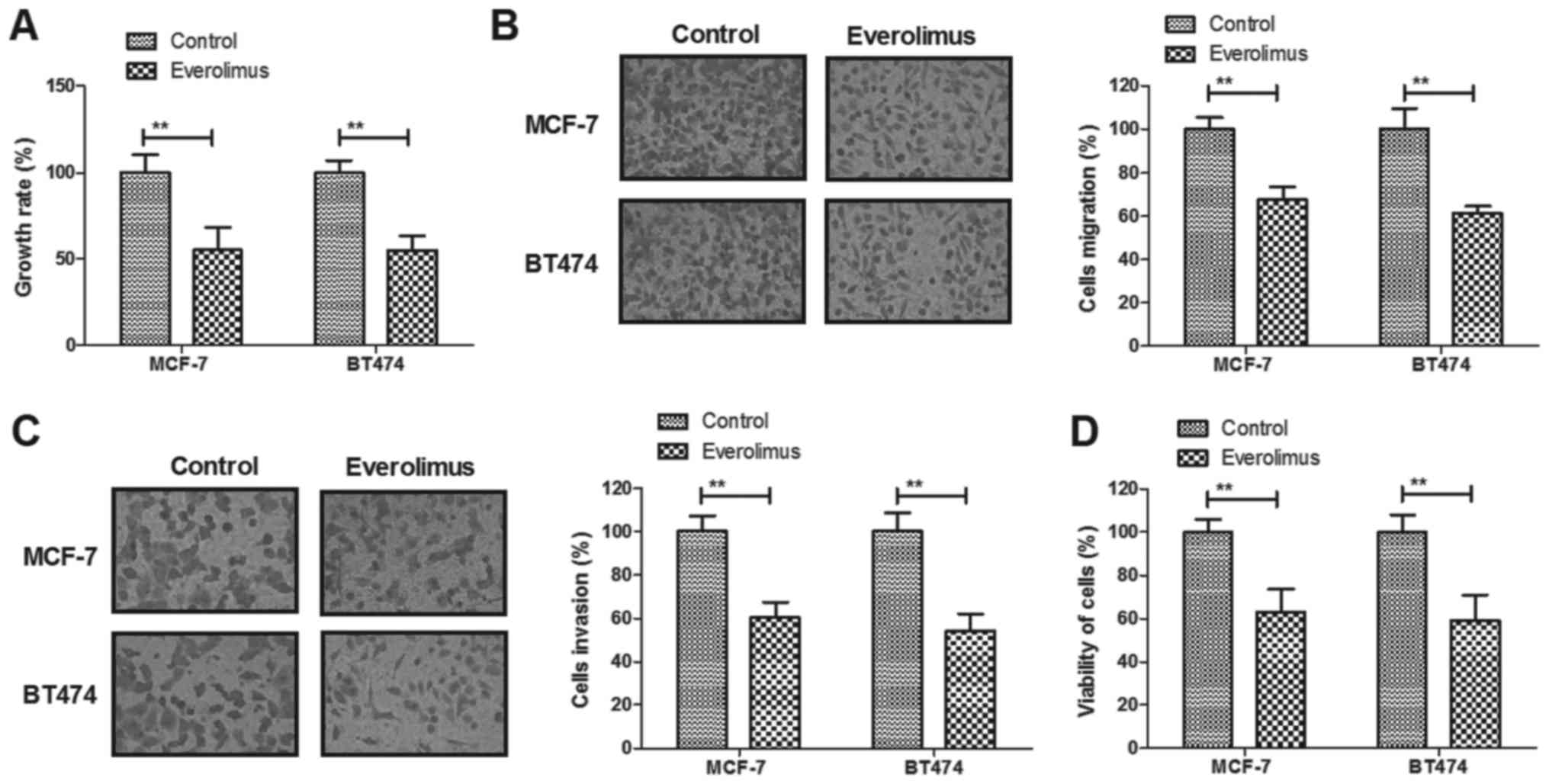
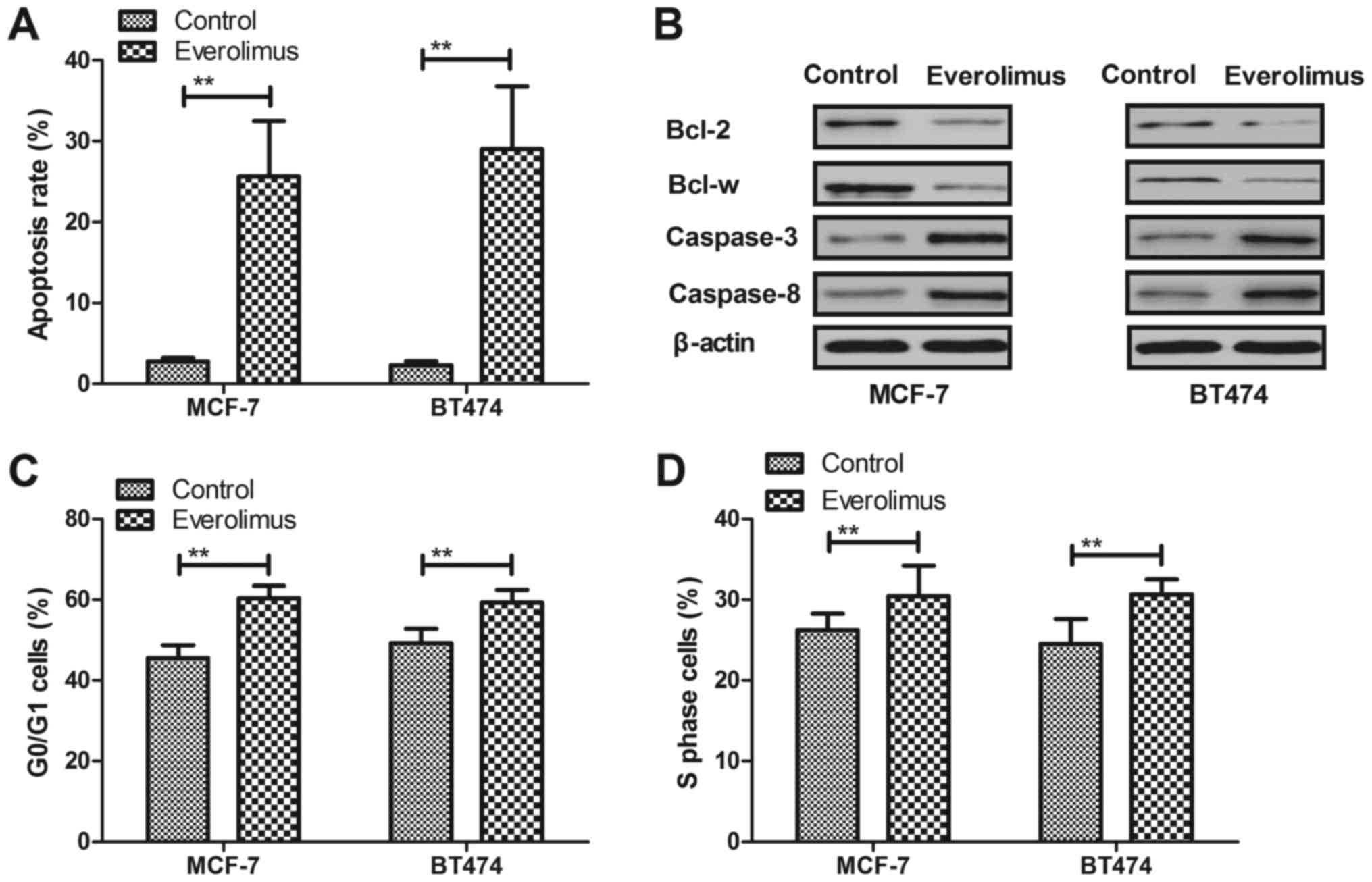
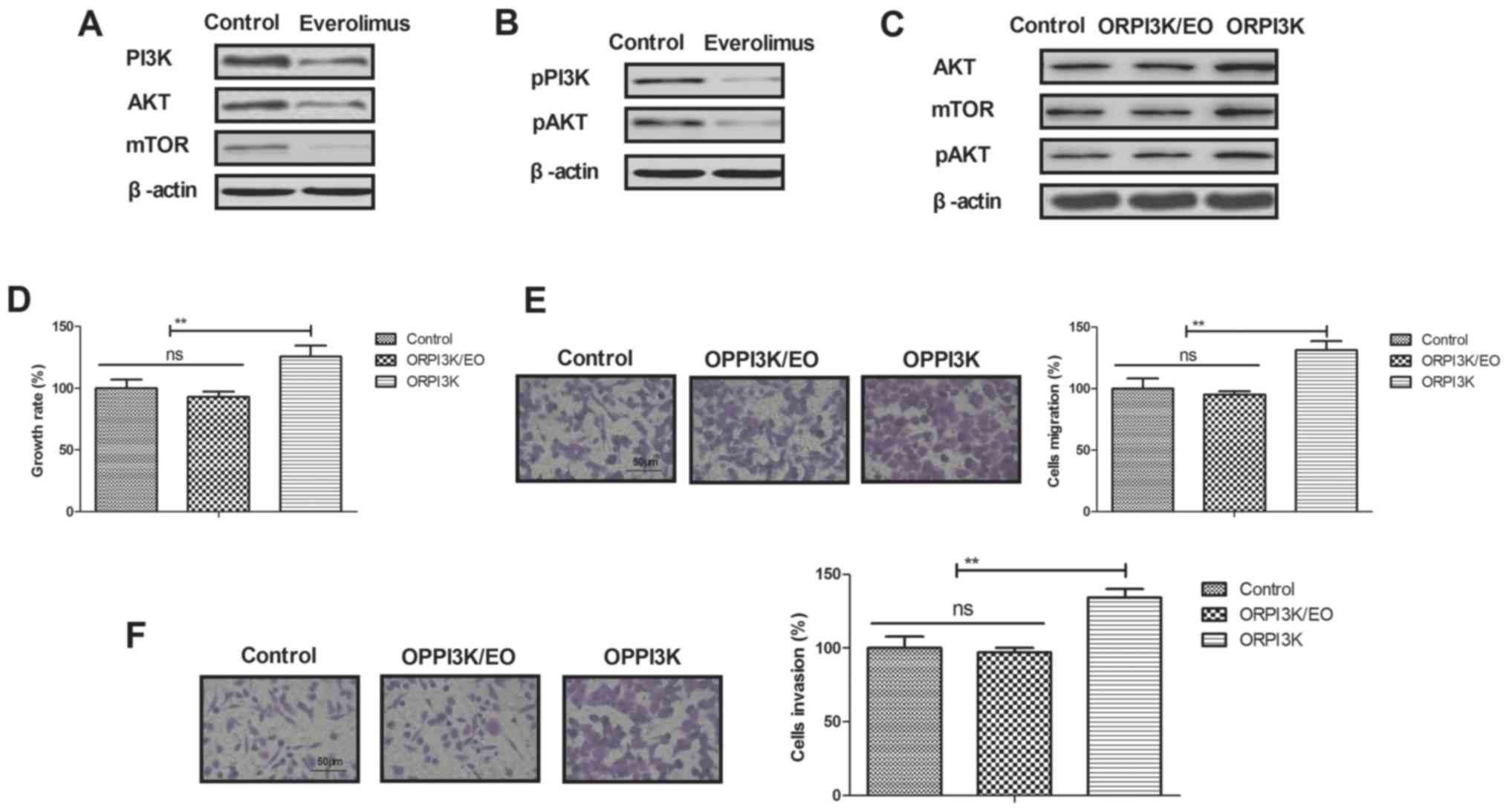
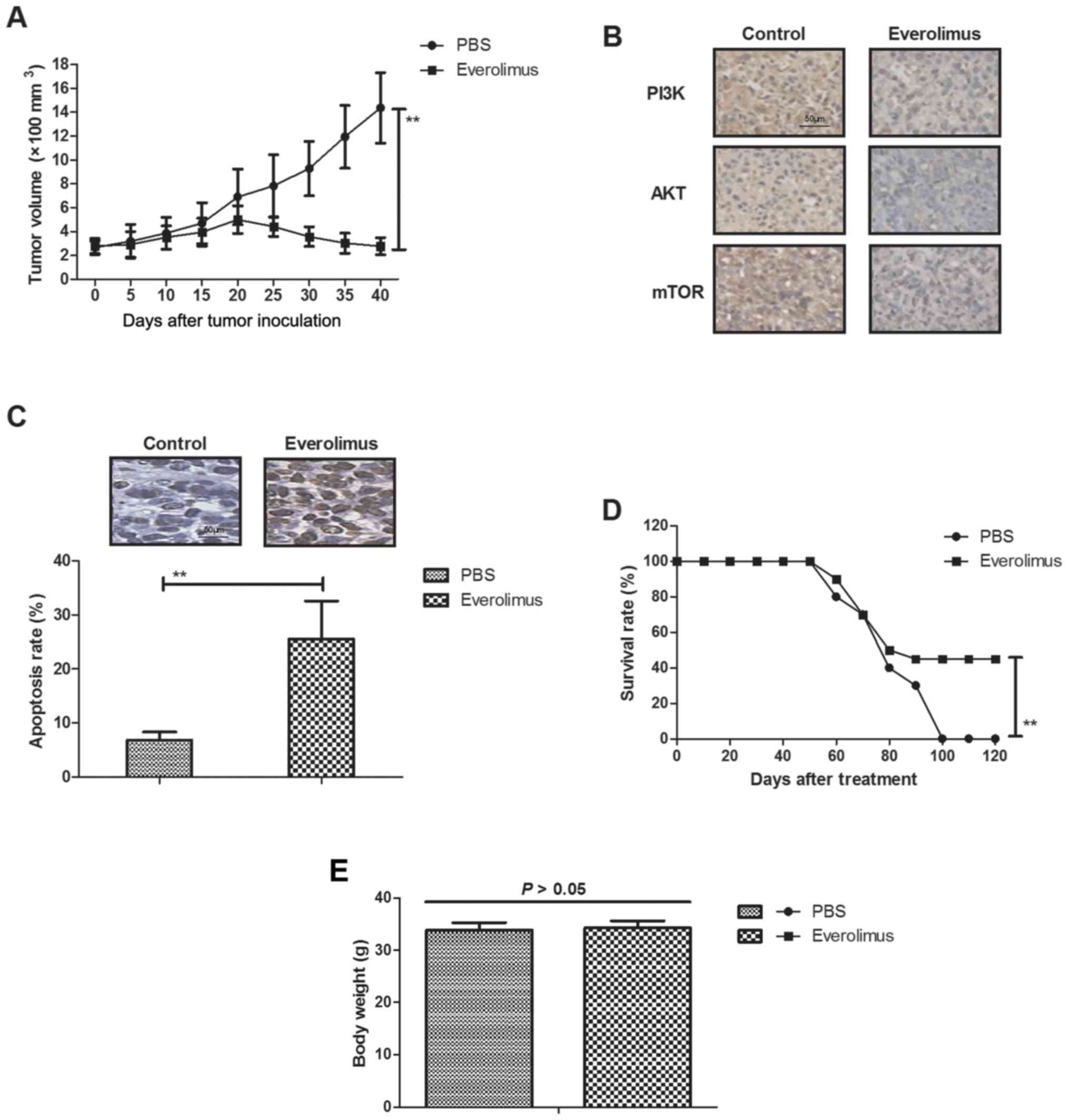
|
1
|
Schipper RJ, Moossdorff M, Beets-Tan RGH,
Smidt ML and Lobbes MBI: Noninvasive nodal restaging in clinically
node positive breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant systemic
therapy: A systematic review. Eur J Radiol. 84:41–47. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jansen LA, Backstein RM and Brown MH:
Breast size and breast cancer: A systematic review. J Plast
Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 67:1615–1623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ziyadi M, Boujoual M, Raiteb H, Babahabib
MA, Kouach J, Moussaoui DR and Dehayni M: Squamous cell carcinoma
of the breast: Report of a case and review of the literature. Pan
Afr Med J. 24:2132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zagelbaum NK, Ward MF II, Okby N and
Karpoff H: Invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast with
osteoclast-like giant cells and clear cell features: A case report
of a novel finding and review of the literature. World J Surg
Oncol. 14:2272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vogl TJ, Farshid P, Naguib NN and Zangos
S: Thermal ablation therapies in patients with breast cancer liver
metastases: A review. Eur Radiol. 23:797–804. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergenfeldt M, Jensen BV, Skjoldbye B and
Nielsen D: Liver resection and local ablation of breast cancer
liver metastases - a systematic review. Eur J Surg Oncol.
37:549–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hamelinck VC, Bastiaannet E, Pieterse AH,
Jannink I, van de Velde CJ, Liefers GJ and Stiggelbout AM:
Patients' preferences for surgical and adjuvant systemic treatment
in early breast cancer: A systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:1005–1018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sawesi S, Carpenter JS and Jones J:
Reasons for nonadherence to tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors for
the treatment of breast cancer: A literature review. Clin J Oncol
Nurs. 18:E50–E57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hidding JT, Beurskens CH, van der Wees PJ,
van Laarhoven HW and Nijhuis-van der Sanden MW: Treatment related
impairments in arm and shoulder in patients with breast cancer: A
systematic review. PLoS One. 9:e967482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hurvitz SA, Andre F, Jiang Z, Shao Z, Mano
MS, Neciosup SP, Tseng LM, Zhang Q, Shen K, Liu D, et al:
Combination of everolimus with trastuzumab plus paclitaxel as
first-line treatment for patients with HER2-positive advanced
breast cancer (BOLERO-1): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind,
multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:816–829. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yardley DA, Noguchi S, Pritchard KI,
Burris HA III, Baselga J, Gnant M, Hortobagyi GN, Campone M,
Pistilli B, Piccart M, et al: Everolimus plus exemestane in
postmenopausal patients with HR(+) breast cancer: BOLERO-2 final
progression-free survival analysis. Adv Ther. 30:870–884. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Amato RJ, Flaherty A, Zhang Y, Ouyang F
and Mohlere V: Clinical prognostic factors associated with outcome
in patients with renal cell cancer with prior tyrosine kinase
inhibitors or immunotherapy treated with everolimus. Urol Oncol.
32:345–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pritchard KI, Burris HA III, Ito Y, Rugo
HS, Dakhil S, Hortobagyi GN, Campone M, Csöszi T, Baselga J,
Puttawibul P, et al: Safety and efficacy of everolimus with
exemestane vs. exemestane alone in elderly patients with
HER2-negative, hormone receptor-positive breast cancer in BOLERO-2.
Clin Breast Cancer. 13:421–432. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sendur MA, Zengin N, Aksoy S and Altundag
K: Everolimus: A new hope for patients with breast cancer. Curr Med
Res Opin. 30:75–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Renshaw A and Elsheikh TM: A validation
study of the focalpoint GS imaging system for gynecologic cytology
screening. Cancer Cytopathol. 121:737–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Macaskill EJ, Bartlett JM, Sabine VS,
Faratian D, Renshaw L, White S, Campbell FM, Young O, Williams L,
Thomas JS, et al: The mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor
everolimus (RAD001) in early breast cancer: Results of a
pre-operative study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:725–734. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Minckwitz G, Eidtmann H, Loibl S,
Blohmer JU, Costa SD, Fasching PA, Kreienberg R, Hilfrich J, Gerber
B, Hanusch C, et al: Integrating bevacizumab, everolimus, and
lapatinib into current neoadjuvant chemotherapy regimen for primary
breast cancer. Safety results of the GeparQuinto trial. Ann Oncol.
22:301–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morrow PK, Wulf GM, Ensor J, Booser DJ,
Moore JA, Flores PR, Xiong Y, Zhang S, Krop IE, Winer EP, et al:
Phase I/II study of trastuzumab in combination with everolimus
(RAD001) in patients with HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast
cancer who progressed on trastuzumab-based therapy. J Clin Oncol.
29:3126–3132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jerusalem G, Fasolo A, Dieras V, Cardoso
F, Bergh J, Vittori L, Zhang Y, Massacesi C, Sahmoud T and Gianni
L: Phase I trial of oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in combination
with trastuzumab and vinorelbine in pre-treated patients with
HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 125:447–455. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andre F, Campone M, O'Regan R, Manlius C,
Massacesi C, Sahmoud T, Mukhopadhyay P, Soria JC, Naughton M and
Hurvitz SA: Phase I study of everolimus plus weekly paclitaxel and
trastuzumab in patients with metastatic breast cancer pretreated
with trastuzumab. J Clin Oncol. 28:5110–5115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Modesto A, Gandy C, Mery E, Filleron T,
Massabeau C, Izar F, Charitansky H, Roché H and de Lafontan B:
Breast ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion: Pathological
review and clinical implications. Cancer Radiother. 18:107–110.
2014.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Falco G, Buggi F, Sanna PA, Dubini A and
Folli S: Breast metastases from a renal cell carcinoma. A case
report and review of the literature. Int J Surg Case Rep.
5:193–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fulda S: Exploiting mitochondrial
apoptosis for the treatment of cancer. Mitochondrion. 10:598–603.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milanesa DM, Choudhury MS, Mallouh C,
Tazaki H and Konno S: Methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis in human
prostate carcinoma: Potential modality for prostate cancer
treatment. Eur Urol. 37:728–734. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng T and Dou QP: Everolimus inhibits
growth of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells via
induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis and G2/M arrest. J Cell
Biochem. 118:2722–2730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Papadopoulos EI, Yousef GM and Scorilas A:
Cytotoxic activity of sunitinib and everolimus in Caki-1 renal
cancer cells is accompanied by modulations in the expression of
apoptosis-related microRNA clusters and BCL2 family genes. Biomed
Pharmacother. 70:33–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu B, Li J, Pan J, Huang B, Liu J and
Zheng D: Everolimus enhances the cytotoxicity of bendamustine in
multiple myeloma cells through a network of pro-apoptotic and
cell-cycle-progression regulatory proteins. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 45:683–691. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Saunders PO, Weiss J, Welschinger R, Baraz
R, Bradstock KF and Bendall LJ: RAD001 (everolimus) induces
dose-dependent changes to cell cycle regulation and modifies the
cell cycle response to vincristine. Oncogene. 32:4789–4797. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shtivelband MI: Everolimus in hormone
receptor-positive advanced breast cancer: Targeting receptor-based
mechanisms of resistance. Breast. 22:405–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bodnar L, Stec R, Cierniak S, Synowiec A,
Wcisło G, Jesiotr M, Koktysz R, Kozłowski W and Szczylik C:
Clinical usefulness of PI3K/Akt/mTOR genotyping in companion with
other clinical variables in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
patients treated with everolimus in the second and subsequent
lines. Ann Oncol. 26:1385–1389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leung EY, Askarian-Amiri M, Finlay GJ,
Rewcastle GW and Baguley BC: Potentiation of growth inhibitory
responses of the mTOR inhibitor everolimus by dual mTORC1/2
inhibitors in cultured breast cancer cell lines. PLoS One.
10:e01314002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Zhang X, Liu J, Hou G, Zhang S and
Zhang J: Everolimus in combination with letrozole inhibit human
breast cancer MCF-7/Aro stem cells via PI3K/mTOR pathway: An
experimental study. Tumour Biol. 35:1275–1286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen X, Zhao M, Hao M, Sun X, Wang J, Mao
Y, Zu L, Liu J, Shen Y, Wang J and Shen K: Dual inhibition of PI3K
and mTOR mitigates compensatory AKT activation and improves
tamoxifen response in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 11:1269–1278.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Generali D, Venturini S, Rognoni C, Ciani
O, Pusztai L, Loi S, Jerusalem G, Bottini A and Tarricone R: A
network meta-analysis of everolimus plus exemestane versus
chemotherapy in the first- and second-line treatment of estrogen
receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 152:95–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie J, Hao Y, Li N, Lin PL, Ohashi E, Koo
V, Signorovitch JE, Wu EQ and Yardley DA: Comparative effectiveness
of everolimus-based therapy versus endocrine monotherapy among
postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2−
metastatic breast cancer: A retrospective chart review in community
oncology practices in the US. Curr Med Res Opin. 31:1095–1103.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hortobagyi GN: Everolimus plus exemestane
for the treatment of advanced breast cancer: A review of
subanalyses from BOLERO-2. Neoplasia. 17:279–288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|