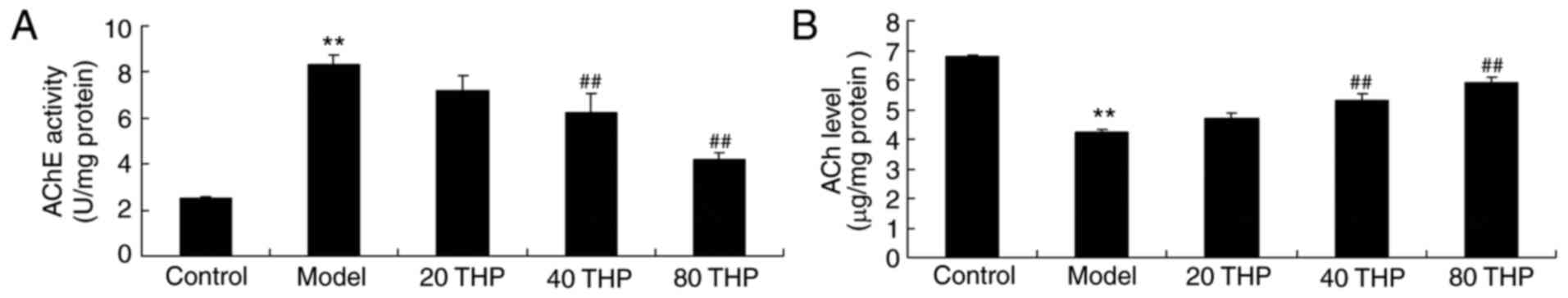
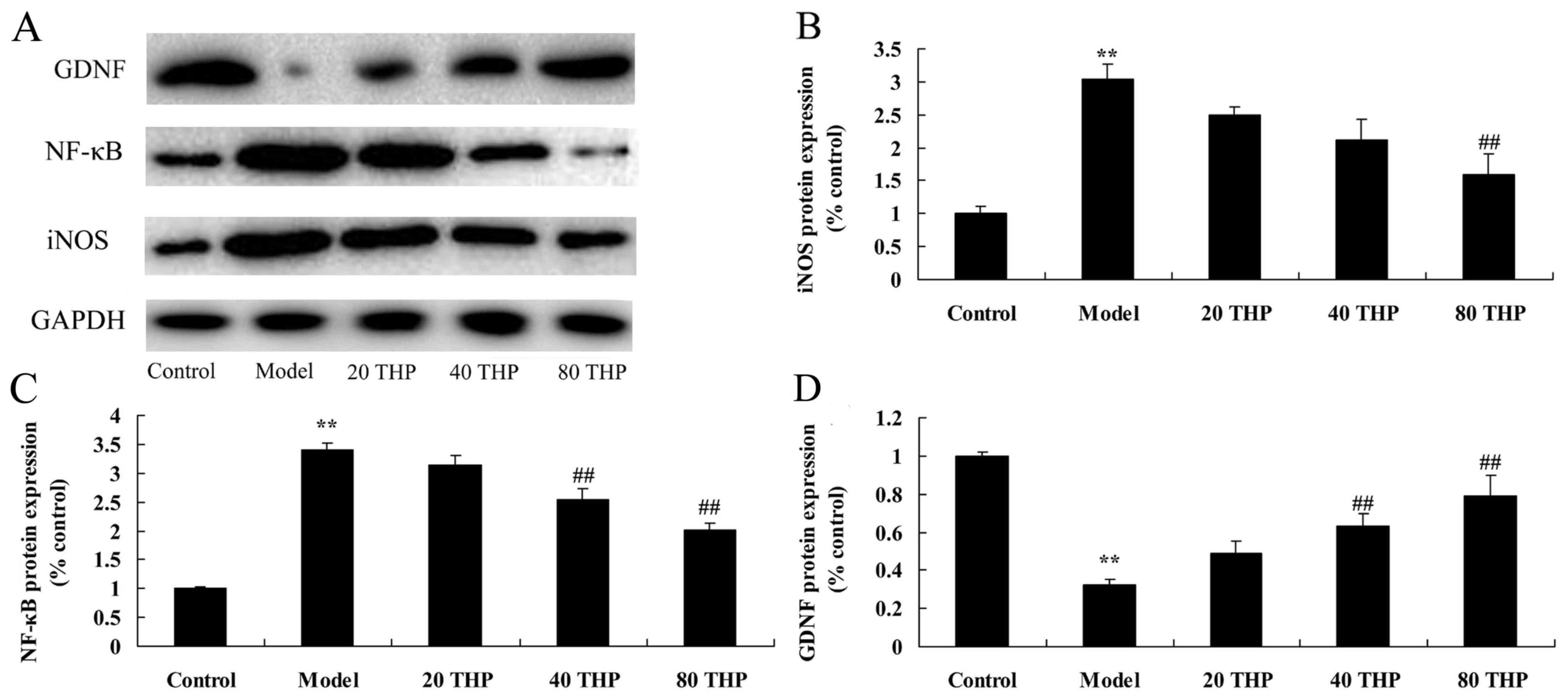
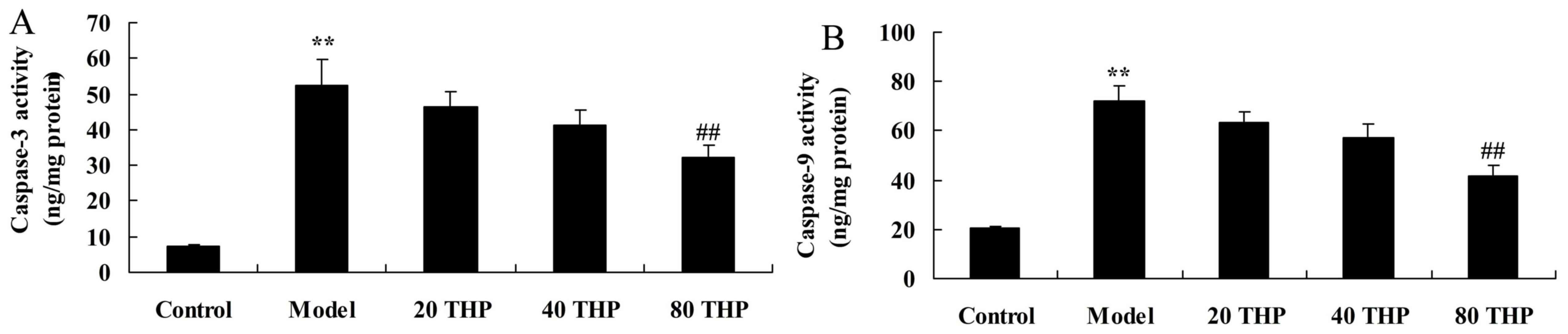
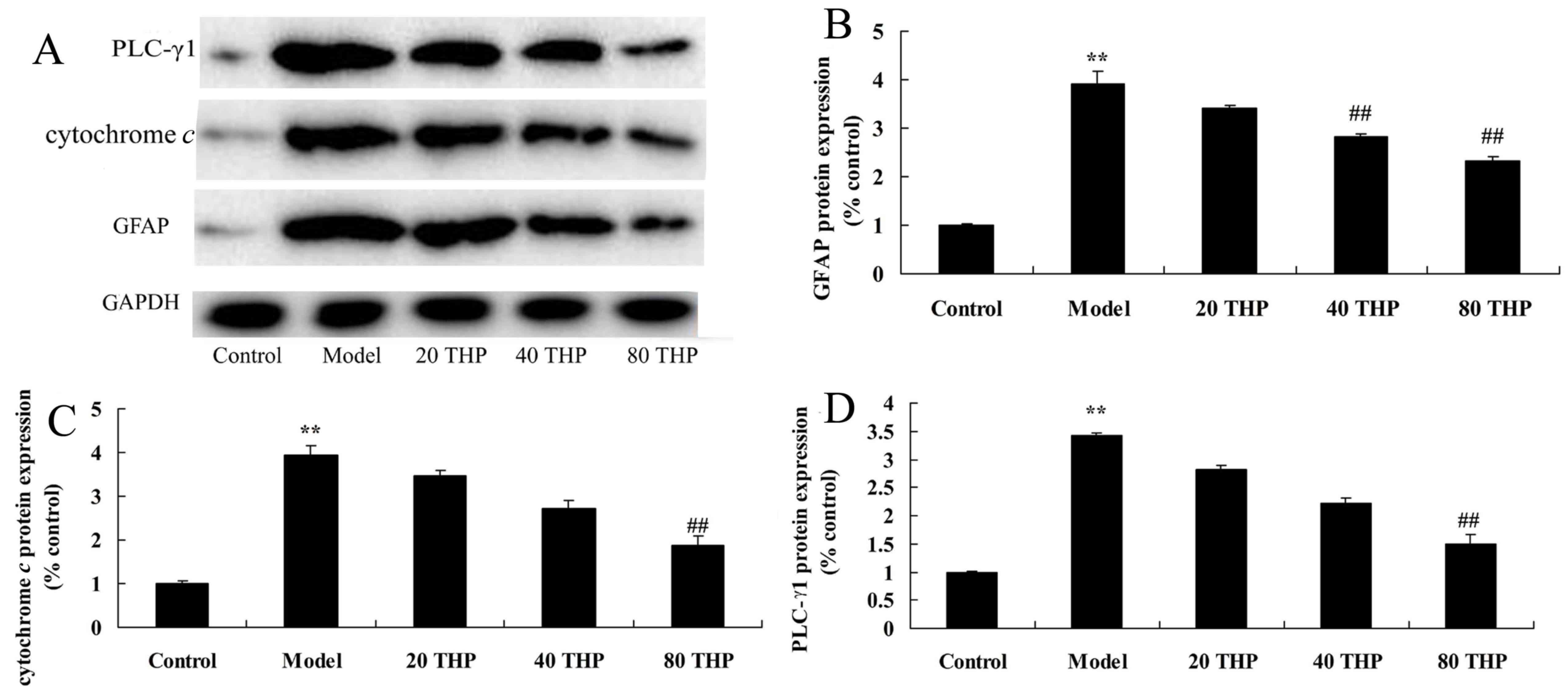
|
1
|
Li J, Yu Y, Wang B, Wu H, Xue G and Hou Y:
Selective regulation of neurosteroid biosynthesis under
ketamine-induced apoptosis of cortical neurons in vitro. Mol Med
Rep. 13:1586–1592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu JR, Baek C, Han XH, Shoureshi P and
Soriano SG: Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3β in ketamine-induced
developmental neuroapoptosis in rats. Br J Anaesth. 110 Suppl
1:Si3–Si9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cetin N, Suleyman B, Altuner D,
Kuyrukluyildiz U, Ozcicek F, Coskun R, Kurt N and Suleyman H:
Effect of disulfiram on ketamine-induced cardiotoxicity in rats.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:13540–13547. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu JR, Liu Q, Li J, Baek C, Han XH,
Athiraman U and Soriano SG: Noxious stimulation attenuates
ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain.
Anesthesiology. 117:64–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
D'Souza DC, Ahn K, Bhakta S, Elander J,
Singh N, Nadim H, Jatlow P, Suckow RF, Pittman B and Ranganathan M:
Nicotine fails to attenuate ketamine-induced cognitive deficits and
negative and positive symptoms in humans: Implications for
schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 72:785–794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang S, Dai Y, Zhang Z, Hao W and Chen H:
Docosahexaenoic acid intake ameliorates ketamine-induced impairment
of spatial cognition and learning ability in ICR mice. Neurosci
Lett. 580:125–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu J, Piao BK, Pei YX, Qi X and Hua BJ:
Protective effects of tetrahydropalmatine against gamma-radiation
induced damage to human endothelial cells. Life Sci. 87:55–63.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu J, Che J, Liu L, Yang F, Zhu X and Cao
B: Tetrahydropalmatine attenuates irradiation induced lung injuries
in rats. Life Sci. 153:74–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Y, Liang A, Zhang Y, Li C, Yi Y and
Nilsen OG: Impact of Tetrahydropalmatine on the pharmacokinetics of
probe drugs for CYP1A2, 2D6 and 3A isoenzymes in beagle dogs.
Phytother Res. 30:906–914. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koffler SP, Hampstead BM, Irani F, Tinker
J, Kiefer RT, Rohr P and Schwartzman RJ: The neurocognitive effects
of 5 day anesthetic ketamine for the treatment of refractory
complex regional pain syndrome. Arch Clin Neuropsychol. 22:719–729.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dahan A, Olofsen E, Sigtermans M, Noppers
I, Niesters M, Aarts L, Bauer M and Sarton E: Population
pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of ketamine-induced pain
relief of chronic pain. Eur J Pain. 15:258–267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hashimoto K: A BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism
and ketamine-induced rapid antidepressant action. Clin
Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 10:59–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou W, Wang N, Yang C, Li XM, Zhou ZQ and
Yang JJ: Ketamine-induced antidepressant effects are associated
with AMPA receptors-mediated upregulation of mTOR and BDNF in rat
hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Eur Psychiatry. 29:419–423.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Wang B, Wu H, Yu Y, Xue G and Hou Y:
17β-estradiol attenuates ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis and
persistent cognitive deficits in the developing brain. Brain Res.
1593:30–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ben-Azu B, Aderibigbe AO, Ajayi AM and
Iwalewa EO: Neuroprotective effects of the ethanol stem bark
extracts of Terminalia ivorensis in ketamine-induced
schizophrenia-like behaviors and oxidative damage in mice. Pharm
Biol. 54:2871–2879. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li J, Liu CN, Wei N, Li XD, Liu YY, Yang R
and Jia YJ: Protective effects of BAY 73–6691, a selective
inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 9, on amyloid-beta peptides-induced
oxidative stress in in-vivo and in-vitro models of Alzheimer's
disease. Brain Res. 1642:327–335. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu KM, Chuang SM, Long CY, Lee YL, Wang
CC, Lu MC, Lin RJ, Lu JH, Jang MY, Wu WJ, et al: Ketamine-induced
ulcerative cystitis and bladder apoptosis involve oxidative stress
mediated by mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 309:F318–F331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
de Araujo FY, de Oliveira GV, Gomes PX,
Soares MA, Silva MI, Carvalho AF, de Moraes MO, de Moraes ME,
Vasconcelos SM, Viana GS, et al: Inhibition of ketamine-induced
hyperlocomotion in mice by the essential oil of Alpinia zerumbet:
Possible involvement of an antioxidant effect. J Pharm Pharmacol.
63:1103–1110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Q, Sun LH, Jia W, Liu XM, Dang HX,
Mai WL, Wang N, Steinmetz A, Wang YQ and Xu CJ: Comparison of
ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1 for their effects on improving
scopolamine-induced learning and memory impairment in mice.
Phytother Res. 24:1748–1754. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hall JM and Savage LM: Exercise leads to
the re-emergence of the cholinergic/nestin neuronal phenotype
within the medial septum/diagonal band and subsequent rescue of
both hippocampal ACh efflux and spatial behavior. Exp Neurol.
278:62–75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen HW, He XH, Yuan R, Wei BJ, Chen Z,
Dong JX and Wang J: Sesquiterpenes and a monoterpenoid with
acetylcholinesterase (AchE) inhibitory activity from Valeriana
officinalis var. Latiofolia in vitro and in vivo. Fitoterapia.
110:142–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu NG, Xiao ZJ, Zou T and Huang ZL:
Ameliorative effects of physcion 8-O-β-glucopyranoside isolated
from Polygonum cuspidatum on learning and memory in dementia rats
induced by Abeta1-40. Pharm Biol. 53:1632–1638. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qu Z, Zhang J, Yang H, Huo L, Gao J, Chen
H and Gao W: Protective effect of tetrahydropalmatine against
d-galactose induced memory impairment in rat. Physiol Behav.
154:114–125. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wan D, Xue L, Zhu H and Luo Y: Catalpol
induces neuroprotection and prevents memory dysfunction through the
cholinergic system and BDNF. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:1348522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li XY, Xu L, Liu CL, Huang LS and Zhu XY:
Electroacupuncture intervention inhibits the decline of
learning-memory ability and overex-pression of cleaved caspase-3
and bax in hippocampus induced by isoflurane in APPswe/PS 1. Zhen
Ci Yan Jiu. 41:24–30. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li M, Peng J, Wang MD, Song YL, Mei YW and
Fang Y: Passive movement improves the learning and memory function
of rats with cerebral infarction by inhibiting neuron cell
apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 49:216–221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xian YF, Mao QQ, Wu JC, Su ZR, Chen JN,
Lai XP, Ip SP and Lin ZX: Isorhynchophylline treatment improves the
amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairment in rats via inhibition of
neuronal apoptosis and tau protein hyperphosphorylation. J
Alzheimers Dis. 39:331–346. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Doniselli N, Monzeglio E, Dal Palù A,
Merli A and Percudani R: The identification of an integral
membrane, cytochrome c urate oxidase completes the catalytic
repertoire of a therapeutic enzyme. Sci Rep. 5:137982015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu J, Zhao L, Liu L, Yang F, Zhu X and Cao
B: Tetrahydropalmatine protects rat pulmonary endothelial cells
from irradiation-induced apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress
and the calcium sensing receptor/phospholipase C-γ1 pathway. Free
Radic Res. 50:611–626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyazaki H, Okuma Y, Nomura J, Nagashima K
and Nomura Y: Age-related alterations in the expression of glial
cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the senescence-accelerated
mouse brain. J Pharmacol Sci. 92:28–34. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang J, Tan H, Jiang W and Zuo Z:
Amantadine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction possibly
by increasing glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in rats.
Anesthesiology. 121:773–785. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pertusa M, Garcia-Matas S, Mammeri H,
Adell A, Rodrigo T, Mallet J, Cristòfol R, Sarkis C and Sanfeliu C:
Expression of GDNF transgene in astrocytes improves cognitive
deficits in aged rats. Neurobiol Aging. 29:1366–1379. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sudo G, Kagawa T, Kokubu Y, Inazawa J and
Taga T: Increase in GFAP-positive astrocytes in histone demethylase
GASC1/KDM4C/JMJD2C hypomorphic mutant mice. Genes Cells.
21:218–225. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Silva AF, Aguiar MS, Carvalho OS, Santana
Lde N, Franco EC, Lima RR, Siqueira NV, Feio RA, Faro LR and
Gomes-Leal W: Hippocampal neuronal loss, decreased GFAP
immunoreactivity and cognitive impairment following experimental
intoxication of rats with aluminum citrate. Brain Res. 1491:23–33.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chuang CM, Hsieh CL, Lin HY and Lin JG:
Panax Notoginseng Burk attenuates impairment of learning and memory
functions and increases ED1, BDNF and beta-secretase immunoreactive
cells in chronic stage ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Am J Chin
Med. 36:685–693. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gu B, Huang YZ, He XP, Joshi RB, Jang W
and McNamara JO: A peptide uncoupling BDNF receptor TrkB from
phospholipase Cγ1 prevents epilepsy induced by status epilepticus.
Neuron. 88:484–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou L, Martinez SJ, Haber M, Jones EV,
Bouvier D, Doucet G, Corera AT, Fon EA, Zisch AH and Murai KK:
EphA4 signaling regulates phospholipase Cgamma1 activation, cofilin
membrane association and dendritic spine morphology. J Neurosci.
27:5127–5138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cortese GP, Barrientos RM, Maier SF and
Patterson SL: Aging and a peripheral immune challenge interact to
reduce mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor and activation of
TrkB, PLCgamma1 and ERK in hippocampal synaptoneurosomes. J
Neurosci. 31:4274–4279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|