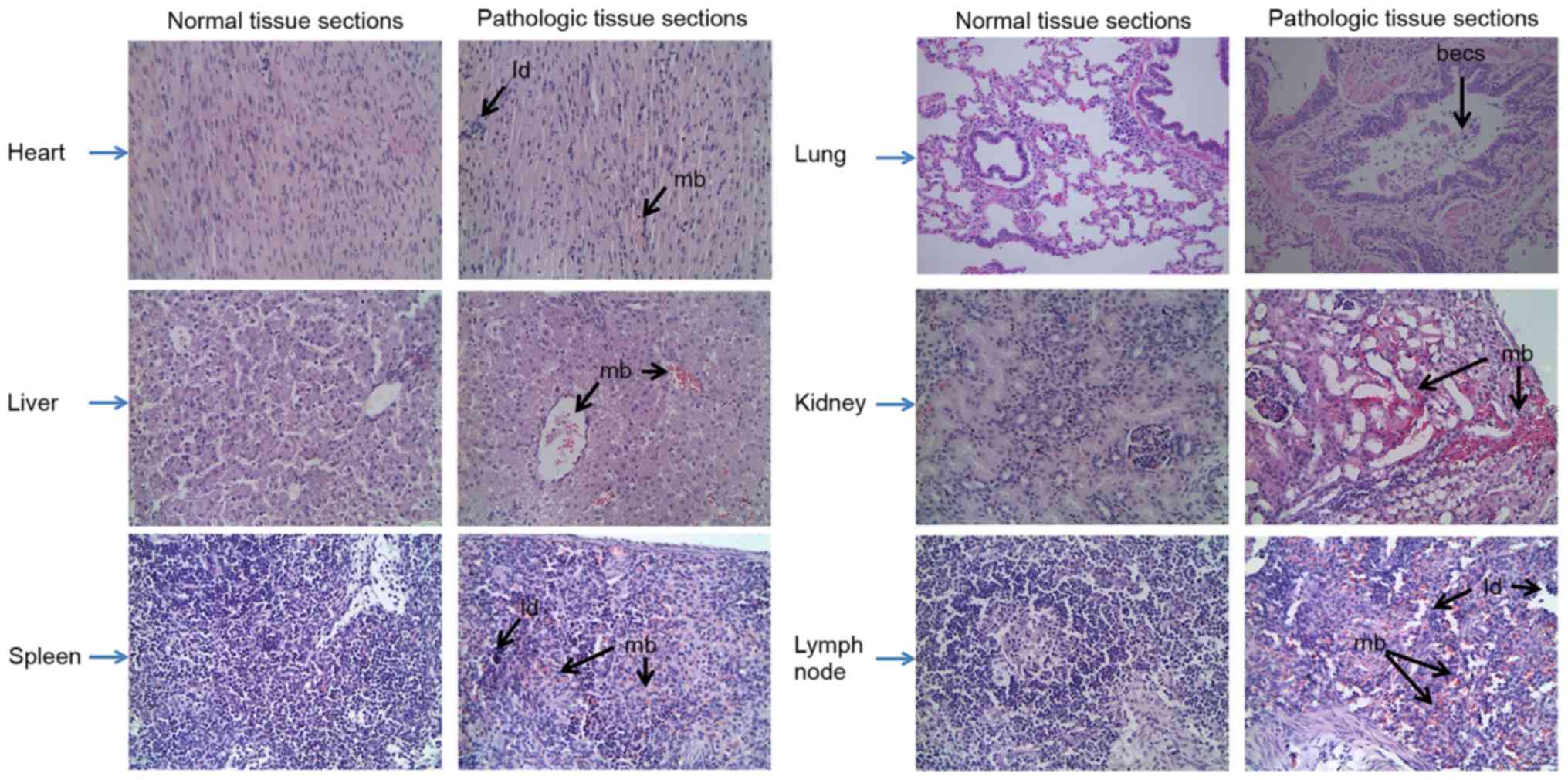
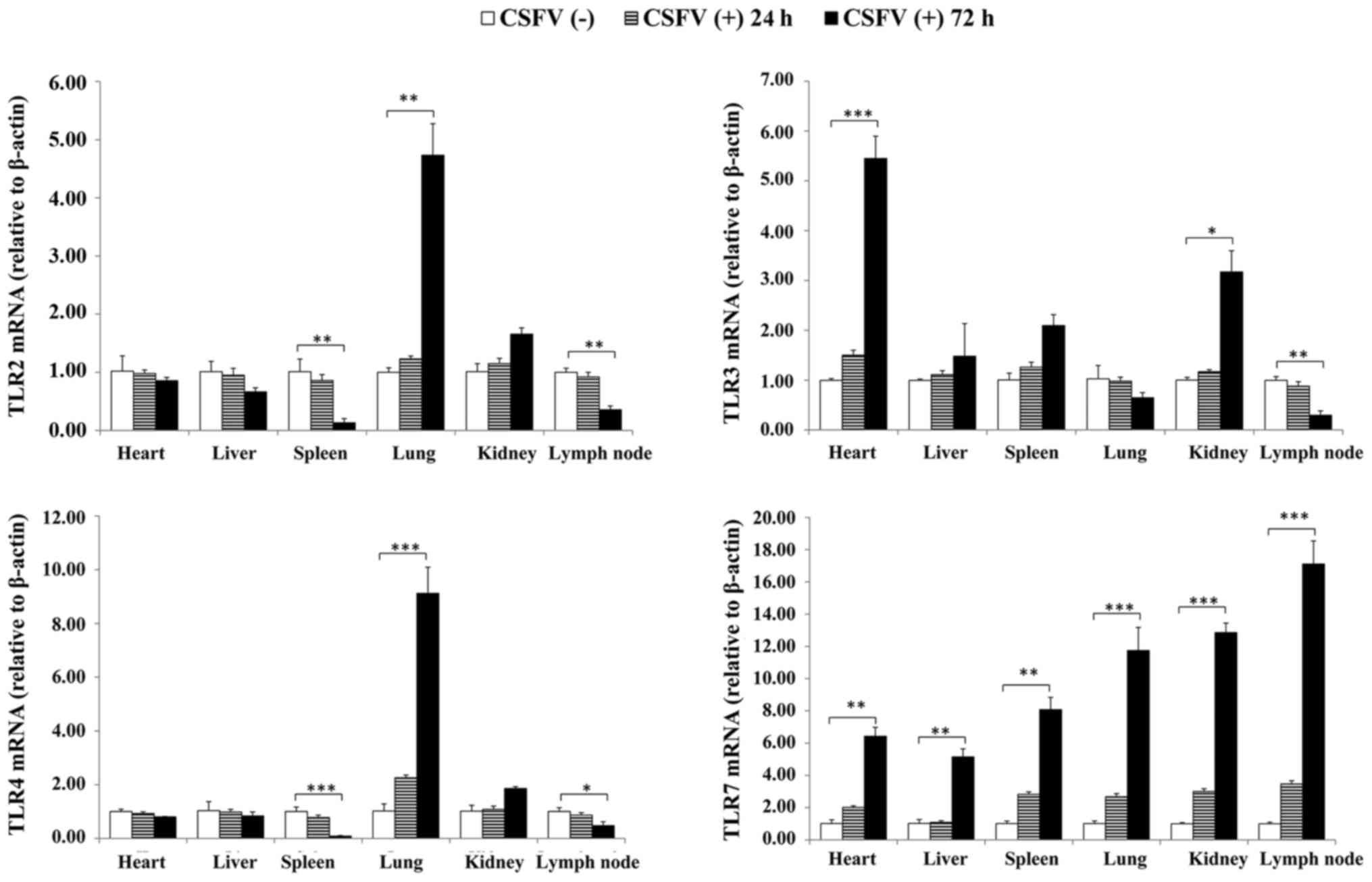
|
1
|
Edwards S, Fukusho A, Lefèvre PC, Lipowski
A, Pejsak Z, Roehe P and Westergaard J: Classical swine fever: The
global situation. Vet Microbiol. 73:103–119. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo Y, Li S, Sun Y and Qiu HJ: Classical
swine fever in China: A minireview. Vet Microbiol. 172:1–6. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paton DJ and Greiser-Wilke I: Classical
swine fever-an update. Res Vet Sci. 75:169–178. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jamin A, Gorin S, Cariolet R, Le Potier MF
and Kuntz-Simon G: Classical swine fever virus induces activation
of plasmacytoid and conventional dendritic cells in tonsil, blood,
and spleen of infected pigs. Vet Res. 39:72008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kawai T and Akira S: The role of
pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on
Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol. 11:373–384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moresco EM, LaVine D and Beutler B:
Toll-like receptors. Curr Biol. 21:R488–R493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lester SN and Li K: Toll-like receptors in
antiviral innate immunity. J Mol Biol. 426:1246–1264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heil F, Hemmi H, Hochrein H, Ampenberger
F, Kirschning C, Akira S, Lipford G, Wagner H and Bauer S:
Species-specific recognition of single-stranded RNA via toll-like
receptor 7 and 8. Science. 303:1526–1529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guillot L, Le Goffic R, Bloch S, Escriou
N, Akira S, Chignard M and Si-Tahar M: Involvement of toll-like
receptor 3 in the immune response of lung evithelial cells to
double-stranded RNA and influenza A virus. J Biol Chem.
280:5571–5580. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cao Z, Guo K, Zheng M, Ning P, Li H, Kang
K, Lin Z, Zhang C, Liang W and Zhang Y: A comparison of the impact
of Shimen and C strains of classical swine fever virus on Toll-like
receptor expression. J Gen Virol. 96:1732–1745. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ning P, Zhang Y, Guo K, Chen R, Liang W,
Lin Z and Li H: Discovering up-regulated VEGF-C expression in swine
umbilical vein endothelial cells by classical swine fever virus
Shimen. Vet Res. 45:482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pei J, Zhao M, Ye Z, Gou H, Wang J, Yi L,
Dong X, Liu W, Luo Y, Liao M and Chen J: Autophagy enhances the
replication of classical swine fever virus in vitro. Autophagy.
10:93–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J and Zeller
R: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH
protocols. 2008:pdb prot4986. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Xiao SY, Zhang H, Guzman H and Tesh RB:
Experimental yellow fever virus infection in the golden hamster
(Mesocricetus auratus). II. pathology. J Infect Dis.
183:1437–1444. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benias PC, Gopal K, Bodenheimer H Jr and
Theise ND: Hepatic expression of toll-like receptors 3, 4 and 9 in
primary biliary cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis C. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 36:448–454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and
immunity. Immunity. 34:637–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang D, Liang J, Li Y and Noble P: The
role of Toll-like receptors in non-infectious lung injury. Cell
Res. 16:693–701. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lund JM, Alexopoulou L, Sato A, Karow M,
Adams NC, Gale NW, Iwasaki A and Flavell RA: Recognition of
single-stranded RNA viruses by Toll-like receptor 7. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 101:pp. 5598–5603. 2004; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R and
Flavell RA: Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of
NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 413:732–738. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsung A, Sahai R, Tanaka H, Nakao A, Fink
MP, Lotze MT, Yang H, Li J, Tracey KJ, Geller DA and Billiar TR:
The nuclear factor HMGB1 mediates hepatic injury after murine liver
ischemia-reperfusion. J Exp Med. 201:1135–1143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stewart CR, Stuart LM, Wilkinson K, van
Gils JM, Deng J, Halle A, Rayner KJ, Boyer L, Zhong R, Frazier WA,
et al: CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly
of a Toll-like receptor 4 and 6 heterodimer. Nat Immunol.
11:155–161. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanzler H, Barrat FJ, Hessel EM and
Coffman RL: Therapeutic targeting of innate immunity with Toll-like
receptor agonists and antagonists. Nat Med. 13:552–559. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O'Neill LA, Bryant CE and Doyle SL:
Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and
inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 61:177–197. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|