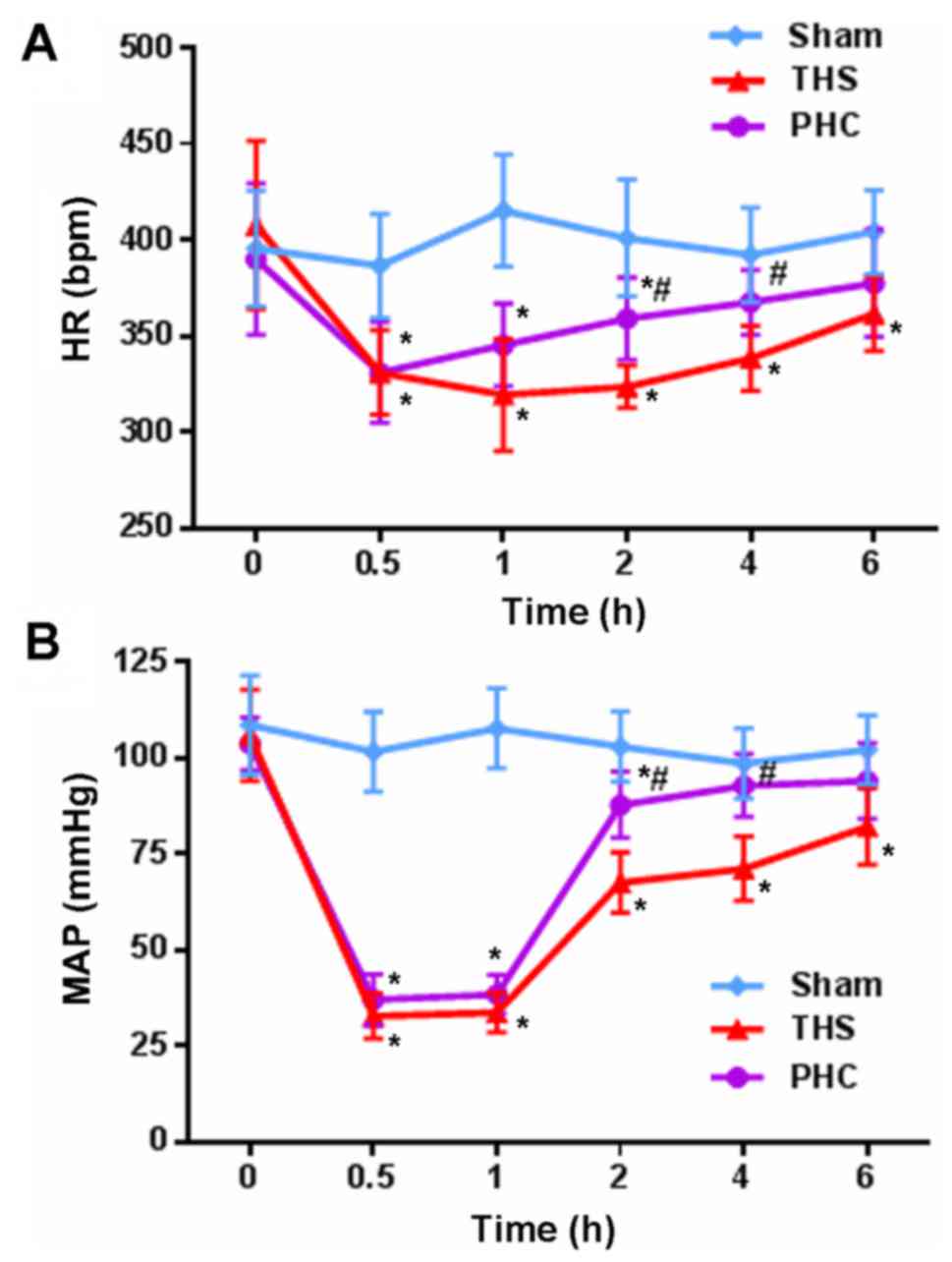
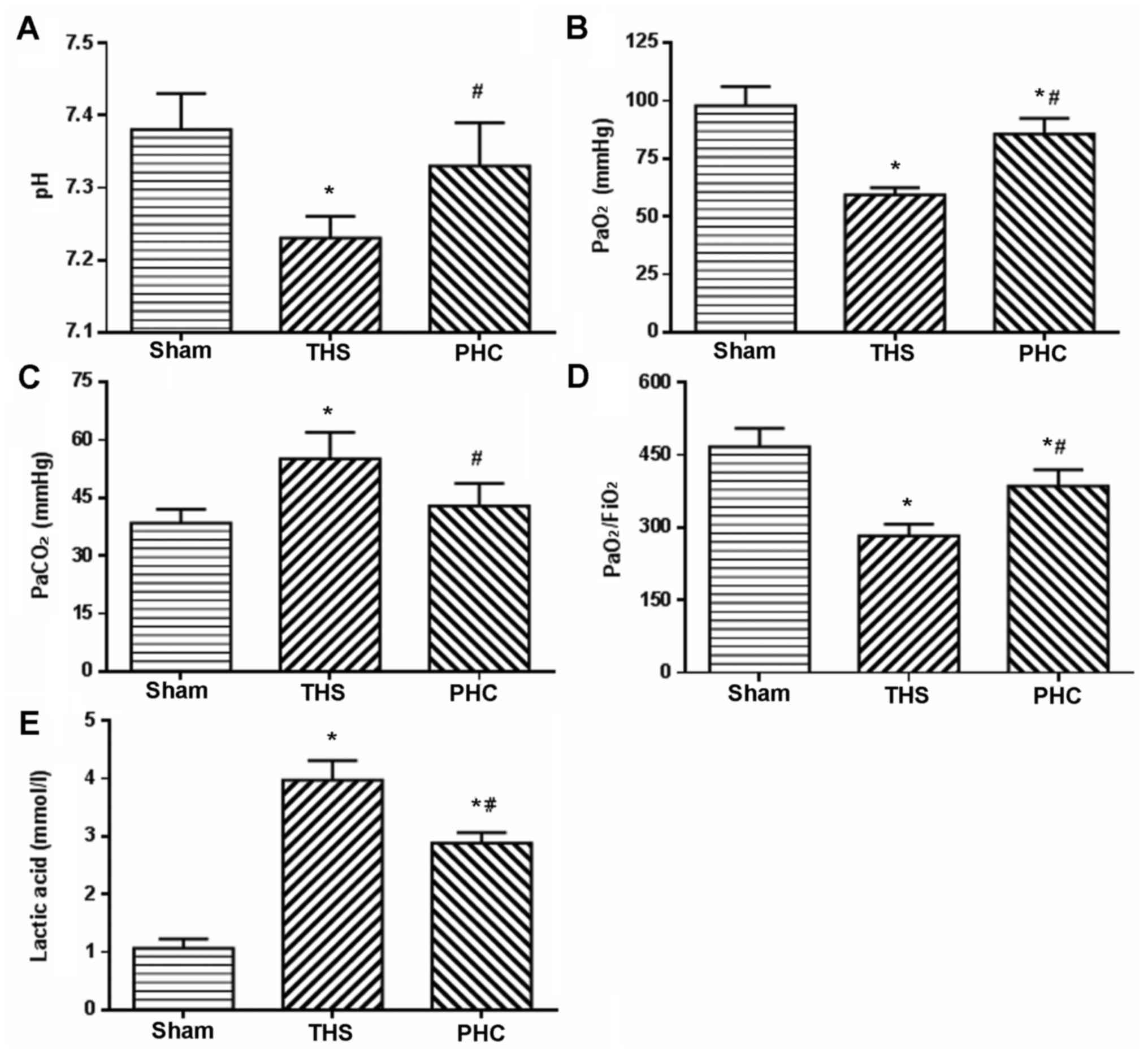
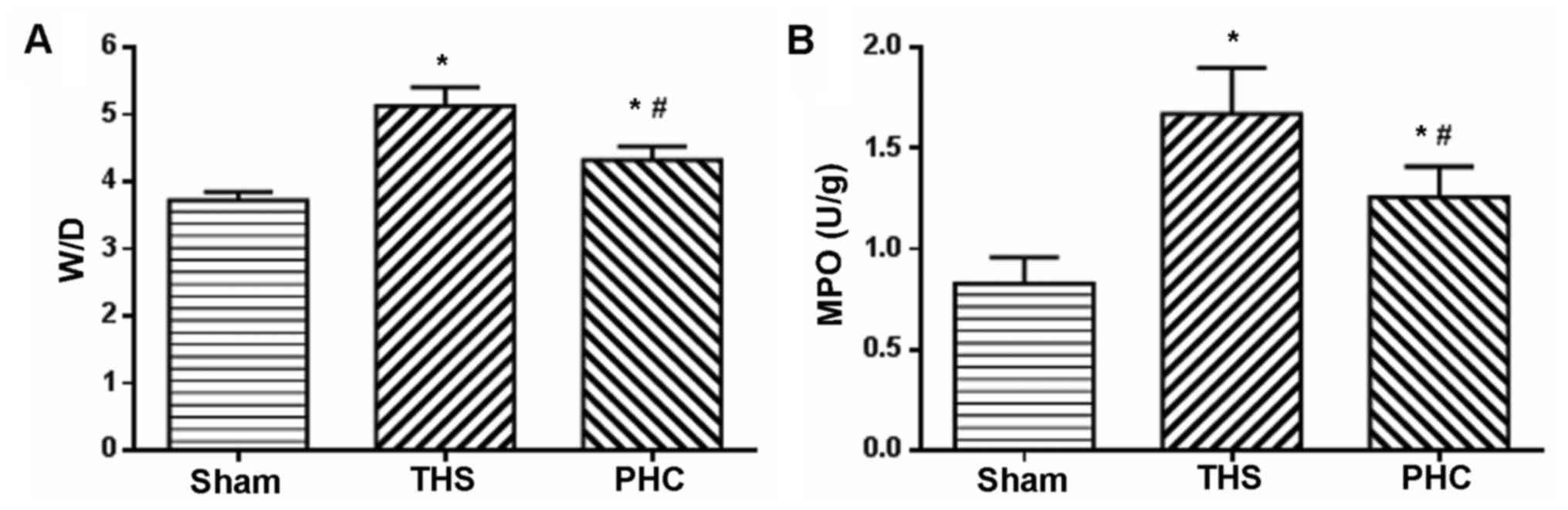
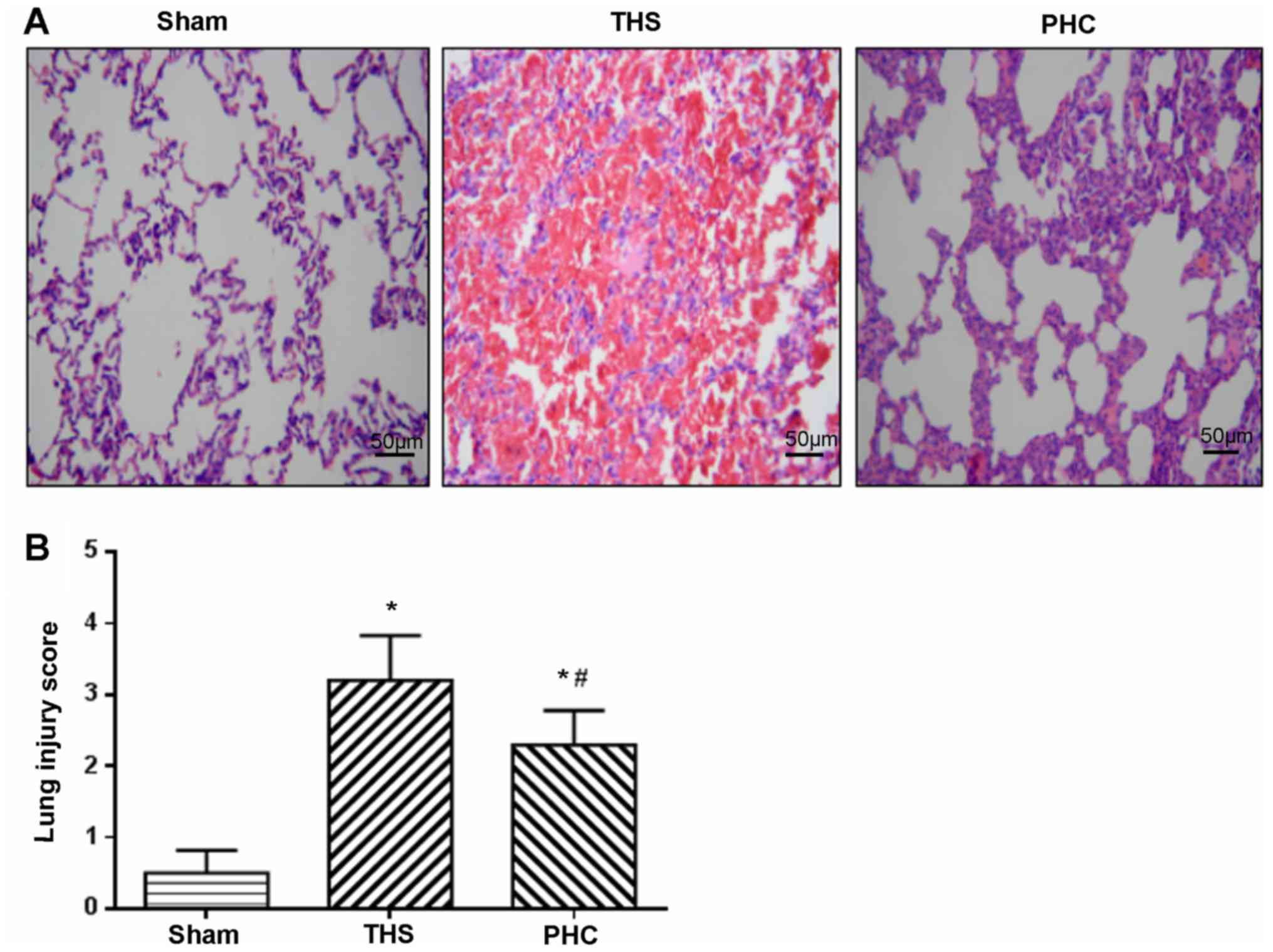
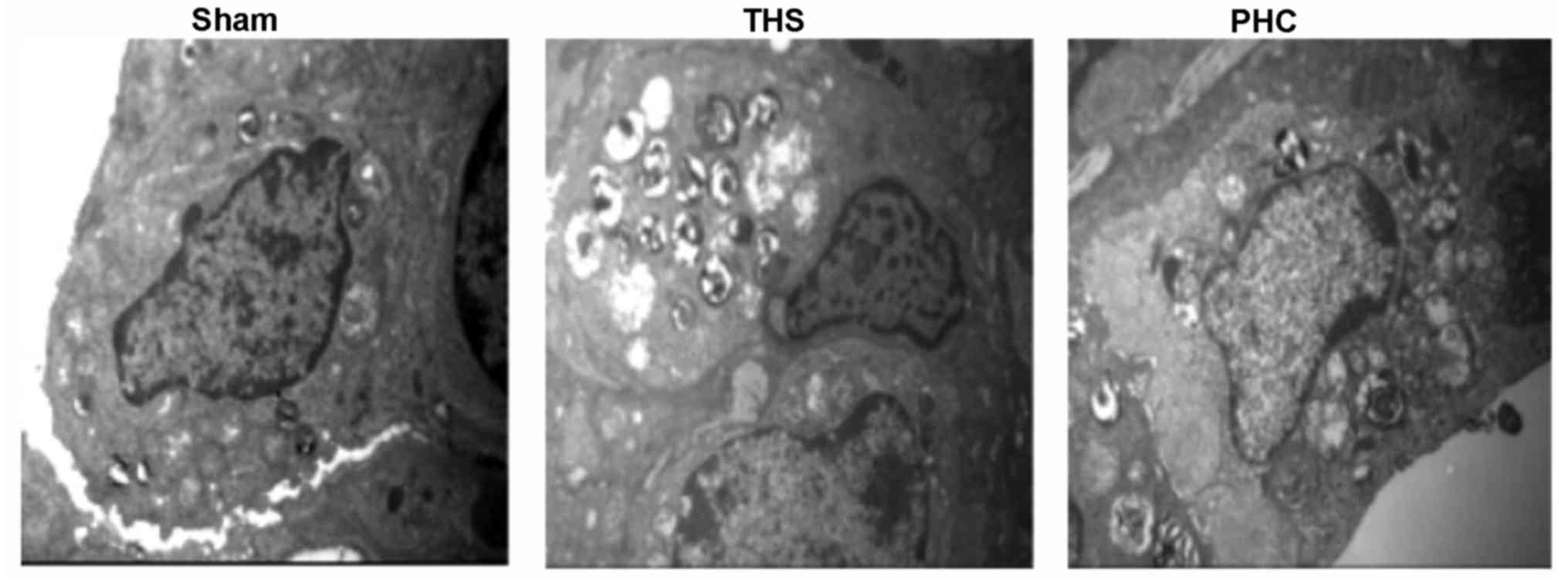
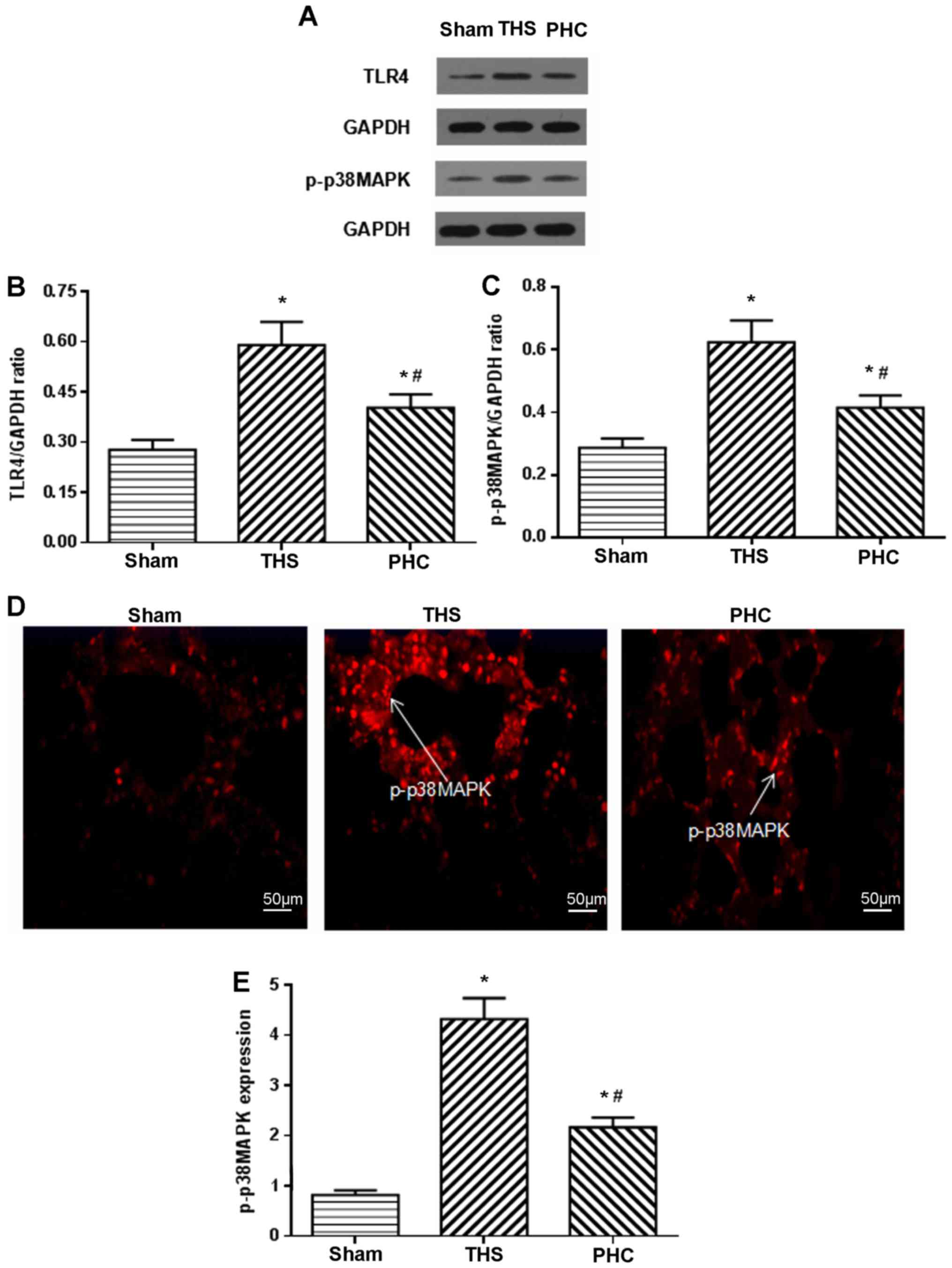
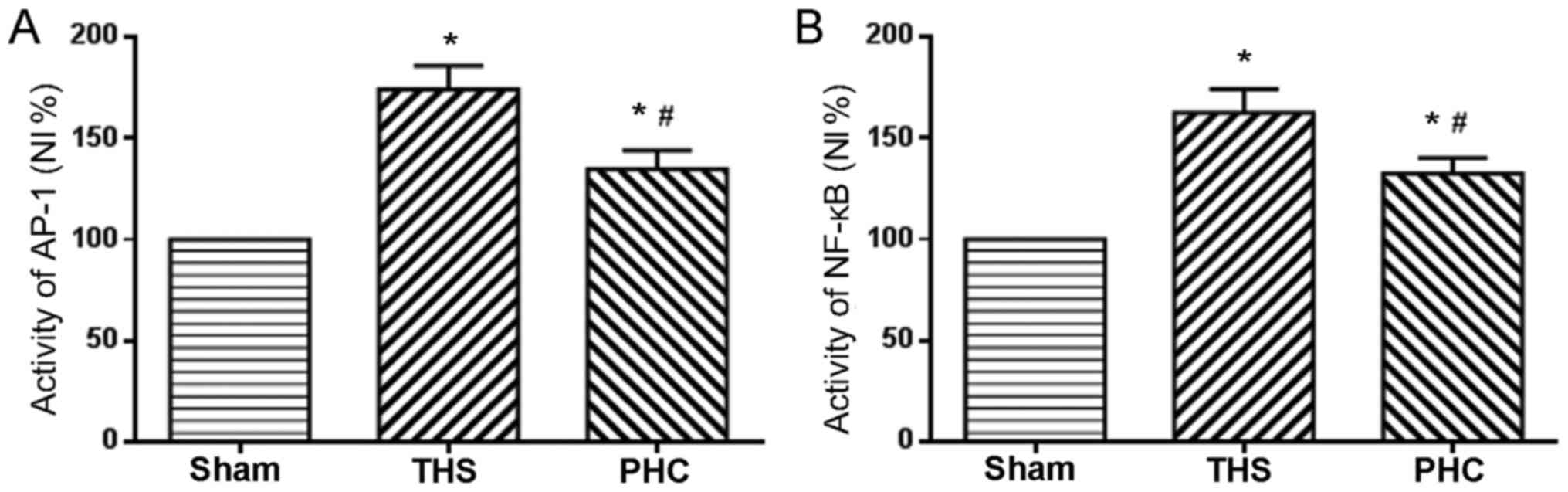
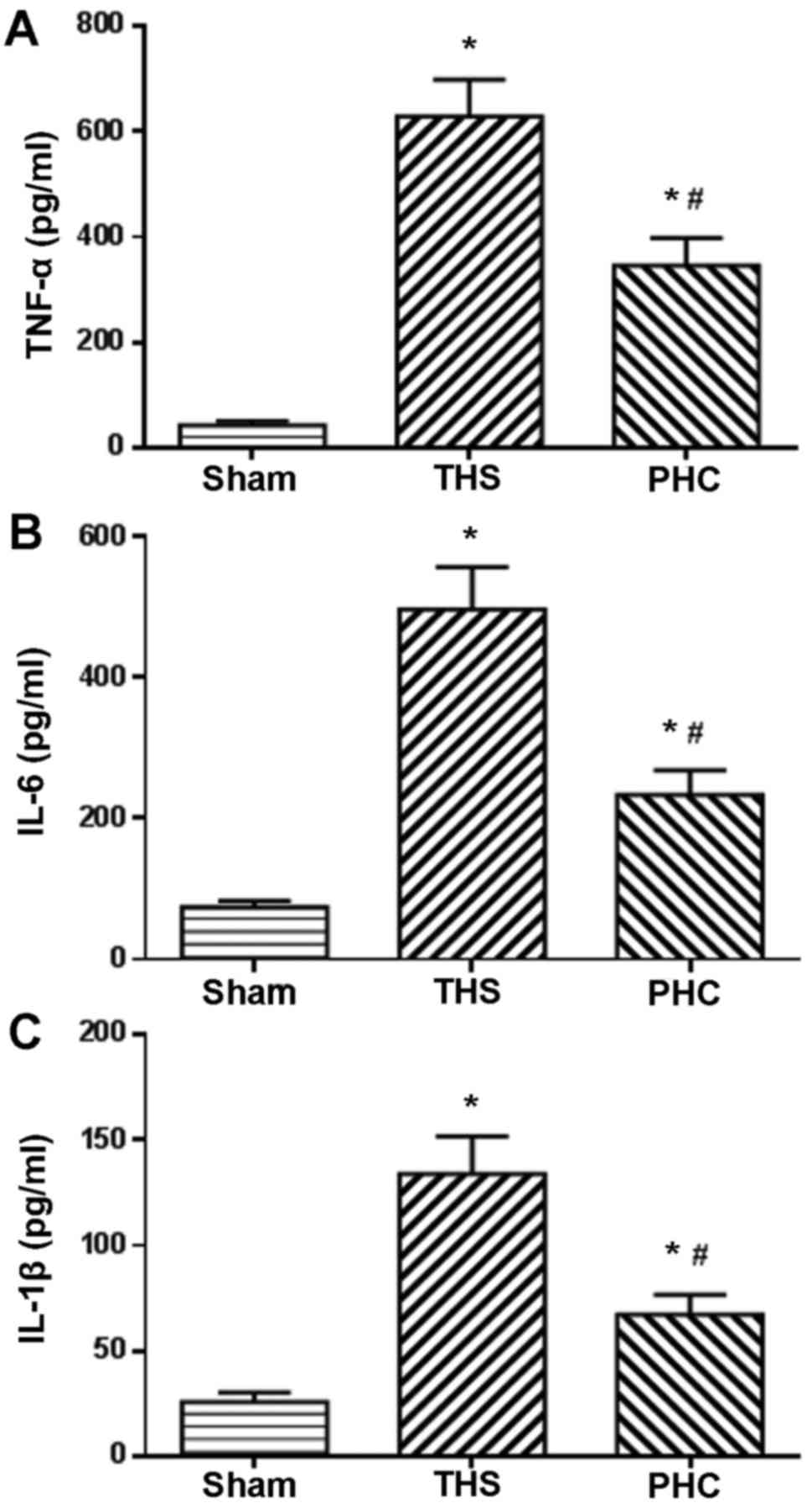
|
1
|
Hildebrand F, Weuster M, Mommsen P, Mohr
J, Fröhlich M, Witte I, Keibl C, Ruchholtz S, Seekamp A, Pape HC,
et al: A combined trauma model of chest and abdominal trauma with
hemorrhagic shock-description of a new porcine model. Shock.
38:664–670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Erickson SE, Martin GS, Davis JL, Matthay
MA and Eisner MD: NIH NHLBI ARDS Network: Recent trends in acute
lung injury mortality: 1996–2005. Crit Care Med. 37:1574–1579.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reino DC, Palange D, Feketeova E, Bonitz
RP, Xu DZ, Lu Q, Sheth SU, Peña G, Ulloa L, De Maio A, et al:
Activation of toll-like receptor 4 is necessary for trauma
hemorrhagic shock-induced gut injury and polymorphonuclear
neutrophil priming. Shock. 38:107–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu Z, Li Y, Liu B, Deperalta DK, Zhao T,
Chong W, Duan X, Zhou P, Velmahos GC and Alam HB: Synergistic
effects of hypertonic saline and valproic acid in a lethal rat
two-hit model. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 74:991–997. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bosmann M, Russkamp NF and Ward PA:
Fingerprinting of the TLR4-induced acute inflammatory response. Exp
Mol Pathol. 93:319–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang L, Li Z, Zhang X, Wang S, Zhu C, Miao
J, Chen L, Cui L and Qiao H: Protective effect of shikonin in
experimental ischemic stroke: Attenuated TLR4, p-p38MAPK, NF-κB,
TNF-α and MMP-9 expression, up-regulated claudin-5 expression,
ameliorated BBB permeability. Neurochem Res. 39:97–106. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Joh EH, Gu W and Kim DH: Echinocystic acid
ameliorates lung inflammation in mice and alveolar macrophages by
inhibiting the binding of LPS to TLR4 in NF-κB and MAPK pathways.
Biochem Pharmacol. 84:331–340. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han XY, Liu H, Liu CH, Wu B, Chen LF,
Zhong BH and Liu KL: Synthesis of the optical isomers of a new
anticholinergic drug, penehyclidine hydrochloride (8018). Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 15:1979–1982. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhan J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Chen C, Chen K and
Wang Y: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on expressions of
MAPK in mice with CLP-induced acute lung injury. Mol Biol Re.
38:1909–1914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li H, Qian Z, Li J, Han X and Liu M:
Effects of early administration of a novel anticholinergic drug on
acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by sepsis. Med Sci
Monit. 11:BR319–BR325. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Li BQ, Sun HC, Nie SN, Shao DB, Liu HM and
Qian XM: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on patients with
acute lung injury and its mechanisms. Chin J Traumatol. 13:329–335.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu XJ, Xia ZY, Wang LL, Luo T, Zhan LY,
Meng QT and Song XM: Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on
pulmonary contusion from blunt chest trauma in rats. Injury.
43:232–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Raghavendran K, Davidson BA, Helinski JD,
Marschke CJ, Manderscheid P, Woytash JA, Notter RH and Knight PR: A
rat model for isolated bilateral lung contusion from blunt chest
trauma. Anesth Analg. 101:1482–1489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Knöferl MW, Angele MK, Diodato MD,
Schwacha MG, Ayala A, Cioffi WG, Bland KI and Chaudry IH: Female
sex hormones regulate macrophage function after trauma-hemorrhage
and prevent increased death rate from subsequent sepsis. Ann Surg.
235:105–112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Du DY, Hu X, Xia DK, Xiang XY,
Huang C, Zhou JH and Jiang JX: Prevalence and mortality of severe
chest trauma in Three Gorges Area of China. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue
Yuan Xue Bao. 34:567–572. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seitz DH, Perl M, Liener UC, Tauchmann B,
Braumüller ST, Brückner UB, Gebhard F and Knöferl MW: Inflammatory
Alterations in a novel nombination model of blunt chest trauma and
hemorrhagic Shock. J Trauma. 70:189–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bhatia M, Zemans RL and Jeyaseelan S: Role
of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 46:566–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wohlauer M, Moore EE, Silliman CC, Fragoso
M, Gamboni F, Harr J, Accurso F, Wright F, Haenel J, Fullerton D
and Banerjee A: Nebulized hypertonic saline attenuates acute lung
injury following trauma and hemorrhagic shock via inhibition of
matrix metalloproteinase-13. Crit Care Med. 40:2647–2653. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoth JJ, Wells JD, Brownlee NA, Hiltbold
EM, Meredith JW, McCall CE and Yoza BK: Toll-like receptor
4-dependent responses to lung injury in a murine model of pulmonary
contusion. Shock. 31:376–381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reino DC, Pisarenko V, Palange D, Doucet
D, Bonitz RP, Lu Q, Colorado I, Sheth SU, Chandler B, Kannan KB, et
al: Trauma hemorrhagic shock-induced lung injury involves a
gut-lymph-induced TLR4 pathway in mice. PLoS One. 6:e148292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feinman R, Deitch EA, Aris V, Chu HB,
Abungu B, Caputo FJ, Galante A, Xu D, Lu Q, Colorado I, et al:
Molecular signatures of trauma-hemorrhagic shock-induced lung
injury. Shock. 28:360–368. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen C, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Wang C and Peng
M: Toll-like receptor 4 regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression after
hemorrhagic shock induced acute lung injury in mice: Requirement of
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Shock. 31:486–492.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu HP, Hwang TL, Hsieh PW and Lau YT: Role
of estrogen receptor-dependent upregulation of p38 MAPK/heme
oxygenase 1 in resveratrol-mediated attenuation of intestinal
injury after trauma-hemorrhage. Shock. 35:517–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barrenschee M, Lex D and Uhlig S: Effects
of the TLR2 agonists MALP-2 and Pam3Cys in isolated mouse lungs.
PLoS One. 5:e138892010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang Z, Deng Y, Su D, Tian J, Gao Y, He Z
and Wang X: TLR4 as receptor for HMGB1-mediated acute lung injury
after liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Lab Invest. 93:792–800.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang YA, Zhou WX, Li JX, Liu YQ, Yue YJ,
Zheng JQ, Liu KL and Ruan JX: Anticonvulsant effects of
phencynonate hydrochloride and other anticholinergic drugs in soman
poisoning: Neurochemical mechanisms. Life Sci. 78:210–223. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao HT, Liao Z, Meng X, Yan X, Chen S and
Mo Z: Effects of the selective muscarinic receptor antagonist
penehyclidine hydrochloride on the respiratory tract. Pharmazie.
64:337–341. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Li J, Zhang L, Huang Y, Pan JH and
Chen KZ: Penehyclidine prevents nuclear factor-кappaB activation in
acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. J Pharm Pharmaco.
60:1197–1205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cai DS, Jin BB, Pei L and Jin Z:
Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on liver injury
in a rat cardiopulmonary bypass model. Eur J Anaesthesiol.
27:824–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He SS, Lin CS, Gu MN, Chen DT, Zong SL and
Chen Y: Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride against
acute renal injury induced by hemorrhagic shock and
lipopolysaccharides in rats. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
31:899–902. 2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhan J, Wang YL, Wang CY, Li JG, Zhang ZZ
and Jia BH: Protective effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on
septic mice and its mechanism. Shock. 28:727–732. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Leng YF, Xue X, Zhang Y, Wang T
and Kang YQ: Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride in small
intestinal damage caused by limb ischemia-reperfusion. World J
Gastroentero. 17:254–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shen W, Gan J, Xu S, Jiang G and Wu H:
Penehyclidine hydrochloride attenuates LPS-induced acute lung
injury involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Pharmacol Res. 60:296–302.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang LL, Zhan LY, Wu XJ and Xia ZY:
Effects of penehyclidine hydrochloride on apoptosis of lung tissues
in rats with traumatic acute lung injury. Chinese J Traumatol.
13:15–19. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Shu LJ and Wei XC: Effect of Penehyclidine
hydrochloride in systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by
cardiopulmonary bypass. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
43:543–546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang YP, Li G, Ma LL, Zheng Y, Zhang SD,
Zhang HX, Qiu M and Ma X: Penehyclidine hydrochloride ameliorates
renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Surg Res. 186:390–397.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|