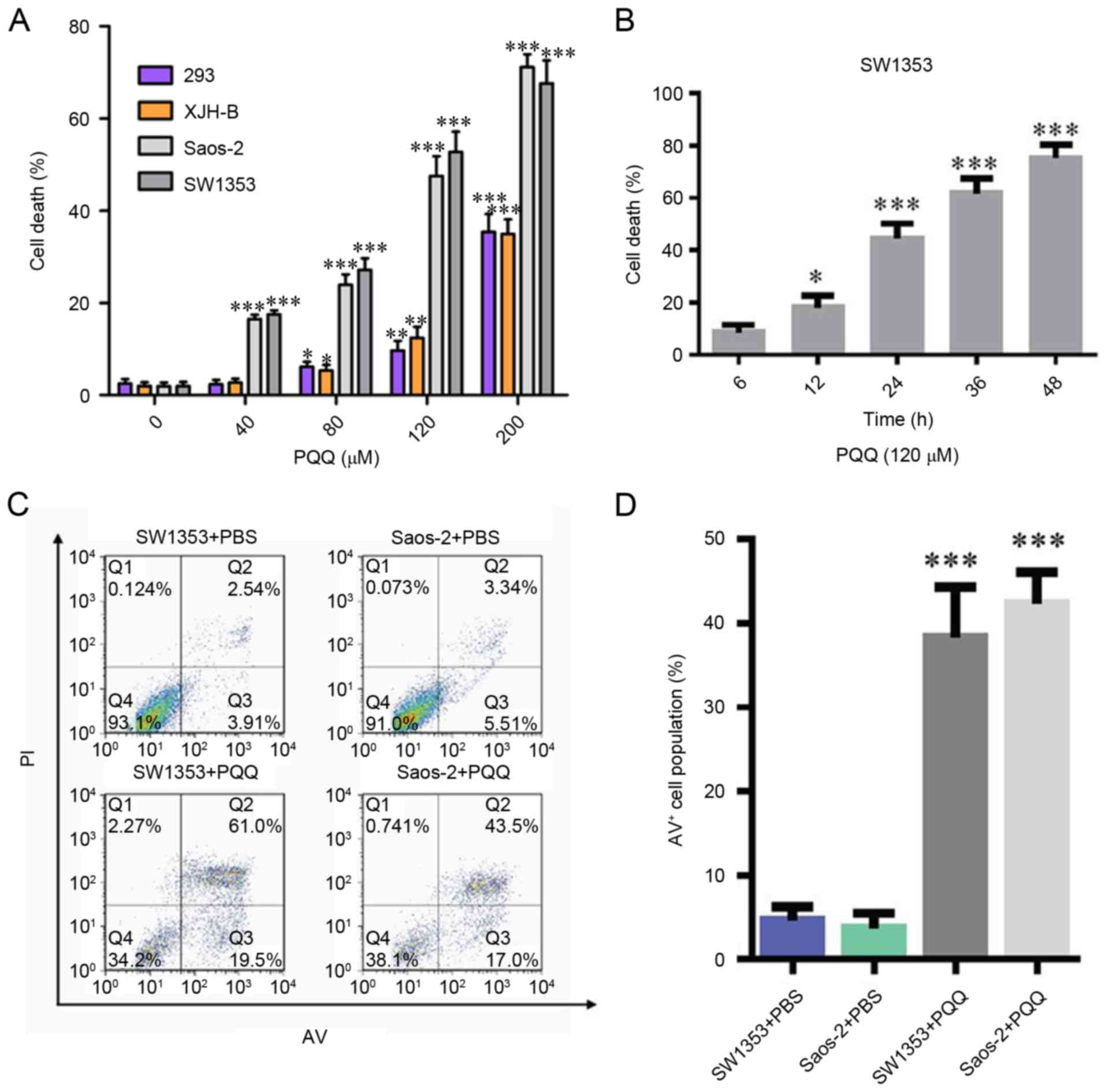
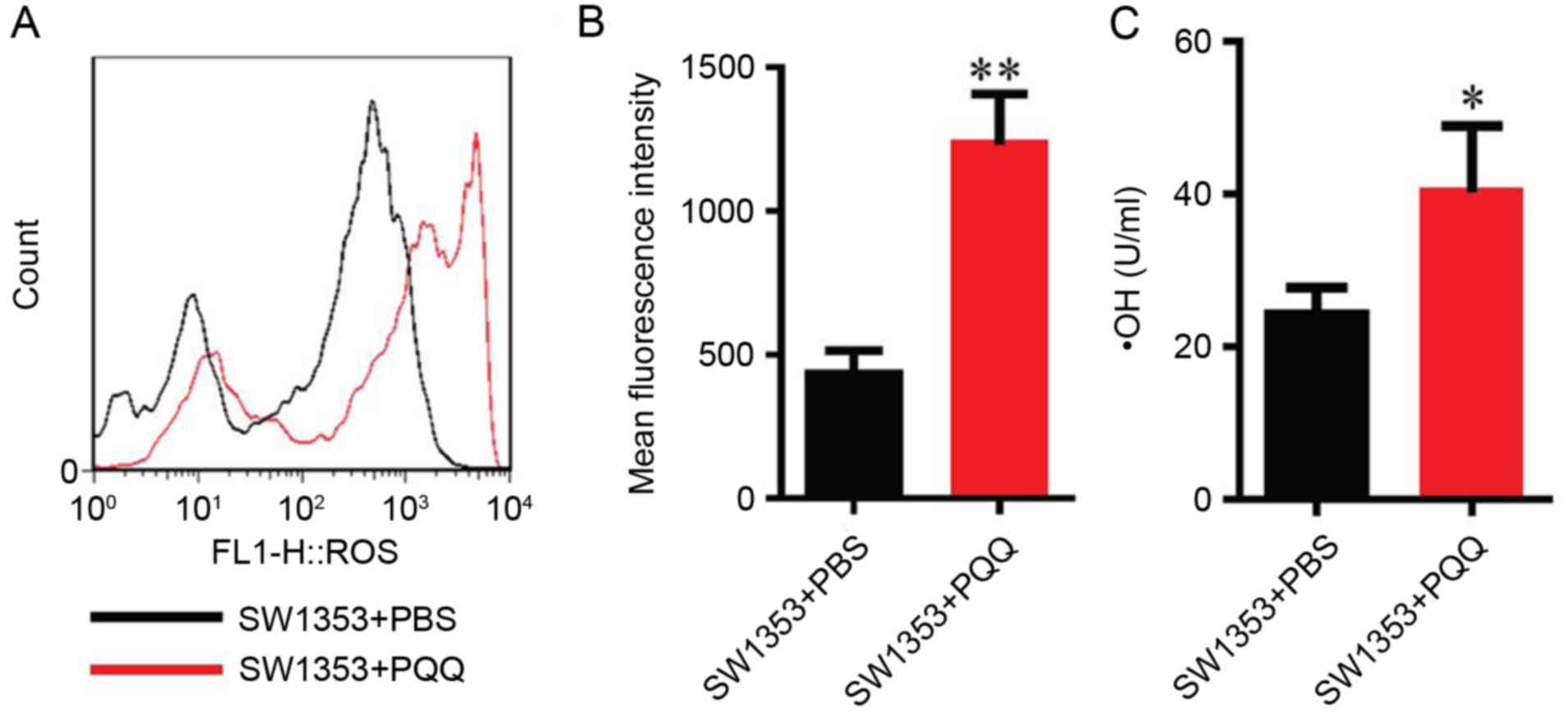
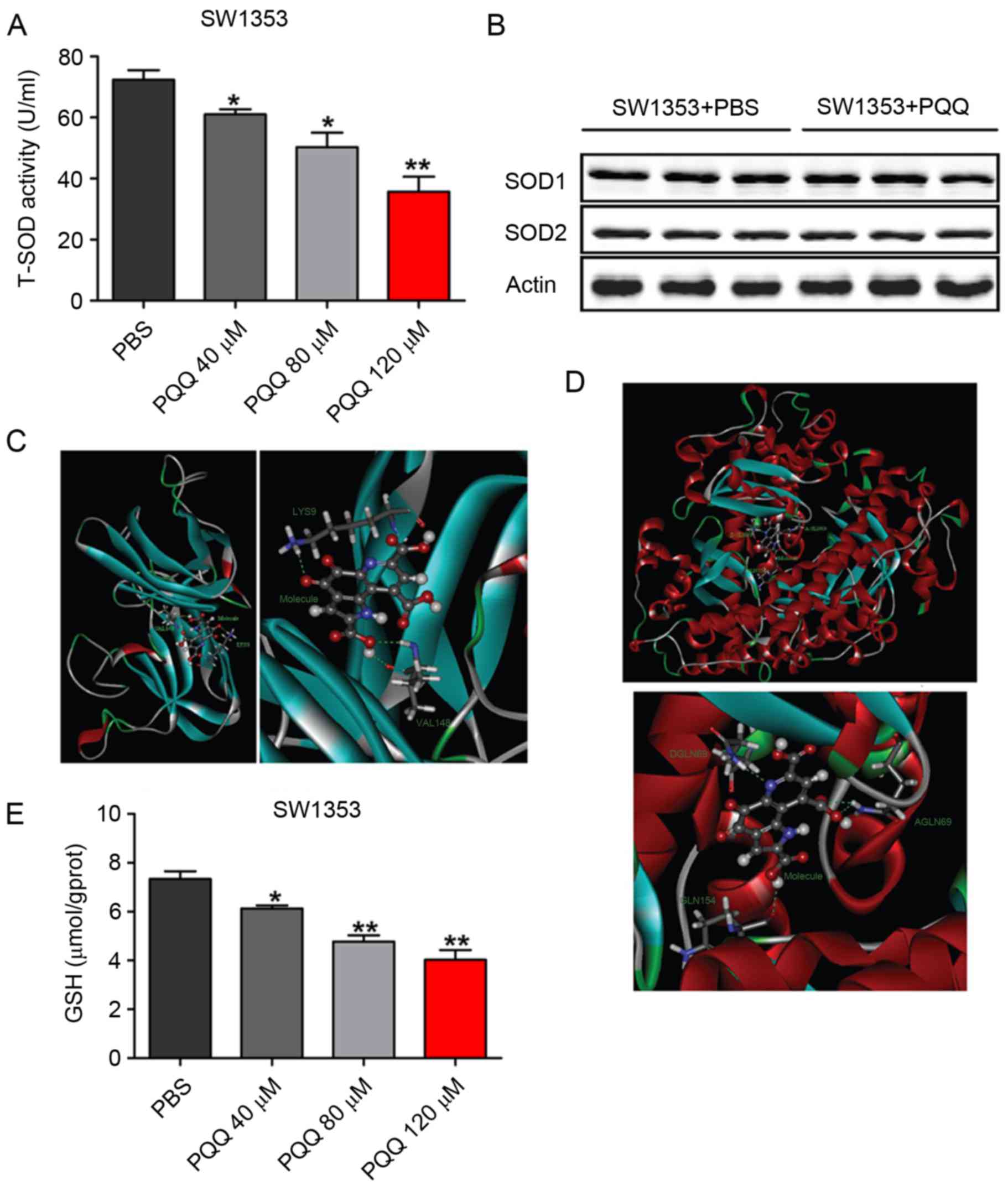
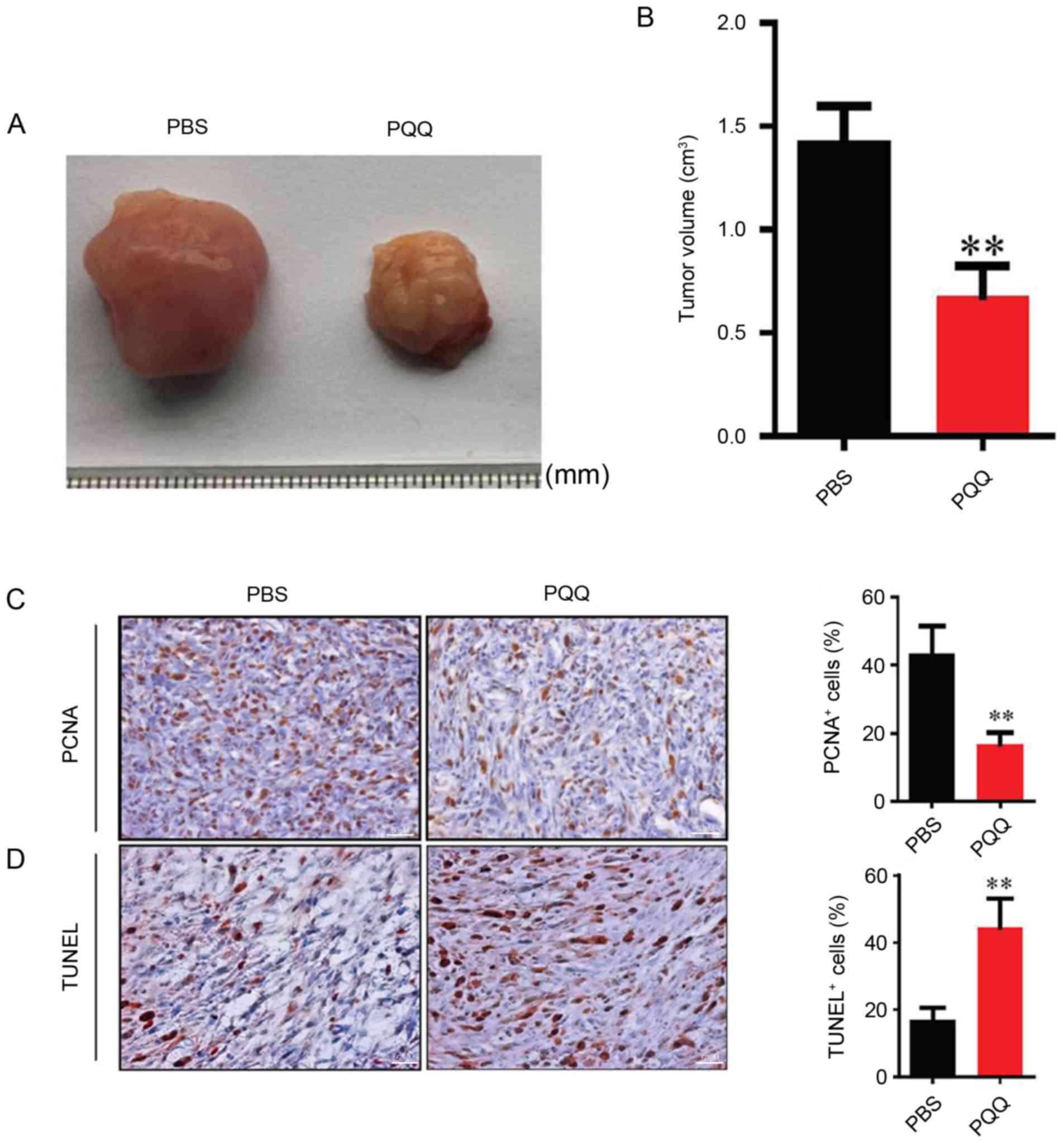
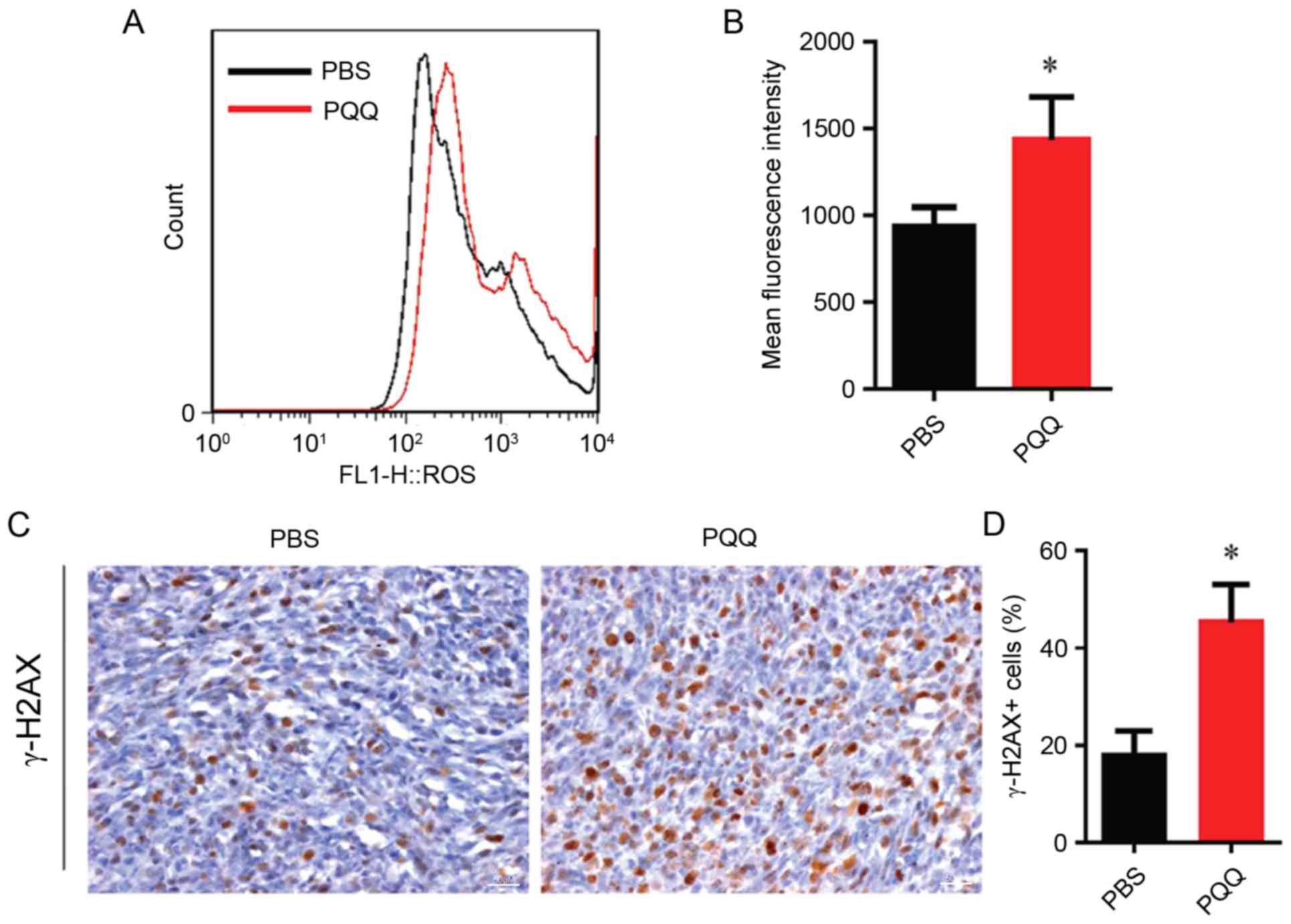
|
1
|
Bauer HC, Brosjö O, Kreicbergs A and
Lindholm J: Low risk of recurrence of enchondroma and low-grade
chondrosarcoma in extremities. 80 patients followed for 2–25 years.
Acta Orthop Scand. 66:283–288. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eriksson AI, Schiller A and Mankin HJ: The
management of chondrosarcoma of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 44–66.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bovée JV, Cleton-Jansen AM, Taminiau AH
and Hogendoorn PC: Emerging pathways in the development of
chondrosarcoma of bone and implications for targeted treatment.
Lancet Oncol. 6:599–607. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bao X, Ren T, Huang Y, Wang S, Zhang F,
Liu K, Zheng B and Guo W: Induction of the mesenchymal to
epithelial transition by demethylation-activated microRNA-125b is
involved in the anti-migration/invasion effects of arsenic trioxide
on human chondrosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:1292016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McIntire WS: Newly discovered redox
cofactors: Possible nutritional, medical, and pharmacological
relevance to higher animals. Annu Rev Nutr. 18:145–177. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Misra HS, Khairnar NP, Barik A, Indira
Priyadarsini K, Mohan H and Apte SK: Pyrroloquinoline-quinone: A
reactive oxygen species scavenger in bacteria. FEBS Lett.
578:26–30. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He K, Nukada H, Urakami T and Murphy MP:
Antioxidant and pro-oxidant properties of pyrroloquinoline quinone
(PQQ): Implications for its function in biological systems. Biochem
Pharmacol. 65:67–74. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smidt CR, Steinberg FM and Rucker RB:
Physiologic importance of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Proc Soc Exp
Biol Med. 197:pp. 19–26. 1991; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bishop A, Gallop PM and Karnovsky ML:
Pyrroloquinoline quinone: A novel vitamin? Nutr Rev. 56:287–293.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shankar BS, Pandey R, Amin P, Misra HS and
Sainis KB: Role of glutathione in augmenting the anticancer
activity of pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ). Redox Rep. 15:146–154.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Min Z, Wang L, Jin J, Wang X, Zhu B, Chen
H and Cheng Y: Pyrroloquinoline quinone induces cancer cell
apoptosis via mitochondrial-dependent pathway and down-regulating
cellular Bcl-2 protein expression. J Cancer. 5:609–624. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pizzimenti S, Toaldo C, Pettazzoni P,
Dianzani MU and Barrera G: Thetwo-faced effects of reactive oxygen
species and the lipid peroxidation product4-hydroxynonenal in the
hallmarks of cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2:338–363. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tripathi DN, Chowdhury R, Trudel LJ, Tee
AR, Slack RS, Walker CL and Wogan GN: Reactive nitrogen species
regulate autophagy through ATM-AMPK-TSC2 mediated suppression of
mTORC1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:pp. E2950–E2957. 2013;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Finkel T and Holbrook NJ: Oxidants,
oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 408:239–247.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martindale JL and Holbrook NJ: Cellular
response to oxidative stress: Signalling for suicide and survival.
J Cell Physiol. 192:1–15. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang J, Nakamura H and Iyer AK: Regulation
of replicative potential of cells. J Drug Target. 15:475–486. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baliga R, Zhang Z, Baliga M, Ueda N and
Shah SV: In vitro and in vivo evidence suggesting a role for iron
in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 53:394–401. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie X, Zhao Y, Ma CY, Xu XM, Zhang YQ,
Wang CG, Jin J, Shen X, Gao JL, Li N, et al: Dimethyl fumarate
induces necroptosis in colon cancer cells through GSH depletion/ROS
increase/MAPKs activation pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 172:3929–3943.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Bao Y, Dong Z, Chen Q, Guo H,
Ziang C and Shao J: WP1130 attenuates cisplatin resistance by
decreasing P53 expression in non-small cell lung carcinomas.
Oncotarget. 8:49033–49043. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Salisbury SA, Forrest HS, Cruse WB and
Kennard O: A novel coenzyme from bacterial primary alcohol
dehydrogenases. Nature. 280:843–844. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Killgore J, Smidt C, Duich L,
Romero-Chapman N, Tinker D, Reiser K, Melko M, Hyde D and Rucker
RB: Nutritional importance of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Science.
245:850–852. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steinberg FM, Gershwin ME and Rucker RB:
Dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone: Growth and immune response in
BALB/c mice. J Nutr. 124:744–753. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tao R, Karliner JS, Simonis U, Zheng J,
Zhang J, Honbo N and Alano CC: Pyrroloquinoline quinone preserves
mitochondrial function and prevents oxidative injury in adult rat
cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 363:257–262. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hara H, Hiramatsu H and Adachi T:
Pyrroloquinoline quinone is a potentneuroprotective nutrient
against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res.
32:489–495. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiong XH, Zhao Y, Ge X, Yuan SJ, Wang JH,
Zhi JJ, Yang YX, Du BH, Guo WJ, Wang SS, et al: Production and
radioprotective effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone. Int J Mol Sci.
12:8913–8923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sato K and Toriyama M: Effect of
pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) on melanogenic protein expression in
murine B16 melanoma. J Dermatol Sci. 53:140–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fadeel B and Orrenius S: Apoptosis: A
basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in human
disease. J Intern Med. 258:479–517. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clarke PG: Developmental cell death:
Morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol
(Berl). 181:195–213. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tibodeau JD, Benson LM, Isham CR, Owen WG
and Bible KC: The Anticanceragent chaetocin is a competitive
substrate and inhibitor ofthioredoxin reductase. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 11:1097–1106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Madan E, Prasad S, Roy P, George J and
Shukla Y: Regulation of apoptosis by resveratrol through JAK/STAT
and mitochondria mediated pathway in human epidermoid carcinoma
A431 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 377:1232–1237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Huang SL, Li MM, Huang ZS, Lee KS
and Gu LQ: Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase by mansonone F
analogues: Implications for anticancer activity. Chem Biol
Interact. 177:48–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|