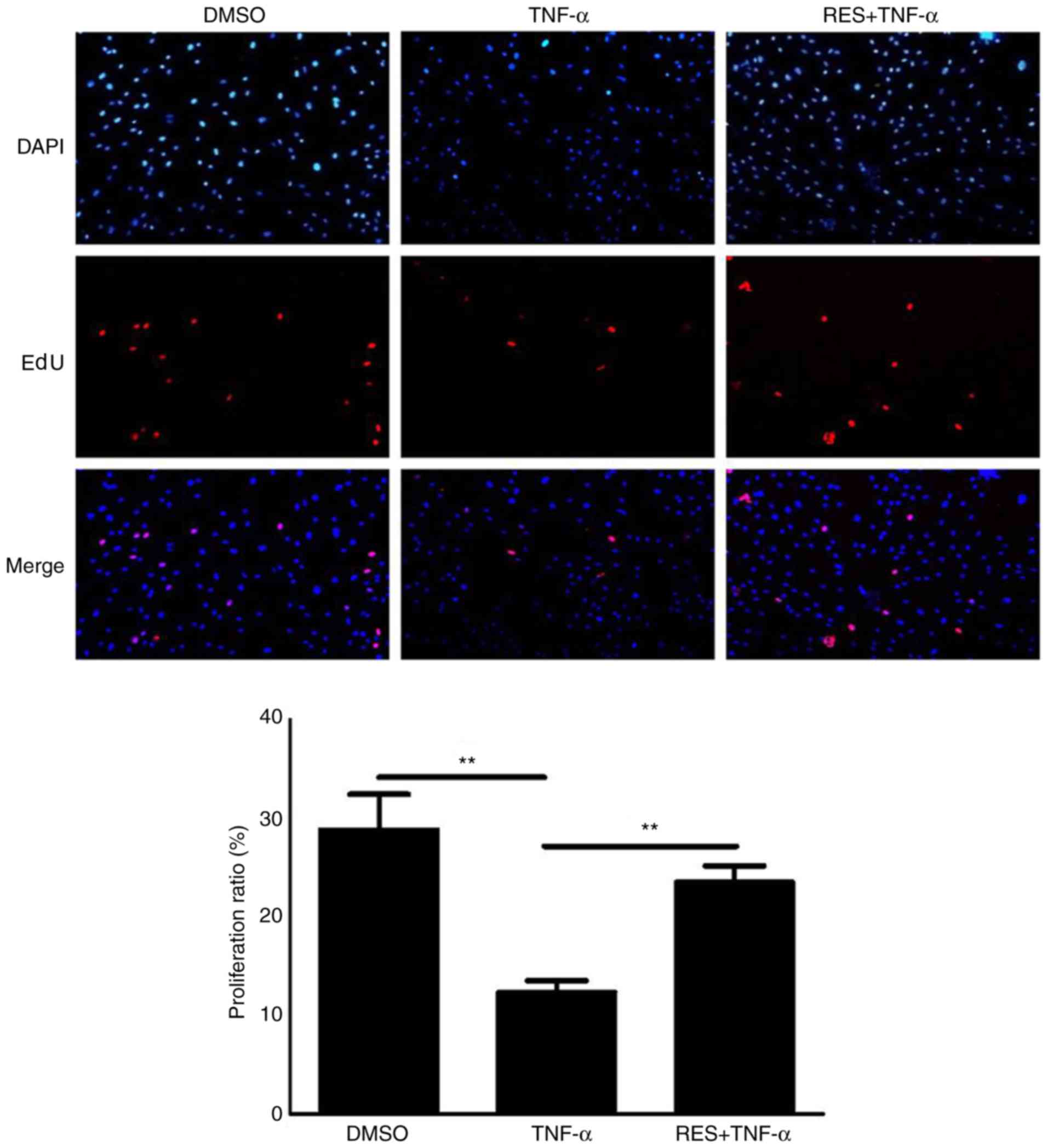
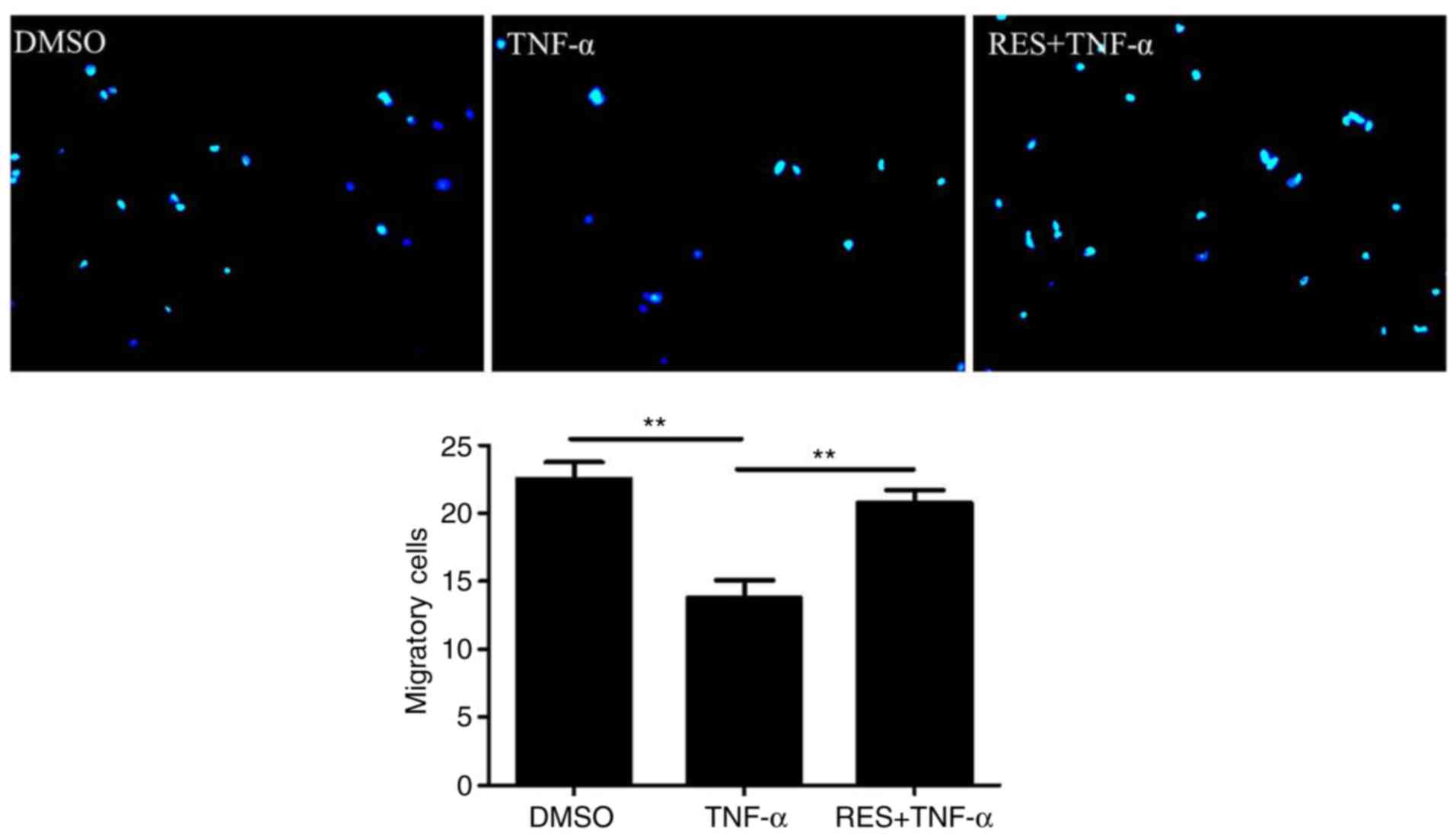
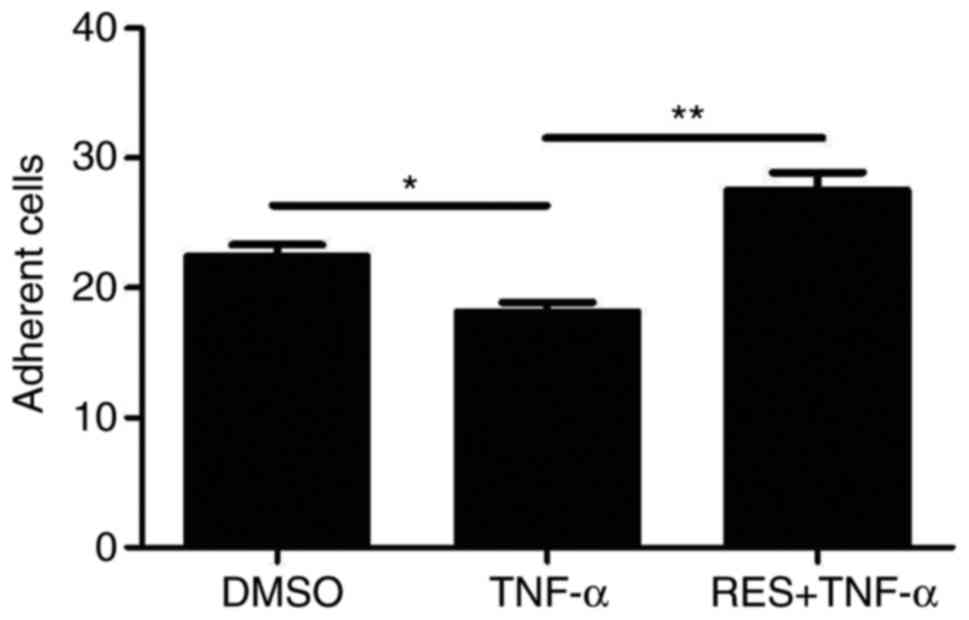
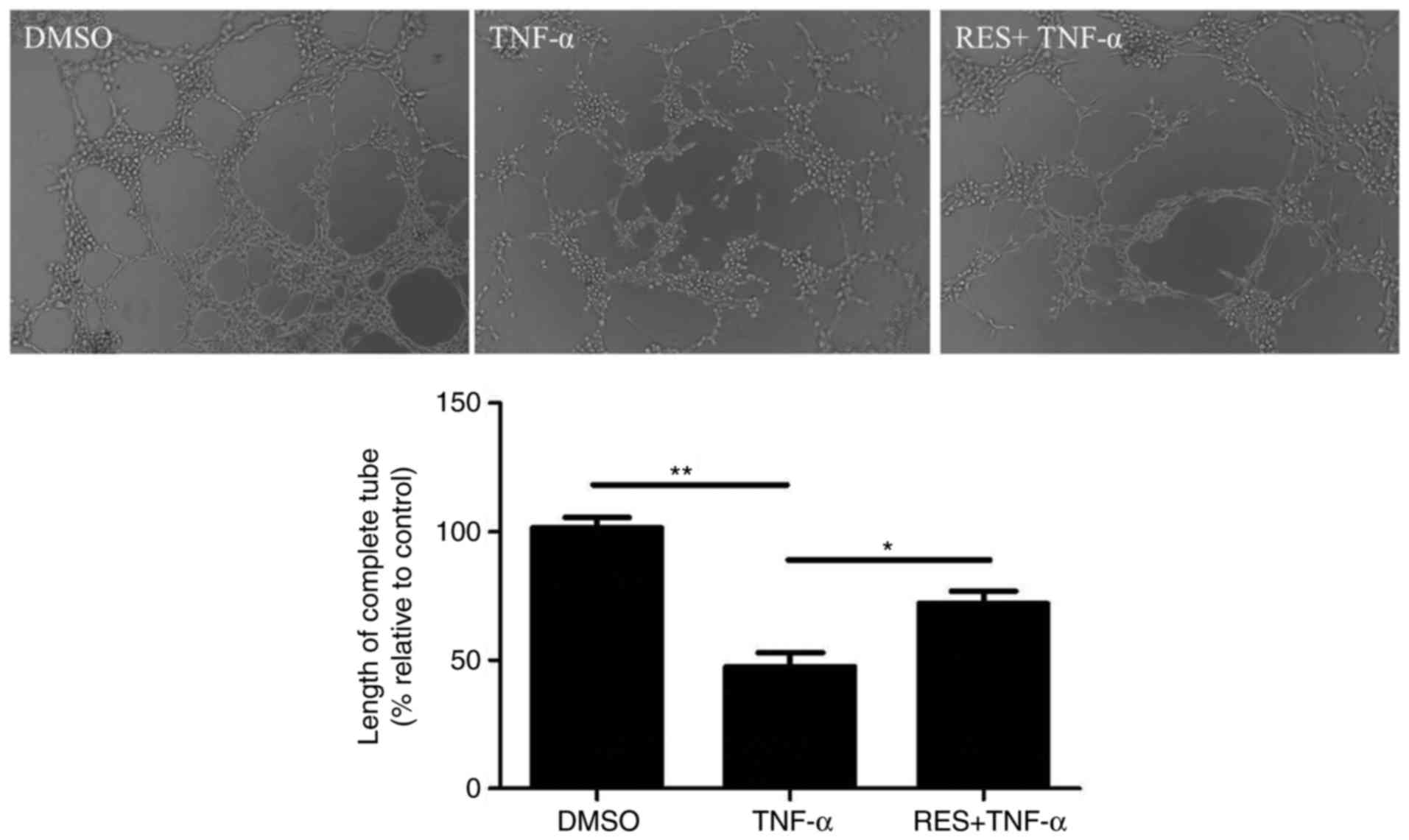
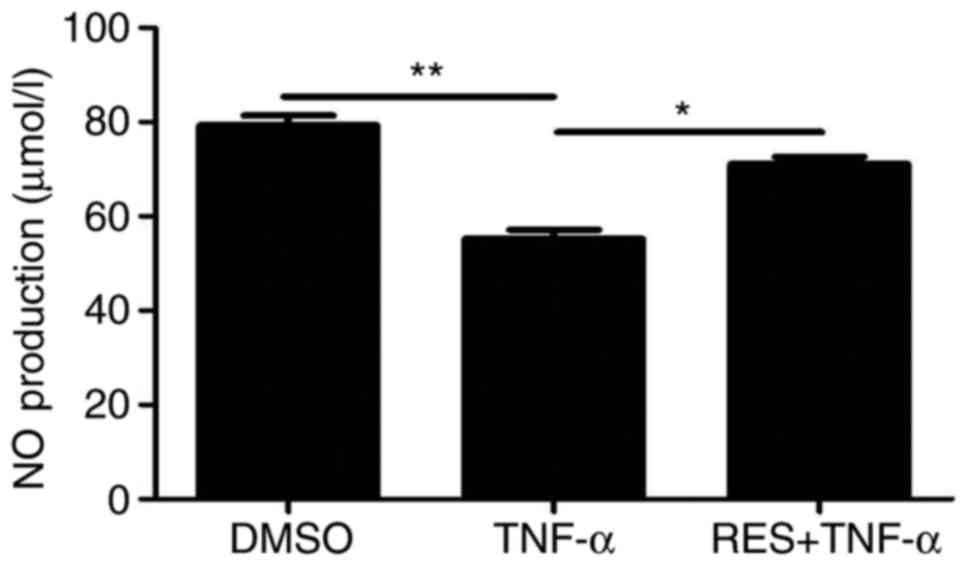
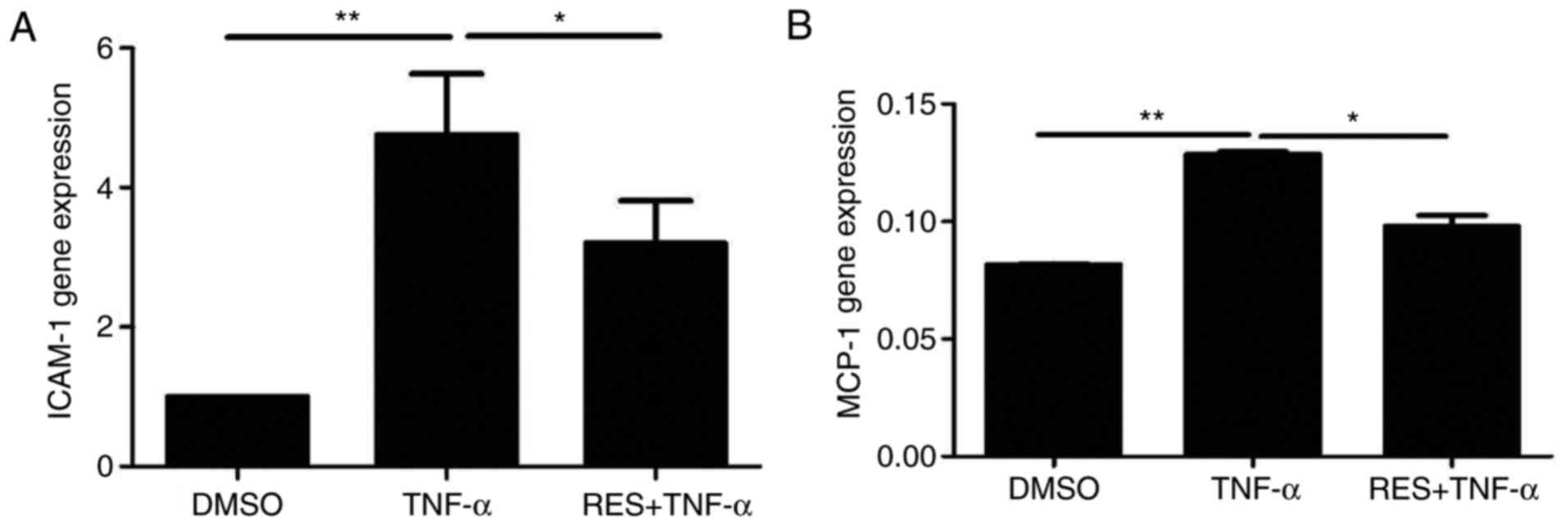
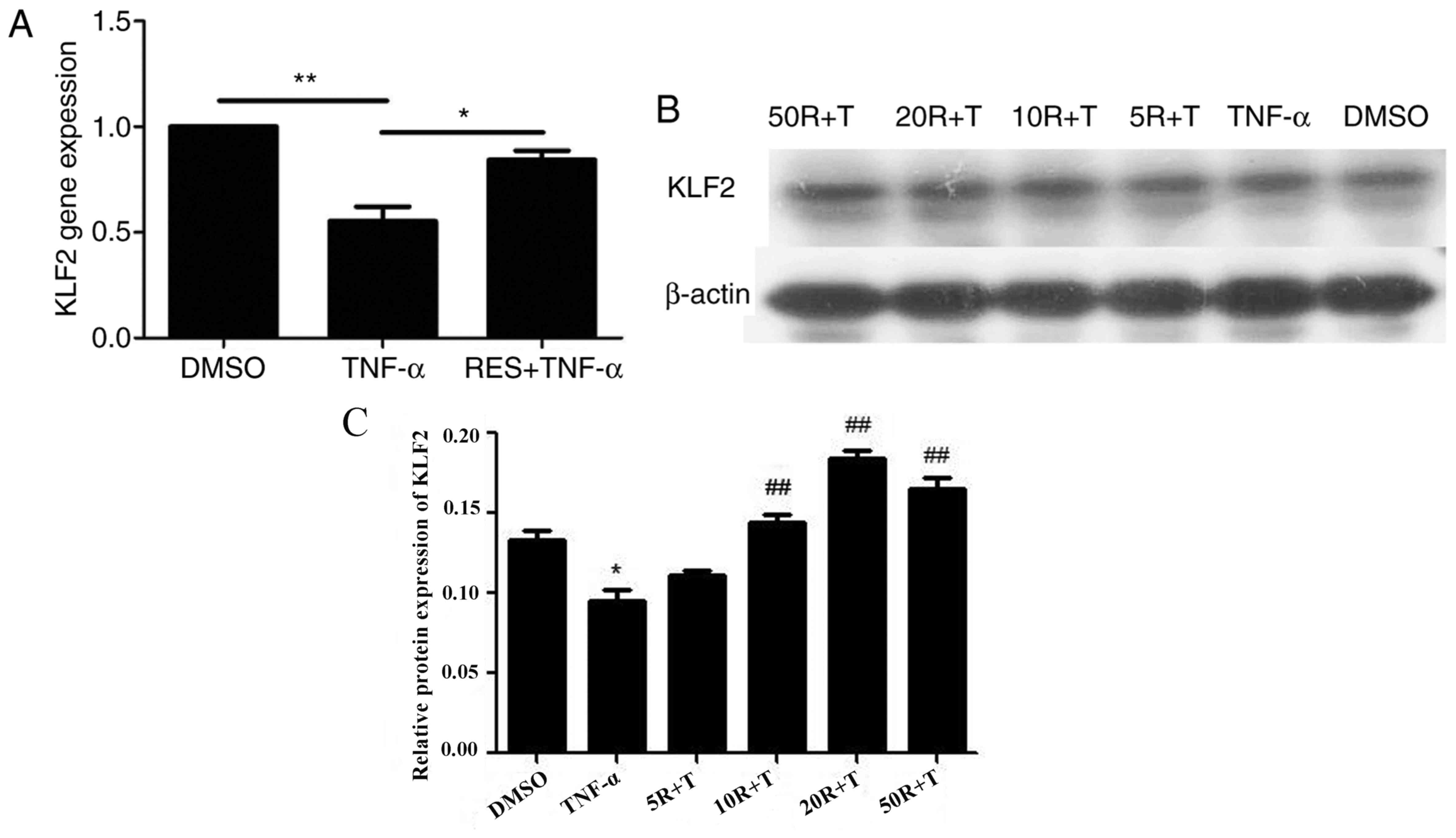
|
1
|
Hill JM, Zalos G, Halcox JP, Schenke WH,
Waclawiw MA, Quyyumi AA and Finkel T: Circulating endothelial
progenitor cells, vascular function, and cardiovascular risk. N
Engl J Med. 348:593–600. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schmidt-Lucke C, Rössig L, Fichtlscherer
S, Vasa M, Britten M, Kämper U, Dimmeler S and Zeiher AM: Reduced
number of circulating endothelial progenitor cells predicts future
cardiovascular events: Proof of concept for the clinical importance
of endogenous vascular repair. Circulation. 111:2981–2987. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zampetaki A, Kirton JP and Xu Q: Vascular
repair by endothelial progenitor cells. Cardiovasc Res. 78:413–421.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller-Kasprzak E and Jagodziński PP:
Endothelial progenitor cells as a new agent contributing to
vascular repair. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 55:247–259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Paramo JA, Rodríguez JA and Orbe J:
Atherosclerosis in inflammatory diseases. Med Clin (Barc).
128:749–756. 2007.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tousoulis D, Andreou I, Antoniades C,
Tentolouris C and Stefanadis C: Role of inflammation and oxidative
stress in endothelial progenitor cell function and mobilization:
Therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases.
Atherosclerosis. 201:236–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jang M, Cai L, Udeani GO, Slowing KV,
Thomas CF, Beecher CW, Fong HH, Farnsworth NR, Kinghorn AD, Mehta
RG, et al: Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a
natural product derived from grapes. Science. 275:218–220. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmitt CA, Heiss EH and Dirsch VM: Effect
of resveratrol on endothelial cell function: Molecular mechanisms.
Biofactors. 36:342–349. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang H, Yang YJ, Qian HY, Zhang Q, Xu H
and Li JJ: Resveratrol in cardiovascular disease: What is known
from current research? Heart Fail Rev. 17:437–448. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bruunsgaard H, Skinhøj P, Pedersen AN,
Schroll M and Pedersen BK: Ageing, tumour necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) and atherosclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 121:255–260.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Zhang J, Ungvari Z and Zhang C:
Resveratrol improves endothelial function: Role of TNF{alpha} and
vascular oxidative stress. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
29:1164–1171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pearson R, Fleetwood J, Eaton S, Crossley
M and Bao S: Krüppel-like transcription factors: A functional
family. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 40:1996–2001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Z, Kumar A, SenBanerjee S,
Staniszewski K, Parmar K, Vaughan DE, Gimbrone MA Jr,
Balasubramanian V, García-Cardeña G and Jain MK: Kruppel-like
factor 2 (KLF2) regulates endothelial thrombotic function. Circ
Res. 96:e48–e57. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu J, Bohanan CS, Neumann JC and Lingrel
JB: KLF2 transcription factor modulates blood vessel maturation
through smooth muscle cell migration. J Biol Chem. 283:3942–3950.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sebzda E, Zou Z, Lee JS, Wang T and Kahn
ML: Transcription factor KLF2 regulates the migration of naive T
cells by restricting chemokine receptor expression patterns. Nat
Immunol. 9:292–300. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dekker RJ, van Thienen JV, Rohlena J, de
Jager SC, Elderkamp YW, Seppen J, de Vries CJ, Biessen EA, van
Berkel TJ, Pannekoek H and Horrevoets AJ: Endothelial KLF2 links
local arterial shear stress levels to the expression of vascular
tone-regulating genes. Am J Pathol. 167:609–618. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumar A, Lin Z, SenBanerjee S and Jain MK:
Tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated reduction of KLF2 is due to
inhibition of MEF2 by NF-kappaB and histone deacetylases. Mol Cell
Biol. 25:5893–5903. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li H, Zhang X, Guan X, Cui X, Wang Y, Chu
H and Cheng M: Advanced glycation end products impair the
migration, adhesion and secretion potentials of late endothelial
progenitor cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 11:462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen YH, Lin SJ, Lin FY, Wu TC, Tsao CR,
Huang PH, Liu PL, Chen YL and Chen JW: High glucose impairs early
and late endothelial progenitor cells by modifying nitric
oxide-related but not oxidative stress-mediated mechanisms.
Diabetes. 56:1559–1568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang C, YR HT, He Z, Jiang Q, Wu J, Zhen
Y, Fan M and Wu Z: Rosiglitazone via upregulation of Akt/eNOS
pathways attenuates dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells,
induced by advanced glycation end products. Br J Pharmacol.
158:1865–1873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Werner N and Nickenig G: Clinical and
therapeutical implications of EPC biology in atherosclerosis. J
Cell Mol Med. 10:318–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ku IA, Imboden JB, Hsue PY and Ganz P:
Rheumatoid arthritis: Model of systemic inflammation driving
atherosclerosis. Circ J. 73:977–985. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xia L, Wang XX, Hu XS, Guo XG, Shang YP,
Chen HJ, Zeng CL, Zhang FR and Chen JZ: Resveratrol reduces
endothelial progenitor cells senescence through augmentation of
telomerase activity by Akt-dependent mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol.
155:387–394. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gu J, Wang CQ, Zhang DD, Fan HH, He B,
Wang BY and Huang DJ: Effect of resveratrol on reendothelialization
and neointimal formation in intimal injury model. Chin J
Arterioscler. 14:829–834. 2006.
|
|
27
|
Wang XB, Zhu L, Huang J, Yin YG, Kong XQ,
Rong QF, Shi AW and Cao KJ: Resveratrol-induced augmentation of
telomerase activity delays senescence of endothelial progenitor
cells. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:4310–4315. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang XB, Huang J, Zou JG, Su EB, Shan QJ,
Yang ZJ and Cao KJ: Effects of resveratrol on number and activity
of endothelial progenitor cells from human peripheral blood. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 34:1109–1115. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matthys KE and Bult H: Nitric oxide
function in atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm. 6:3–21. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leifeld L, Fielenbach M, Dumoulin FL,
Speidel N, Sauerbruch T and Spengler U: Inducible nitric oxide
synthase (iNOS) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)
expression in fulminant hepatic failure. J Hepatol. 37:613–619.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Klinge CM, Blankenship KA, Risinger KE,
Bhatnagar S, Noisin EL, Sumanasekera WK, Zhao L, Brey DM and
Keynton RS: Resveratrol and estradiol rapidly activate MAPK
signaling through estrogen receptors alpha and beta in endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 280:7460–7468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wallerath T, Deckert G, Ternes T, Anderson
H, Li H, Witte K and Förstermann U: Resveratrol, a polyphenolic
phytoalexin present in red wine, enhances expression and activity
of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation. 106:1652–1658.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gracia-Sancho J, Villarreal G Jr, Zhang Y
and García-Cardeña G: Activation of SIRT1 by resveratrol induces
KLF2 expression conferring an endothelial vasoprotective
phenotypee. Cardiovasc Res. 85:514–519. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Scalera F, Fulge B, Martens-Lobenhoffer J,
Heimburg A and Bode-Böger SM: Red wine decreases asymmetric
dimethylarginine via SIRT1 induction in human endothelial cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 390:703–709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Piga R, Naito Y, Kokura S, Handa O and
Yoshikawa T: Short-term high glucose exposure induces
monocyte-endothelial cells adhesion and transmigration by
increasing VCAM-1 and MCP-1 expression in human aortic endothelial
cells. Atherosclerosis. 193:328–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Zhao X, Wang YS, Song SL, Liang H
and Ji AG: An extract from medical leech improve the function of
endothelial cells in vitro and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE
null mice by reducing macrophages in the lesions. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 455:119–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu J, Yong W, Wu X, Yu Y, Lv J and Liu C,
Mao X, Zhu Y, Xu K, Han X and Liu C: Anti-inflammatory effect of
resveratrol on TNF-alpha-induced MCP-1 expression in adipocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 369:471–477. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xiao J, Song J, Hodara V, Ford A, Wang XL,
Shi Q, Chen L and Vandeberg JL: Protective effects of resveratrol
on TNF-α-induced endothelial cytotoxicity in baboon femoral
arterial endothelial cells. J Diabetes Res 2013. 2013.doi:
10.1155/2013/185172.
|
|
39
|
Senbanerjee S, Lin Z, Atkins GB, Greif DM,
Rao RM, Kumar A, Feinberg MW, Chen Z, Simon DI, Luscinskas FW, et
al: KLF2 is a novel transcriptional regulator of endothelial
proinflammatory activation. J Exp Med. 199:1305–1315. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hampole AV, Mahabeleshwar GH, Sharma N and
Jain MK: Abstract 5546: Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF)2 inhibits
macrophage pro-inflammatory activation. Circulation.
120:S1113–S1114. 2009.
|
|
41
|
Zhou XB and Yang LX: Krüppel-like factor 2
and atherosclerosis. Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 33:224–246. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Jia YJ and Li JJ: Research Progress of
KLF2 anti-atherosclerosis. Mol Cardiol China. 5:303–307. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|