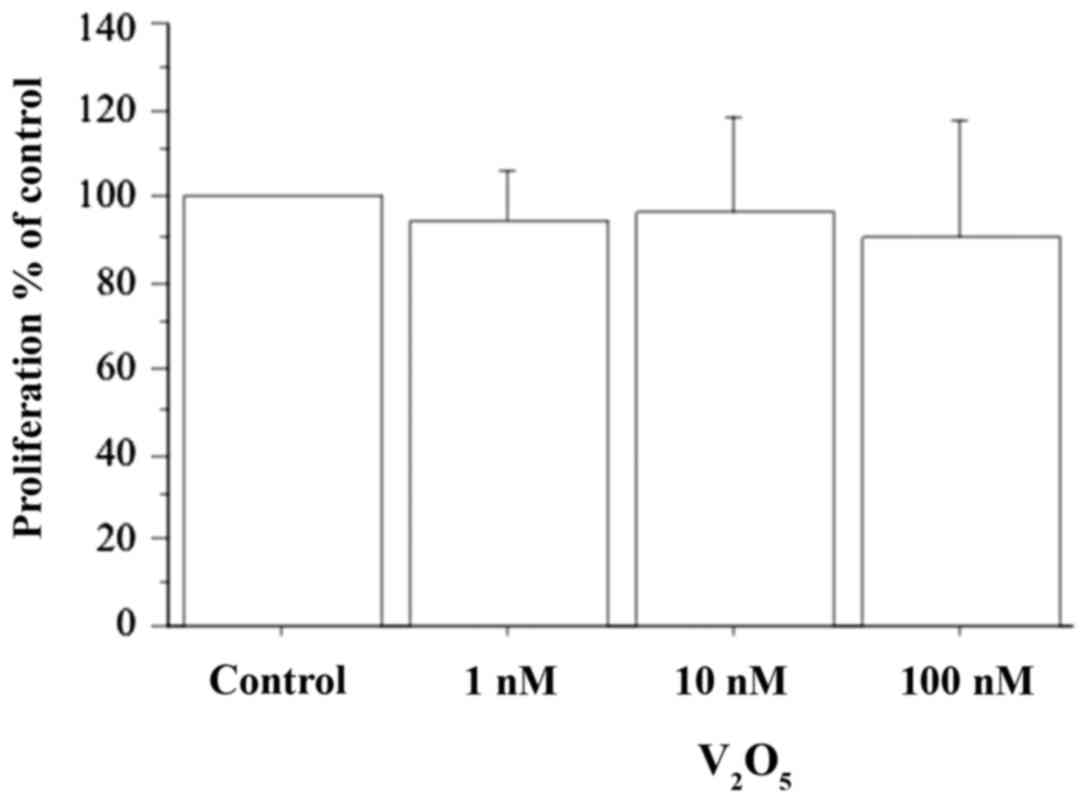
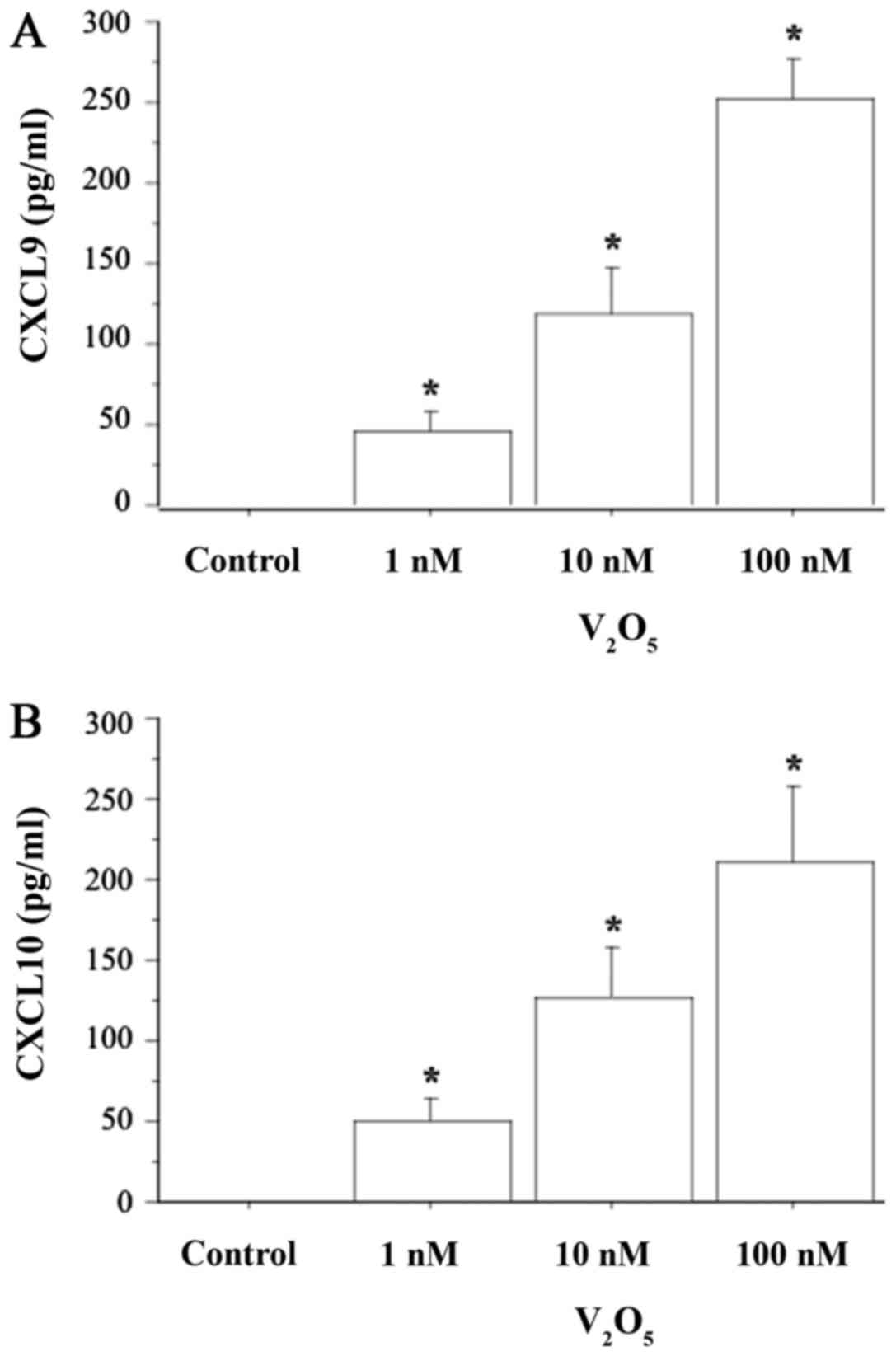
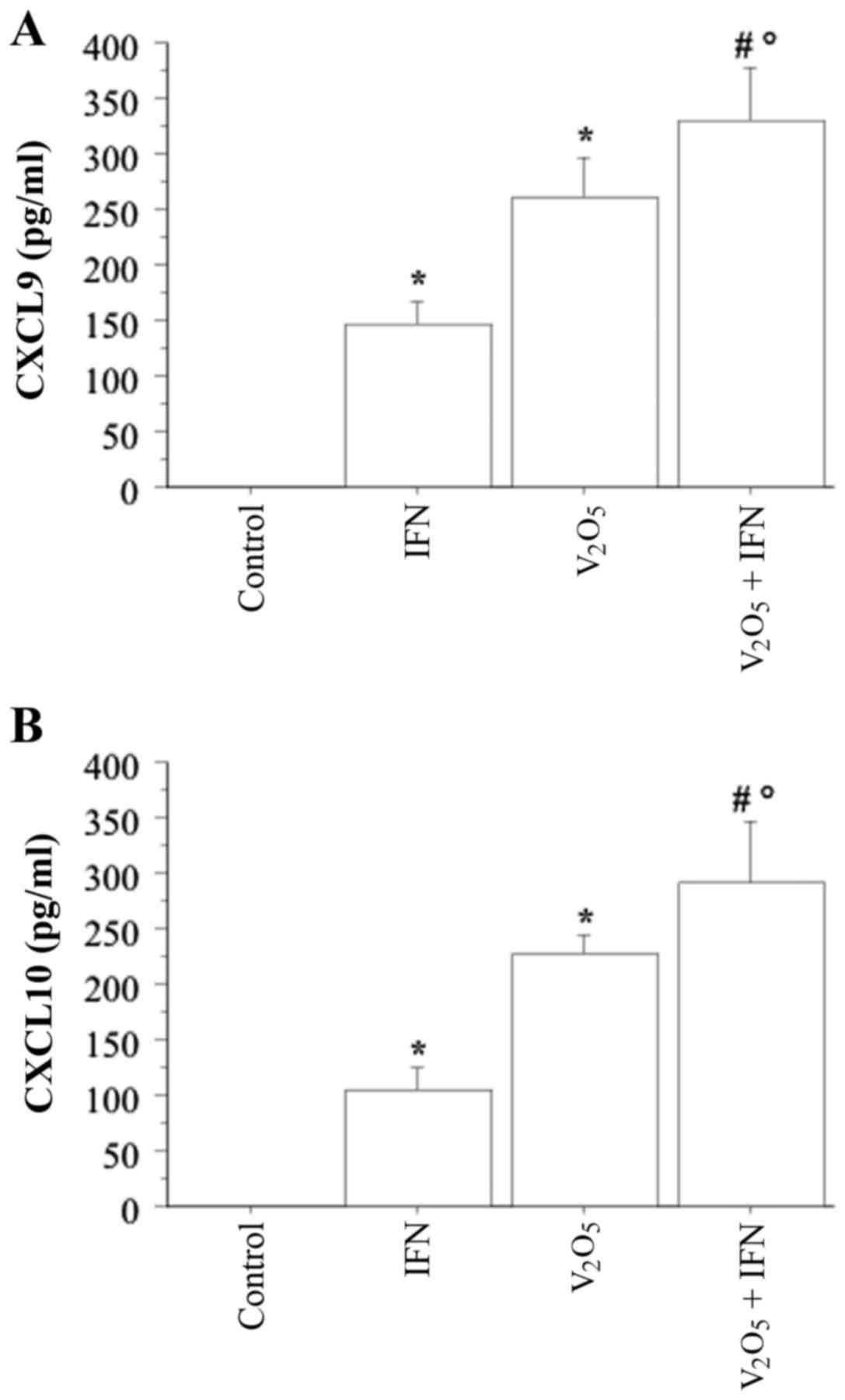
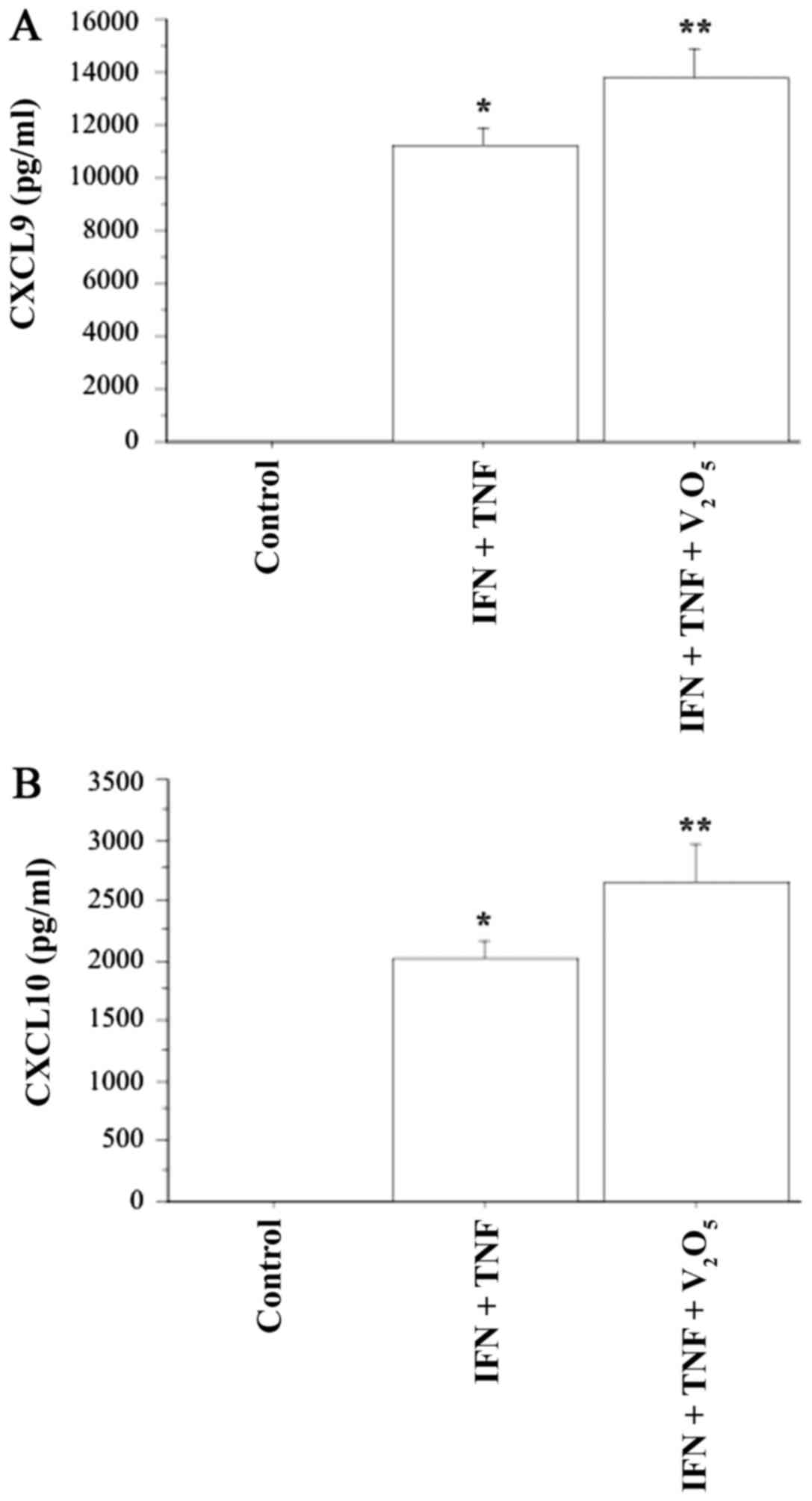
|
1
|
Ingram JL, Antao-Menezes A, Turpin EA,
Wallace DG, Mangum JB, Pluta LJ, Thomas RS and Bonner JC: Genomic
analysis of human lung fibroblasts exposed to vanadium pentoxide to
identify candidate genes for occupational bronchitis. Respir Res.
8:342007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA): Occupational safety and health guideline for
vanadium pentoxide dust. OSHA; Washington, DC: 2007
|
|
3
|
Sax NI: Dangerous Properties of Industrial
Materials. 6th. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company; New York, NY: pp.
2717–2720. 1984
|
|
4
|
Ress NB, Chou BJ, Renne RA, Dill JA,
Miller RA, Roycroft JH, Hailey JR, Haseman JK and Bucher JR:
Carcinogenicity of inhaled vanadium pentoxide in F344/N rats and
B6C3F1 mice. Toxicol Sci. 74:287–296. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wörle-Knirsch JM, Kern K, Schleh C,
Adelhelm C, Feldmann C and Krug HF: Nanoparticulate vanadium oxide
potentiated vanadium toxicity in human lung cells. Environ Sci
Technol. 41:331–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scibior A, Zaporowska H and Ostrowski J:
Selected haematological and biochemical parameters of blood in rats
after subchronic administration of vanadium and/or magnesium in
drinking water. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 51:287–295. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
González-Villalva A, Fortoul T,
Avila-Costa MR, Piñón-Zarate G, Rodriguez-Laraa V, Martínez-Levy G,
Rojas-Lemus M, Bizarro-Nevarez P, Díaz-Bech P, Mussali-Galante P
and Colin-Barenque L: Thrombocytosis induced in mice after subacute
and subchronic V2O5 inhalation. Toxicol Ind
Health. 22:113–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soazo M and Garcia GB: Vanadium exposure
through lactation produces behavioral alterations and CNS myelin
deficit in neonatal rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 29:503–510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kobayashi K, Himeno S, Satoh M, Kuroda J,
Shibata N, Seko Y and Hasegawa T: Pentavalent vanadium induces
hepatic metallothionein through interleukin-6-dependent and
-independent mechanisms. Toxicology. 228:162–170. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barceloux DG: Vanadium. J Toxicol Clin
Toxicol. 37:265–278. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Antonelli A, Ferri C, Fallahi P, Ferrari
SM, Frascerra S, Sebastiani M, Franzoni F, Galetta F and Ferrannini
E: High values of CXCL10 serum levels in patients with hepatitis C
associated mixed cryoglobulinemia in presence or absence of
autoimmune thyroiditis. Cytokine. 42:137–143. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Valyasevi RW, Harteneck DA, Dutton CM and
Bahn RS: Stimulation of adipogenesis, peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma), and thyrotropin
receptor by PPARgamma agonist in human orbital preadipocyte
fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:2352–2358. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Antonelli A, Rotondi M, Fallahi P,
Romagnani P, Ferrari SM, Buonamano A, Ferrannini E and Serio M:
High levels of circulating CXC chemokine ligand 10 are associated
with chronic autoimmune thyroiditis and hypothyroidism. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:5496–5499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kemp EH, Metcalfe RA, Smith KA, Woodroofe
MN, Watson PF and Weetman AP: Detection and localization of
chemokine gene expression in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin
Endocrinol (Oxf). 59:207–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Fallahi P,
Frascerra S, Santini E, Franceschini SS and Ferrannini E: Monokine
induced by interferon gamma (IFNgamma) (CXCL9) and IFNgamma
inducible T-cell alpha-chemoattractant (CXCL11) involvement in
Graves' disease and ophthalmopathy: Modulation by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 94:1803–1809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Frascerra S,
Pupilli C, Mancusi C, Metelli MR, Orlando C, Ferrannini E and
Fallahi P: CXCL9 and CXCL11 chemokines modulation by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha agonists secretion in Graves'
and normal thyrocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:E413–E420. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Garcià-Lòpez MA, Sancho D, Sànchez-Madrid
F and Marazuela M: Thyrocytes from autoimmune thyroid disorders
produce the chemokines IP-10 and Mig and attract CXCR3v
lymphocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:5008–5016. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Corrado A,
Ferrannini E and Fallahi P: CXCR3, CXCL10 and type 1 diabetes.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 25:57–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Antonelli A, Ferrari SM, Giuggioli D,
Ferrannini E, Ferri C and Fallahi P: Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand
(CXCL)10 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 13:272–280. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Antonelli A, Fallahi P, Delle Sedie A,
Ferrari SM, Maccheroni M, Bombardieri S, Riente L and Ferrannini E:
High values of Th1 (CXCL10) and Th2 (CCL2) chemokines in patients
with psoriatic arthtritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 27:22–27.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fallahi P, Ferrari SM, Ruffilli I, Elia G,
Biricotti M, Vita R, Benvenga S and Antonelli A: The association of
other autoimmune diseases in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis:
Review of the literature and report of a large series of patients.
Autoimmun Rev. 15:1125–1128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Antao-Menezes A, Turpin EA, Bost PC,
Ryman-Rasmussen JP and Bonner JC: STAT-1 signaling in human lung
fibroblasts is induced by vanadium pentoxide through an IFN-beta
autocrine loop. J Immunol. 180:4200–4207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sabbioni E, Kuèera J, Pietra R and
Vesterberg O: A critical review on normal concentrations of
vanadium in human blood, serum, and urine. Sci Total Environ.
188:49–58. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Diem E, Schaffer A
and Rüdiger HW: Vanadate induces DNA strand breaks in cultured
human fibroblasts at doses relevant to occupational exposure. Mutat
Res. 519:25–35. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|