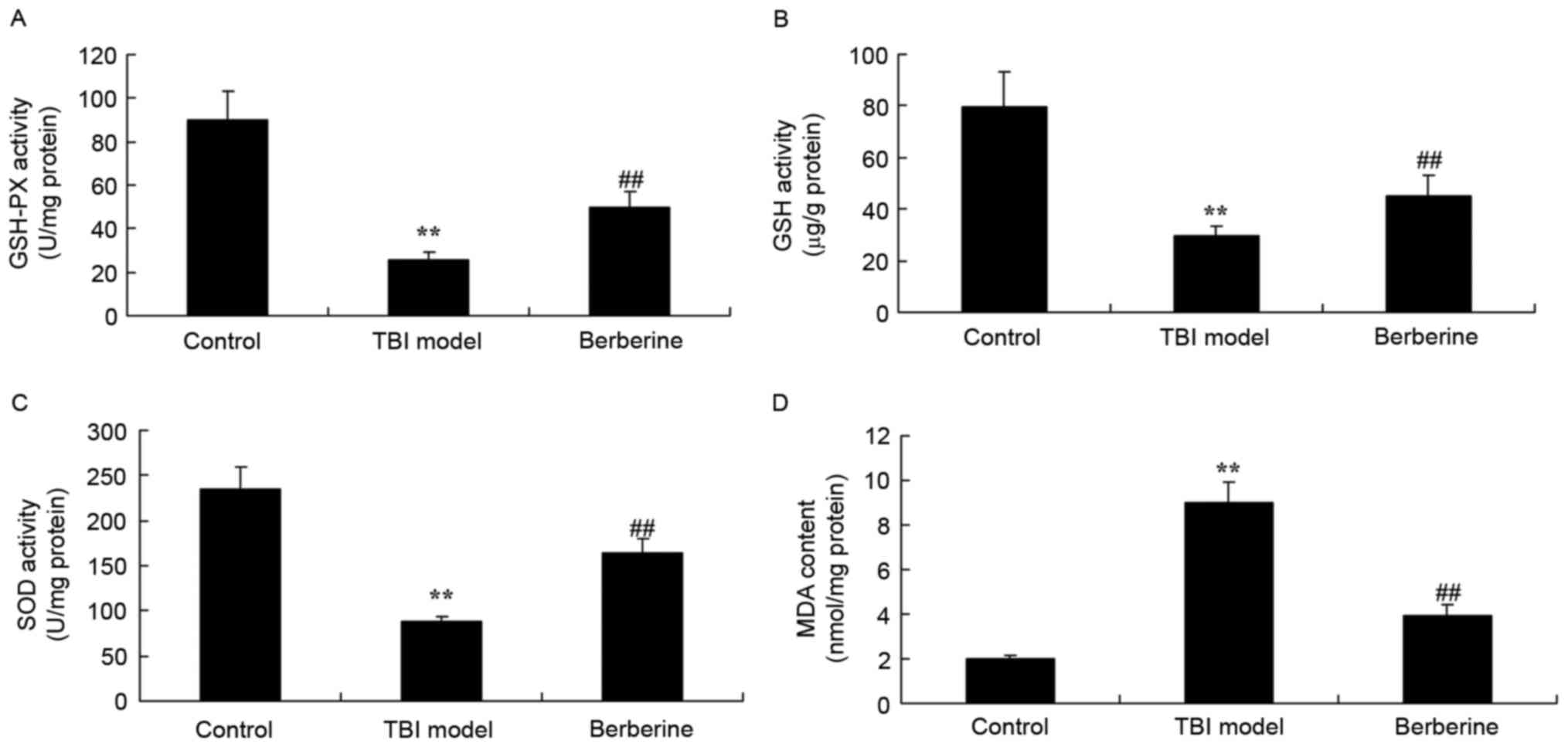
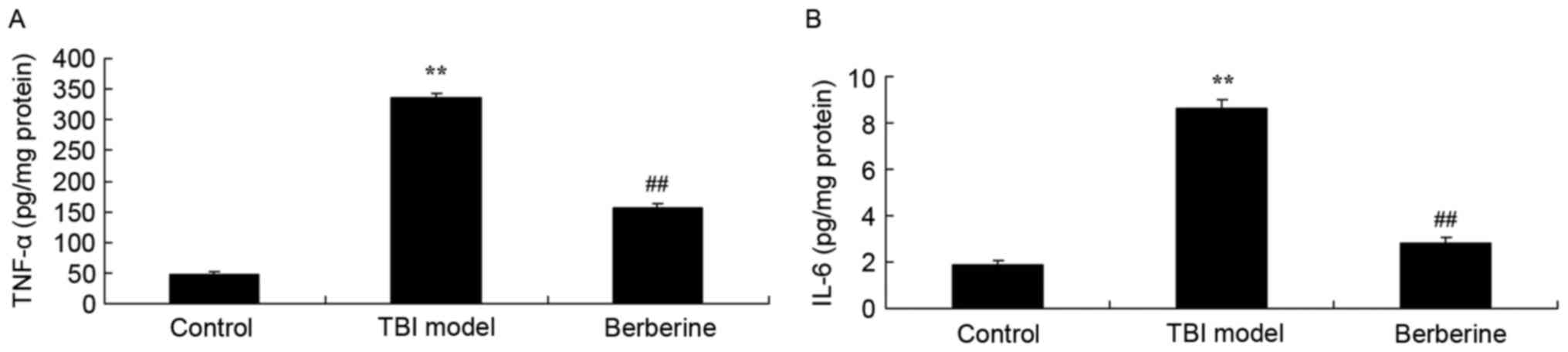
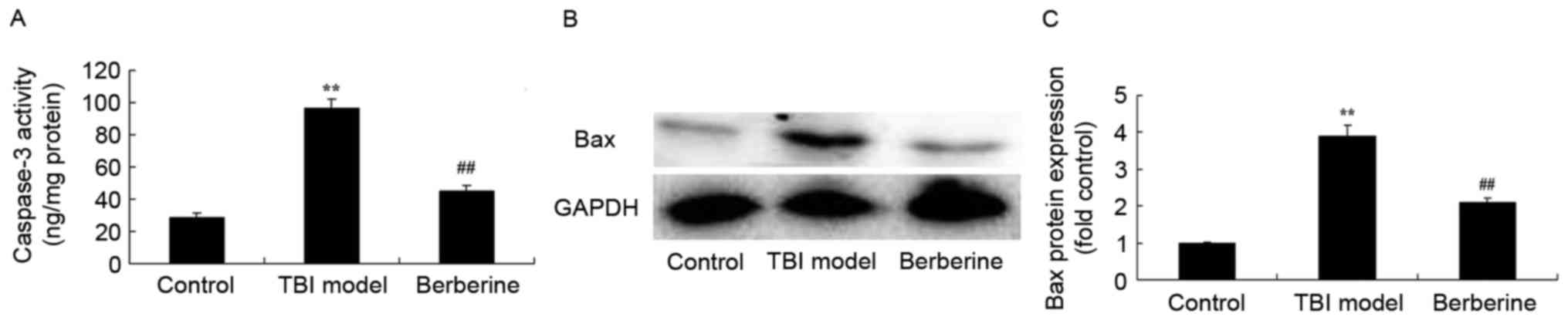
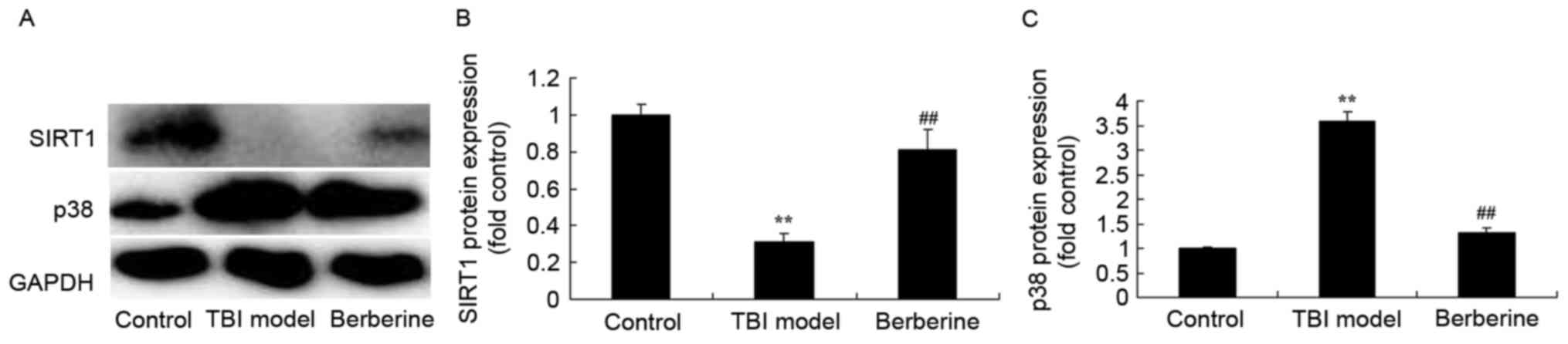
|
1
|
Wade SL, Kurowski BG, Kirkwood MW, Zhang
N, Cassedy A, Brown TM, Nielsen B, Stancin T and Taylor HG: Online
problem-solving therapy after traumatic brain injury: A randomized
controlled trial. Pediatrics. 135:e487–e495. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hammond FM, Alexander DN, Cutler AJ,
D'Amico S, Doody RS, Sauve W, Zorowitz RD, Davis CS, Shin P, Ledon
F, et al: PRISM II: An open-label study to assess effectiveness of
dextromethorphan/quinidine for pseudobulbar affect in patients with
dementia, stroke or traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol. 16:892016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang X, Ji J, Fen L and Wang A: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on cerebral blood flow in critically ill patients
with or without traumatic brain injury: A prospective controlled
trial. Brain Inj. 27:1617–1622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
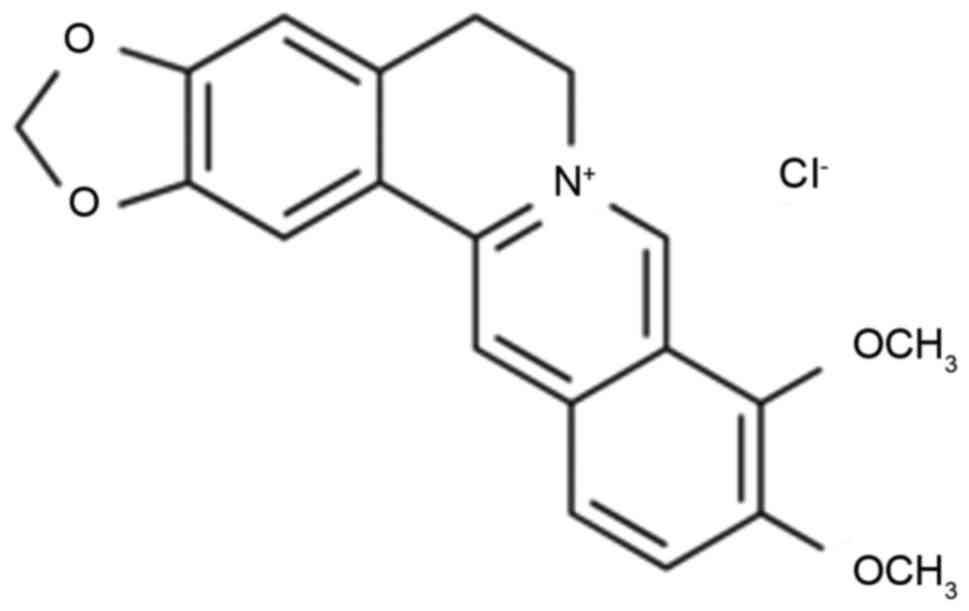
|
|
4
|
Saxena MK, Taylor C, Billot L, Bompoint S,
Gowardman J, Roberts JA, Lipman J and Myburgh J: The effect of
paracetamol on core body temperature in acute traumatic brain
injury: A randomised, controlled clinical trial. PLoS One.
10:e01447402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Du G, Zhao Z, Chen Y, Li Z, Tian Y, Liu Z,
Liu B and Song J: Quercetin attenuates neuronal autophagy and
apoptosis in rat traumatic brain injury model via activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurol Res. Oct 3–2016.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Chuang CH, Hsu YC, Wang CC, Hu C and Kuo
JR: Cerebral blood flow and apoptosis-associated factor with
electroacupuncture in a traumatic brain injury rat model. Acupunct
Med. 31:395–403. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu ZG, Wang HD, Qiao L, Yan W, Tan QF and
Yin HX: The protective effect of the ketogenic diet on traumatic
brain injury-induced cell death in juvenile rats. Brain Inj.
23:459–465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Wang Q, Xie M, Liu P, Qi X, Liu X
and Li Z: Berberine exerts an anti-inflammatory role in ocular
Behcet's disease. Mol Med Rep. 15:97–102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Habtemariam S: Berberine and inflammatory
bowel disease: A concise review. Pharmacol Res. 113:592–599. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma L and Zhang L, Wang B, Wei J, Liu J and
Zhang L: Berberine inhibits Chlamydia pneumoniae infection-induced
vascular smooth muscle cell migration through downregulating MMP3
and MMP9 via PI3K. Eur J Pharmacol. 755:102–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
NICE-SUGAR Study Investigators for the
Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials
Group and the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, . Finfer S,
Chittock D, Li Y, Foster D, Dhingra V, Bellomo R, Cook D, Dodek P,
Hebert P, et al: Intensive versus conventional glucose control in
critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury: Long-term
follow-up of a subgroup of patients from the NICE-SUGAR study.
Intensive Care Med. 41:1037–1047. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matuseviciene G, Borg J, Stålnacke BM,
Ulfarsson T and de Boussard C: Early intervention for patients at
risk for persisting disability after mild traumatic brain injury: A
randomized, controlled study. Brain Inj. 27:318–324. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nägeli M, Fasshauer M, Sommerfeld J,
Fendel A, Brandi G and Stover JF: Prolonged continuous intravenous
infusion of the dipeptide L-alanine-L-glutamine significantly
increases plasma glutamine and alanine without elevating brain
glutamate in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Crit
Care. 18:R1392014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu S, Zhang L, Wu Q, Wu Q and Wang T:
Chemokine CCL2 induces apoptosis in cortex following traumatic
brain injury. J Mol Neurosci. 51:1021–1029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ge X, Huang S, Gao H, Han Z, Chen F, Zhang
S, Wang Z, Kang C, Jiang R, Yue S, et al: miR-21-5p alleviates
leakage of injured brain microvascular endothelial barrier in vitro
through suppressing inflammation and apoptosis. Brain Res.
1650:31–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bentz K, Molcanyi M, Schneider A, Riess P,
Maegele M, Bosche B, Hampl JA, Hescheler J, Patz S and Schäfer U:
Extract derived from rat brains in the acute phase following
traumatic brain injury impairs survival of undifferentiated stem
cells and induces rapid differentiation of surviving cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 26:821–830. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu SJ, Zou Y, Belegu V, Lv LY, Lin N,
Wang TY, McDonald JW, Zhou X, Xia QJ and Wang TH: Co-grafting of
neural stem cells with olfactory en sheathing cells promotes
neuronal restoration in traumatic brain injury with an
anti-inflammatory mechanism. J Neuroinflammation. 11:662014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reinhard SM, Razak K and Ethell IM: A
delicate balance: Role of MMP-9 in brain development and
pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. Front Cell
Neurosci. 9:2802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grossetete M, Phelps J, Arko L, Yonas H
and Rosenberg GA: Elevation of matrix metalloproteinases 3 and 9 in
cerebrospinal fluid and blood in patients with severe traumatic
brain injury. Neurosurgery. 65:702–708. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wiggins-Dohlvik K, Merriman M, Shaji CA,
Alluri H, Grimsley M, Davis ML, Smith RW and Tharakan B: Tumor
necrosis factor-α disruption of brain endothelial cell barrier is
mediated through matrix metalloproteinase-9. Am J Surg.
208:954–960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Fan X, Tang T, Fan R, Zhang C,
Huang Z, Peng W, Gan P, Xiong X, Huang W and Huang X: Rhein and
rhubarb similarly protect the blood-brain barrier after
experimental traumatic brain injury via gp91phox subunit of NADPH
oxidase/ROS/ERK/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:370982016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dixon CE, Flinn P, Bao J, Venya R and
Hayes RL: Nerve growth factor attenuates cholinergic deficits
following traumatic brain injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 146:479–490.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cha Y, Lee SH, Jang SK, Guo H, Ban YH,
Park D, Jang GY, Yeon S, Lee JY, Choi EK, et al: A silk peptide
fraction restores cognitive function in AF64A-induced Alzheimer
disease model rats by increasing expression of choline
acetyltransferase gene. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 314:48–54. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pineda RG, Neil J, Dierker D, Smyser CD,
Wallendorf M, Kidokoro H, Reynolds LC, Walker S, Rogers C, Mathur
AM, et al: Alterations in brain structure and neurodevelopmental
outcome in preterm infants hospitalized in different neonatal
intensive care unit environments. J Pediatr. 164(52–60): e22014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Yang JQ, He BC, Zhou QX, Yu HR,
Tang Y and Liu BZ: Berberine and total base from rhizoma Coptis
chinensis attenuate brain injury in an aluminum-induced rat
model of neurodegenerative disease. Saudi Med J. 30:760–766.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|