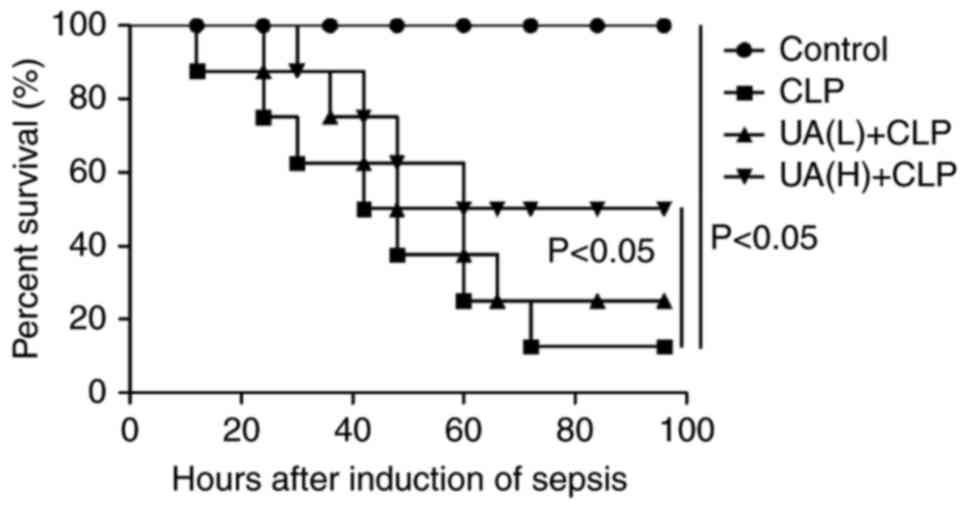
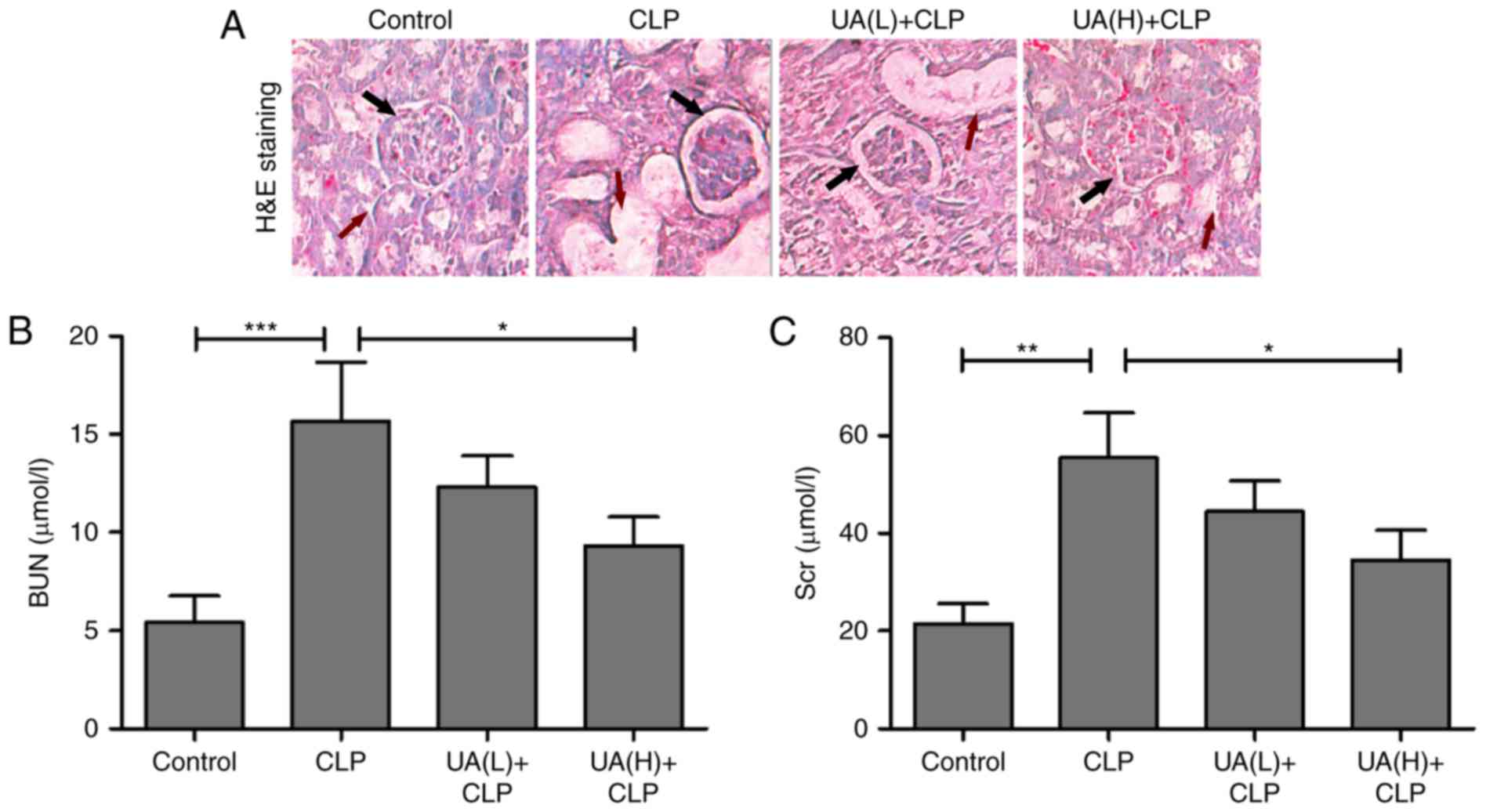
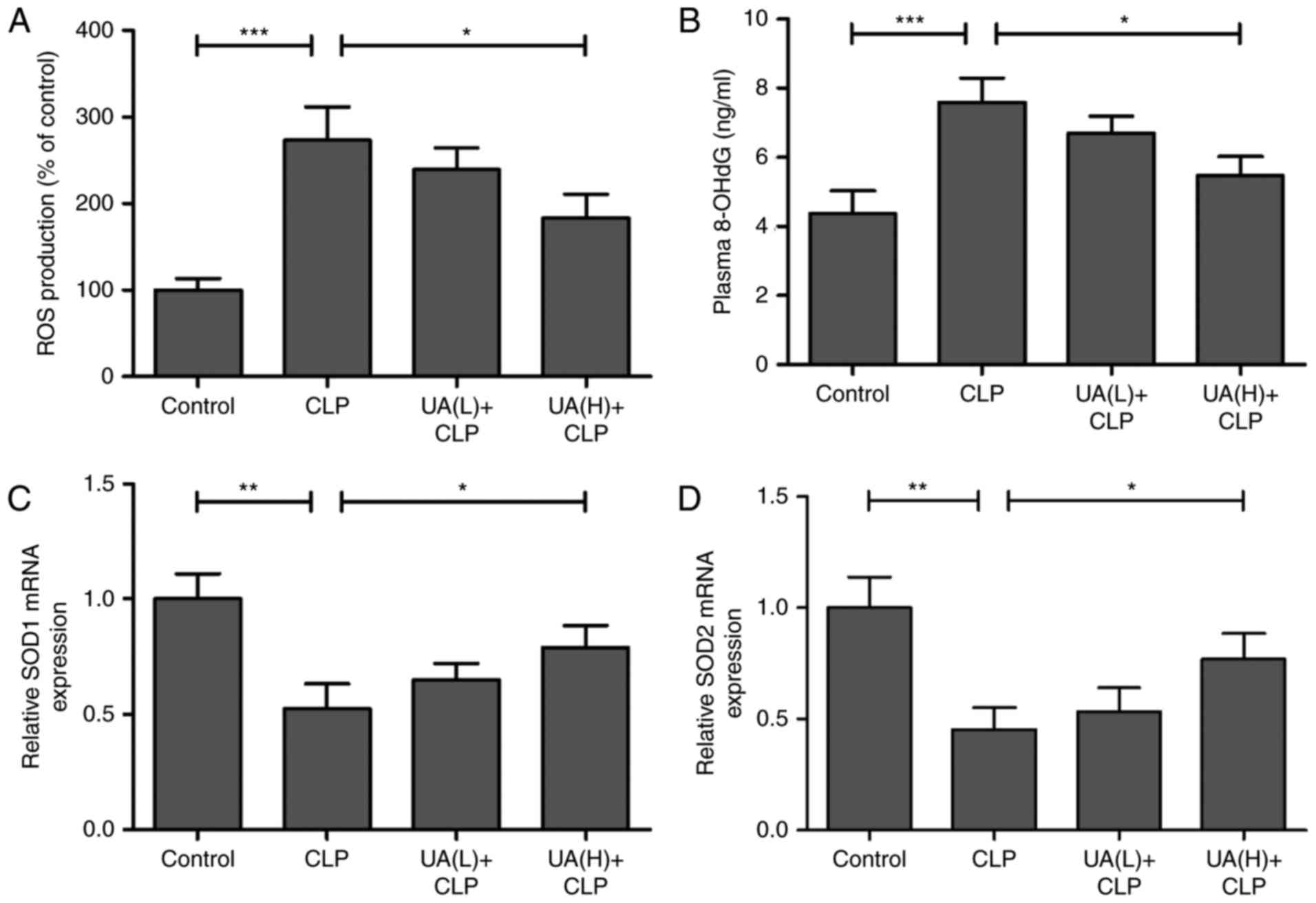
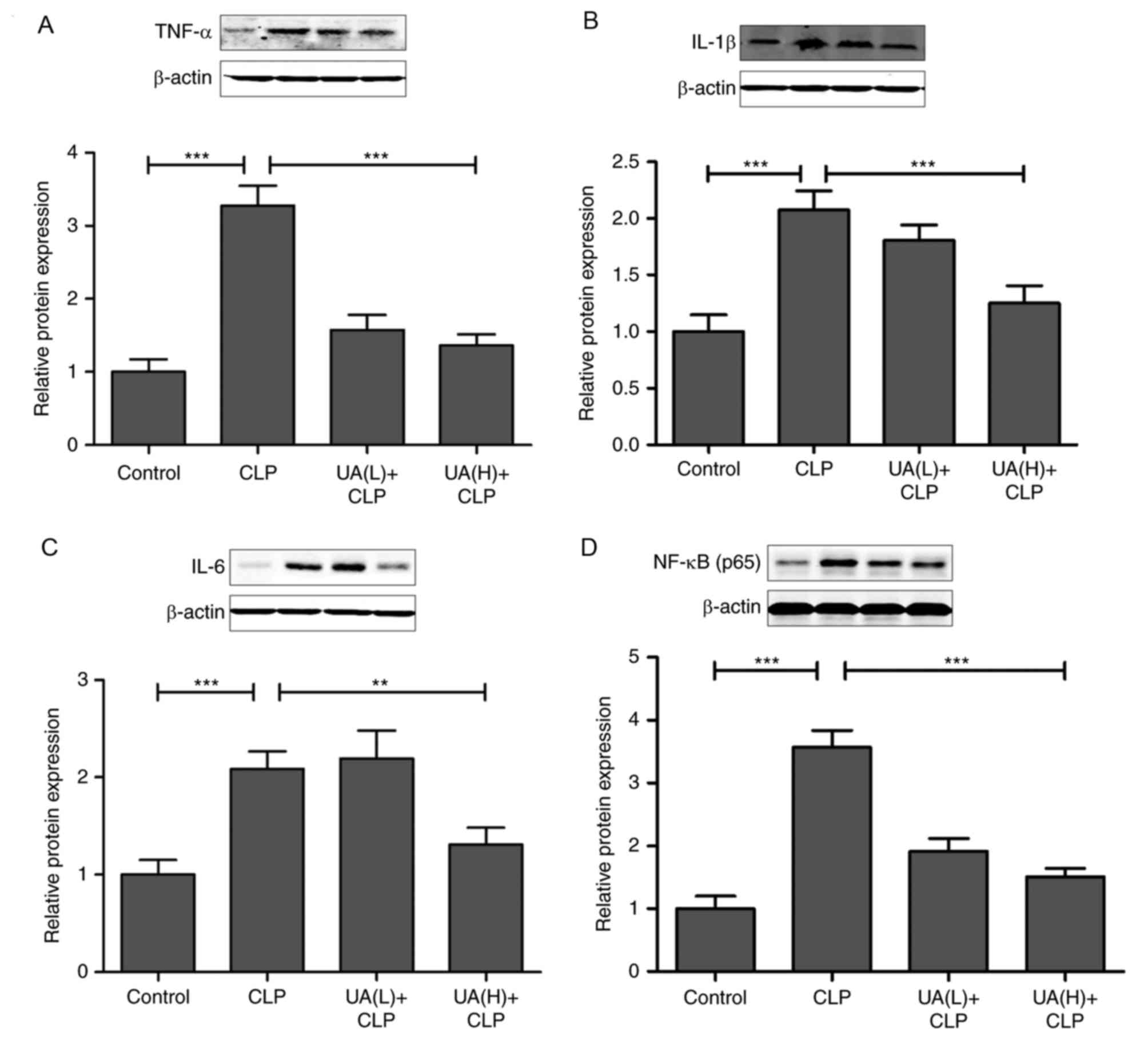
|
1
|
Zhang A, Cai Y, Wang PF, Qu JN, Luo ZC,
Chen XD, Huang B, Liu Y, Huang WQ, Wu J and Yin YH: Diagnosis and
prognosis of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute
kidney injury with sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Crit Care. 20:412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lopes JA, Fernandes P, Jorge S, Resina C,
Santos C, Pereira A, Neves J, Antunes F and Gomes da Costa A:
Long-term risk of mortality after acute kidney injury in patients
with sepsis: A contemporary analysis. BMC Nephrol. 11:92010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zarjou A and Agarwal A: Sepsis and acute
kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:999–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murugan R, Karajala-Subramanyam V, Lee M,
Yende S, Kong L, Carter M, Angus DC and Kellum JA: Genetic and
Inflammatory Markers of Sepsis (GenIMS) Investigators: Acute kidney
injury in non-severe pneumonia is associated with an increased
immune response and lower survival. Kidney Int. 77:527–535. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li N, Xie H, Li L, Wang J, Fang M, Yang N
and Lin H: Effects of honokiol on sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury in an experimental model of sepsis in rats. Inflammation.
37:1191–1199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Quoilin C, Mouithys-Mickalad A, Lécart S,
Fontaine-Aupart MP and Hoebeke M: Evidence of oxidative stress and
mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in an in vitro model of
sepsis-induced kidney injury. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1837:1790–1800.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weng TI, Wu HY, Kuo CW and Liu SH:
Honokiol rescues sepsis-associated acute lung injury and lethality
via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Intensive
Care Med. 37:533–541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jin H, Pi J, Yang F, Jiang J, Wang X, Bai
H, Shao M, Huang L, Zhu H, Yang P, et al: Folate-chitosan
nanoparticles loaded with ursolic acid confer anti-breast cancer
activities in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep. 6:307822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chu SM, Shih WT, Yang YH, Chen PC and Chu
YH: Use of traditional Chinese medicine in patients with
hyperlipidemia: A population-based study in Taiwan. J
Ethnopharmacol. 168:129–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo X, Zhang L, Quan S, Hong Y, Sun L and
Liu M: Isolation and identification of Triterpenoid compounds in
the fruits of Chaenomeles lagenaria (Loisel.) Koidz. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 23(546–547): 5761998.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Shen H, Cheng T, Qiao C, Su Z and Li C:
Antitumor effect in vitro and immuno-response in vivo of fructus
Mume. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 20:365–368. 1995.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alvarado HL, Abrego G, Garduño-Ramirez ML,
Clares B, Calpena AC and García ML: Design and optimization of
oleanolic/ursolic acid-loaded nanoplatforms for ocular
anti-inflammatory applications. Nanomedicine. 11:521–530. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L and Liu CM: Ursolic
acid protects mouse liver against CCl4-induced oxidative stress and
inflammation by the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
37:975–983. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Gupta SC,
Tyagi AK and Aggarwal BB: Ursolic acid inhibits the growth of human
pancreatic cancer and enhances the antitumor potential of
gemcitabine in an orthotopic mouse model through suppression of the
inflammatory microenvironment. Oncotarget. 7:13182–13196. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang ZH, Hsu CC, Huang CN and Yin MC:
Anti-glycative effects of oleanolic acid and ursolic acid in kidney
of diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 628:255–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ma JQ, Ding J, Xiao ZH and Liu CM: Ursolic
acid ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative DNA damage
and inflammation in mouse kidney by inhibiting the STAT3 and NF-κB
activities. Int Immunopharmacol. 21:389–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu Z, Gu Z, Sun M, Zhang K, Gao P, Yang Q
and Yuan Y: Ursolic acid improves survival and attenuates lung
injury in septic rats induced by cecal ligation and puncture. J
Surg Res. 194:528–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen X, Wan Y, Zhou T, Li J and Wei Y:
Ursolic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury in a mouse model. Immunotherapy. 5:39–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Oh SJ, Kim JH and Chung DH: NOD2-mediated
suppression of CD55 on neutrophils enhances C5a generation during
polymicrobial sepsis. PLoS Pathog. 9:e10033512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Huang J, Li Y, Chang R, Wu H, Lin
J and Huang Z: Exogenous carbon monoxide decreases sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury and inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation in
rats. Int J Mol Sci. 16:20595–20608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Johns EJ, O'Shaughnessy B, O'Neill S, Lane
B and Healy V: Impact of elevated dietary sodium intake on NAD(P)H
oxidase and SOD in the cortex and medulla of the rat kidney. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 299:R234–R240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li X, Wang X, Zheng M and Luan QX:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species mediate the
lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory response in human
gingival fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 347:212–221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Closa D and Folch-Puy E: Oxygen free
radicals and the systemic inflammatory response. IUBMB Life.
56:185–191. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leslie KL, Song GJ, Barrick S, Wehbi VL,
Vilardaga JP, Bauer PM and Bisello A: Ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding
phosphoprotein 50 (EBP50) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB): A
feed-forward loop for systemic and vascular inflammation. J Biol
Chem. 288:36426–36436. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Souza AC, Volpini RA, Shimizu MH, Sanches
TR, Camara NO, Semedo P, Rodrigues CE, Seguro AC and Andrade L:
Erythropoietin prevents sepsis-related acute kidney injury in rats
by inhibiting NF-κB and upregulating endothelial nitric oxide
synthase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F1045–F1054. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Galley HF, Davies MJ and Webster NR:
Xanthine oxidase activity and free radical generation in patients
with sepsis syndrome. Crit Care Med. 24:1649–1653. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao H, Liu Z, Shen H, Jin S and Zhang S:
Glycyrrhizic acid pretreatment prevents sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury via suppressing inflammation, apoptosis and oxidative
stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 781:92–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yao L, Liu Z, Zhu J, Li B, Chai C and Tian
Y: Clinical evaluation of circulating microRNA-25 level change in
sepsis and its potential relationship with oxidative stress. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7675–7684. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Q, Yu W, Shi J, Shen J, Gao T, Zhang
J, Xi F, Li J and Li N: Insulin alleviates the inflammatory
response and oxidative stress injury in cerebral tissues in septic
rats. J Inflamm (Lond). 11:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
He L, Peng X, Zhu J, Chen X, Liu H, Tang
C, Dong Z, Liu F and Peng Y: Mangiferin attenuate sepsis-induced
acute kidney injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Am J Nephrol. 40:441–450. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sedlár M, Kudrnová Z, Erhart D, Trca S,
Kvasnicka J, Krska Z, Mazoch J, Malíková I, Zeman M and Linhart A:
Older age and type of surgery predict the early inflammatory
response to hip trauma mediated by interleukin-6 (IL-6). Arch
Gerontol Geriatr. 51:e1–e6. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Canault M, Peiretti F, Mueller C, Kopp F,
Morange P, Rihs S, Portugal H, Juhan-Vague I and Nalbone G:
Exclusive expression of transmembrane TNF-alpha in mice reduces the
inflammatory response in early lipid lesions of aortic sinus.
Atherosclerosis. 172:211–218. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kajahn J, Franz S, Rueckert E, Forstreuter
I, Hintze V, Moeller S and Simon JC: Artificial extracellular
matrices composed of collagen I and high sulfated hyaluronan
modulate monocyte to macrophage differentiation under conditions of
sterile inflammation. Biomatter. 2:226–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moldawer LL: Interleukin-1, TNF alpha and
their naturally occurring antagonists in sepsis. Blood Purif.
11:128–133. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Wang Y, Ning Q, Gong C, Zhang Y,
Zhang L, Bu X and Jing G: The role of spleen in the treatment of
experimental lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis with
dexmedetomidine. Springerplus. 4:8002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu H, Liu J, Li W, Liu G and Li Z:
LncRNA-HOTAIR promotes TNF-α production in cardiomyocytes of
LPS-induced sepsis mice by activating NF-κB pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 471:240–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Luo CJ, Luo F, Zhang L, Xu Y, Cai GY, Fu
B, Feng Z, Sun XF and Chen XM: Knockout of interleukin-17A protects
against sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Ann Intensive Care.
6:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ogiku M, Kono H, Hara M, Tsuchiya M and
Fujii H: Interleukin-17A plays a pivotal role in polymicrobial
sepsis according to studies using IL-17A knockout mice. J Surg Res.
174:142–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|