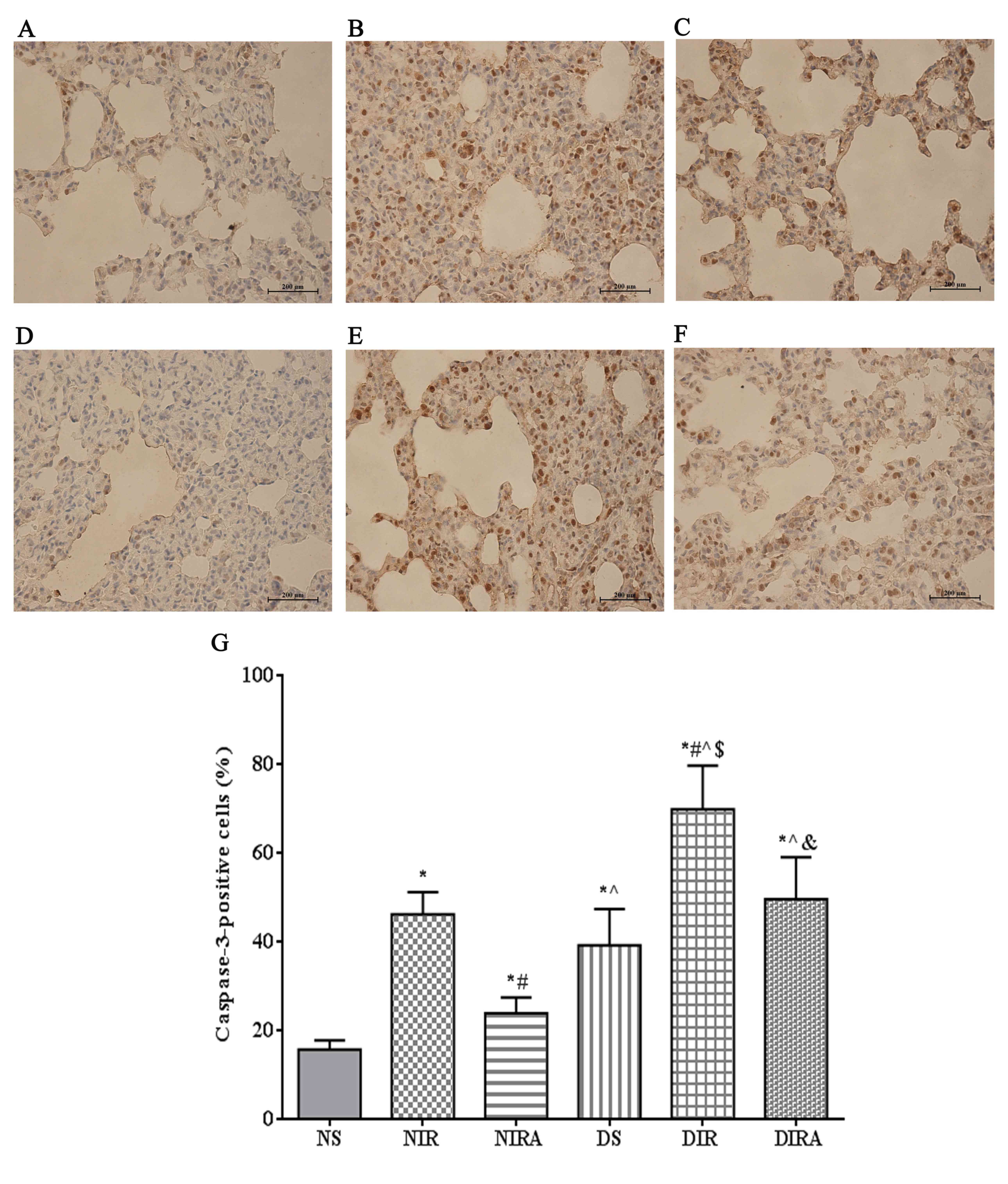
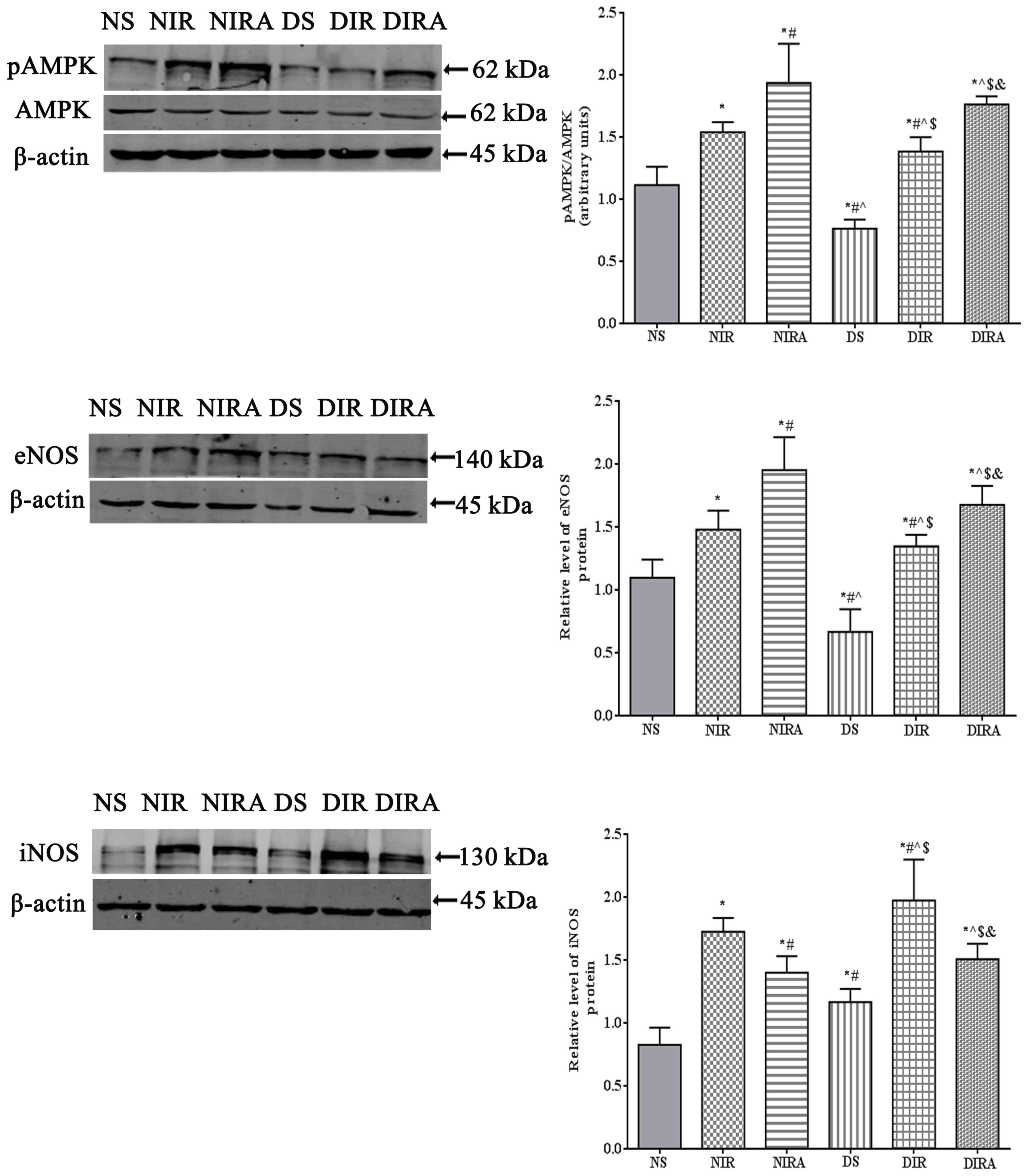
|
1
|
Fernandez LG, Sharma AK, LaPar DJ, Kron IL
and Laubach VE: Adenosine A1 receptor activation attenuates lung
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
145:1654–1659. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
den Hengst WA, Gielis JF, Lin JY, Van
Schil PE, De Windt LJ and Moens AL: Lung ischemia-reperfusion
injury: A molecular and clinical view on a complex
pathophysiological process. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H1283–H1299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen GM, Hu N, Liu L, Xie SS, Wang P, Li
J, Xie L, Wang GJ and Liu XD: Pharmacokinetics of verapamil in
diabetic rats induced by combination of high-fat diet and
streptozotocin injection. Xenobiotica. 41:494–500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tao L, Gao E, Jiao X, Yuan Y, Li S,
Christopher TA, Lopez BL, Koch W, Chan L, Goldstein BJ and Ma XL:
Adiponectin cardioprotection after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
involves the reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Circulation.
115:1408–1416. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yi W, Sun Y, Gao E, Wei X, Lau WB, Zheng
Q, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Wang X, Tao L, et al: Reduced cardioprotective
action of adiponectin in high-fat diet-induced type II diabetic
mice and its underlying mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:1779–1788. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sattar N, Wannamethee G, Sarwar N,
Tchernova J, Cherry L, Wallace AM, Danesh J and Whincup PH:
Adiponectin and coronary heart disease: A prospective study and
meta-analysis. Circulation. 114:623–629. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: Ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Whitehead JP, Richards AA, Hickman IJ,
Macdonald GA and Prins JB: Adiponectin-a key adipokine in the
metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Obes Metab. 8:264–280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thakur V, Pritchard MT, McMullen MR and
Nagy LE: Adiponectin normalizes LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha production
by rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 290:G998–G1007. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen B, Liao WQ, Xu N, Xu H, Wen JY, Yu
CA, Liu XY, Li CL, Zhao SM and Campbell W: Adiponectin protects
against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through
anti-inflammatory action. Brain Res. 1273:129–137. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kola B, Boscaro M, Rutter GA, Grossman AB
and Korbonits M: Expanding role of AMPK in endocrinology. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 17:205–215. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Viollet B, Foretz M, Guigas B, Horman S,
Dentin R, Bertrand L, Hue L and Andreelli F: Activation of
AMP-activated protein kinase in the liver: A new strategy for the
management of metabolic hepatic disorders. J Physiol. 574:41–53.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ouchi N, Kobayashi H, Kihara S, Kumada M,
Sato K, Inoue T, Funahashi T and Walsh K: Adiponectin stimulates
angiogenesis by promoting cross-talk between AMP-activated protein
kinase and Akt signaling in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
279:1304–1309. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K,
Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T,
et al: Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules:
Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation.
100:2473–2476. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumada M, Kihara S, Sumitsuji S, Kawamoto
T, Matsumoto S, Ouchi N, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Shimomura I, Hiraoka
H, et al: Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery
disease in men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 23:85–89. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bouhali T, Brisson D, St-Pierre J,
Tremblay G, Perron P, Laprise C, Vohl MC, Vissers MN, Hutten BA,
Després JP, et al: Low plasma adiponectin exacerbates the risk of
premature coronary artery disease in familial hypercholesterolemia.
Atherosclerosis. 196:262–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Laubach VE and Kron IL: Pulmonary
inflammation after lung transplantation. Surgery. 146:1–4. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zheng H, Wu J, Jin Z and Yan LJ: Potential
biochemical mechanisms of lung injury in diabetes. Aging Dis.
8:7–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J,
Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, et al: Prevalence of diabetes among
men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 362:1090–1101. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hackman KL, Snell GI and Bach LA: An
unexpectedly high prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes in patients
awaiting lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 32:86–91.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ambur V, Taghavi S, Jayarajan S, Kadakia
S, Zhao H, Gomez-Abraham J and Toyoda Y: The impact of lungs from
diabetic donors on lung transplant recipients†. Eur J Cardiothorac
Surg. 51:285–290. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuitert LM: The lung in diabetes-yet
another target organ? Chron Respir Dis. 5:67–68. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pitocco D, Fuso L, Conte EG, Zaccardi F,
Condoluci C, Scavone G, Incalzi RA and Ghirlanda G: The diabetic
lung-a new target organ? Rev Diabet Stud. 9:23–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Williams JG, Morris AI, Hayter RC and
Ogilvie CM: Respiratory responses of diabetics to hypoxia,
hypercapnia, and exercise. Thorax. 39:529–534. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dennis RJ, Maldonado D, Rojas MX, Aschner
P, Rondón M, Charry L and Casas A: Inadequate glucose control in
type 2 diabetes is associated with impaired lung function and
systemic inflammation: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pulm Med.
10:382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Engström G, Hedblad B, Nilsson P, Wollmer
P, Berglund G and Janzon L: Lung function, insulin resistance and
incidence of cardiovascular disease: A longitudinal cohort study. J
Intern Med. 253:574–581. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim CH, Kim HK, Kim EH, Bae SJ, Jung YJ,
Choi J and Park JY: Association of restrictive ventilatory
dysfunction with the development of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes
in Koreans. Acta Diabetol. 52:357–363. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiang CH, Hsu K, Yan HC, Harn HJ and
Chang DM: PGE1, dexamethasone, U-74389G, or Bt2-cAMP as an additive
to promote protection by UW solution in I/R injury. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 83:583–590. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pirat A, Zeyneloglu P, Aldemir D, Yücel M,
Ozen O, Candan S and Arslan G: Pretreatment with simvastatin
reduces lung injury related to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion in
rats. Anesth Analg. 102:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kadowaki T, Yamauchi T, Kubota N, Hara K,
Ueki K and Tobe K: Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin
resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest.
116:784–792. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Xu LY, Lam KS, Lu G, Cooper GJ and
Xu A: Proteomic characterization of human serum proteins associated
with the fat-derived hormone adiponectin. Proteomics. 6:3862–3870.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fruebis J, Tsao TS, Javorschi S,
Ebbets-Reed D, Erickson MR, Yen FT, Bihain BE and Lodish HF:
Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related
protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight
loss in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:pp. 2005–2010. 2001;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y,
Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N,
et al: The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin
resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med.
7:941–946. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iwashima Y, Katsuya T, Ishikawa K, Ouchi
N, Ohishi M, Sugimoto K, Fu Y, Motone M, Yamamoto K, Matsuo A, et
al: Hypoadiponectinemia is an independent risk factor for
hypertension. Hypertension. 43:1318–1323. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y,
Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, et al:
Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation
by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med. 8:1288–1295.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shibata R, Sato K, Pimentel DR, Takemura
Y, Kihara S, Ohashi K, Funahashi T, Ouchi N and Walsh K:
Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
through AMPK- and COX-2-dependent mechanisms. Nat Med.
11:1096–1103. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hardie DG, Carling D and Carlson M: The
AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: Metabolic sensors of
the eukaryotic cell? Annu Rev Biochem. 67:821–855. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shibata R, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Sato K,
Funahashi T and Walsh K: Adiponectin stimulates angiogenesis in
response to tissue ischemia through stimulation of amp-activated
protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:28670–28674. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kobayashi H, Ouchi N, Kihara S, Walsh K,
Kumada M, Abe Y, Funahashi T and Matsuzawa Y: Selective suppression
of endothelial cell apoptosis by the high molecular weight form of
adiponectin. Circ Res. 94:e27–e31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen H, Montagnani M, Funahashi T,
Shimomura I and Quon MJ: Adiponectin stimulates production of
nitric oxide in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem.
278:45021–45026. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Konter JM, Parker JL, Baez E, Li SZ,
Ranscht B, Denzel M, Little FF, Nakamura K, Ouchi N, Fine A, et al:
Adiponectin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
through suppression of endothelial cell activation. J Immunol.
188:854–863. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He Y, Zou L, Zhou Y, Hu H, Yao R, Jiang Y,
Lau WB, Yuan T, Huang W, Zeng Z and Cao Y: Adiponectin ameliorates
the apoptotic effects of paraquat on alveolar type cells via
improvements in mitochondrial function. Mol Med Rep. 14:746–752.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao X, Zmijewski JW, Lorne E, Liu G, Park
YJ, Tsuruta Y and Abraham E: Activation of AMPK attenuates
neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of
acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
295:L497–L504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Becker J, Delayre-Orthez C, Frossard N and
Pons F: Regulation of inflammation by PPARs: A future approach to
treat lung inflammatory diseases? Fundam Clin Pharmacol.
20:429–447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Alba G, El Bekay R, Alvarez-Maqueda M,
Chacón P, Vega A, Monteseirín J, Santa María C, Pintado E, Bedoya
FJ, Bartrons R and Sobrino F: Stimulators of AMP-activated protein
kinase inhibit the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. FEBS
Lett. 573:219–225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song P and Zou MH: Regulation of NAD(P)H
oxidases by AMPK in cardiovascular systems. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:1607–1619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M and
Scherer PE: The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic
insulin action. Nat Med. 7:947–953. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang PH, Sata M, Nishimatsu H, Sumi M,
Hirata Y and Nagai R: Pioglitazone ameliorates endothelial
dysfunction and restores ischemia-induced angiogenesis in diabetic
mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 62:46–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|