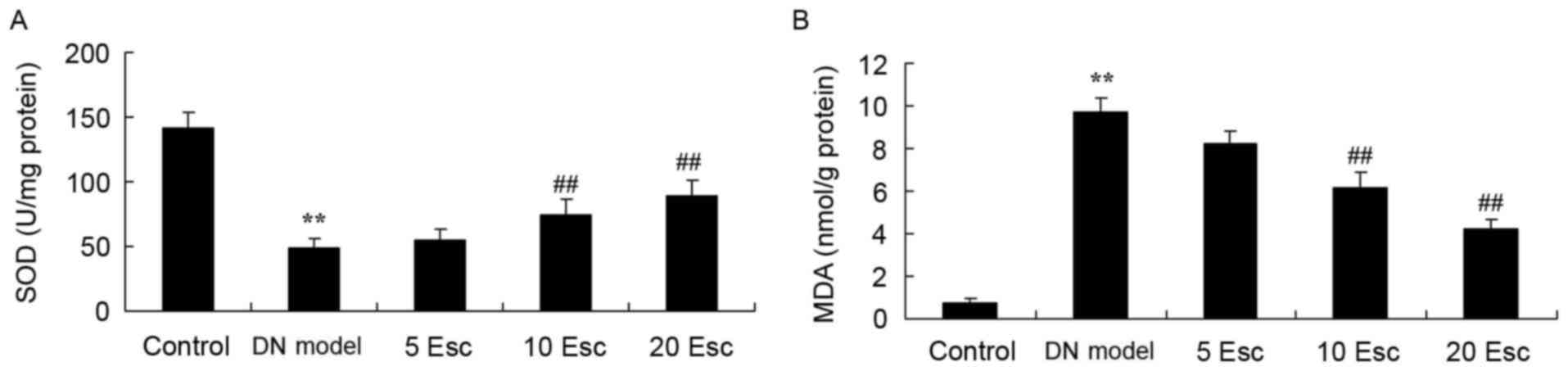
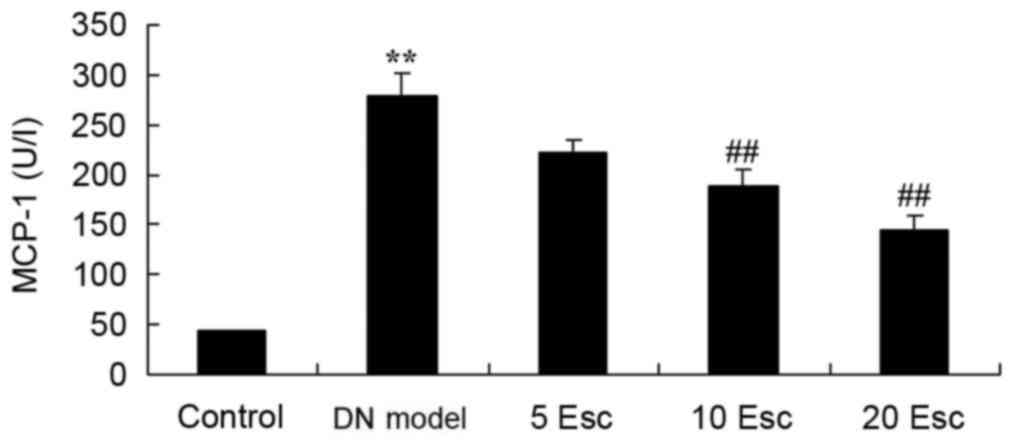
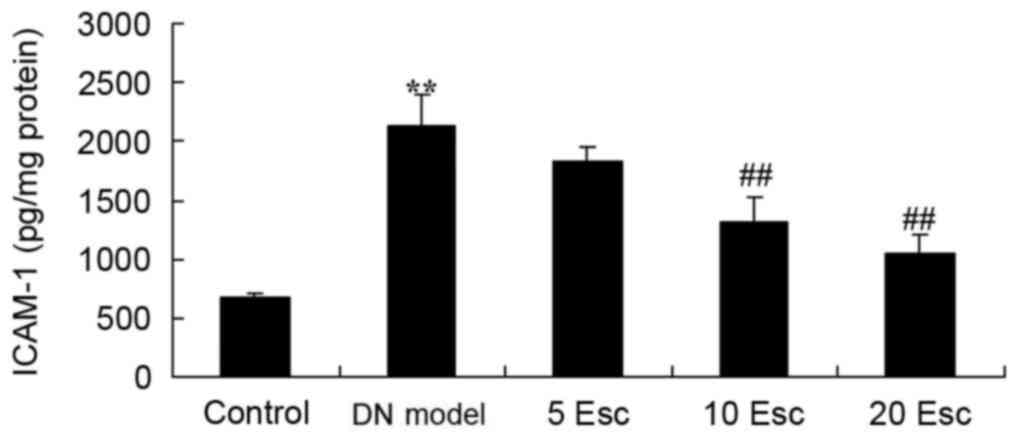
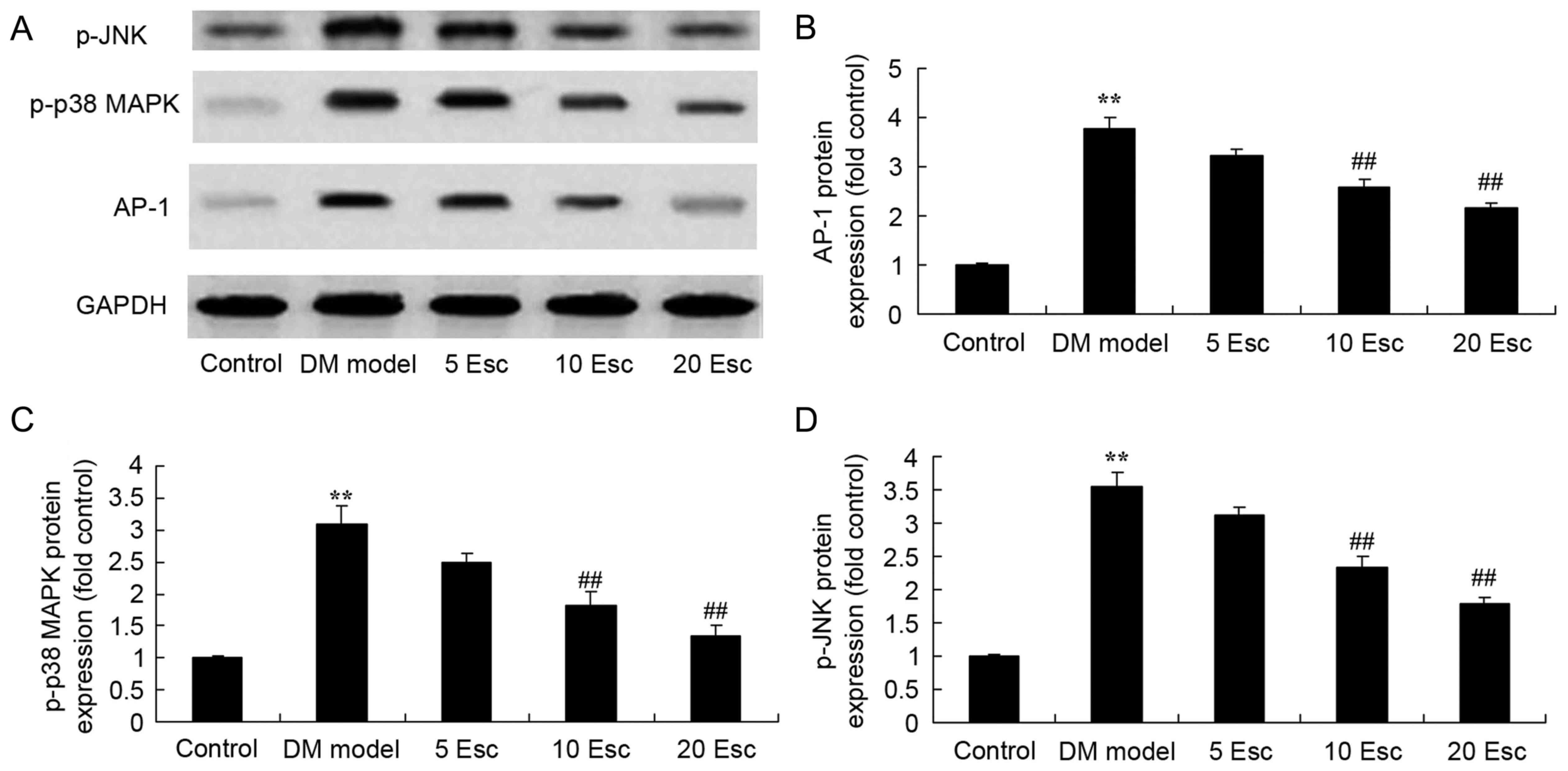
|
1
|
Zilişteanu DS, Atasie T and Voiculescu M:
Efficacy of long-term low-dose sulodexide in diabetic and
non-diabetic nephropathies. Rom J Intern Med. 53:161–169.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Imamura S, Hirai K and Hirai A: The
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, liraglutide, attenuates
the progression of overt diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic
patients. Tohoku J Exp Med. 231:57–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schutte E, Lambers Heerspink HJ, Lutgers
HL, Bakker SJ, Vart P, Wolffenbuttel BH, Umanath K, Lewis JB, de
Zeeuw D and Gansevoort RT: Serum bicarbonate and kidney disease
progression and cardiovascular outcome in patients with diabetic
nephropathy: A Post Hoc analysis of the RENAAL (Reduction of end
points in non-insulin-dependent diabetes with the angiotensin II
antagonist losartan) study and IDNT (Irbesartan diabetic
nephropathy trial). Am J Kidney Dis. 66:450–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryan CM, Williams TM, Finegold DN and
Orchard TJ: Cognitive dysfunction in adults with type 1
(insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus of long duration: Effects of
recurrent hypoglycaemia and other chronic complications.
Diabetologia. 36:329–334. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gorska-Ciebiada M, Saryusz-Wolska M,
Borkowska A, Ciebiada M and Loba J: C-reactive protein, advanced
glycation end products, and their receptor in type 2 diabetic,
elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment. Front Aging
Neurosci. 7:2092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ba-Tin L, Strike P and Tabet N: Diabetic
peripheral microvascular complications: Relationship to cognitive
function. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2011:7234342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frier BM: Cognitive functioning in type 1
diabetes: The diabetes control and complications trial (DCCT)
revisited. Diabetologia. 54:233–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Price TO, Farr SA, Niehoff ML, Ercal N,
Morley JE and Shah GN: Protective effect of topiramate on
hyperglycemia-induced cerebral oxidative stress, pericyte loss and
learning behavior in diabetic mice. Int Libr Diabetes Metab.
1:6–12. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang X, Song X, Takata T, Miichi Y, Yokono
K and Sakurai T: Amyloid-beta neurotoxicity restricts glucose
window for neuronal survival in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Exp
Gerontol. 45:904–908. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang ZJ, Zou W, Yuan J, Zhang P, Tian Y,
Xiao ZF, Li MH, Wei HJ and Tang XQ: Antidepressant-like and
anxiolytic-like effects of hydrogen sulfide in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats through inhibition of
hippocampal oxidative stress. Behav Pharmacol. 26:427–435. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou X, Zhang F, Hu X, Chen J, Wen X, Sun
Y, Liu Y, Tang R, Zheng K and Song Y: Inhibition of inflammation by
astaxanthin alleviates cognition deficits in diabetic mice. Physiol
Behav. 151:412–420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wong TY and McIntosh R: Systemic
associations of retinal microvascular signs: A review of recent
population-based studies. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 25:195–204. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohashi N, Urushihara M, Satou R and Kobori
H: Glomerular angiotensinogen is induced in mesangial cells in
diabetic rats via reactive oxygen species-ERK/JNK pathways.
Hypertens Res. 33:1174–1181. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang T, Chen SS, Chen R, Yu DM and Yu P:
Reduced beta 2 glycoprotein I improve diabetic nephropathy via
inhibiting TGF-β1-p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Clin Exp Med.
8:6852–6865. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lim AK, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Ma FY, Ozols
E, Thomas MC, Flavell RA, Davis RJ and Tesch GH: Role of MKK3-p38
MAPK signalling in the development of type 2 diabetes and renal
injury in obese db/db mice. Diabetologia. 52:347–358. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng L, Yang L, Wang Z, Chen C and Su Y:
Protective effect of Esculin in adjuvant-induced arthritic (AIA)
rats via attenuating pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative
stress. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 61:1–5. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
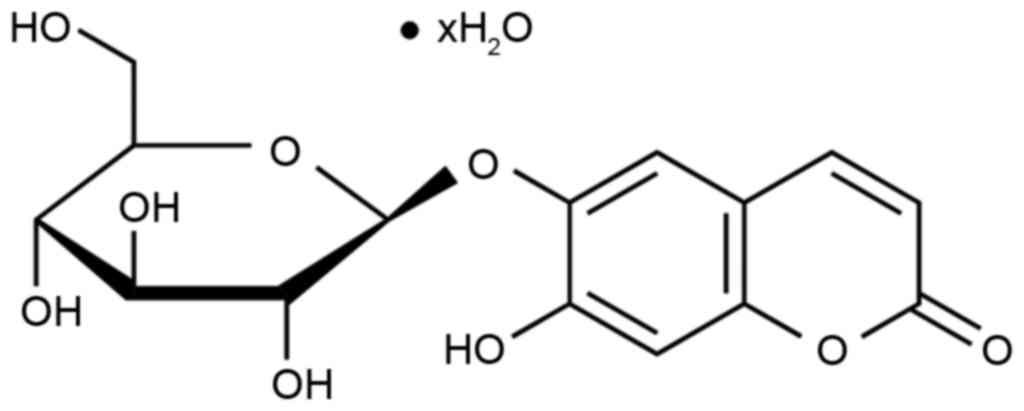
Niu X, Wang Y, Li W, Zhang H, Wang X, Mu
Q, He Z and Yao H: Esculin exhibited anti-inflammatory activities
in vivo and regulated TNF-α and IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated
mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro through MAPK pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 29:779–786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen Z, Zhang L and Chen G: Carbon
nanotube/poly(ethylene-co-vinyl acetate) composite electrode for
capillary electrophoretic determination of esculin and esculetin in
Cortex Fraxini. Electrophoresis. 30:3419–3426. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YH, Liu YH, He GR, Lv Y and Du GH:
Esculin improves dyslipidemia, inflammation and renal damage in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement Altern Med.
15:4022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakamura T, Sato E, Amaha M, Kawagoe Y,
Maeda S and Yamagishi S: Addition of aliskiren to angiotensin II
receptor blockers ameliorates renal tubular injury and reduces
intima media thickness of carotid artery in patients with diabetic
nephropathy. Int J Cardiol. 155:294–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kimura S, Inoguchi T, Yokomizo H, Maeda Y,
Sonoda N and Takayanagi R: Randomized comparison of pitavastatin
and pravastatin treatment on the reduction of urinary albumin in
patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Obes Metab.
14:666–669. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Martynyuk L, Martynyuk L, Ruzhitska O and
Martynyuk O: Effect of the herbal combination Canephron N on
diabetic nephropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: Results of
a comparative cohort study. J Altern Complement Med. 20:472–478.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bakris GL, Agarwal R, Chan JC, Cooper ME,
Gansevoort RT, Haller H, Remuzzi G, Rossing P, Schmieder RE, Nowack
C, et al: Effect of Finerenone on Albuminuria in patients with
diabetic nephropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA.
314:884–894. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim BH, Lee ES, Choi R, Nawaboot J, Lee
MY, Lee EY, Kim HS and Chung CH: Protective effects of curcumin on
renal oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in a rat model of type
2 diabetic nephropathy. Yonsei Med J. 57:664–673. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Persson P, Friederich-Persson M, Fasching
A, Hansell P, Inagi R and Palm F: Adenosine A2 a receptor
stimulation prevents proteinuria in diabetic rats by promoting an
anti-inflammatory phenotype without affecting oxidative stress.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 214:311–318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Feng L, Gu J, Ma L, Qin D, Wu C
and Jia X: The attenuation of Moutan Cortex on oxidative stress for
renal injury in AGEs-induced mesangial cell dysfunction and
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2014:4638152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pérez-Gallardo RV, Noriega-Cisneros R,
Esquivel-Gutiérrez E, Calderón-Cortés E, Cortés-Rojo C,
Manzo-Avalos S, Campos-García J, Salgado-Garciglia R, Montoya-Pérez
R, Boldogh I and Saavedra-Molina A: Effects of diabetes on
oxidative and nitrosative stress in kidney mitochondria from aged
rats. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 46:511–518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nam JS, Cho MH, Lee GT, Park JS, Ahn CW,
Cha BS, Lim SK, Kim KR, Ha HJ and Lee HC: The activation of
NF-kappaB and AP-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated
from patients with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
81:25–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gorska-Ciebiada M, Saryusz-Wolska M,
Borkowska A, Ciebiada M and Loba J: Serum soluble adhesion
molecules and markers of systemic inflammation in elderly diabetic
patients with mild cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:8261802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang X, Wang Y and Gao G: High glucose
induces rat mesangial cells proliferation and MCP-1 expression via
ROS-mediated activation of NF-κB pathway, which is inhibited by
eleutheroside E. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 36:152–157. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ellina O, Chatzigeorgiou A, Kouyanou S,
Lymberi M, Mylona-Karagianni C, Tsouvalas E and Kamper EF:
Extracellular matrix-associated (GAGs, CTGF), angiogenic (VEGF) and
inflammatory factors (MCP-1, CD40, IFN-γ) in type 1 diabetes
mellitus nephropathy. Clin Chem Lab Med. 50:167–174. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zafra-Stone S, Yasmin T, Bagchi M,
Chatterjee A, Vinson JA and Bagchi D: Berry anthocyanins as novel
antioxidants in human health and disease prevention. Mol Nutr Food
Res. 51:675–683. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu H, Shi Y, Deng X, Su Y, Du C, Wei J,
Ren Y, Wu M, Hou Y and Duan H: Inhibition of c-Src/p38 MAPK pathway
ameliorates renal tubular epithelial cells apoptosis in db/db mice.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 417:27–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rane MJ, Song Y, Jin S, Barati MT, Wu R,
Kausar H, Tan Y, Wang Y, Zhou G, Klein JB, et al: Interplay between
Akt and p38 MAPK pathways in the regulation of renal tubular cell
apoptosis associated with diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 298:F49–F61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng X, Gao W, Dang Y, Liu X, Li Y, Peng
X and Ye X: Both ERK/MAPK and TGF-Beta/Smad signaling pathways play
a role in the kidney fibrosis of diabetic mice accelerated by blood
glucose fluctuation. J Diabetes Res. 2013:4637402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lakshmanan AP, Thandavarayan RA, Watanabe
K, Sari FR, Meilei H, Giridharan VV, Sukumaran V, Soetikno V,
Arumugam S, Suzuki K and Kodama M: Modulation of AT-1R/MAPK cascade
by an olmesartan treatment attenuates diabetic nephropathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
348:104–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|