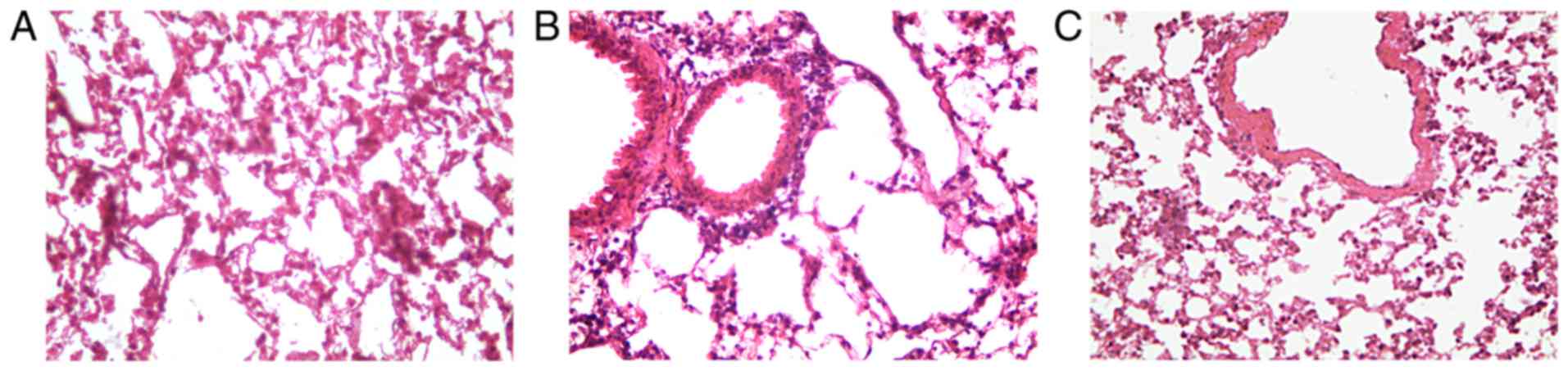
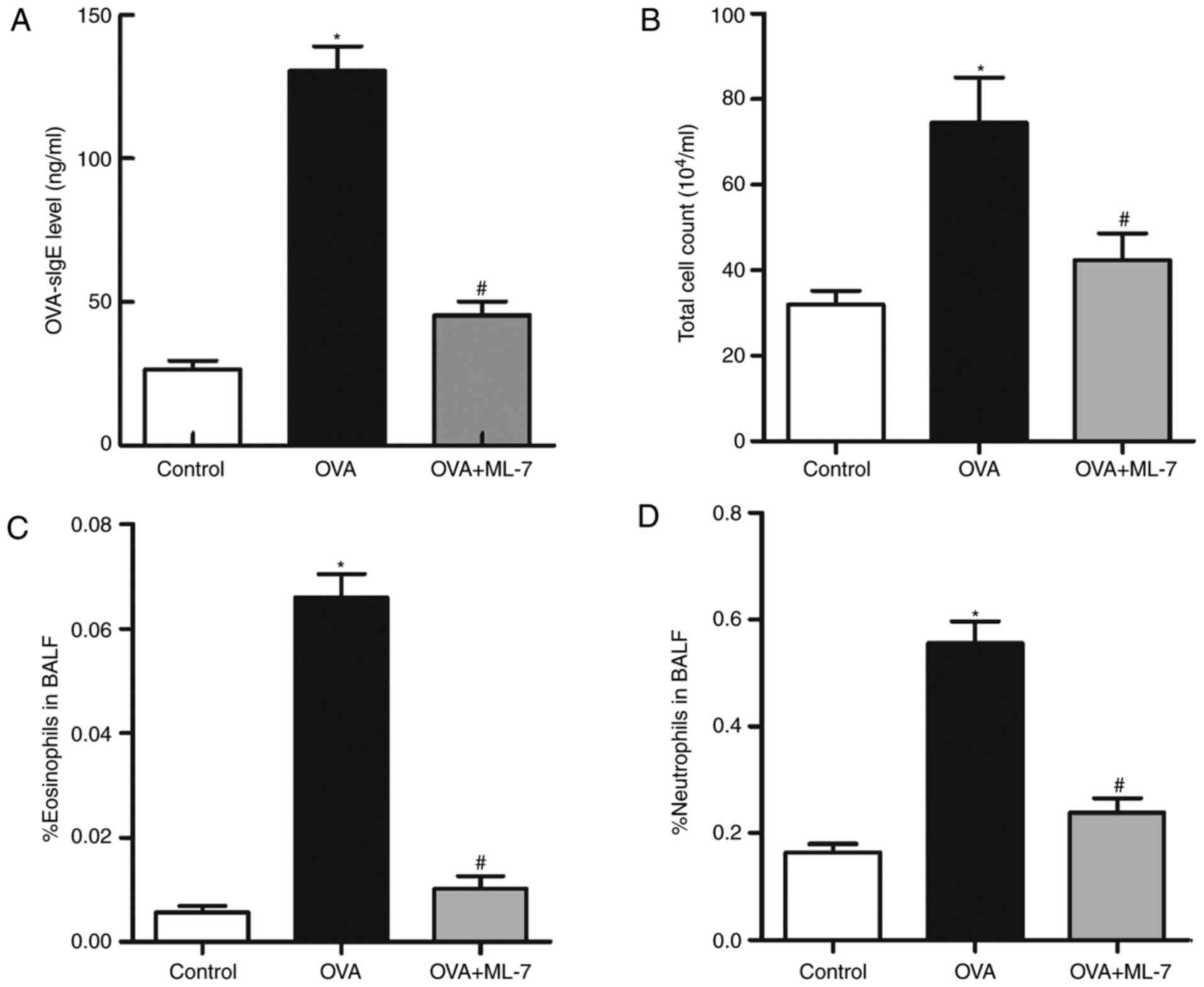
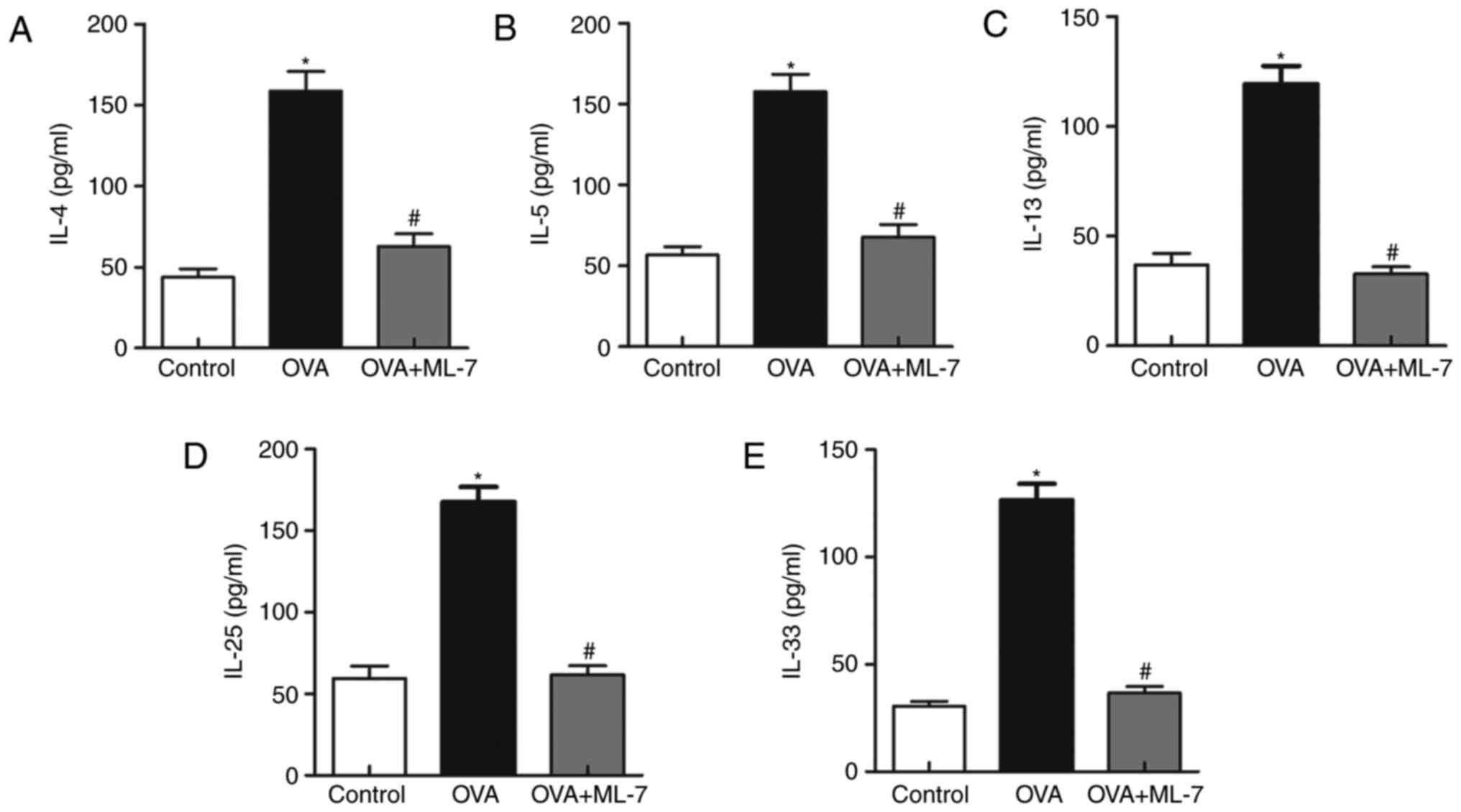
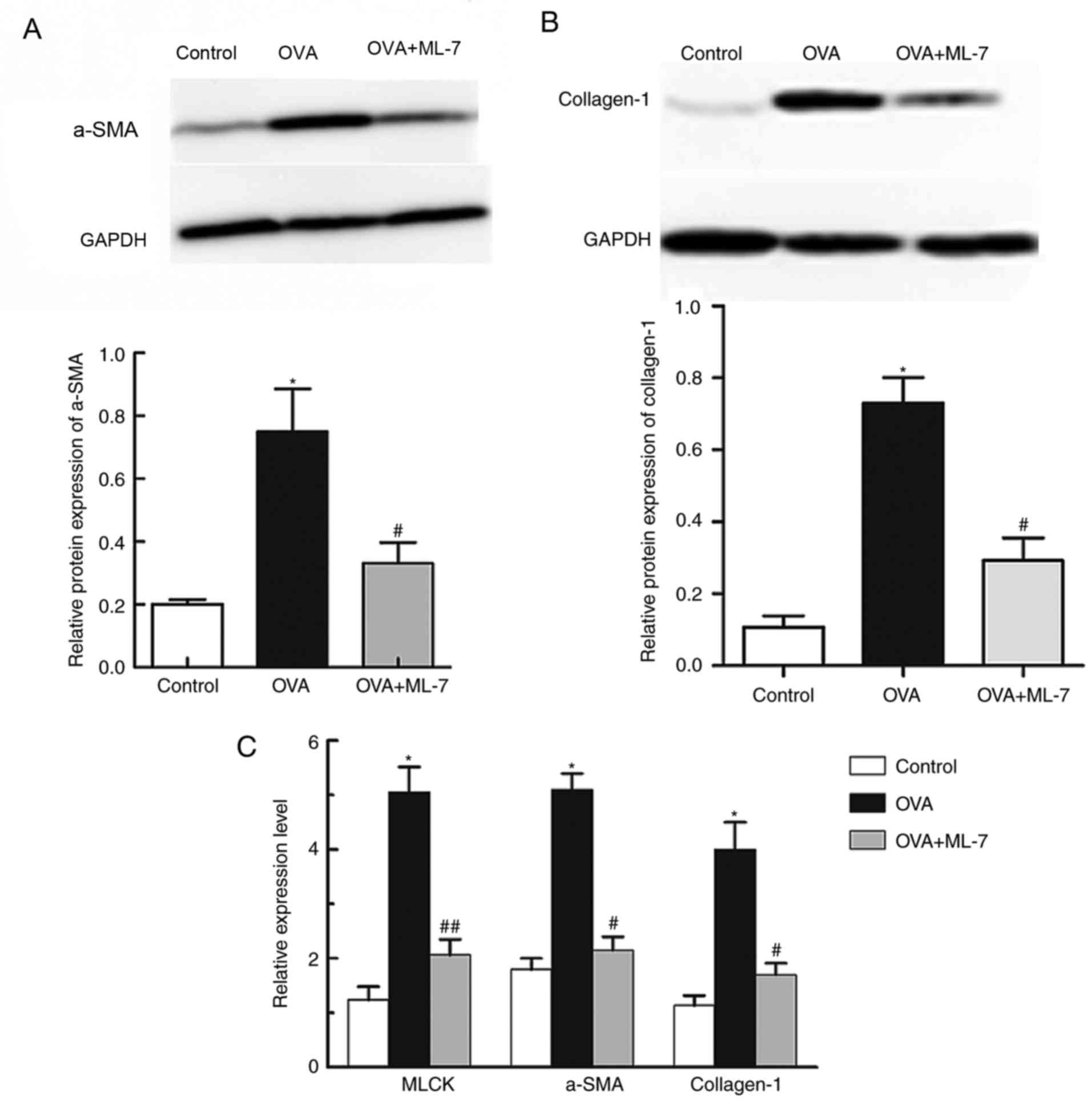
|
1
|
Yang ZC, Yi MJ, Shan YC, Wang C, Ran N,
Jin LY, Fu P, Feng XY, Xu L and Qu ZH: Targeted inhibition of Six1
attenuates allergic airway inflammation and remodeling in asthmatic
mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:1820–1825. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tabeling C, Herbert J, Hocke AC, Lamb DJ,
Wollin SL, Erb KJ, Boiarina E, Movassagh H, Scheffel J, Doehn JM,
et al: Spleen tyrosine kinase inhibition blocks airway constriction
and protects from Th2-induced airway inflammation and remodeling.
Allergy. 72:1061–1072. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jang YH, Choi JK, Jin M, Choi YA, Ryoo ZY,
Lee HS, Park PH, Kim SU, Kwon TK, Jang MH, et al: House dust mite
increases pro-Th2 cytokines, IL-25 and IL-33 via the activation of
TLR1/6 signaling. J Invest Dermatol. 137:2354–2361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ujino M, Sugimoto N, Koizumi Y, Ro S,
Kojima Y, Asae KH, Yamashita N, Ohta K and Nagase H: Leukotriene
receptor antagonist attenuated airway inflammation and
hyperresponsiveness in a double-stranded RNA-induced asthma
exacerbation model. Allergol Int. 66S:S21–S26. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Khapchaev AY and Shirinsky VP: Myosin
light chain kinase MYLK1: Anatomy, interactions, functions, and
regulation. Biochemistry (Mosc). 81:1676–1697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Inam A, Shahzad M, Shabbir A, Shahid H,
Shahid K and Javeed A: Carica papaya ameliorates allergic asthma
via down regulation of IL-4, IL-5, eotaxin, TNF-α, NF-kB, and iNOS
levels. Phytomedicine. 32:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Weigand L, Foxson J, Shimoda LA
and Sylvester JT: Ca2+ signaling in hypoxic pulmonary
vasoconstriction: Effects of myosin light chain and Rho kinase
antagonists. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L674–L685.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang WC, Peng YJ, Zhang GS, He WQ, Qiao
YN, Dong YY, Gao YQ, Chen C, Zhang CH, Li W, et al: Myosin light
chain kinase is necessary for tonic airway smooth muscle
contraction. J Biol Chem. 285:5522–5531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alcala DB, Haldeman BD, Brizendine RK,
Krenc AK, Baker JE, Rock RS and Cremo CR: Myosin light chain kinase
steady-state kinetics: Comparison of smooth muscle myosin II and
nonmuscle myosin IIB as substrates. Cell Biochem Funct. 34:469–474.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Connolly SC, Smith PG, Fairbank NJ, Lall
CA, Cole DJ, Mackinnon JD and Maksym GN: Chronic oscillatory strain
induces MLCK associated rapid recovery from acute stretch in airway
smooth muscle cells. J Appl Physiol (1985). 111:955–963. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flores C, Ma SF, Maresso K, Ober C and
Garcia JG: A variant of the myosin light chain kinase gene is
associated with severe asthma in African Americans. Genet
Epidemiol. 31:296–305. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao L, Grant AV, Rafaels N,
Stockton-Porter M, Watkins T, Gao P, Chi P, Muñoz M, Watson H,
Dunston G, et al: Polymorphisms in the myosin light chain kinase
gene that confer risk of severe sepsis are associated with a lower
risk of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 119:1111–1118. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suzuki M, Nagaishi T, Yamazaki M, Onizawa
M, Watabe T, Sakamaki Y, Ichinose S, Totsuka M, Oshima S, Okamoto
R, et al: Myosin light chain kinase expression induced via tumor
necrosis factor receptor 2 signaling in the epithelial cells
regulates the development of colitis-associated carcinogenesis.
PLoS One. 9:e883692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Basu S and Proweller A: Autoregulatory
control of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase promoter by
notch signaling. J Biol Chem. 291:2988–2999. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou T, Wang T and Garcia JG: A nonmuscle
myosin light chain kinase-dependent gene signature in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells is linked to human asthma severity and
exacerbation status. Pulm Circ. 5:335–338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clayburgh DR, Barrett TA, Tang Y, Meddings
JB, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM, Clarke LL, Mrsny RJ and Turner JR:
Epithelial myosin light chain kinase-dependent barrier dysfunction
mediates T cell activation-induced diarrhea in vivo. J Clin Invest.
115:2702–2715. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang T, Moreno-Vinasco L, Ma SF, Zhou T,
Shimizu Y, Sammani S, Epshtein Y, Watterson DM, Dudek SM and Garcia
JG: Nonmuscle myosin light chain kinase regulates murine asthmatic
inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:1129–1135. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khapchaev AY, Kazakova OA, Samsonov MV,
Sidorova MV, Bushuev VN, Vilitkevich EL, Az'muko AA, Molokoedov AS,
Bespalova ZD and Shirinsky VP: Design of peptidase-resistant
peptide inhibitors of myosin light chain kinase. J Pept Sci.
22:673–681. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Antoine TE and Shukla D: Inhibition of
myosin light chain kinase can be targeted for the development of
new therapies against herpes simplex virus type-1 infection.
Antivir Ther. 19:15–29. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng L, Geisselbrecht Y, Blanck S, Wilbuer
A, Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Filippakopoulos P, Kräling K, Celik MA,
Harms K, Maksimoska J, et al: Structurally sophisticated octahedral
metal complexes as highly selective protein kinase inhibitors. J Am
Chem Soc. 133:5976–5986. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Odani K, Kobayashi T, Ogawa Y, Yoshida S
and Seguchi H: ML-7 inhibits exocytosis of superoxide-producing
intracellular compartments in human neutrophils stimulated with
phorbol myristate acetate in a myosin light chain
kinase-independent manner. Histochem Cell Biol. 119:363–370.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng X, Wang X, Wan Y, Zhou Q, Zhu H and
Wang Y: Myosin light chain kinase inhibitor ML7 improves vascular
endothelial dysfunction via tight junction regulation in a rabbit
model of atherosclerosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:4109–4116. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chua YL, Liong KH, Huang CH, Wong HS, Zhou
Q, Ler SS, Tang Y, Low CP, Koh HY, Kuo IC, et al: Blomia
tropicalis-specific TCR transgenic Th2 cells induce inducible BALT
and severe asthma in mice by an IL-4/IL-13-dependent mechanism. J
Immunol. 197:3771–3781. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogasawara T, Hatano M, Satake H, Ikari J,
Taniguchi T, Tsuruoka N, Watanabe-Takano H, Fujimura L, Sakamoto A,
Hirata H, et al: Development of chronic allergic responses by
dampening Bcl6-mediated suppressor activity in memory T helper 2
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:pp. E741–E750. 2017; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tashiro H, Takahashi K, Hayashi S, Kato G,
Kurata K, Kimura S and Sueoka-Aragane N: Interleukin-33 from
monocytes recruited to the lung contributes to house dust
mite-induced airway inflammation in a mouse model. PLoS One.
11:e01575712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glück J, Rymarczyk B, Kasprzak M and
Rogala B: Increased levels of interleukin-33 and thymic stromal
lymphopoietin in exhaled breath condensate in chronic bronchial
asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 169:51–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Salter BM, Oliveria JP, Nusca G, Smith SG,
Tworek D, Mitchell PD, Watson RM, Sehmi R and Gauvreau GM: IL-25
and IL-33 induce type 2 inflammation in basophils from subjects
with allergic asthma. Respir Res. 17:52016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mahmutovic Persson I, Akbarshahi H, Menzel
M, Brandelius A and Uller L: Increased expression of upstream
TH2-cytokines in a mouse model of viral-induced asthma
exacerbation. J Transl Med. 14:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo Z, Wu J, Zhao J, Liu F, Chen Y, Bi L,
Liu S and Dong L: IL-33 promotes airway remodeling and is a marker
of asthma disease severity. J Asthma. 51:863–869. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang Y, Luo X, Li X, Song X, Wei L, Li Z,
You Q, Guo Q and Lu N: Wogonin inhibits LPS-induced vascular
permeability via suppressing MLCK/MLC pathway. Vascul Pharmacol.
72:43–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Walsh GM: Biologics targeting IL-5, IL-4
or IL-13 for the treatment of asthma-an update. Expert Rev Clin
Immunol. 13:143–149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang C, Liu Q, Chen F, Xu W, Zhang C and
Xiao W: IL-25 promotes Th2 immunity responses in asthmatic mice via
nuocytes activation. PLoS One. 11:e01623932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chung KF: Targeting the interleukin
pathway in the treatment of asthma. Lancet. 386:1086–1096. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bagnasco D, Ferrando M, Varricchi G,
Passalacqua G and Canonica GW: A critical evaluation of anti-IL-13
and anti-IL-4 strategies in severe asthma. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 170:122–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Papathanassiou E, Loukides S and Bakakos
P: Severe asthma: Anti-IgE or anti-IL-5? Eur Clin Respir J.
3:318132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jia Y, Fang X, Zhu X, Bai C, Zhu L, Jin M,
Wang X, Hu M, Tang R and Chen Z: IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid
cells correlate with asthma control status and treatment response.
Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 55:675–683. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tang W, Smith SG, Beaudin S, Dua B, Howie
K, Gauvreau G and O'Byrne PM: IL-25 and IL-25 receptor expression
on eosinophils from subjects with allergic asthma. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 163:5–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shan S, Li Y, Wang J, Lv Z, Yi D, Huang Q,
Corrigan CJ, Wang W, Quangeng Z and Ying S: Nasal administration of
interleukin-33 induces airways angiogenesis and expression of
multiple angiogenic factors in a murine asthma surrogate.
Immunology. 148:83–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|