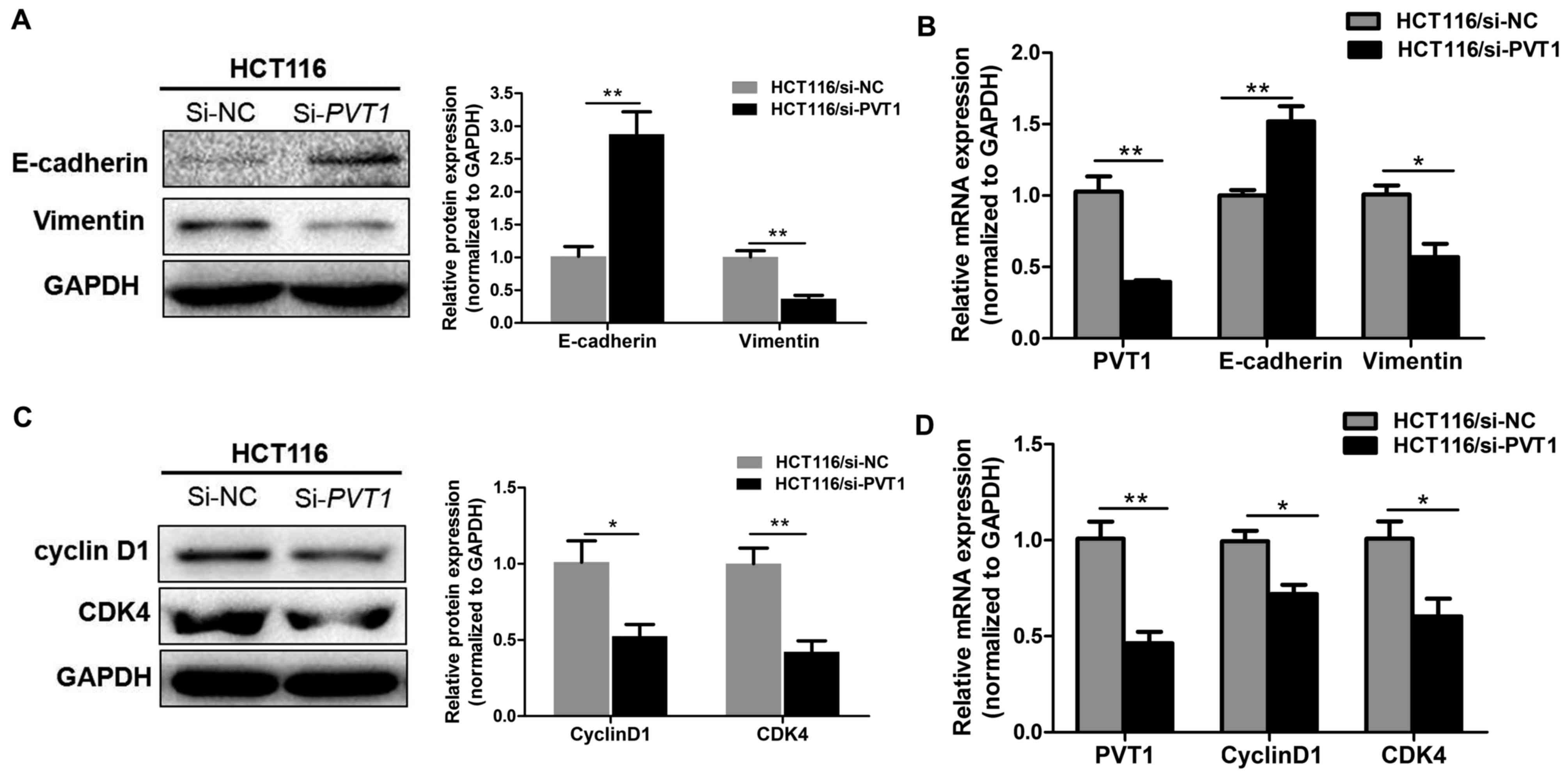
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen C, Wang L, Liao Q, Huang Y, Ye H,
Chen F, Xu L, Ye M and Duan S: Hypermethylation of EDNRB promoter
contributes to the risk of colorectal cancer. Diagn Pathol.
8:1992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sunkara V and Hebert JR: The colorectal
cancer mortality-to-incidence ratio as an indicator of global
cancer screening and care. Cancer. 121:1563–1569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rupnarain C, Dlamini Z, Naicker S and
Bhoola K: Colon cancer: Genomics and apoptotic events. Biol Chem.
385:449–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Li S, Li G, Li X and Ma J:
Dual roles of yes-associated protein (YAP) in colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:75727–75741. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Edwards BK, Ward E, Kohler BA, Eheman C,
Zauber AG, Anderson RN, Jemal A, Schymura MJ, Lansdorp-Vogelaar I,
Seeff LC, et al: Annual report to the nation on the status of
cancer, 1975–2006, featuring colorectal cancer trends and impact of
interventions (risk factors, screening and treatment) to reduce
future rates. Cancer. 116:544–573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Colussi D, Brandi G, Bazzoli F and
Ricciardiello L: Molecular pathways involved in colorectal cancer:
Implications for disease behavior and prevention. Int J Mol Sci.
14:16365–16385. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vaiopoulos AG, Athanasoula K and
Papavassiliou AG: Epigenetic modifications in colorectal cancer:
Molecular insights and therapeutic challenges. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:971–980. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guttman M and Rinn JL: Modular regulatory
principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 482:339–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bazzini AA, Johnstone TG, Christiano R,
Mackowiak SD, Obermayer B, Fleming ES, Vejnar CE, Lee MT, Rajewsky
N, Walther TC and Giraldez AJ: Identification of small ORFs in
vertebrates using ribosome footprinting and evolutionary
conservation. EMBO J. 33:981–993. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song H, Sun W, Ye G, Ding X, Liu Z, Zhang
S, Xia T, Xiao B, Xi Y and Guo J: Long non-coding RNA expression
profile in human gastric cancer and its clinical significances. J
Transl Med. 11:2252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shang C, Zhu W, Liu T, Wang W, Huang G,
Huang J, Zhao P, Zhao Y and Yao S: Characterization of long
non-coding RNA expression profiles in lymph node metastasis of
early-stage cervical cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:3185–3197. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Li H, Hou S, Hu B, Liu J and Wang
J: The noncoding RNA expression profile and the effect of lncRNA
AK126698 on cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer
cell. PLoS One. 8:e653092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu H, Wu R, Chen M, Li D, Dai J, Zhang Y,
Gao K, Yu J, Hu G, Guo Y, et al: Comprehensive analysis of
differentially expressed profiles of lncRNAs and construction of
miR-133b mediated ceRNA network in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:21095–21105. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tseng YY, Moriarity BS, Gong W, Akiyama R,
Tiwari A, Kawakami H, Ronning P, Reuland B, Guenther K, Beadnell
TC, et al: PVT1 dependence in cancer with MYC copy-number increase.
Nature. 512:82–86. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kong R, Zhang EB, Yin DD, You LH, Xu TP,
Chen WM, Xia R, Wan L, Sun M, Wang ZX, et al: Long noncoding RNA
PVT1 indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell
proliferation through epigenetically regulating p15 and p16. Mol
Cancer. 14:822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cui D, Yu CH, Liu M, Xia QQ, Zhang YF and
Jiang WL: Long non-coding RNA PVT1 as a novel biomarker for
diagnosis and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol.
37:4127–4134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang F, Yuan JH, Wang SB, Yang F, Yuan SX,
Ye C, Yang N, Zhou WP, Li WL, Li W and Sun SH: Oncofetal long
noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes proliferation and stem cell-like
property of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by stabilizing NOP2.
Hepatology. 60:1278–1290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hong Y, Downey T, Eu KW, Koh PK and Cheah
PY: A ‘metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair
proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications
for possible therapeutics. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:83–90. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Uddin S, Ahmed M, Hussain A, Abubaker J,
Al-Sanea N, AbdulJabbar A, Ashari LH, Alhomoud S, Al-Dayel F, Jehan
Z, et al: Genome-wide expression analysis of Middle Eastern
colorectal cancer reveals FOXM1 as a novel target for cancer
therapy. Am J Pathol. 178:537–547. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okazaki S, Ishikawa T, Iida S, Ishiguro M,
Kobayashi H, Higuchi T, Enomoto M, Mogushi K, Mizushima H, Tanaka
H, et al: Clinical significance of UNC5B expression in colorectal
cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:209–216. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smith JJ, Deane NG, Wu F, Merchant NB,
Zhang B, Jiang A, Lu P, Johnson JC, Schmidt C, Bailey CE, et al:
Experimentally derived metastasis gene expression profile predicts
recurrence and death in patients with colon cancer.
Gastroenterology. 138:958–968. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SK, Kim SY, Kim JH, Roh SA, Cho DH,
Kim YS and Kim JC: A nineteen gene-based risk score classifier
predicts prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Mol Oncol.
8:1653–1666. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Zhang H, Xiong W, Ma J, Zhou
M, Lu J, Zeng Z, Bo X, Chen P, et al: SPLUNC1 reduces the
inflammatory response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells infected
with the EB virus by inhibiting the TLR9/NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep.
33:2779–2788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Li X, Li X, Ren W, Qin Z,
Zhang X, Yuan W, Wang J, Yu W, et al: MiR-590-5p, a
density-sensitive microRNA, inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting
YAP1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 399:53–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Antonov AV: BioProfiling.de: Analytical
web portal for high-throughput cell biology. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:W323–W327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Amelio I, Tsvetkov PO, Knight RA, Lisitsa
A, Melino G and Antonov AV: SynTarget: An online tool to test the
synergetic effect of genes on survival outcome in cancer. Cell
Death Differ. 23:9122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bray F, Ren JS, Masuyer E and Ferlay J:
Global estimates of cancer prevalence for 27 sites in the adult
population in 2008. Int J Cancer. 132:1133–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He X, Ou C, Xiao Y, Han Q, Li H and Zhou
S: LncRNAs: Key players and novel insights into diabetes mellitus.
Oncotarget. 8:71325–71341. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ou C and Li G: Long non-coding RNA TUG1: A
novel therapeutic target in small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis.
9:E644–E645. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prensner JR and Chinnaiyan AM: The
emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 1:391–407.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ou C and Li G: Exosome-transmitted
lncARSR: A novel therapeutic target in renal cancer. Transl Cancer
Res. 6:656–657. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yin DD, Liu ZJ, Zhang E, Kong R, Zhang ZH
and Guo RH: Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA MEG3 affects
cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with
colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:4851–4859. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yin D, He X, Zhang E, Kong R, De W and
Zhang Z: Long noncoding RNA GAS5 affects cell proliferation and
predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med
Oncol. 31:2532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng HT, Shi DB, Wang YW, Li XX, Xu Y,
Tripathi P, Gu WL, Cai GX and Cai SJ: High expression of lncRNA
MALAT1 suggests a biomarker of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:3174–3181. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun J, Ding C, Yang Z, Liu T, Zhang X,
Zhao C and Wang J: The long non-coding RNA TUG1 indicates a poor
prognosis for colorectal cancer and promotes metastasis by
affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Transl Med.
14:422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Svoboda M, Slyskova J, Schneiderova M,
Makovicky P, Bielik L, Levy M, Lipska L, Hemmelova B, Kala Z,
Protivankova M, et al: HOTAIR long non-coding RNA is a negative
prognostic factor not only in primary tumors, but also in the blood
of colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 35:1510–1515. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Takahashi Y, Sawada G, Kurashige J, Uchi
R, Matsumura T, Ueo H, Takano Y, Eguchi H, Sudo T, Sugimachi K, et
al: Amplification of PVT-1 is involved in poor prognosis via
apoptosis inhibition in colorectal cancers. Br J Cancer.
110:164–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Q, Dai Y, Wang F and Hou S:
Differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs and the prognostic
potential in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma. 63:977–983. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Colombo T, Farina L, Macino G and Paci P:
PVT1: A rising star among oncogenic long noncoding RNAs. Biomed Res
Int. 2015:3042082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang C, Liu S, Wang H, Zhang Z, Yang Q
and Gao F: LncRNA PVT1 overexpression is a poor prognostic
biomarker and regulates migration and invasion in small cell lung
cancer. Am J Transl Res. 8:5025–5034. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shen CJ, Cheng YM and Wang CL: LncRNA PVT1
epigenetically silences miR-195 and modulates EMT and
chemoresistance in cervical cancer cells. J Drug Target.
25:637–644. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo K, Yao J, Yu Q, Li Z, Huang H, Cheng
J, Wang Z and Zhu Y: The expression pattern of long non-coding RNA
PVT1 in tumor tissues and in extracellular vesicles of colorectal
cancer correlates with cancer progression. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176991222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|