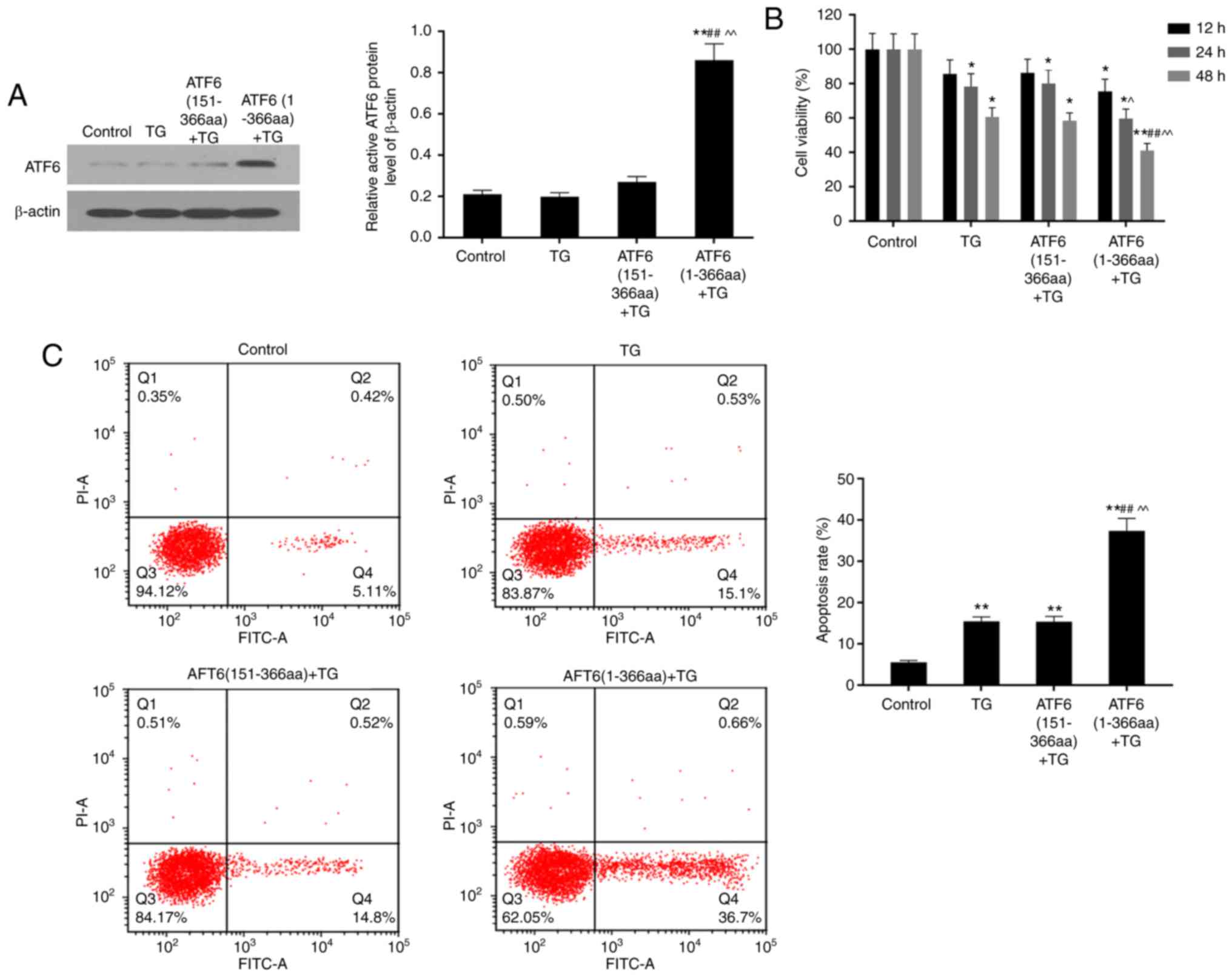
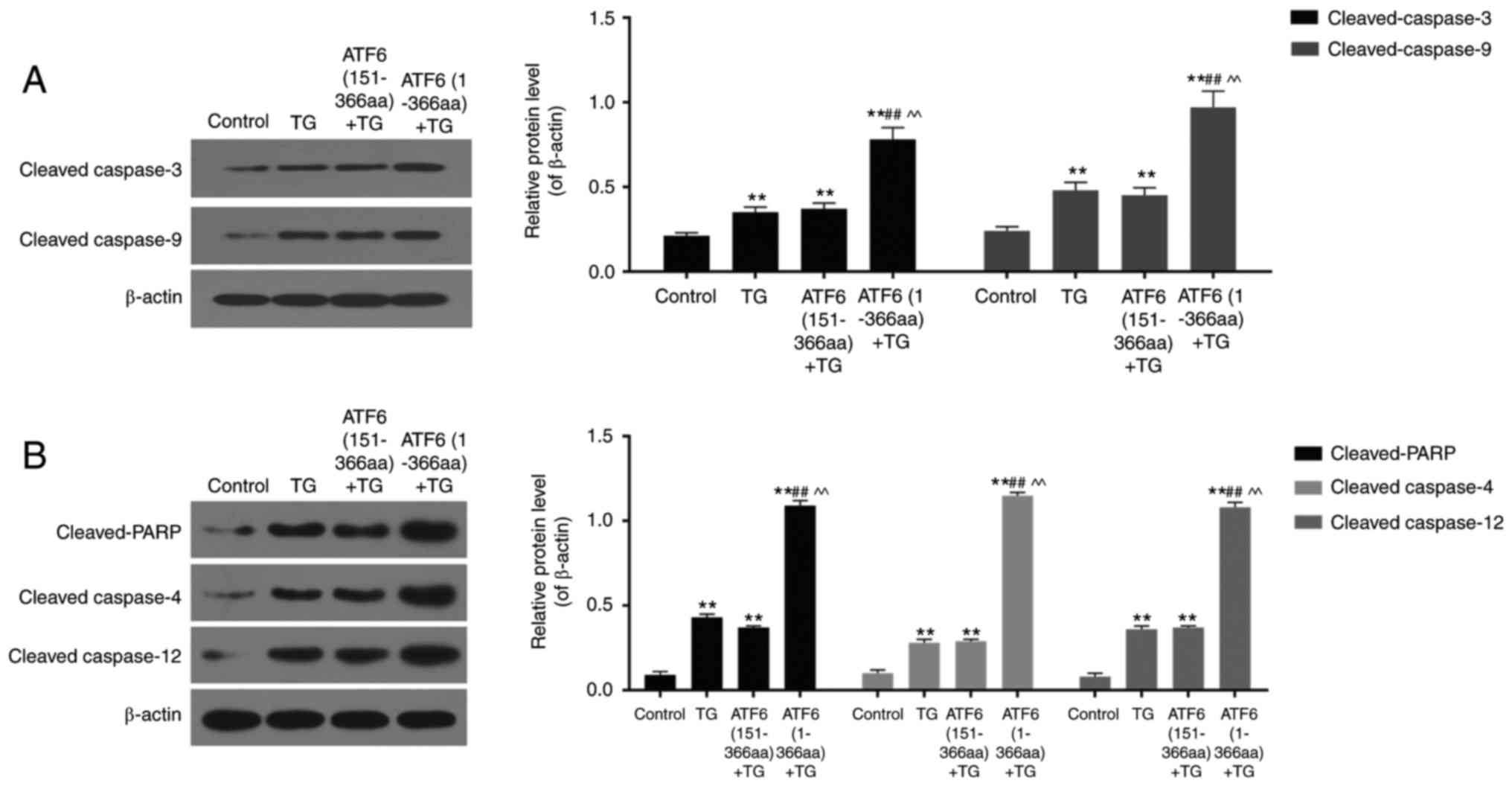
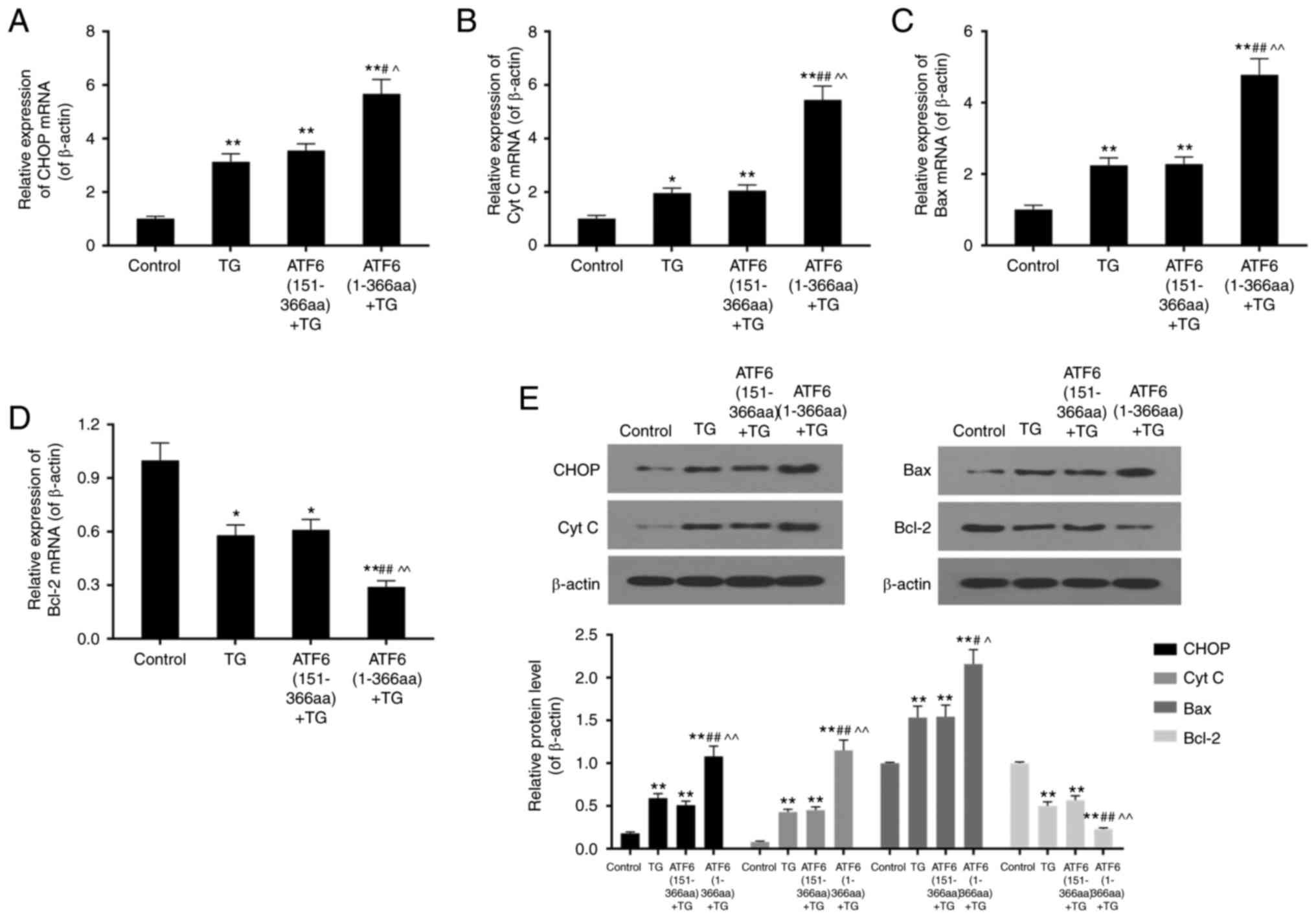
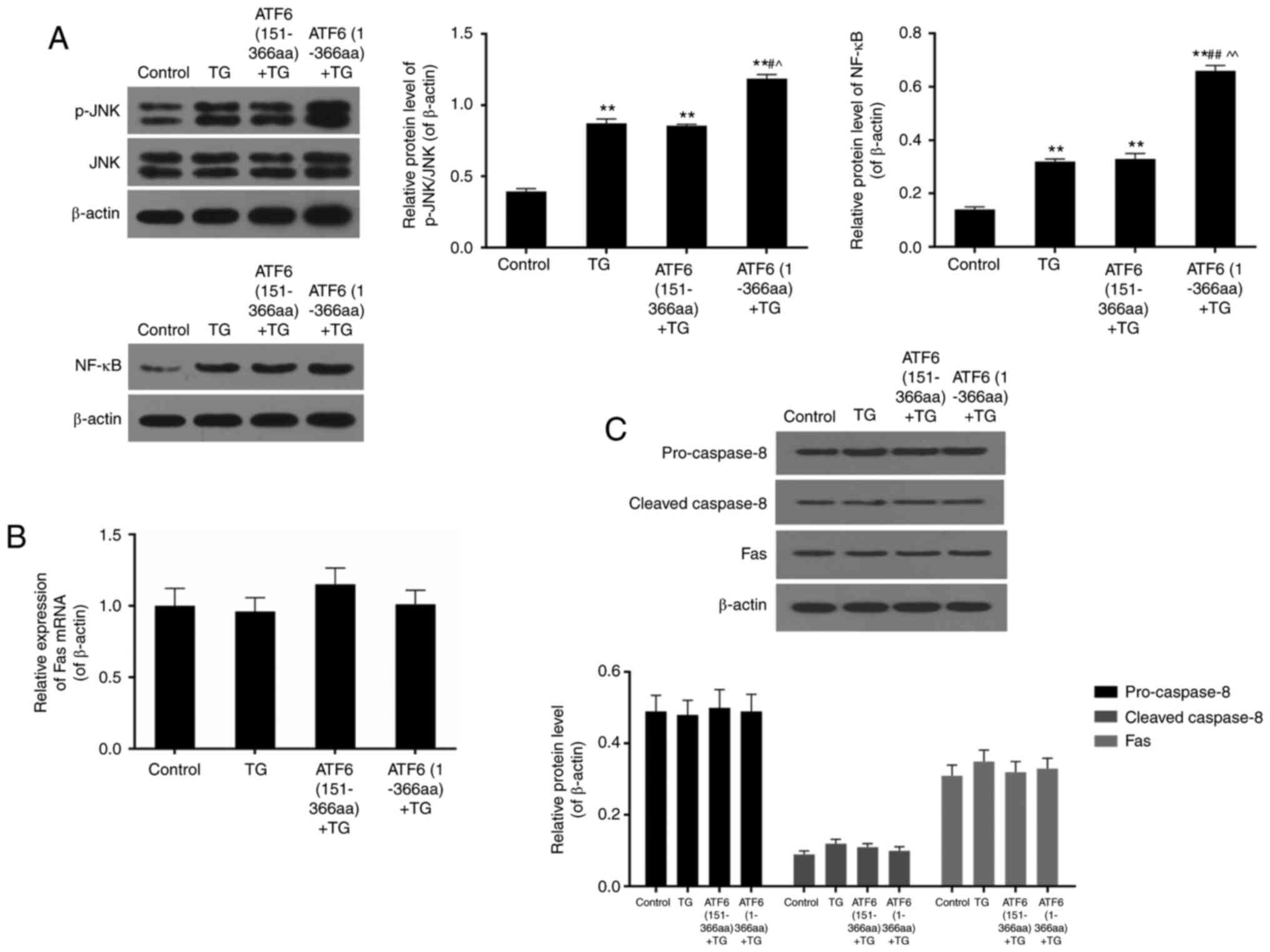
|
1
|
Mannarino E and Pirro M: Endothelial
injury and repair: A novel theory for atherosclerosis. Angiology.
59 2 Suppl:69S–72S. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luchetti F, Crinelli R, Cesarini E,
Canonico B, Guid L, Zerbinati C, Di Sario G, Zamai L, Magnani M,
Papa S and Iuliano L: Endothelial cells, endoplasmic reticulum
stress and oxysterols. Redox Biol. 13:581–587. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Battson ML, Lee DM and Gentile CL:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the development of endothelial
dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 312:H355–H367. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verkhratsky A and Toescu EC: Endoplasmic
reticulum Ca(2+) homeostasis and neuronal death. J Cell Mol Med.
7:351–361. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marciniak SJ and Ron D: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signaling in disease. Physiol Rev. 86:1133–1149.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Verras M, Papandreou I, Lim AL and Denko
NC: Tumor hypoxia blocks Wnt processing and secretion through the
induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Cell Biol.
28:7212–7224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kammoun HL, Hainault I, Ferré P and
Foufelle F: Nutritional related liver disease: Targeting the
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
12:575–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fu S, Yang L, Li P, Hofmann O, Dicker L,
Hide W, Lin X, Watkins SM, Ivanov AR and Hotamisligil GS: Aberrant
lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver
endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity. Nature. 473:528–531. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He S, Yaung J, Kim YH, Barron E, Ryan SJ
and Hinton DR: Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by oxidative
stress in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Graefes Arch Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 246:677–683. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu J and Kaufman RJ: From acute ER stress
to physiological roles of the unfolded protein response. Cell Death
Differ. 13:374–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su HL, Liao CL and Lin YL: Japanese
encephalitis virus infection initiates endoplasmic reticulum stress
and an unfolded protein response. J Virol. 76:4162–4171. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pahl HL: Signal transduction from the
endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus. Physiol Rev. 79:683–701.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Patil C and Walter P: Intracellular
signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus: The
unfolded protein response in yeast and mammals. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 13:349–355. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bertolotti A, Zhang Y, Hendershot LM,
Harding HP and Ron D: Dynamic interaction of BiP and ER stress
transducers in the unfolded-protein response. Nat Cell Biol.
2:326–332. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schroder M and Kaufman RJ: The mammalian
unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem. 74:739–789. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakanishi K, Sudo T and Morishima N:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling transmitted by ATF6 mediates
apoptosis during muscle development. J Cell Biol. 169:555–560.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morishima N, Nakanishi K and Nakano A:
Activating transcription factor-6 (ATF6) mediates apoptosis with
reduction of myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (Mcl-1) protein via
induction of WW domain binding protein 1. J Biol Chem.
286:35227–35235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Toya SP and Malik AB: Role of endothelial
injury in disease mechanisms and contribution of progenitor cells
in mediating endothelial repair. Immunobiology. 217:569–580. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szegezdi E, Logue SE, Gorman AM and Samali
A: Mediators of endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis.
EMBO Rep. 7:880–885. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Colell A, Ricci JE, Tait S, Milasta S,
Maurer U, Bouchier-Hayes L, Fitzgerald P, Guio-Carrion A,
Waterhouse NJ, Li CW, et al: GAPDH and autophagy preserve survival
after apoptotic cytochrome c release in the absence of caspase
activation. Cell. 129:983–997. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rathmell JC and Kornbluth S: Filling a
GAP(DH) in caspase-independent cell death. Cell. 129:861–863. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Momoi T: Conformational diseases and ER
stress-mediated cell death: Apoptotic cell death and autophagic
cell death. Curr Mol Med. 6:111–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng XQ, You Y, Xiao J and Zou P:
Thapsigargin-induced apoptosis of K562 cells and its mechanism.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 14:25–30. 2006.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ito Y, Pandey P, Mishra N, Kumar S, Narula
N, Kharbanda S, Saxena S and Kufe D: Targeting of the c-Abl
tyrosine kinase to mitochondria in endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:6233–6242. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rizzuto R, Pinton P, Carrington W, Fay FS,
Fogarty KE, Lifshitz LM, Tuft RA and Pozzan T: Close contacts with
the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+
responses. Science. 280:1763–1766. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adams JM and Cory S: Apoptosomes: Engines
for caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:715–720. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hengartner MO: Apoptosis. Death cycle and
Swiss army knives. Nature. 391:441–442. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Fatlawi AA, Al-Fatlawi AA, Irshad M,
Zafaryab M, Rizvi MM and Ahmad A: Rice bran phytic acid induced
apoptosis through regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and p53 genes in HepG2
human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:3731–3736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Płonka J, Latocha M, Kuśmierz D and
Zielińska A: Expression of proapoptotic BAX and TP53 genes and
antiapoptotic BCL-2 gene in MCF-7 and T-47D tumour cell cultures of
the mammary gland after a photodynamic therapy with photolon. Adv
Clin Exp Med. 24:37–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry
DE and Oltvai ZN: Bcl-2/Bax: A rheostat that regulates an
anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 4:327–332.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamana K, Bilim V, Hara N, Kasahara T,
Itoi T, Maruyama R, Nishiyama T, Takahashi K and Tomita Y:
Prognostic impact of FAS/CD95/APO-1 in urothelial cancers:
Decreased expression of Fas is associated with disease progression.
Br J Cancer. 93:544–551. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
Signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Scatena R, Bottoni P, Botta G, Martorana
GE and Giardina B: The role of mitochondria in pharmacotoxicology:
A reevaluation of an old, newly emerging topic. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 293:C12–C21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gehring S, Rottmann S, Menkel AR,
Mertsching J, Krippner-Heidenreich A and Lüscher B: Inhibition of
proliferation and apoptosis by the transcriptional repressor Mad1.
Repression of Fas-induced caspase-8 activation. J Biol Chem.
275:10413–10420. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|