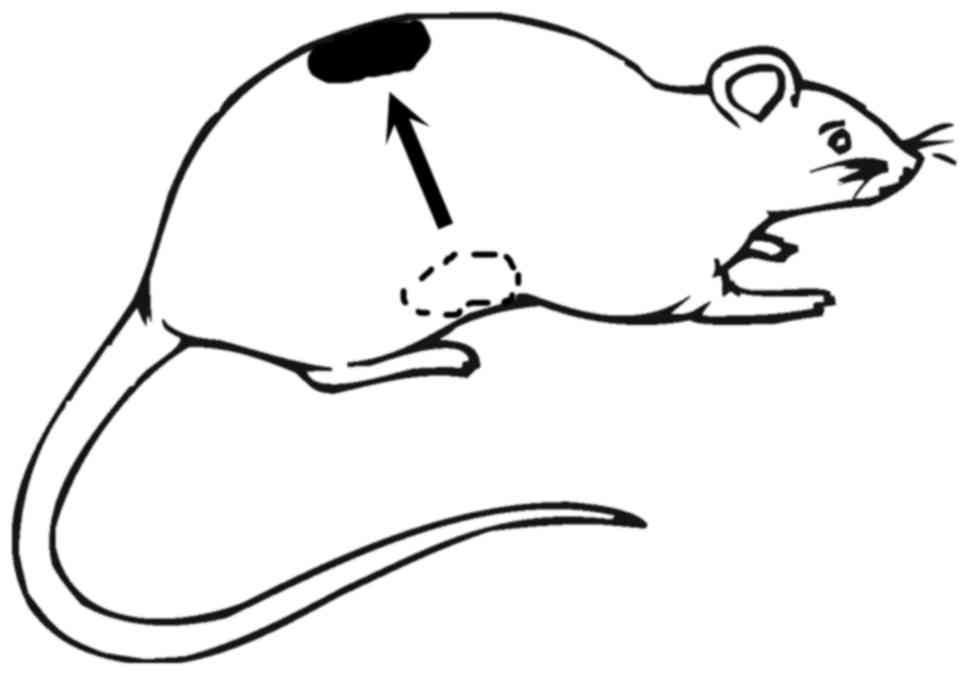
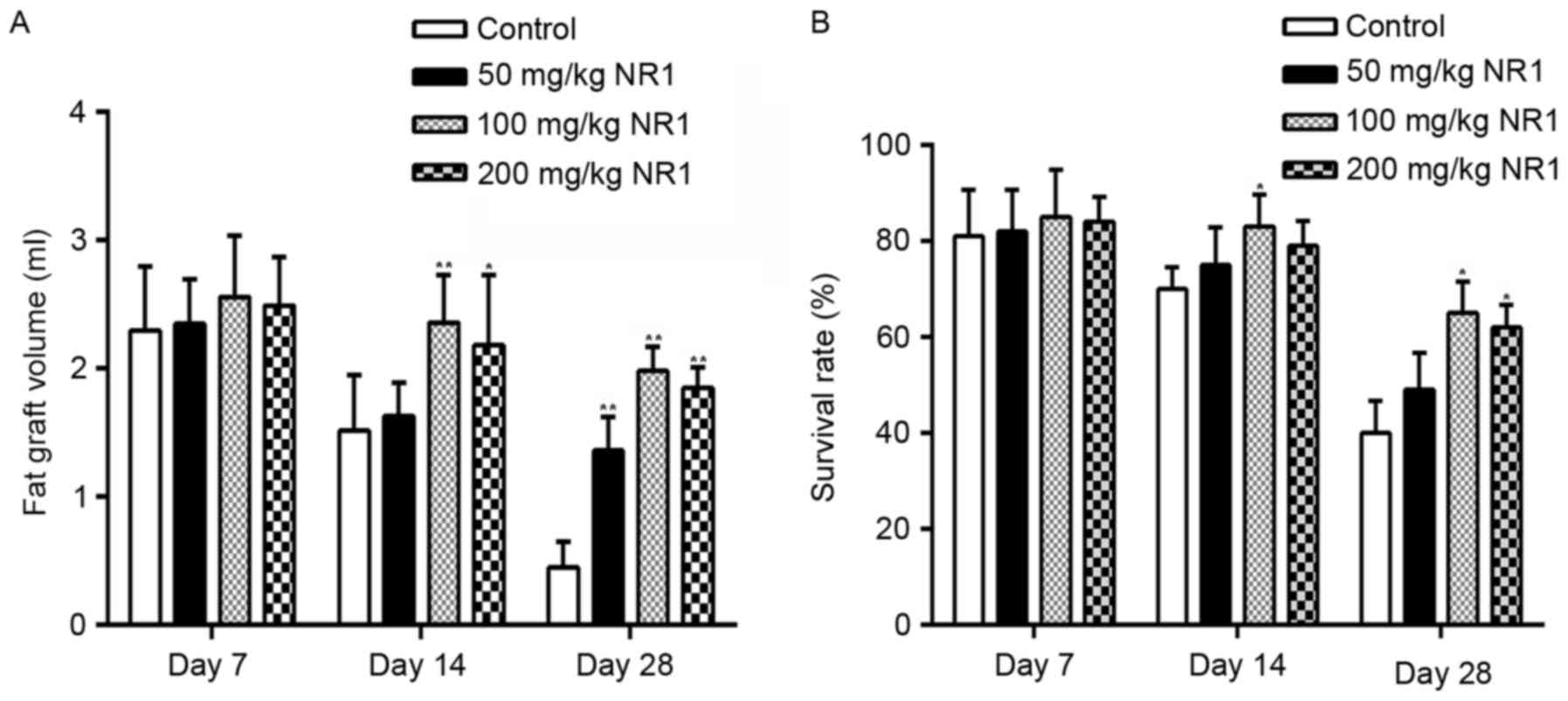
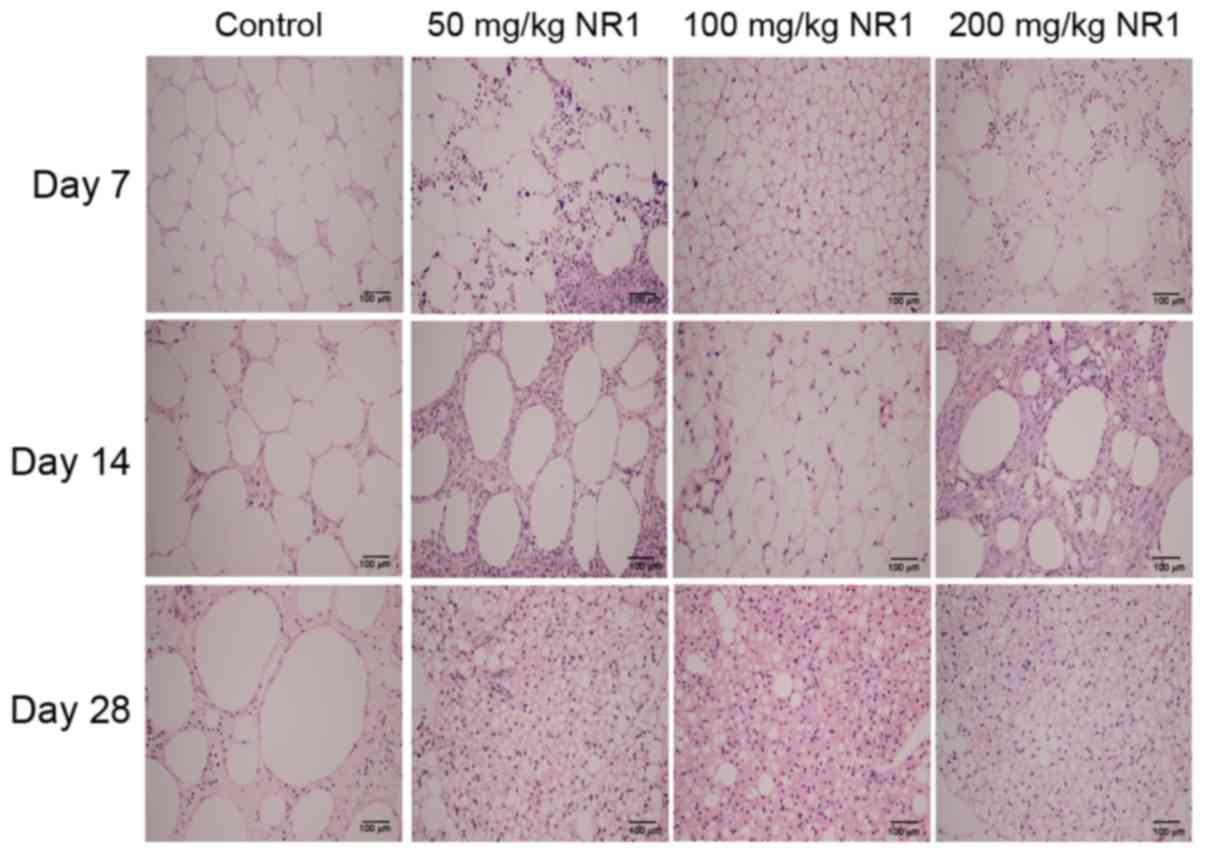
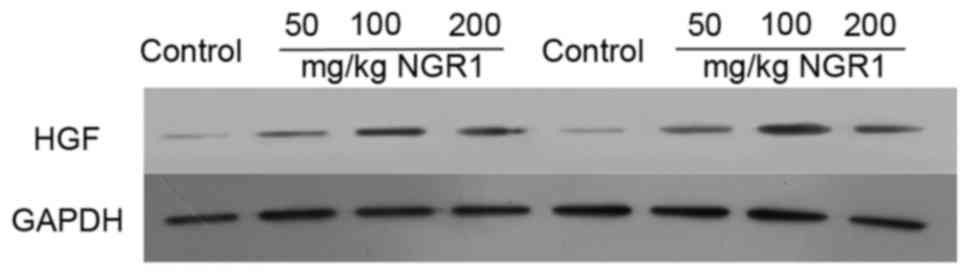
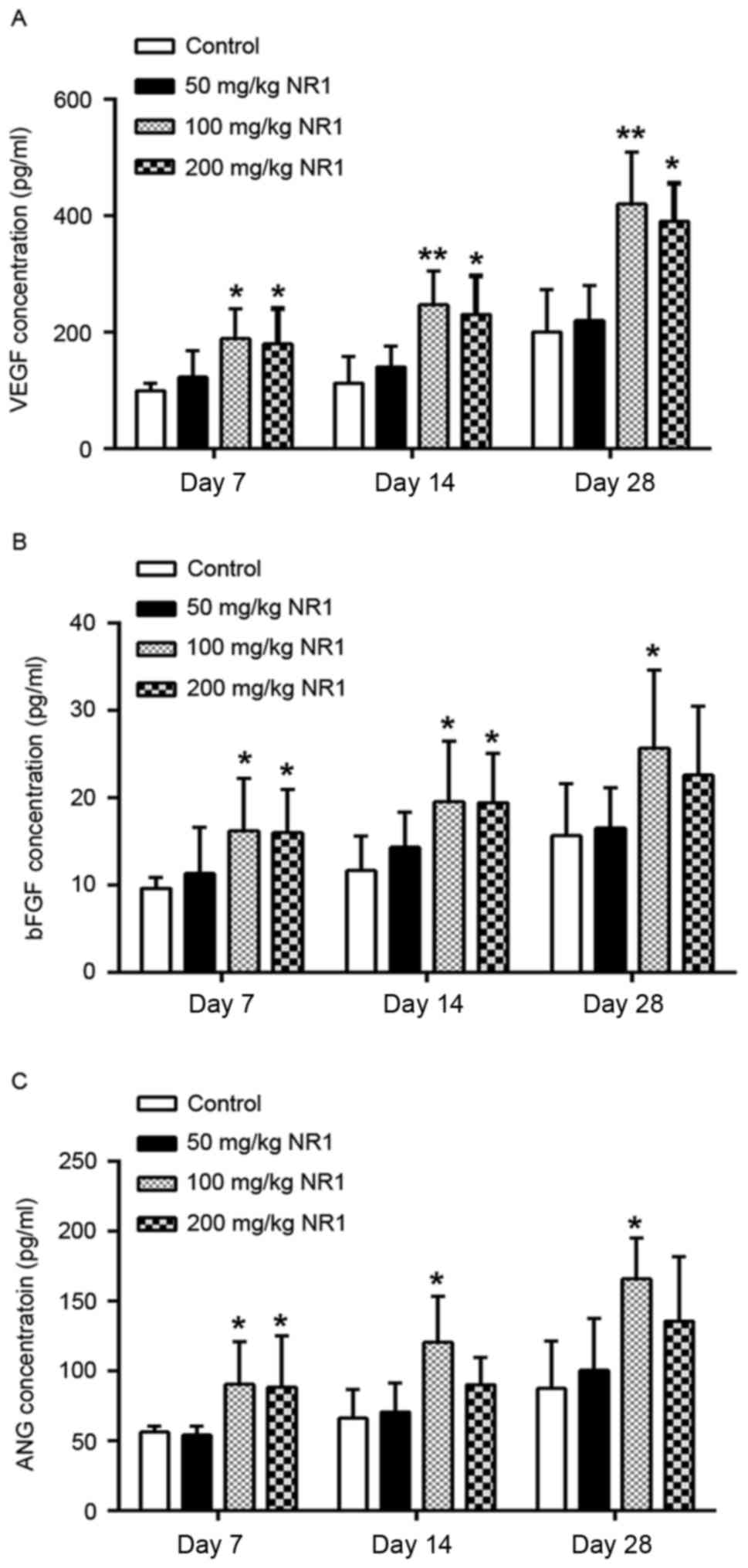
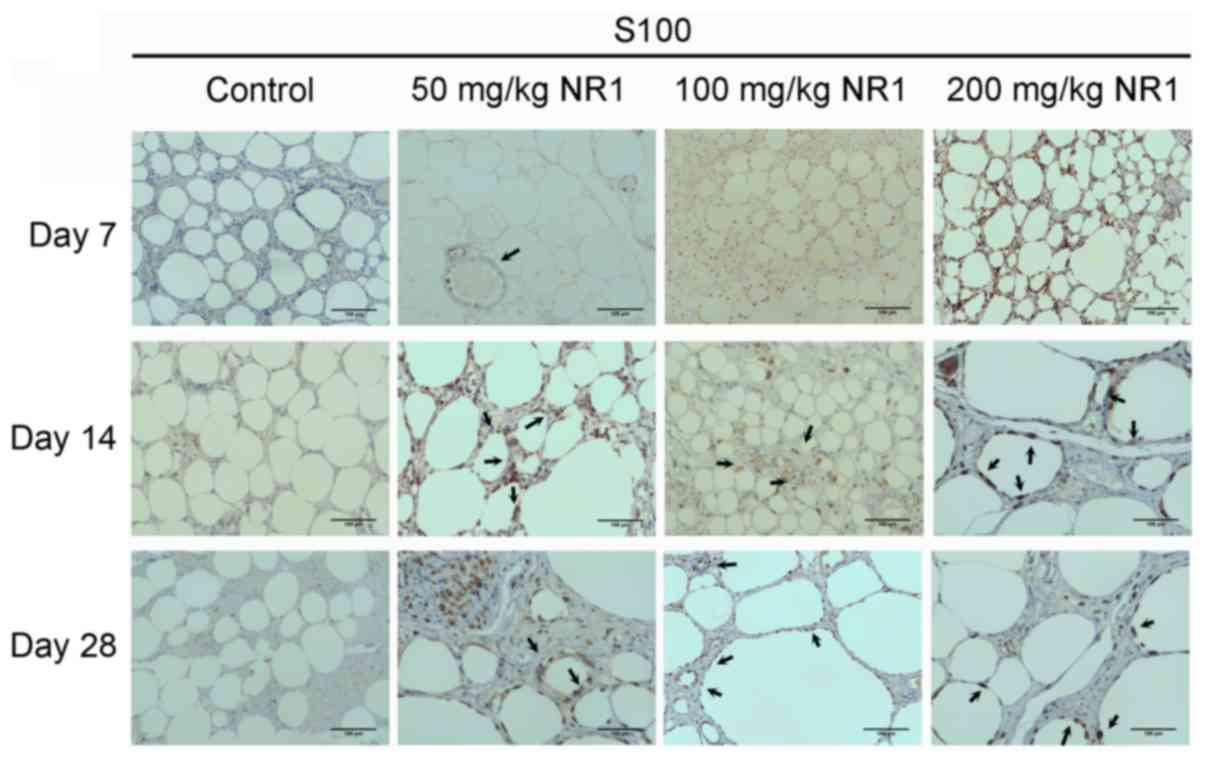
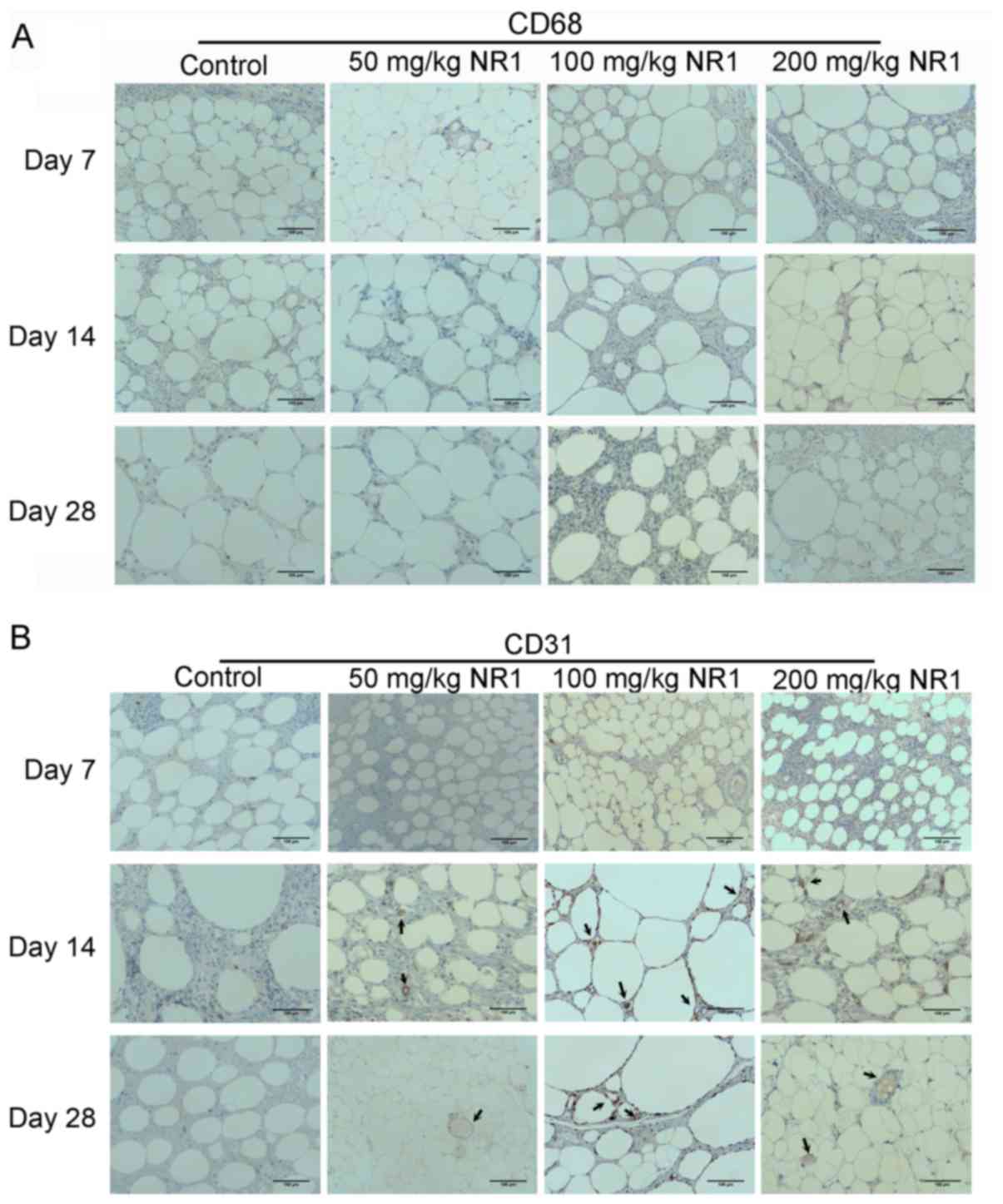
|
1
|
Vertemati M, Goffredi M, Moscheni C,
Callegari S and Vizzotto L: Human visceral fat in different
anthropometric patterns and in diabetes: A morphometric study. Anal
Quant Cytol Histol. 30:39–46. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huffman DM and Barzilai N: Contribution of
adipose tissue to health span and longevity. Interdiscip Top
Gerontol. 37:1–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cervelli D, Gasparini G, Grussu F, Moro A,
Matteo Marianetti T, Foresta E, Azzuni C and Pelo S: Autologous fat
transplantation for the temporalis muscle flap donor site: Our
experience with 45 cases. Head Neck. 36:1296–1304. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suszynski TM, Sieber DA, Van Beek AL and
Cunningham BL: Characterization of adipose tissue for autologous
fat grafting. Aesthet Surg J. 35:194–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kakaqia D and Pallua N: Autologous fat
grafting: In search of the optimal technique. Surg Innov.
21:327–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwon SG, Lee DW, Rah DK and Lee WJ:
Skin-fat composite grafts on full-thickness facial skin defects.
Ann Plast Surg. 71:176–180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pereira LH, Nicaretta B and Sterodimas A:
Correction of liposuction sequelae by autologous fat
transplantation. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 35:1000–1008. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li BQ, Chen J, Wu TX, Zhai HL and Zhang
XY: Fast determination of four active compounds in Sanqi Panax
Notoginseng Injection samples by high-performance liquid
chromatography with a chemometric method. J Sep Sci. 38:1449–1457.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo Q, Li P, Wang Z, Cheng Y, Wu H, Yang
B, Du S and Lu Y: Brain distribution pharmacokinetics and
integrated pharmacokinetics of Panax Notoginsenoside R1,
Ginsenosides Rg1, Rb1, Re and Rd in rats after intranasal
administration of Panax Notoginseng Saponins assessed by
UPLC/MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
969:264–271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ding RB, Tian K, Cao YW, Bao JL, Wang M,
He C, Hu Y, Su H and Wan JB: Protective effect of Panax notoginseng
saponins on acute ethanol-induced liver injury is associated with
ameliorating hepatic lipid accumulation and reducing
ethanol-mediated oxidative stress. J Agric Food Chem. 63:2413–2422.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao Y, Wu WY, Liu AH, Deng SS, Bi KS, Liu
X and Guo DA: Interaction of salvianolic acids and
notoginsengnosides in inhibition of ADP-induced platelet
aggregation. Am J Chin Med. 36:313–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan Z, Liao Y, Tian G, Li H, Jia Y, Zhang
H, Tan Z, Li X, Deng W, Liu K and Zhang Y: Panax notoginseng
saponins inhibit Zymosan A induced atherosclerosis by suppressing
integrin expression, FAK activation and NF-κB translocation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 138:150–155. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu HZ, Liu ZL, Zhao SP, Sun CZ and Yang
MS: Protective mechanism of Panax notoginseng saponins on rat
hemorrhagic shock model in recovery stage. Cell Biochem Biophys.
70:1719–1724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang N, Wan JB, Chan SW, Deng YH, Yu N,
Zhang QW, Wang YT and Lee SM: Comparative study on saponin
fractions from Panax notoginseng inhibiting inflammation-induced
endothelial adhesion molecule expression and monocyte adhesion.
Chin Med. 6:372011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin JH, Zhu LQ and Cui W: Effects of Panax
notoginseng saponins on expression of intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells injury induced
by oxidized low-density lipoprotein. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za
Zhi. 28:1096–1099. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin F and Gou X: Panax notoginseng
saponins improve the erectile dysfunction in diabetic rats by
protecting the endothelial function of the penile corpus
cavernosum. Int J Impot Res. 25:206–211. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang WJ, Wojta J and Binder BR:
Notoginsenoside R1 counteracts endotoxin-induced activation of
endothelial cells in vitro and endotoxin-induced lethality in mice
in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17:465–474. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Foster MT, Solomon MB, Huhman KL and
Bartness TJ: Social defeat increases food intake, body mass, and
adiposity in Syrian hamsters. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp
Physiol. 290:R1284–R1293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bartness TJ, Kay Song C, Shi H, Bowers RR
and Foster MT: Brain-adipose tissue cross talk. Proc Nutr Soc.
64:pp. 53–64. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim J, Lee H, Lim J, Oh J, Shin SS and
Yoon M: The angiogenesis inhibitor ALS-L1023 from lemon-balm leaves
attenuates high-fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases
through regulation the visceral adipose-tissue functions. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(pii): E8462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Gao J, Song L and Wu X: Clinical
evaluation of effect of transplantation by auto-fat granule
injection for mastatrophy post suckling. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 22:343–345. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kurisu M, Nakasone R, Miyamae Y, Matsuura
D, Kanatani H, Yano S and Shigemori H: Induction of hepatocyte
growth factor production in human dermal fibroblasts by caffeic
acid derivatives. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:2018–2021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Neuss S, Becher E, Wöltje M, Tietze L and
Jahnen-Dechent W: Functional expression of HGF and HGF
receptor/c-met in adult human mesenchymal stem cells suggests a
role in cell mobilization, tissue repair, and wound healing. Stem
Cells. 22:405–414. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan Y, Lu F and Gao J: Mechanism of
vascular stromal fraction at early stage after aspirated fat
transplantation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.
27:449–453. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Slevin M, Krupinski J, Rovira N, Turu M,
Luque A, Baldellou M, Sanfeliu C, de Vera N and Badimon L:
Identification of pro-angiogenic markers in blood vessels from
stroked-affected brain tissue using laser-capture microdissection.
BMC Genomics. 10:1132009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han D, Ma Z, Zhang P, Yang JF, Zhang Y,
Yang D and Liu J: Muscle derived stem cell contains the potential
to enhance long term retention as well as an aesthetic outcome of
autologous fat grafting. Med Hypotheses. 76:805–808. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu M, Dong Z, Gao J, Liao Y, Xue J, Yuan
Y, Liu L, Chang Q and Lu F: Adipocyte regeneration after free fat
transplantation: Promotion by stromal vascular fraction cells. Cell
Transplant. 24:49–62. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suga H, Glotzbach JP, Sorkin M, Longaker
MT and Gurtner GC: Paracrine mechanism of angiogenesis in
adipose-derived stem cell transplantation. Ann Plast Surg.
72:234–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang A, Li M, Duan W, Dong Y and Wang Y:
Improvement of the survival of human autologous fat transplantation
by adipose-derived stem-cells-assisted lipotransfer combined with
bFGF. ScientificWorldJournal. 2015:9680572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Krawiec JT, Weinbaum JS, St Croix CM,
Phillippi JA, Watkins SC, Rubin JP and Vorp DA: A cautionary tale
for autologous vascular tissue engineering: Impact of human
demographics on the ability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem
cells to recruit and differentiate into smooth muscle cells. Tissue
Eng Part A. 21:426–437. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bargut TC, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA and
Aguila MB: A high-fish-oil diet prevents adiposity and modulates
white adipose tissue inflammation pathways in mice. J Nutr Biochem.
26:960–969. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dost T, Kafkas S, Gokalp F, Karul A and
Birincioglu M: Effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition
on adiponectin levels and lipid profile in the ovariectomized-aged
rats. J Pharmacol Pharmacother. 5:21–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hira VV, Ploegmakers KJ, Grevers F,
Verbovšek U, Silvestre-Roig C, Aronica E, Tigchelaar W, Turnšek TL,
Molenaar RJ and Van Noorden CJ: CD133+ and
nestin+ glioma stem-like cells reside around
CD31+ arterioles in niches that express SDF-1α, CXCR4,
osteopontin and cathepsin K. J Histochem Cytochem. 63:481–493.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|