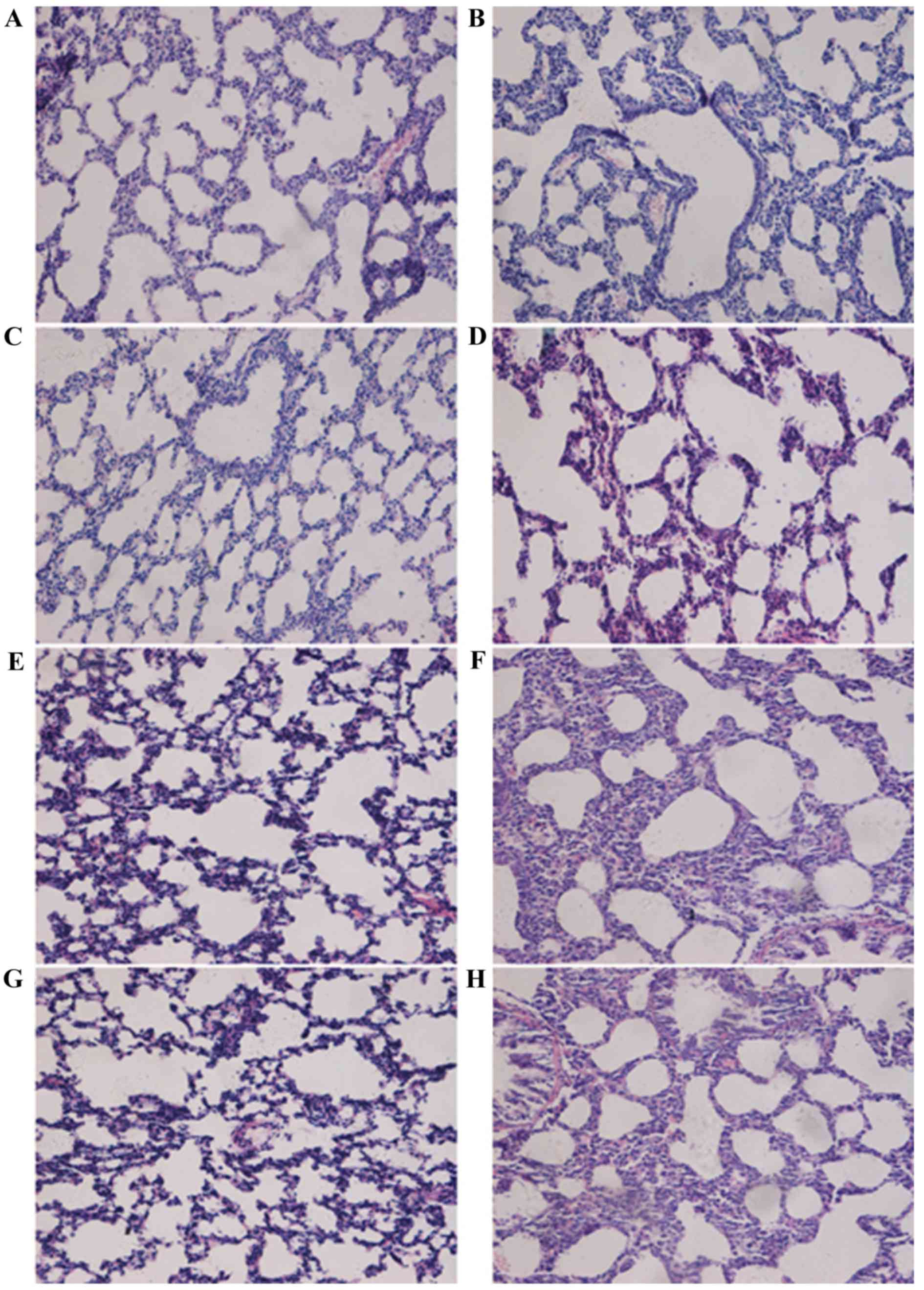
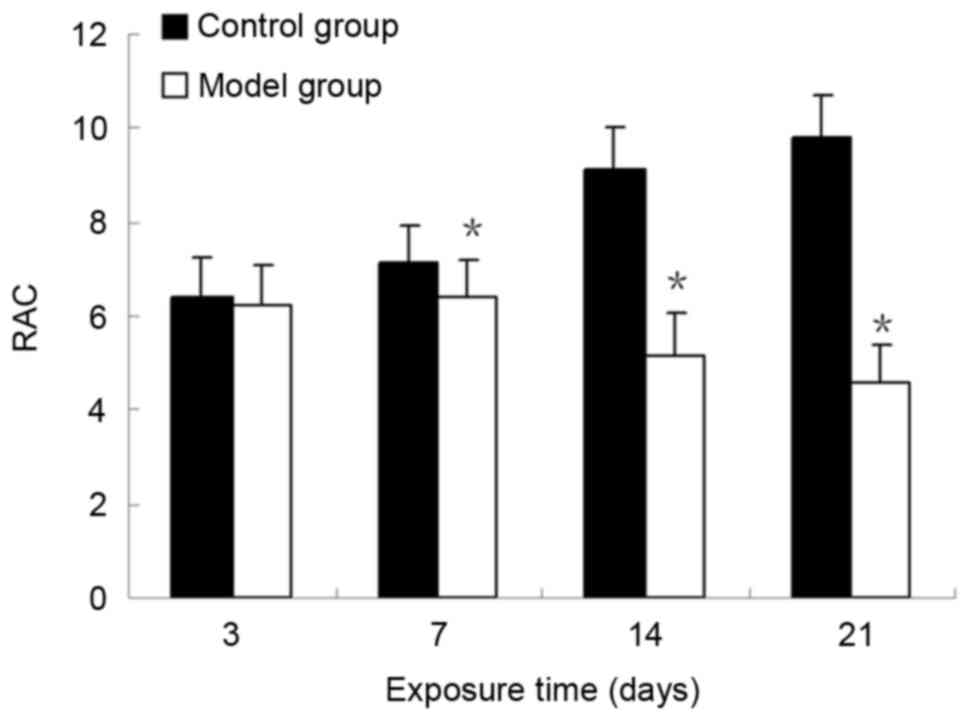
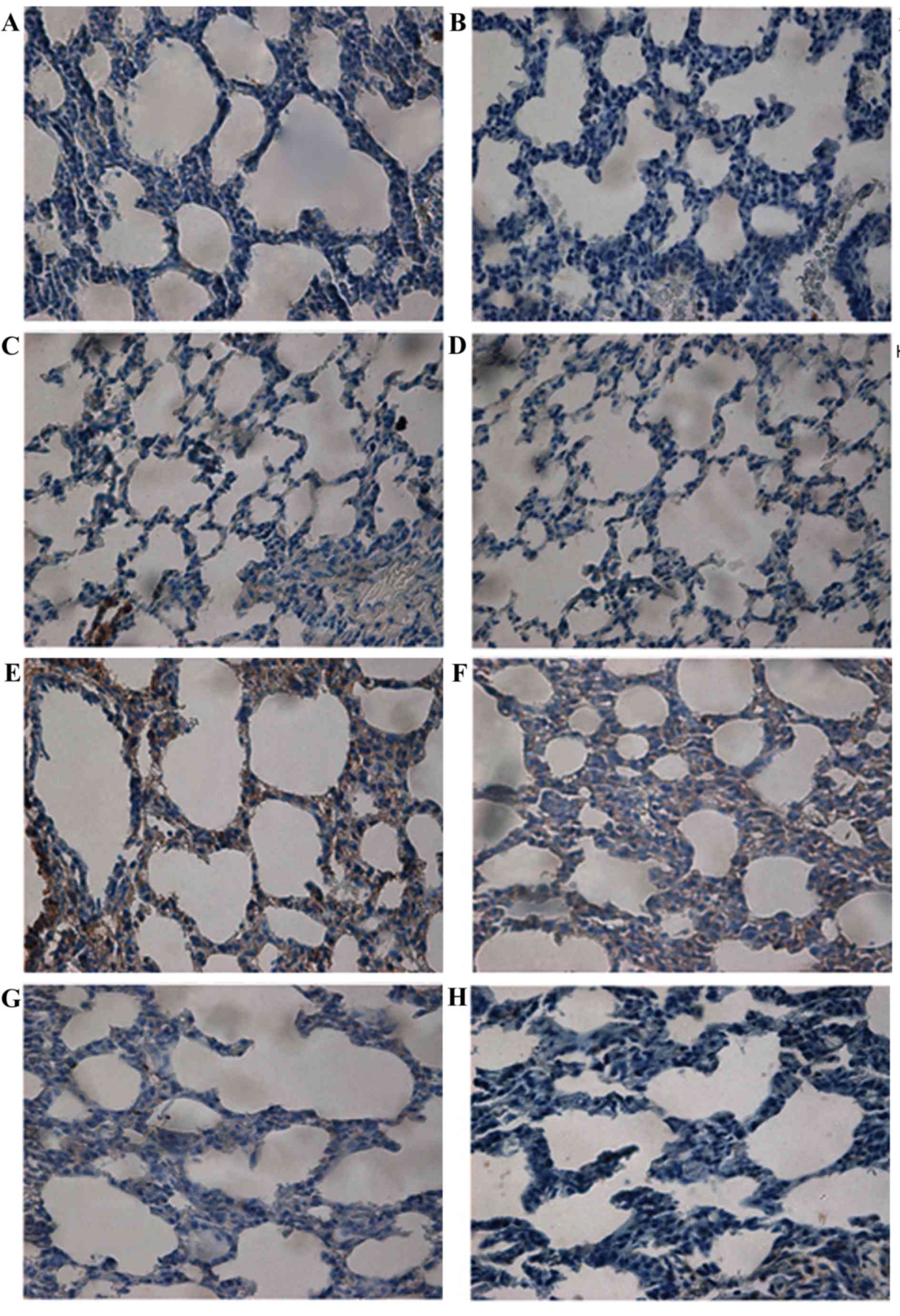
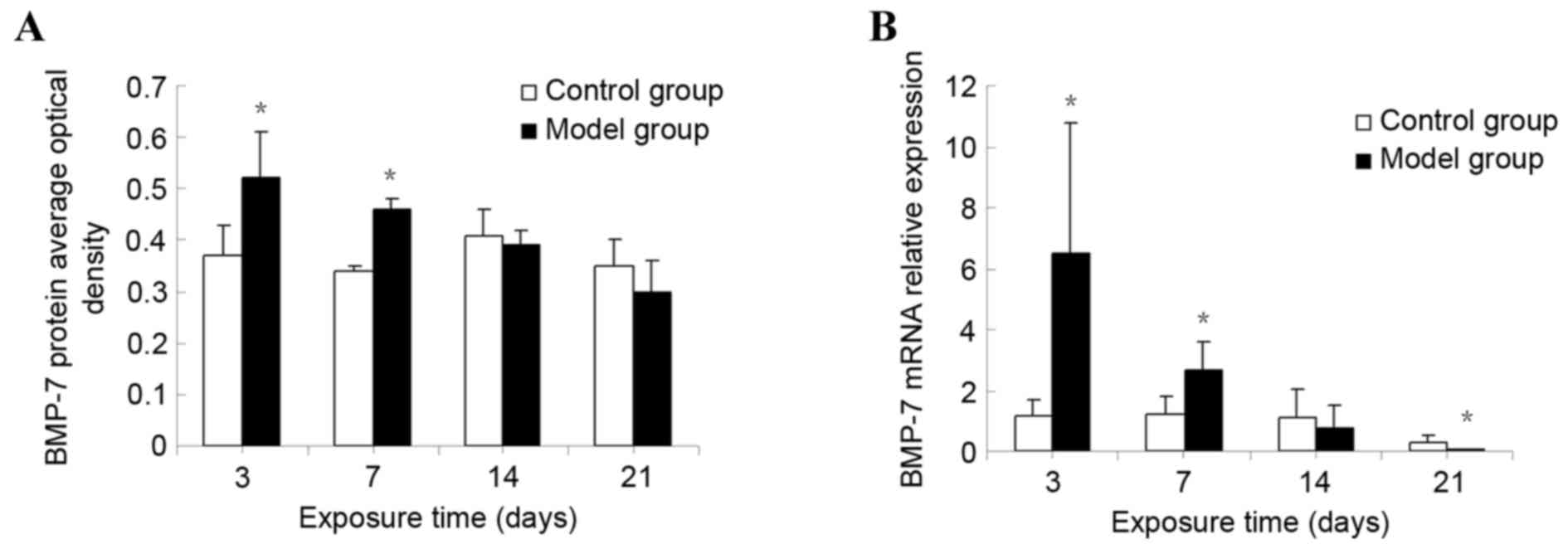
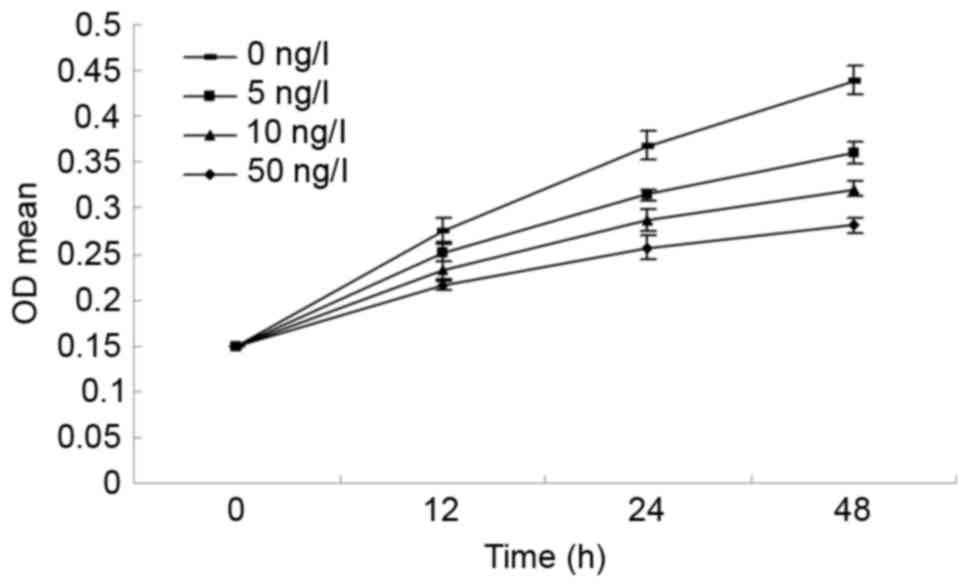
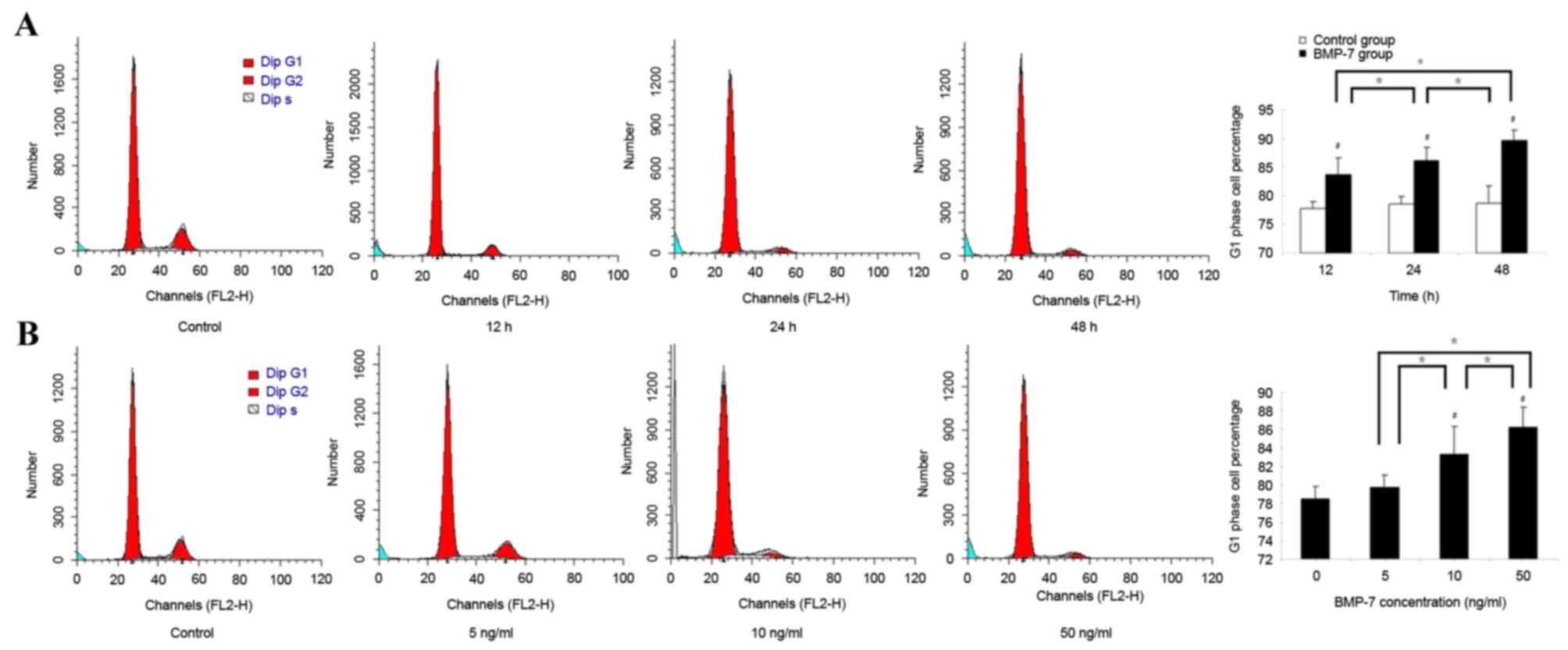
|
1
|
Bhandari A and Bhandari V: Pitfalls,
problems, and progress in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics.
123:1562–1573. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Trembath A and Laughon MM: Predictors of
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clin Perinatol. 39:585–601. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S,
Laptook AR, Walsh MC, Hale EC, Newman NS, Schibler K, Carlo WA, et
al: Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD
Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics. 126:443–456. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Özdemir ÖM, Gözkeser E, Bir F and Yenisey
Ç: The effects of resveratrol on hyperoxia-induced lung injury in
neonatal rats. Pediatr Neonatol. 55:352–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gien J and Kinsella JP: Pathogenesis and
treatment of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Curr Opin Pediatr.
23:305–313. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jobe AH and Bancalari E: Bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 163:1723–1729. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thébaud B and Abman SH: Bronchopulmonary
dysplasia: Where have all the vessels gone? Roles of angiogenic
growth factors in chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
175:978–985. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Husain AN, Siddiqui NH and Stocker JT:
Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol. 29:710–717. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dasgupta C, Sakurai R, Wang Y, Guo P,
Ambalavanan N, Torday JS and Rehan VK: Hyperoxia-induced neonatal
rat lung injury involves activation of TGF-{beta} and Wnt signaling
and is protected by rosiglitazone. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 296:L1031–L1041. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boon MR, van der Horst G, van der Pluijm
G, Tamsma JT, Smit JW and Rensen PC: Bone morphogenetic protein 7:
A broad-spectrum growth factor with multiple target therapeutic
potency. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:221–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ali IH and Brazil DP: Bone morphogenetic
proteins and their antagonists: Current and emerging clinical uses.
Br J Pharmacol. 171:3620–3632. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bragdon B, Moseychuk O, Saldanha S, King
D, Julian J and Nohe A: Bone morphogenetic proteins: A critical
review. Cell Signal. 23:609–620. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szabò H, Fiorino G, Spinelli A, Rovida S,
Repici A, Malesci AC and Danese S: Review article: Anti-fibrotic
agents for the treatment of Crohn's disease-lessons learnt from
other diseases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 31:189–201. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Djamali A and Samaniego M: Fibrogenesis in
kidney transplantation: Potential targets for prevention and
therapy. Transplantation. 88:1149–1156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yanagita M: Inhibitors/antagonists of
TGF-β system in kidney fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
27:3686–3691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weiskirchen R, Meurer SK, Gressner OA,
Herrmann J, Borkham-Kamphorst E and Gressner AM: BMP-7 as
antagonist of organ fibrosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
14:4992–5012. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gressner OA, Rizk MS, Kovalenko E,
Weiskirchen R and Gressner AM: Changing the pathogenetic roadmap of
liver fibrosis? Where did it start; where will it go? J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1024–1035. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weiskirchen R and Meurer SK: BMP-7
counteracting TGF-beta1 activities in organ fibrosis. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 18:1407–1434. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Myllärniemi M, Lindholm P, Ryynänen MJ,
Kliment CR, Salmenkivi K, Keski-Oja J, Kinnula VL, Oury TD and Koli
K: Gremlin-mediated decrease in bone morphogenetic protein
signaling promotes pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
177:321–329. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kinoshita K, Iimuro Y, Otogawa K, Saika S,
Inagaki Y, Nakajima Y, Kawada N, Fujimoto J, Friedman SL and Ikeda
K: Adenovirus-mediated expression of BMP-7 suppresses the
development of liver fibrosis in rats. Gut. 56:706–714. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gressner OA and Gao C: Monitoring
fibrogenic progression in the liver. Clin Chim Acta. 433:111–122.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyazaki Y, Ueda H, Yokoo T, Utsunomiya Y,
Kawamura T, Matsusaka T, Ichikawa I and Hosoya T: Inhibition of
endogenous BMP in the glomerulus leads to mesangial matrix
expansion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 340:681–688. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morrissey J, Hruska K, Guo G, Wang S, Chen
Q and Klahr S: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 improves renal fibrosis
and accelerates the return of renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13
Suppl 1:S14–S21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ohnuma-Koyama A, Yoshida T,
Tajima-Horiuchi H, Takahashi N, Yamaguchi S, Ohtsuka R,
Takeuchi-Kashimoto Y, Kuwahara M, Takeda M, Nakashima N and Harada
T: Didecyldimethylammonium chloride induces pulmonary fibrosis in
association with TGF-β signaling in mice. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
65:1003–1009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Izumi N, Mizuguchi S, Inagaki Y, Saika S,
Kawada N, Nakajima Y, Inoue K, Suehiro S, Friedman SL and Ikeda K:
BMP-7 opposes TGF-beta1-mediated collagen induction in mouse
pulmonary myofibroblasts through Id2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 290:L120–L126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang H, Fu J, Xue X, Yao L, Qiao L, Hou A,
Jin L and Xing Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
bronchopulmonary dysplasia of newborn rats. Pediatr Pulmonol.
49:1112–1123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kelleher MD, Naureckas ET, Solway J and
Hershenson MB: In vivo hyperoxic exposure increases cultured lung
fibroblast proliferation and c-Ha-ms expression. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 12:19–26. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakanishi H, Sugiura T, Streisand JB,
Lonning SM and Roberts JD Jr: TGF-beta-neutralizing antibodies
improve pulmonary alveologenesis and vasculogenesis in the injured
newborn lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L151–L161.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumarasamy A, Schmitt I, Nave AH, Reiss I,
van der Horst I, Dony E, Roberts JD Jr, de Krijger RR, Tibboel D,
Seeger W, et al: Lysyl oxidase activity is dysregulated during
impaired alveolarization of mouse and human lungs. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 180:1239–1252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahn SY, Chang YS, Sung DK, Yoo HS, Sung
SI, Choi SJ and Park WS: Cell type-dependent variation in paracrine
potency determines therapeutic efficacy against neonatal hyperoxic
lung injury. Cytotherapy. 17:1025–1035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sieber C, Kopf J, Hiepen C and Knaus P:
Recent advances in BMP receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 20:343–355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Danesh SM, Villasenor A, Chong D, Soukup C
and Cleaver O: BMP and BMP receptor expression during murine
organogenesis. Gene Expr Patterns. 9:255–265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kazama I, Mahoney Z, Miner JH, Graf D,
Economides AN and Kreidberg JA: Podocyte-derived BMP7 is critical
for nephron development. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:2181–2191. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang G, Zhu Z, Wang Y, Gao A, Niu P and
Tian L: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 inhibits silica-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Toxicol Lett. 220:103–108. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Leppäranta O, Tikkanen JM, Bespalov MM,
Koli K and Myllärniemi M: Bone morphogenetic protein-inducer
tilorone identified by high-throughput screening is antifibrotic in
vivo. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 48:448–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang T, Chen SL, Lu XJ, Shen CY, Liu Y and
Chen YP: Bone morphogenetic protein 7 suppresses the progression of
hepatic fibrosis and regulates the expression of gremlin and
transforming growth factor β1. Mol Med Rep. 6:246–252.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang S, de Caestecker M, Kopp J, Mitu G,
Lapage J and Hirschberg R: Renal bone morphogenetic protein-7
protects against diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
17:2504–2512. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alejandre-Alcázar MA, Kwapiszewska G,
Reiss I, Amarie OV, Marsh LM, Sevilla-Pérez J, Wygrecka M, Eul B,
Köbrich S, Hesse M, et al: Hyperoxia modulates TGF-beta/BMP
signaling in a mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 292:L537–L549. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tan HC, Poh CK, Cai Y and Wang W:
Anti-fibrosis effect of BMP-7 peptide functionalization on cobalt
chromium alloy. J Orthop Res. 31:983–990. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yamada S, Nakamura J, Asada M, Takase M,
Matsusaka T, Iguchi T, Yamada R, Tanaka M, Higashi AY, Okuda T, et
al: Twisted gastrulation, a BMP antagonist, exacerbates podocyte
injury. PLoS One. 9:e891352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Douet V, Arikawa-Hirasawa E and Mercier F:
Fractone-heparan sulfates mediate BMP-7 inhibition of cell
proliferation in the adult subventricular zone. Neurosci Lett.
528:120–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Miyazaki H, Watabe T, Kitamura T and
Miyazono K: BMP signals inhibit proliferation and in vivo tumor
growth of androgen-insensitive prostate carcinoma cells. Oncogene.
23:9326–9335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|