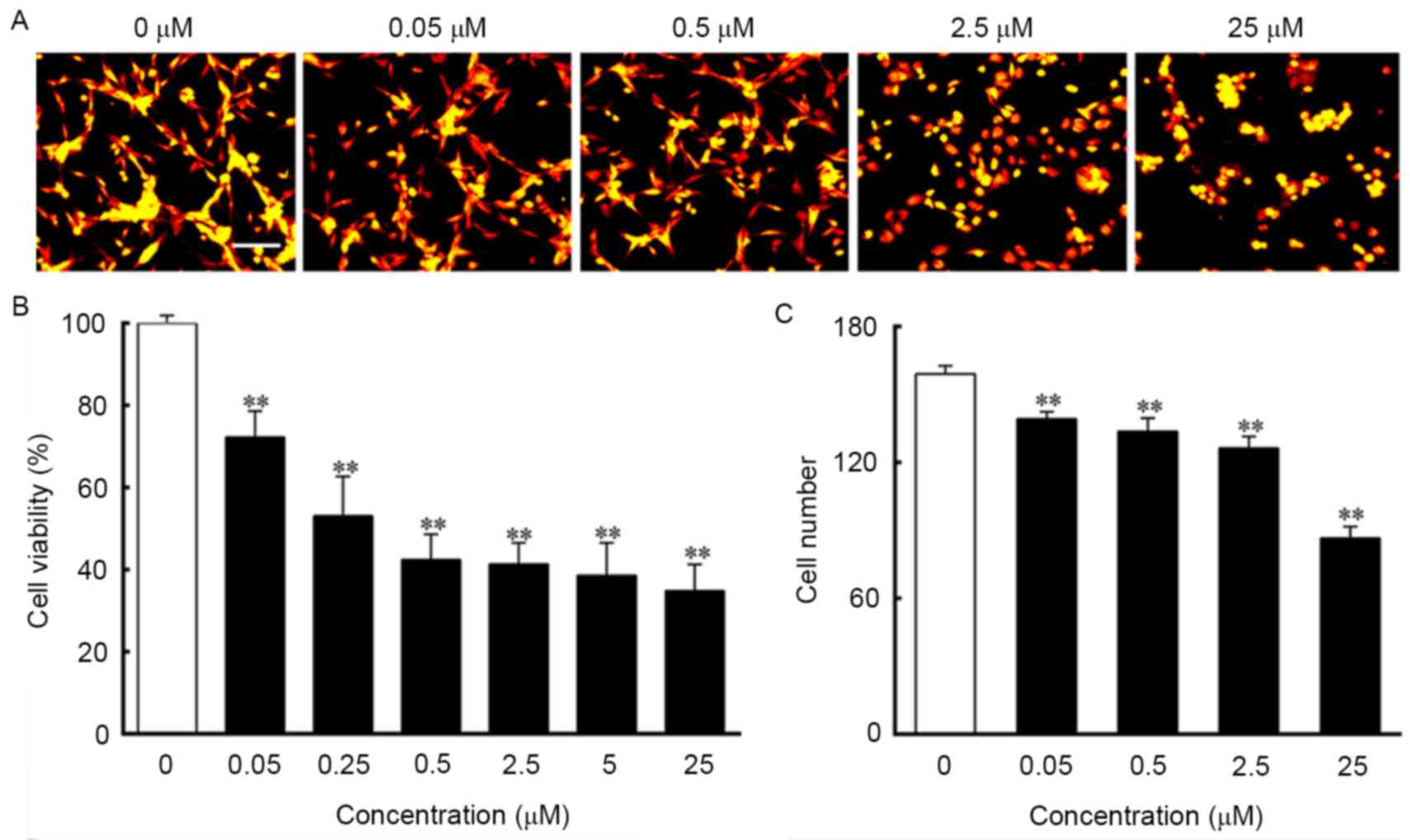
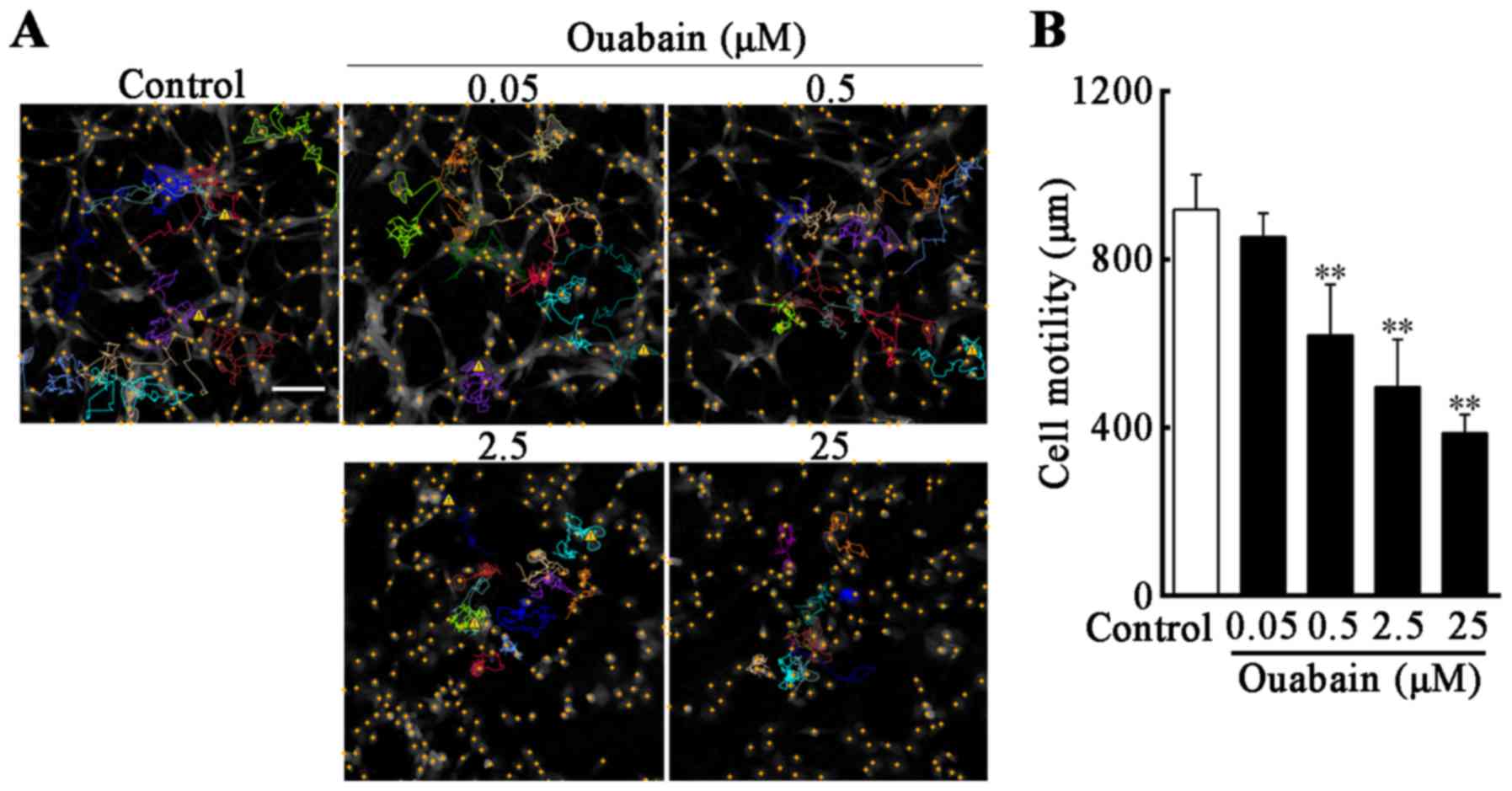
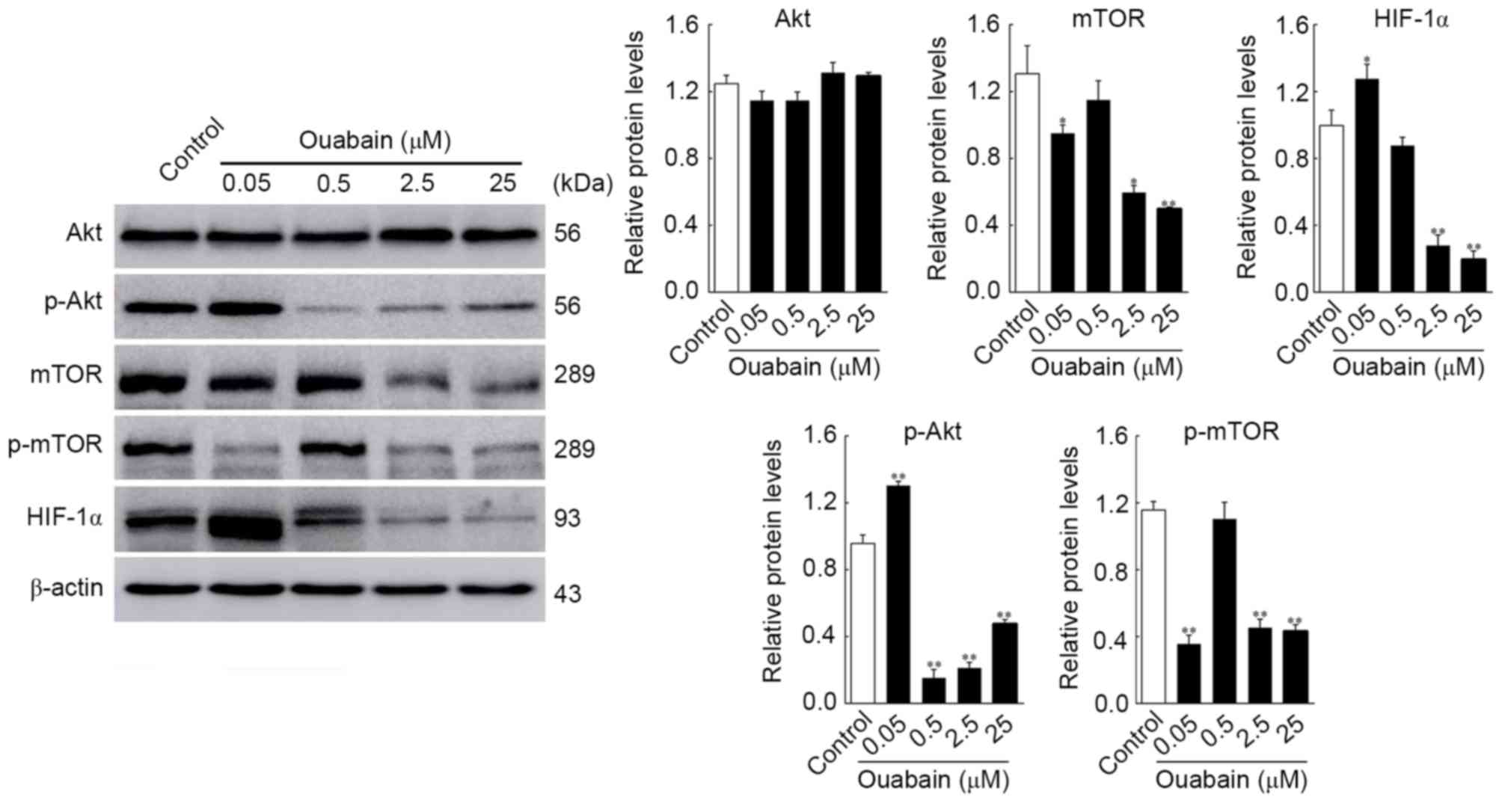
|
1
|
Jain A, Lai JC and Bhushan A: Biochanin A
inhibits endothelial cell functions and proangiogenic pathways:
Implications in glioma therapy. Anticancer Drugs. 26:323–330. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bagrov AY, Shapiro JI and Fedorova OV:
Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: Physiology, pharmacology, and
novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol Rev. 61:9–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kulikov A, Eva A, Kirch U, Boldyrev A and
Scheiner-Bobis G: Ouabain activates signaling pathways associated
with cell death in human neuroblastoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1768:1691–1702. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim N, Yim HY, He N, Lee CJ, Kim JH, Choi
JS, Lee HS, Kim S, Jeong E, Song M, et al: Cardiac glycosides
display selective efficacy for STK11 mutant lung cancer. Sci Rep.
6:297212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu Z, Wang F, Fan F, Gu Y, Shan N, Meng X,
Cheng S, Liu Y, Wang C, Song Y and Xu R: Quantitative proteomics
reveals that the inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase
activity affects S-phase progression leading to a chromosome
segregation disorder by attenuating the Aurora A function in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Proteome Res. 14:4594–4602. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan X, Liang F, Li D and Zheng J: Ouabain
elicits human glioblastoma cells apoptosis by generating reactive
oxygen species in ERK-p66SHC-dependent pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
398:95–104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang L, Zhang Z, Guo H and Wang Y:
Na+/K+-ATPase-mediated signal transduction
and Na+/K+- ATPase regulation. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 22:615–621. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Desfrere L, Karlsson M, Hiyoshi H,
Malmersjö S, Nanou E, Estrada M, Miyakawa A, Lagercrantz H, El
Manira A, Lal M and Uhlén P: Na, K-ATPase signal transduction
triggers CREB activation and dendritic growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:pp. 2212–2217. 2009; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prassas I and Diamandis EP: Novel
therapeutic applications of cardiac glycosides. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 7:926–935. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei L, Su YK, Lin CM, Chao TY, Huang SP,
Huynh TT, Jan HJ, Whang-Peng J, Chiou JF, Wu AT and Hsiao M:
Preclinical investigation of ibrutinib, a Bruton's kinase tyrosine
(Btk) inhibitor, in suppressing glioma tumorigenesis and stem cell
phenotypes. Oncotarget. 7:69961–69975. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie Z: Molecular mechanisms of
Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
986:497–503. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ahmed Z, Deyama Y, Yoshimura Y and Suzuki
K: Cisplatin sensitivity of oral squamous carcinoma cells is
regulated by Na+, K+-ATPase activity rather
than copper-transporting P-type ATPases, ATP7A and ATP7B. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 63:643–650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin Y, Ho DH and Newman RA: Human tumor
cell sensitivity to oleandrin is dependent on relative expression
of Na+, K+-ATPase subunitst. J Exp Ther
Oncol. 8:271–286. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu J, Akkuratov EE, Bai Y, Gaskill CM,
Askari A and Liu L: Cell signaling associated with
Na+/K+-ATPase: Activation of
phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase IA/Akt by ouabain is independent of
Src. Biochemistry. 52:9059–9067. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Joy A, Kapoor M, Georges J, Butler L,
Chang Y, Li C, Crouch A, Smirnov I, Nakada M, Hepler J, et al: The
role of AKT isoforms in glioblastoma: AKT3 delays tumor
progression. J Neurooncol. 130:43–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clark PA, Bhattacharya S, Elmayan A,
Darjatmoko SR, Thuro BA, Yan MB, van Ginkel PR, Polans AS and Kuo
JS: Resveratrol targeting of AKT and p53 in glioblastoma and
glioblastoma stem-like cells to suppress growth and infiltration. J
Neurosurg. 126:1448–1460. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Zheng J, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Yang Y,
Bai M and Dai Y: Fucoxanthin activates apoptosis via inhibition of
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and suppresses invasion and migration by
restriction of p38-MMP-2/9 pathway in human glioblastoma cells.
Neurochem Res. 41:2728–2751. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rapisarda A, Uranchimeg B, Sordet O,
Pommier Y, Shoemaker RH and Melillo G: Topoisomerase I-mediated
inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1: Mechanism and therapeutic
implications. Cancer Res. 64:1475–1482. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thomas GV, Tran C, Mellinghoff IK, Welsbie
DS, Chan E, Fueger B, Czernin J and Sawyers CL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor determines sensitivity to inhibitors of mTOR in kidney
cancer. Nat Med. 12:122–127. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jensen RL, Ragel BT, Whang K and Gillespie
D: Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha)
decreases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and
tumor growth in malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol. 78:233–247. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Soeda A, Park M, Lee D, Mintz A,
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, McKay RD, Engh J, Iwama T, Kunisada T,
Kassam AB, et al: Hypoxia promotes expansion of the CD133-positive
glioma stem cells through activation of HIF-1alpha. Oncogene.
28:3949–3959. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lum JJ, Bui T, Gruber M, Gordan JD,
DeBerardinis RJ, Covello KL, Simon MC and Thompson CB: The
transcription factor HIF-1alpha plays a critical role in the growth
factor-dependent regulation of both aerobic and anaerobic
glycolysis. Genes Dev. 21:1037–1049. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
García-Maceira P and Mateo J: Silibinin
inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1
signalling pathway in human cervical and hepatoma cancer cells:
Implications for anticancer therapy. Oncogene. 28:313–324. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|