|
1
|
Odén A, McCloskey EV, Kanis JA, Harvey NC
and Johansson H: Burden of high fracture probability worldwide:
Secular increases 2010–2040. Osteoporos Int. 26:2243–2248. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zambelli PY, Tercier S, Newman CJ and
Bregou A: Targeted approach to osteoporosis for children and
teenagers. Rev Med Suisse. 10:116–118. 2014.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tyagi AM, Srivastava K, Mansoori MN,
Trivedi R, Chattopadhyay N and Singh D: Estrogen deficiency induces
the differentiation of IL-17 secreting Th17 cells: A new candidate
in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. PLoS One. 7:e445522012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurt-Sirin O, Yilmaz-Aydogan H, Uyar M,
Seyhan MF, Isbir T and Can A: Combined effects of collagen type I
alpha1 (COL1A1) Sp1 polymorphism and osteoporosis risk factors on
bone mineral density in Turkish postmenopausal women. Gene.
540:226–231. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheung A, Papaioannou A and Morin S:
Osteoporosis Canada Scientific Advisory Council: Postmenopausal
osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 374:20962016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen H, Liu N, Xu X, Qu X and Lu E:
Smoking, radiotherapy, diabetes and osteoporosis as risk factors
for dental implant failure: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
8:e719552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyamoto T: Mechanism underlying
post-menopausal osteoporosis: HIF1α is required for osteoclast
activation by estrogen deficiency. Keio J Med. 64:44–47. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ahn HJ, Kim HJ, Kim YS, Kim MS, Huh KH,
Kim JH, Lee JH, Jeon KO and Kim SI: Risk factors for changes in
bone mineral density and the effect of antiosteoporosis management
after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc. 38:pp. 2074–2076.
2006; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Díez-Pérez A, Adachi JD, Adami S, Anderson
FA Jr, Boonen S, Chapurlat R, Compston JE, Cooper C, Gehlbach SH,
Greenspan SL, et al: Risk factors for treatment failure with
antiosteoporosis medication: The global longitudinal study of
osteoporosis in women (GLOW). J Bone Miner Res. 29:260–267. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee MK, Choi YJ, Sung SH, Shin DI, Kim JW
and Kim YC: Antihepatotoxic activity of icariin, a major
constituent of Epimedium koreanum. Planta Med. 61:523–526. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen KM, Ge BF, Ma HP, Liu XY, Bai MH and
Wang Y: Icariin, a flavonoid from the herb Epimedium enhances the
osteogenic differentiation of rat primary bone marrow stromal
cells. Pharmazie. 60:939–942. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng FH, Li YB, Xiong ZL, Jiang ZM and Li
FM: Osteoblastic proliferative activity of Epimedium brevicornum
Maxim. Phytomedicine. 12:189–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xue L, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Han T, Nie Y, Zhao
L, Zhang Q and Qin L: Comparative effects of er-xian decoction,
epimedium herbs, and icariin with estrogen on bone and reproductive
tissue in ovariectomized rats. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med.
2012:2414162012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Lu D, Guo J, Meng X, Zhang G and
Wang F: Icariin from Epimedium brevicornum Maxim promotes the
biosynthesis of estrogen by aromatase (CYP19). J Ethnopharmacol.
145:715–721. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen G, Wang C, Wang J, Yin S, Gao H,
Xiang LU, Liu H, Xiong Y, Wang P, Zhu X, et al: Antiosteoporotic
effect of icariin in ovariectomized rats is mediated via the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Exp Ther Med. 12:279–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, Xiong Y, Zhu X, Gao H, Yin S, Wang
J, Chen G, Wang C, Xiang L, Wang P, et al: Icariin improves
osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4 mRNA,
N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in
ovariectomized rats. Exp Ther Med. 13:1360–1368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li XF, Xu H, Zhao YJ, Tang DZ, Xu GH, Holz
J, Wang J, Cheng SD, Shi Q and Wang YJ: Icariin augments bone
formation and reverses the phenotypes of osteoprotegerin-deficient
mice through the activation of Wnt/β-catenin-BMP signaling. Evid
Based Complementary Altern Med. 2013:6523172013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xue L, Jiang Y, Han T, Zhang N, Qin L, Xin
H and Zhang Q: Comparative proteomic and metabolomic analysis
reveal the antiosteoporotic molecular mechanism of icariin from
Epimedium brevicornu maxim. J Ethnopharmacol. 192:370–381. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bakker A and Klein-Nulend J: Osteoblast
isolation from murine calvariae and long bones. Methods Mol Med.
80:19–28. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Chang H, Jin TY, Jin WF, Gu SZ and Zhou
YF: Modulation of isoflavones on bone-nodule formation in rat
calvaria osteoblasts in vitro. Biomed Environ Sci. 16:83–89.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Honda H, Tamai N, Naka N, Yoshikawa H and
Myoui A: Bone tissue engineering with bone marrow-derived stromal
cells integrated with concentrated growth factor in Rattus
norvegicus calvaria defect model. J Artif Organs. 16:305–315. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coutu DL, Wu JH, Monette A, Rivard GE,
Blostein MD and Galipeau J: Periostin, a member of a novel family
of vitamin K-dependent proteins, is expressed by mesenchymal
stromal cells. J Biol Chem. 283:17991–18001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao Y, Ju F, Zhao Y, Wang L, Sun Z, Liu M
and Gao L: The expression of αA- and βB1-crystallin during normal
development and regeneration, and proteomic analysis for the
regenerating lens in Xenopus laevi. Mol Vis. 17:768–778.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xing X, Lai M, Gartner W, Xu E, Huang Q,
Li H and Chen G: Identification of differentially expressed
proteins in colorectal cancer by proteomics: Down-regulation of
secretagogin. Proteomics. 6:2916–2923. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma X, Liu G, Wang S, Chen Z, Lai M, Liu Z
and Yang J: Evaluation of sphingolipids changes in brain tissues of
rats with pentylenetetrazol-induced kindled seizures using
MALDI-TOF-MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
859:170–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Powell TJ, Strutt T, Reome J, Hollenbaugh
JA, Roberts AD, Woodland DL, Swain SL and Dutton RW: Priming with
cold-adapted influenza A does not prevent infection but elicits
long-lived protection against supralethal challenge with
heterosubtypic virus. J Immunol. 178:1030–1038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
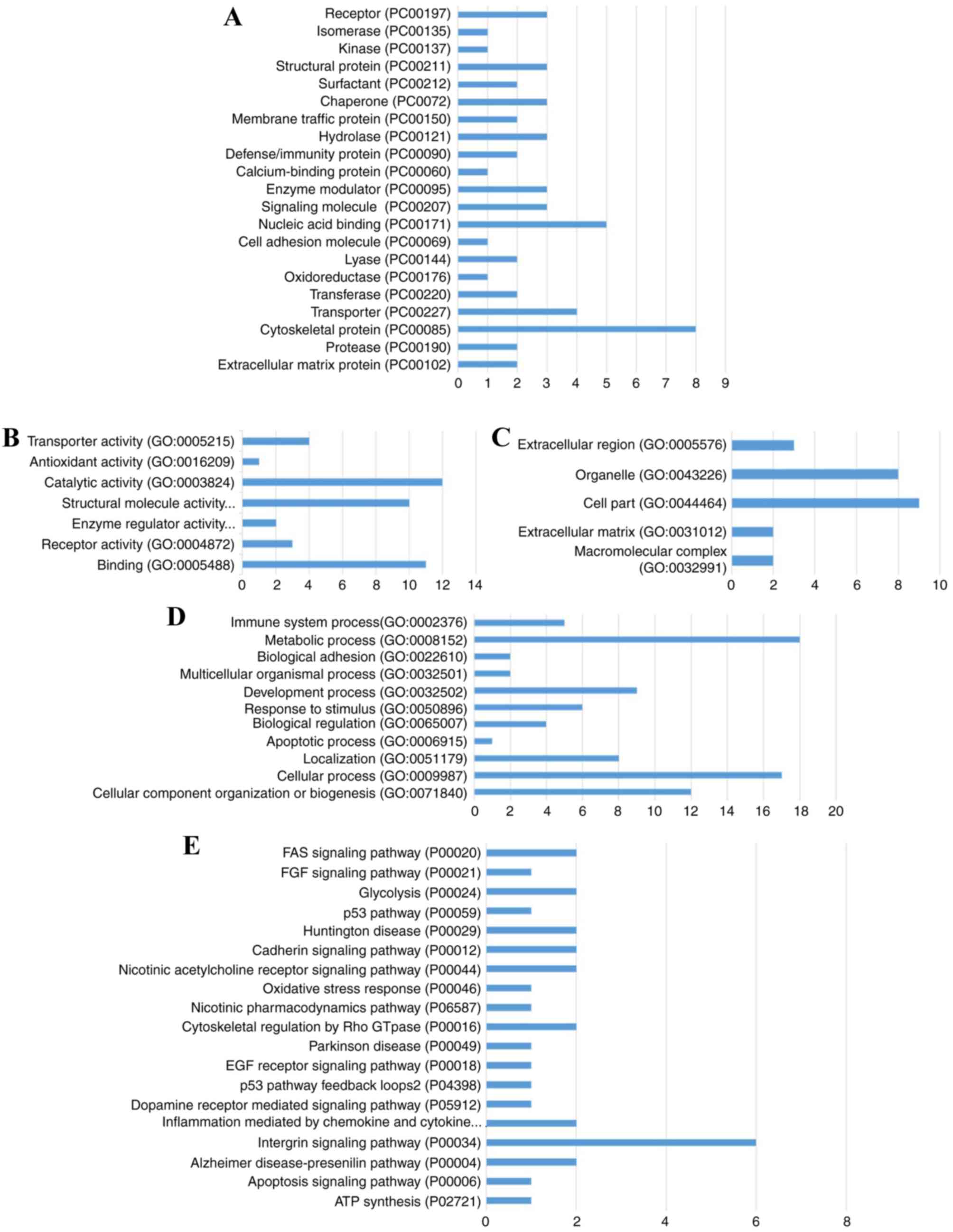
Mi H, Muruganujan A, Casagrande JT and
Thomas PD: Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER
classification system. Nat Protoc. 8:1551–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mi H and Thomas P: PANTHER pathway: An
ontology-based pathway database coupled with data analysis tools.
Methods Mol Biol. 563:123–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bogan R, Riddle RC, Li Z, Kumar S, Nandal
A, Faugere MC, Boskey A, Crawford SE and Clemens TL: A mouse model
for human osteogenesis imperfecta type VI. J Bone Miner Res.
28:1531–1536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gattu AK, Swenson ES, Iwakiri Y, Samuel
VT, Troiano N, Berry R, Church CD, Rodeheffer MS, Carpenter TO and
Chung CH: Determination of mesenchymal stem cell fate by pigment
epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) results in increased adiposity and
reduced bone mineral content. FASEB J. 27:4384–4394. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Doroudi M: Essential roles of Pdia3/PLAA
receptor complex and CaMKII IN 1α,25(OH)2D3
and Wnt5a calcium-dependent signaling pathways in osteoblasts and
chondrocytes. 2014.
|
|
33
|
Frank SR, Schroeder M, Fernandez P,
Taubert S and Amati B: Binding of c-Myc to chromatin mediates
mitogen-induced acetylation of histone H4 and gene activation.
Genes Dev. 15:2069–2082. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaibuchi K, Tsuda T, Kikuchi A, Tanimoto
T, Yamashita T and Takai Y: Possible involvement of protein kinase
C and calcium ion in growth factor-induced expression of c-myc
oncogene in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 261:1187–1192.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vadde R, Radhakrishnan S, Kurundu HEK,
Reddivari L and Vanamala JK: Indian gooseberry (Emblica officinalis
Gaertn.) suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human colon cancer stem cells independent of p53 status via
suppression of c-Myc and cyclin D1. J Funct Foods. 25:267–278.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang W, Shen X, Wan C, Zhao Q, Zhang L,
Zhou Q and Deng L: Effects of insulin and insulin-like growth
factor 1 on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation:
differential signalling via Akt and ERK. Cell Biochem Funct.
30:297–302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen BJ, Wu YL, Tanaka Y and Zhang W:
Small molecules targeting c-Myc oncogene: promising anti-cancer
therapeutics. Int J Biol Sci. 10:1084–1096. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zirath H, Frenzel A, Oliynyk G, Segerström
L, Westermark UK, Larsson K, Munksgaard Persson M, Hultenby K,
Lehtiö J, Einvik C, et al: MYC inhibition induces metabolic changes
leading to accumulation of lipid droplets in tumor cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. 10258–10263. 2013; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Banerjee D, Upadhyay RC, Chaudhary UB,
Kumar R, Singh S, Ashutosh G JM, Polley S, Mukherjee A, Das TK and
De S: Seasonal variation in expression pattern of genes under
HSP70: Seasonal variation in expression pattern of genes underHSP70
family in heat- and cold-adapted goats (Capra hircus). Cell Stress
Chaperones. 19:401–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qian W, Yin H and Sun H: Influence of
different concentrations of Icariin on osteoblast metabolism of
rats. China Med Herald. 8:23–25. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
41
|
Song L, Zhao J, Zhang X, Li H and Zhou Y:
Icariin induces osteoblast proliferation, differentiation and
mineralization through estrogen receptor-mediated ERK and JNK
signal activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 714:15–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cao H, Ke Y, Zhang Y, Zhang CJ, Qian W and
Zhang GL: Icariin stimulates MC3T3-E1 cell proliferation and
differentiation through up-regulation of bone morphogenetic
protein-2. Int J Mol Med. 29:435–439. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang DW, Cheng Y, Wang NL, Zhang JC, Yang
MS and Yao XS: Effects of total flavonoids and flavonol glycosides
from Epimedium koreanum Nakai on the proliferation and
differentiation of primary osteoblasts. Phytomedicine. 15:55–61.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Duan P, Hu C, Butler HJ, Quan C, Chen W,
Huang W, Tang S, Zhou W, Yuan M, Shi Y, et al: 4-Nonylphenol
induces disruption of spermatogenesis associated with oxidative
stress-related apoptosis by targeting p53-Bcl-2/Bax-Fas/FasL
signaling. Environ Toxicol. 32:739–753. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han Y, Jiang Q, Wang Y, Li W, Geng M, Han
Z and Chen X: The anti-proliferative effects of oleanolic acid on
A7r5 cells-Role of UCP2 and downstream FGF-2/p53/TSP-1. Cell Biol
Int. 41:1296–1306. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang SX, Wang JJ, Gao G, Shao C, Mott R
and Ma JX: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is an
endogenous antiinflammatory factor. FASEB J. 20:323–325. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Jarvis CL, Nelius T, Martinez-Marin D,
Cheerla S and Filleur S: Low-dose cabazitaxel inhibits the growth
of prostate cancer cells and enhances the anti-tumor properties of
PEDF with greater efficacy than docetaxel. Cancer Res. 76:2882016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Nelius T, Hirsch J and Filleur S: PEDF
inhibits bone metastases formation, prolongs survival and enhances
the antitumor efficacy of low-dose chemotherapy in
castration-refractory prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 73:50972013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ho TC, Chen SL, Yang YC, Liao CL, Cheng HC
and Tsao YP: PEDF induces p53-mediated apoptosis through PPAR gamma
signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cardiovasc
Res. 76:213–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sun H, Kim JK, Mortensen R, Mutyaba LP,
Hankenson KD and Krebsvach PH: Osteoblast-targeted suppression of
PPARγ increases osteogenesis through activation of mTOR signaling.
Stem Cells. 31:2183–2192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brusotti G, Montanari R, Capelli D,
Cattaneo G, Laghezza A, Tortorella P, Loiodice F, Peiretti F,
Bonardo B, Paiardini A, et al: Betulinic acid is a PPARγ antagonist
that improves glucose uptake, promotes osteogenesis and inhibits
adipogenesis. Scienti Rep. 7:57772017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ling Zheng L, Wang FY, Cong XX, Shen Y,
Rao XS, Huang DS, Fan W, Yi P, Wang XB, Zheng L, et al: Interaction
of heat shock protein Cpn10 with the Cyclin E/Cdk2 substrate
nuclear protein ataxia-telangiectasia (NPAT) is involved in
regulating histone transcription. J Biol Chem. 290:29290–29300.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao J: Coordination of DNA synthesis and
histone gene expression during normal cell cycle progression and
after DNA damage. Cell Cycle. 3:693–695. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lin CY, Lovén J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM,
Burge CB, Bradner JE, Lee TI and Young RA: Transcriptional
amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell. 151:56–67.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Miller DM, Thomas SD, Islam A, Muench D
and Sedoris K: c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin Cancer Res.
18:5546–5553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Indo Y, Takeshita S, Ishii KA, Hoshii T,
Aburatani H, Hirao A and Ikeda K: Metabolic regulation of
osteoclast differentiation and function. J Bone Miner Res.
28:2392–2399. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen J, Olivares-Navarrete R, Wang Y,
Herman TR, Boyan BD and Schwartz Z: Protein-disulfide
isomerase-associated 3 (Pdia3) mediates the membrane response to
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem.
285:37041–37050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen E, Xue D, Zhang W, Lin F and Pan Z:
Extracellular heat shock protein 70 promotes osteogenesis of human
mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the ERK signaling
pathway. FEBS Lett. 589:4088–4096. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kingston RE, Baldwin AS Jr and Sharp PA:
Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc.
Nature. 312:280–282. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taira T, Sawai M, Ikeda M, Tamai K,
Iguchi-Ariga SM and Ariga H: Cell cycle-dependent switch of up-and
down-regulation of human hsp70 gene expression by interaction
between c-Myc and CBF/NF-Y. J Biol Chem. 274:24270–24279. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|