|
1
|
Pawlowski JW, Martin BR, McCabe GP, McCabe
L, Jackson GS, Peacock M, Barnes S and Weaver CM: Impact of
equol-producing capacity and soy-isoflavone profiles of supplements
on bone calcium retention in postmenopausal women: A randomized
crossover trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 102:695–703. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pfeifer M, Kohlwey L, Begerow B and Minne
HW: Effects of two newly developed spinal orthoses on trunk muscle
strength, posture, and quality-of-life in women with postmenopausal
osteoporosis: A randomized trial. Am J Phys Med Rehabil.
90:805–815. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
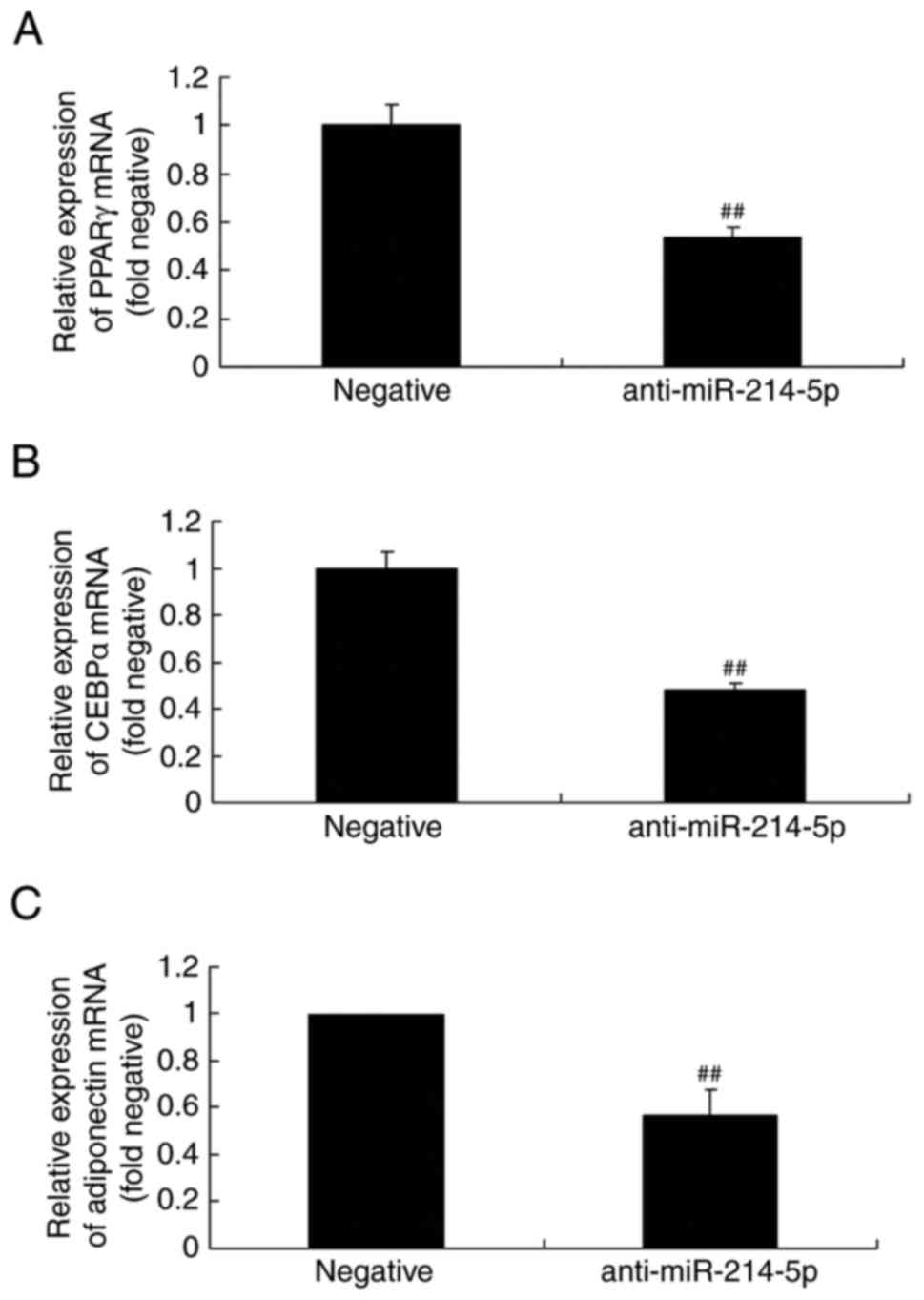
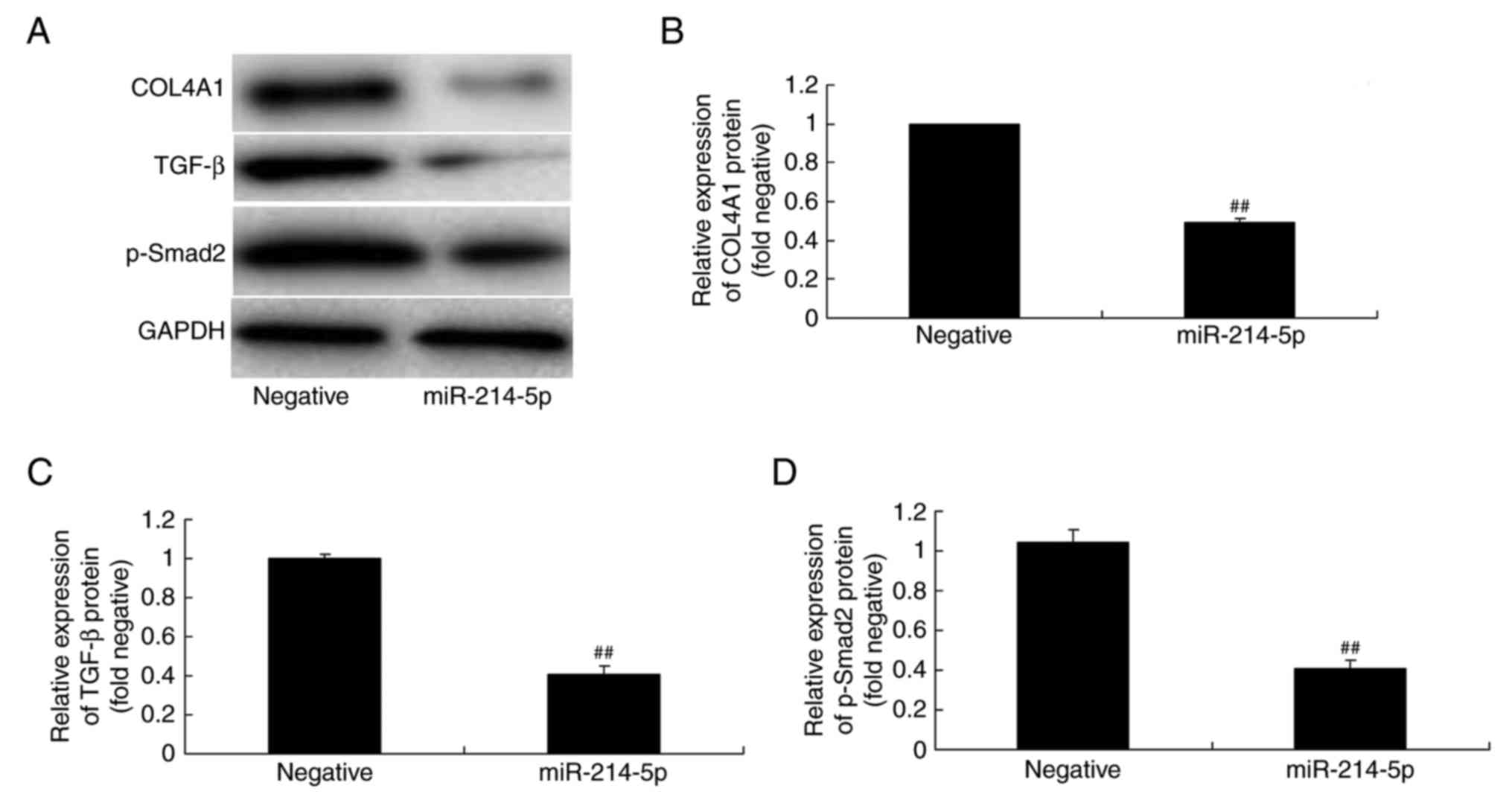
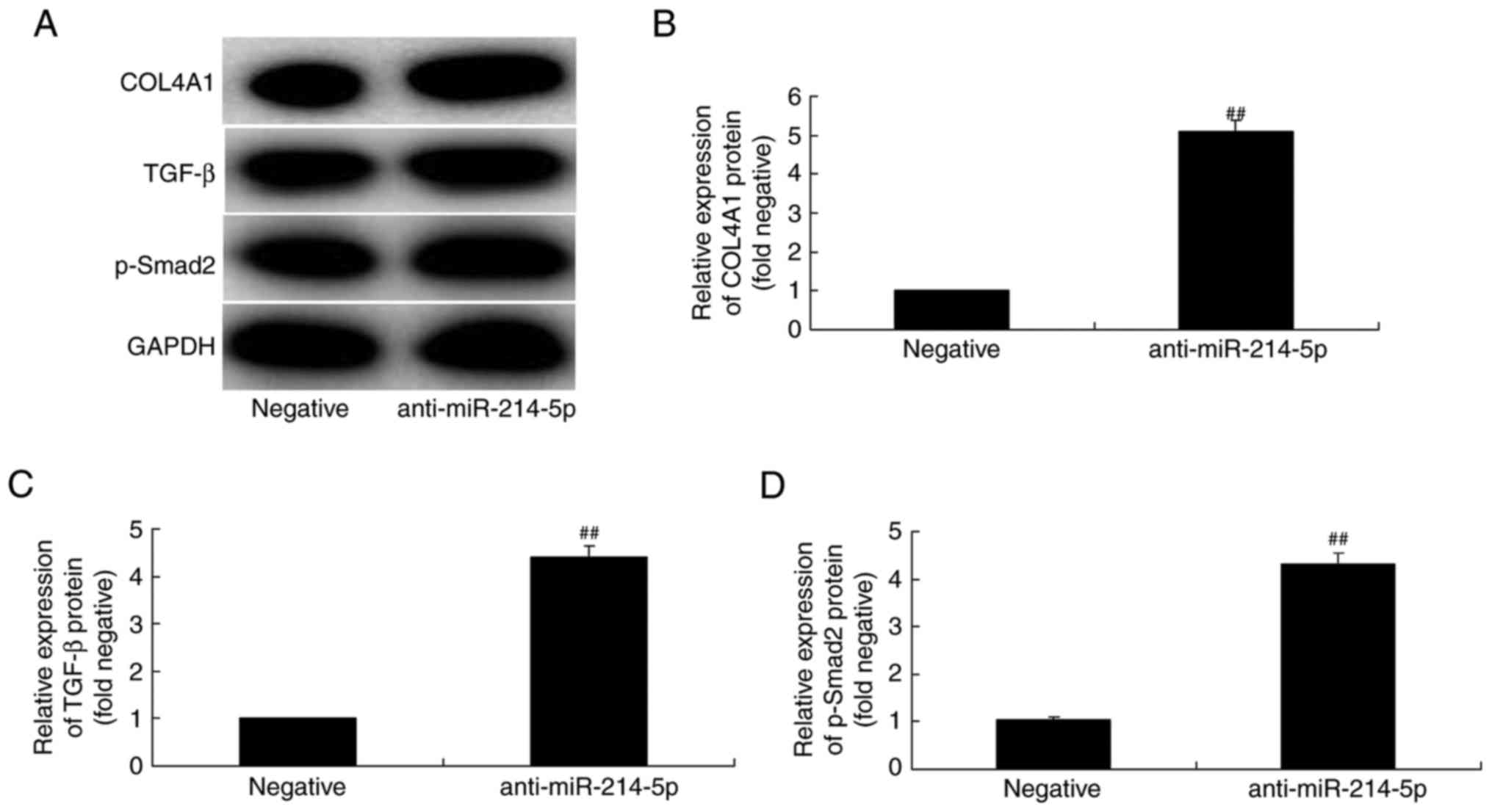
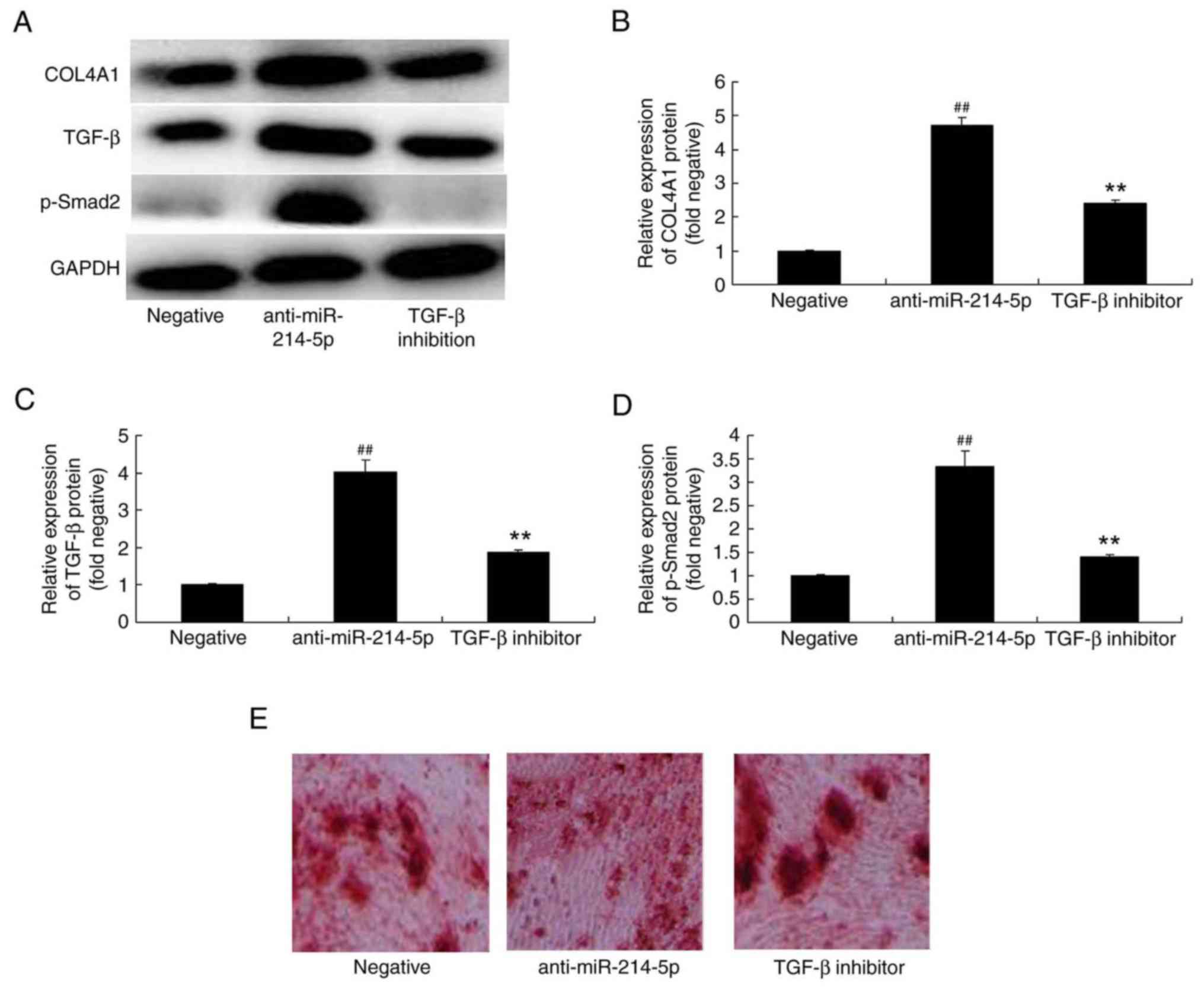
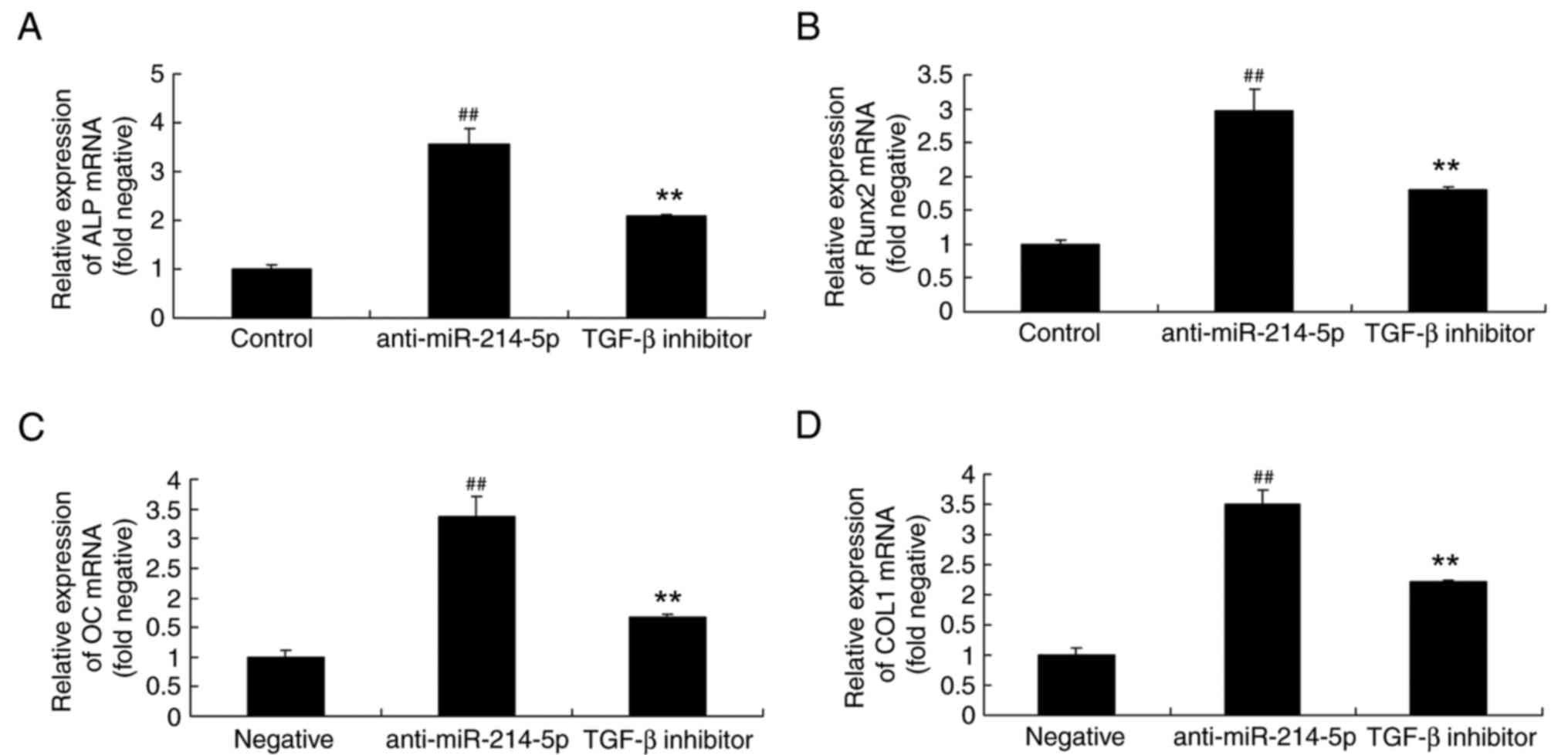
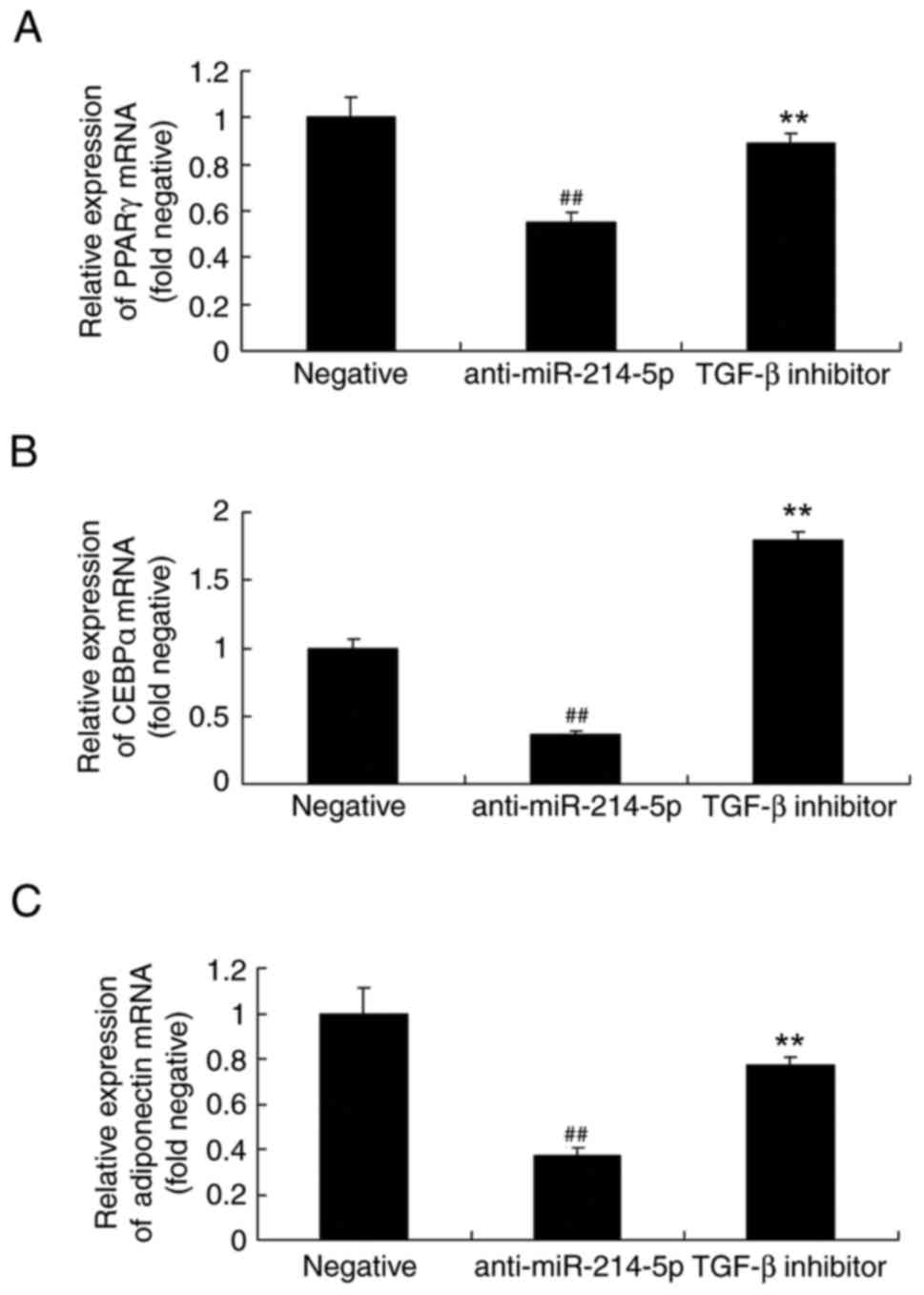
Kessous R, Weintraub AY, Mattan Y,
Dresner-Pollak R, Brezis M, Liebergall M and Kandel L: Improving
compliance to osteoporosis workup and treatment in postmenopausal
patients after a distal radius fracture. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol.
53:206–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Itabashi A, Yoh K, Chines AA, Miki T,
Takada M, Sato H, Gorai I, Sugimoto T, Mizunuma H, Ochi H, et al:
Bridging analysis of the efficacy and safety of bazedoxifene in
Japanese and global populations of postmenopausal women with
osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 33:61–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Filip R, Possemiers S, Heyerick A,
Pinheiro I, Raszewski G, Davicco MJ and Coxam V: Twelve-month
consumption of a polyphenol extract from olive (Olea europaea) in a
double blind, randomized trial increases serum total osteocalcin
levels and improves serum lipid profiles in postmenopausal women
with osteopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 19:77–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gu JM, Wang L, Lin H, Chen DC, Tang H, Jin
XL, Xia WB, Hu YQ, Fu WZ, He JW, et al: The efficacy and safety of
weekly 35-mg risedronate dosing regimen for Chinese postmenopausal
women with osteoporosis or osteopenia: 1-year data. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 36:841–846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang C, Zhang GF, Han J, Liao GJ and Zou
BG: Mechanism of age-related changes of bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells in senile osteoporosis. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
30:565–569. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li F, Zhou C, Xu L, Tao S, Zhao J and Gu
Q: Effect of stem cell therapy on bone mineral density: A
meta-analysis of preclinical studies in animal models of
osteoporosis. PLoS One. 11:e01494002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zavrski I, Naujokat C, Niemöller K, Jakob
C, Heider U, Langelotz C, Fleissner C, Eucker J, Possinger K and
Sezer O: Proteasome inhibitors induce growth inhibition and
apoptosis in myeloma cell lines and in human bone marrow myeloma
cells irrespective of chromosome 13 deletion. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 129:383–391. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heilmeier U, Hackl M, Skalicky S, Weilner
S, Schroeder F, Vierlinger K, Patsch JM, Baum T, Oberbauer E,
Lobach I, et al: Serum microRNAs are indicative of skeletal
fractures in postmenopausal women with and without type 2 diabetes
and influence osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of
adipose-tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J
Bone Miner Res. 31:2173–2192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Wang Y, Yang N, Wu S, Lv Y and Xu
L: In silico analysis of the molecular mechanism of
postmenopausal osteoporosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:6584–6590. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao Z, Moore BT, Wang Y, Peng XH, Lappe
JM, Recker RR and Xiao P: MiR-422a as a potential cellular microRNA
biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis. PLoS One. 9:e970982014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu XD, Cai F, Liu L, Zhang Y and Yang AL:
MicroRNA-210 is involved in the regulation of postmenopausal
osteoporosis through promotion of VEGF expression and osteoblast
differentiation. Biol Chem. 396:339–347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng Q, Tang W, Sheu TJ, Du Y, Gan J, Li
H, Hong W, Zhu X, Xue S and Zhang X: Circulating TGF-β1 levels are
negatively correlated with sclerostin levels in early
postmenopausal women. Clin Chim Acta. 455:87–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun J, Zhang C, Xu L, Yang M and Yang H:
The transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) gene polymorphisms
(TGF-β1 T869C and TGF-β1 T29C) and susceptibility to postmenopausal
osteoporosis: a meta-analysis. Medicine. 94:e4612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Utennam D, Tungtrongchitr A, Phonrat B,
Tungtrongchitr R and Preutthipan S: Association of T869C gene
polymorphism of transforming growth factor-β1 with low protein
levels and anthropometric indices in osteopenia/osteoporosis
postmenopausal Thai women. Genet Mol Res. 11:87–99. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun X, Cao Z, Zhang Q, Li M, Han L and Li
Y: Aluminum trichloride inhibits osteoblast mineralization via
TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 244:9–15. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li B: Bone morphogenetic protein-Smad
pathway as drug targets for osteoporosis and cancer therapy. Endocr
Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 8:208–219. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Donoso O, Pino AM, Seitz G, Osses N and
Rodriguez JP: Osteoporosis-associated alteration in the signalling
status of BMP-2 in human MSCs under adipogenic conditions. J Cell
Biochem. 116:1267–1277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsumoto T, Miyakoshi K, Fukutake M,
Ochiai D, Minegishi K and Tanaka M: Intracranial sonographic
features demonstrating in utero development of hemorrhagic brain
damage leading to schizencephaly-associated COL4A1 mutation.
J Med Ultrason. 42:445–446. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li QS, Meng FY, Zhao YH, Jin CL, Tian J
and Yi XJ: Inhibition of microRNA-214-5p promotes cell survival and
extracellular matrix formation by targeting collagen type IV alpha
1 in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Bone Joint Res. 6:464–471. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tomotaki S, Mizumoto H, Hamabata T,
Kumakura A, Shiota M, Arai H, Haginoya K and Hata D: Severe
hemolytic jaundice in a neonate with a novel COL4A1
mutation. Pediatr Neonatol. 57:522–525. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Plaisier E and Ronco P: COL4A1-Related
Disorders. In: GeneReviews®Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon
RA, Wallace SE, Bean LJH, Stephens K and Amemiya A: University of
Washington, Seattle University of Washington, Seattle. GeneReviews
is a registered trademark of the University of Washington; Seattle.
All rights reserved, Seattle (WA): 1993
|
|
24
|
Wen Y, Guo X, Hao J, Xiao X, Wang W, Wu C,
Wang S, Yang T, Shen H, Chen X, et al: Integrative analysis of
genome-wide association studies and gene expression profiles
identified candidate genes for osteoporosis in Kashin-Beck disease
patients. Osteoporos Int. 27:1041–1046. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bi D, Wang H, Shang Q, Xu Y, Wang F, Chen
M, Ma C, Sun Y, Zhao X, Gao C, et al: Association of COL4A1 gene
polymorphisms with cerebral palsy in a Chinese Han population. Clin
Genet. 90:149–155. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hopwood B, Tsykin A, Findlay DM and
Fazzalari NL: Microarray gene expression profiling of
osteoarthritic bone suggests altered bone remodelling, WNT and
transforming growth factor-beta/bone morphogenic protein
signalling. Arthritis Res Ther. 9:R1002007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martin PJ, Haren N, Ghali O, Clabaut A,
Chauveau C, Hardouin P and Broux O: Adipogenic RNAs are transferred
in osteoblasts via bone marrow adipocytes-derived extracellular
vesicles (EVs). BMC Cell Biol. 16:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hooshmand S, Brisco JR and Arjmandi BH:
The effect of dried plum on serum levels of receptor activator of
NF-κB ligand, osteoprotegerin and sclerostin in osteopenic
postmenopausal women: A randomised controlled trial. Br J Nutr.
112:55–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Catalano A, Morabito N, Basile G,
Brancatelli S, Cucinotta D and Lasco A: Zoledronic acid acutely
increases sclerostin serum levels in women with postmenopausal
osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:1911–1915. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saad MN, Mabrouk MS, Eldeib AM and Shaker
OG: Effect of MTHFR, TGFβ1, and TNFB polymorphisms on osteoporosis
in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Gene. 568:124–128. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Komatsu Y, Ibi M, Chosa N, Kyakumoto S,
Kamo M, Shibata T, Sugiyama Y and Ishisaki A: Zoledronic acid
suppresses transforming growth factor-β-induced fibrogenesis by
human gingival fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. 38:139–147. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iizuka M, Ogawa T, Enomoto M, Motoyama H,
Yoshizato K, Ikeda K and Kawada N: Induction of microRNA-214-5p in
human and rodent liver fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair.
5:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Li A, Strait K, Zhang H, Nanes MS
and Weitzmann MN: Endogenous TNFalpha lowers maximum peak bone mass
and inhibits osteoblastic Smad activation through NF-kappaB. J Bone
Miner Res. 22:646–655. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gale DP, Oygar DD, Lin F, Oygar PD, Khan
N, Connor TM, Lapsley M, Maxwell PH and Neild GH: A novel COL4A1
frameshift mutation in familial kidney disease: The importance of
the C-terminal NC1 domain of type IV collagen. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 31:1908–1914. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saeed H and Iqtedar M: Aberrant gene
expression profiles, during in vitro osteoblast
differentiation, of telomerase deficient mouse bone marrow stromal
stem cells (mBMSCs). J Biomed Sci. 22:112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|