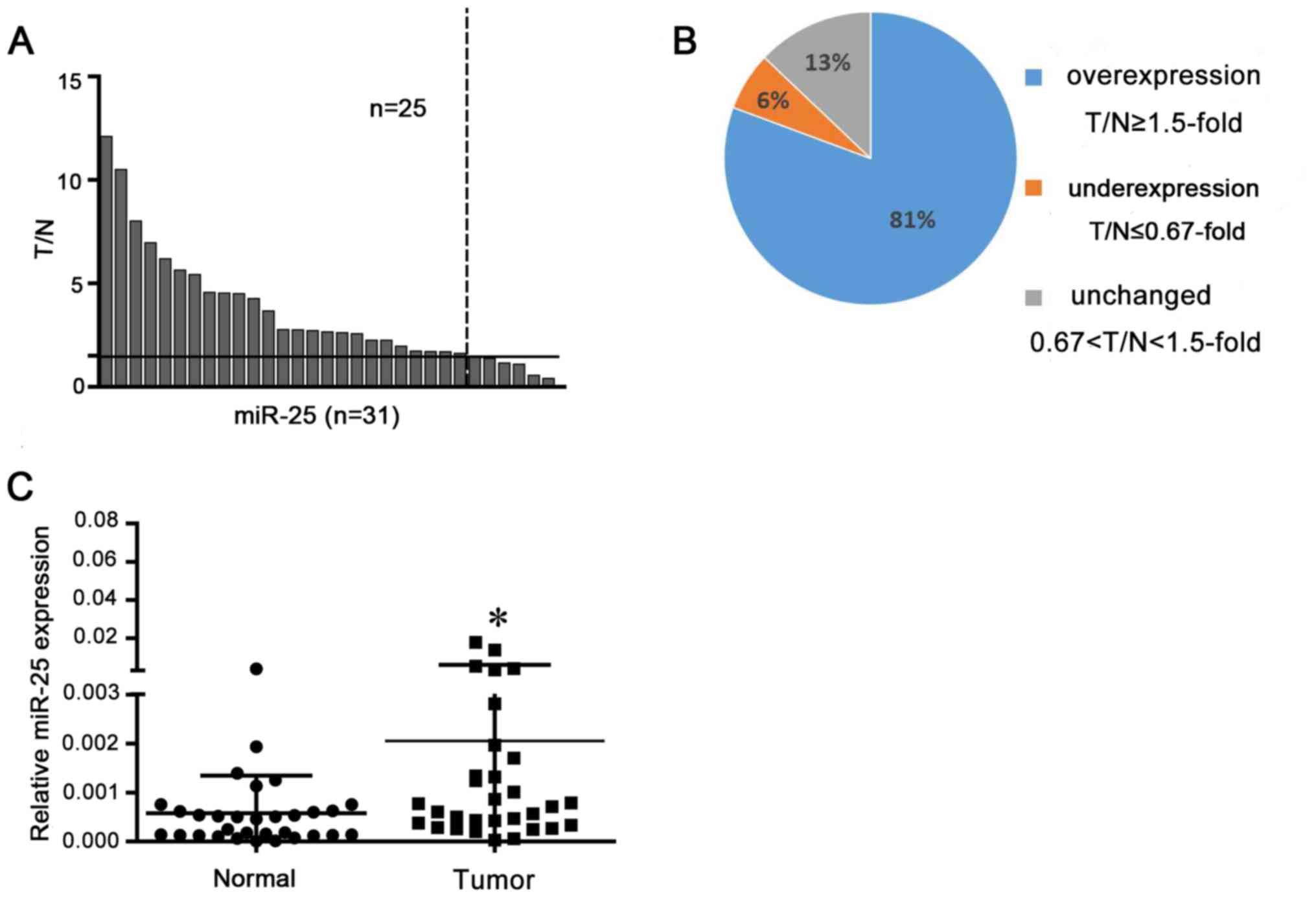
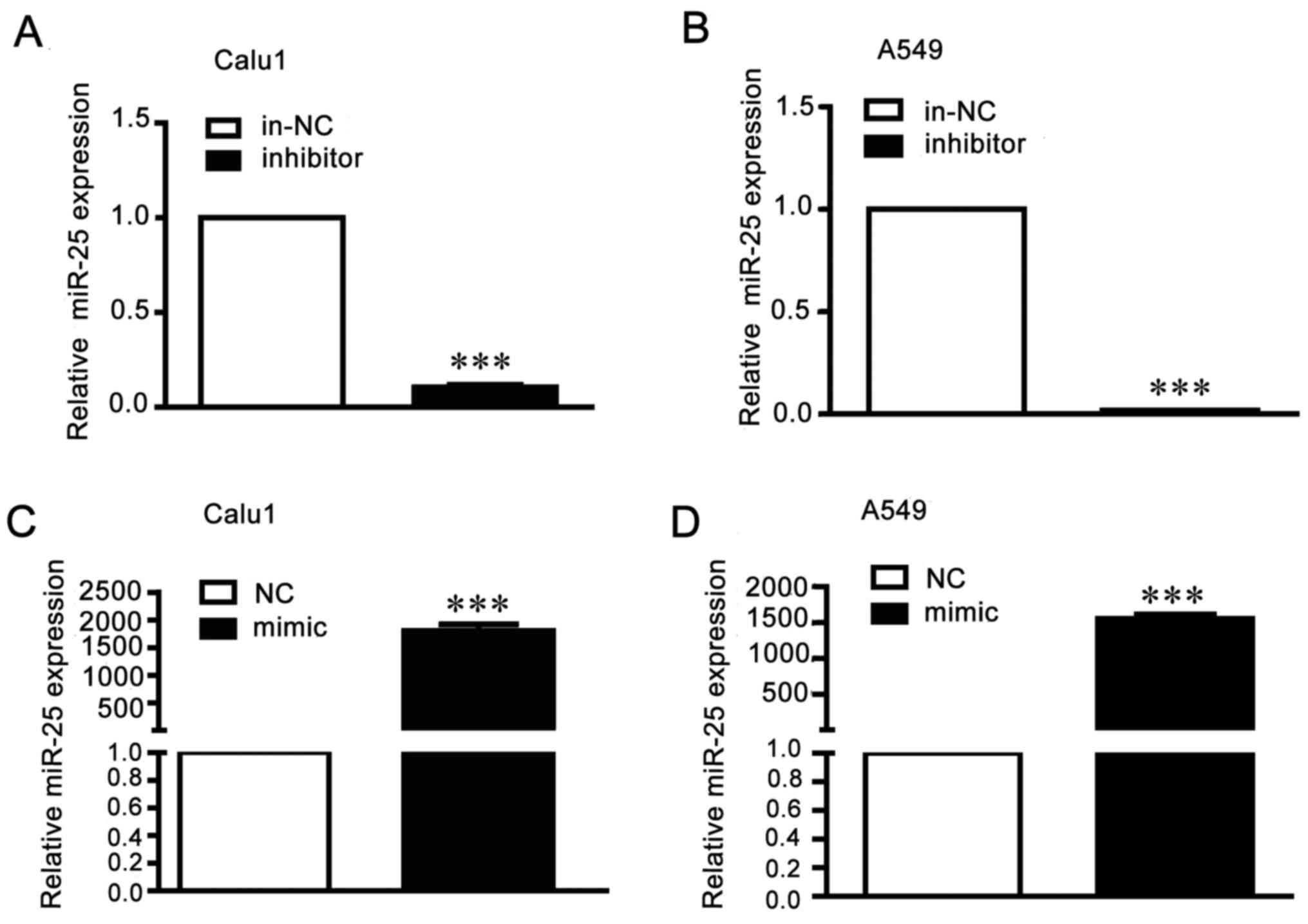
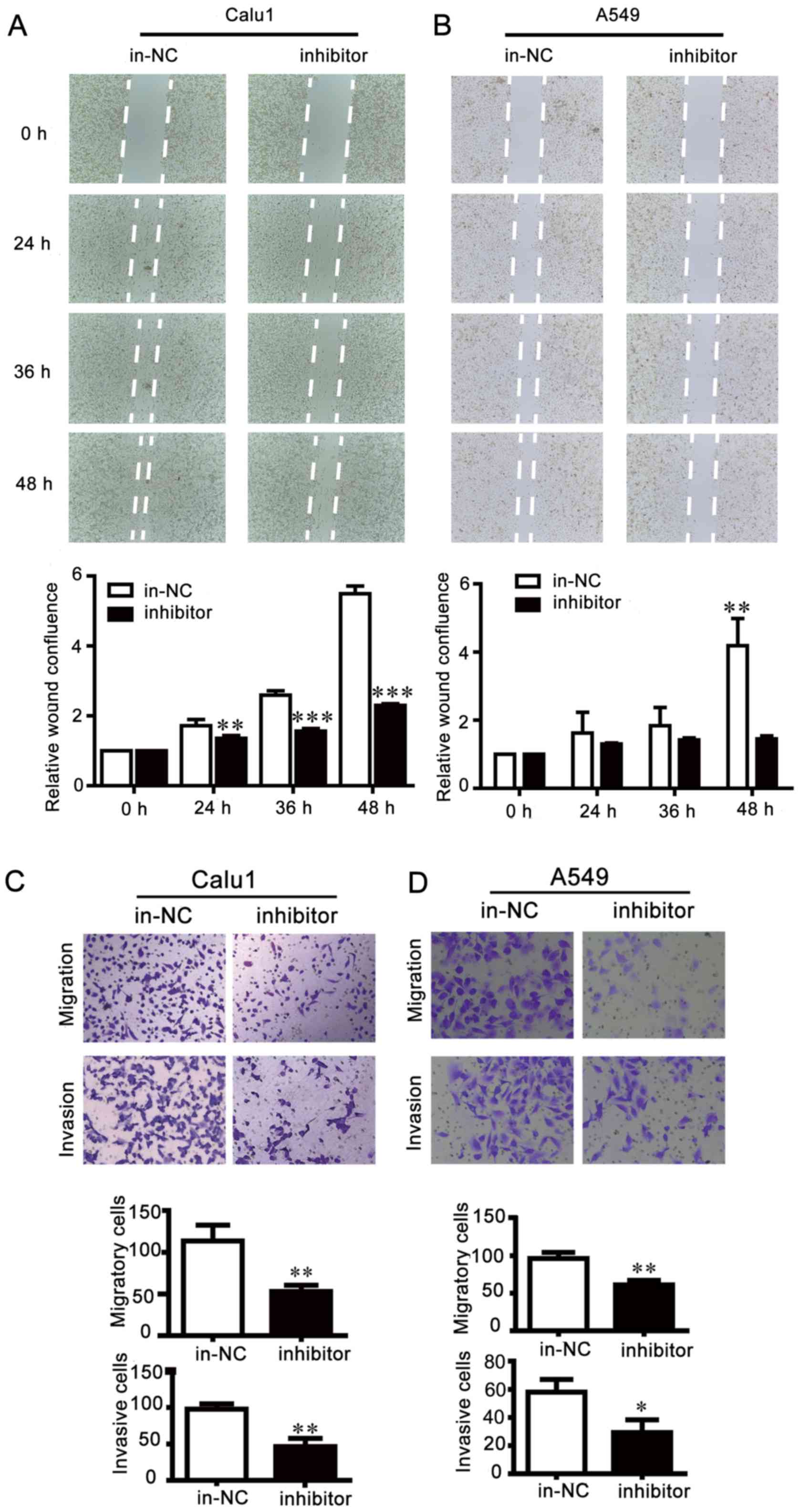
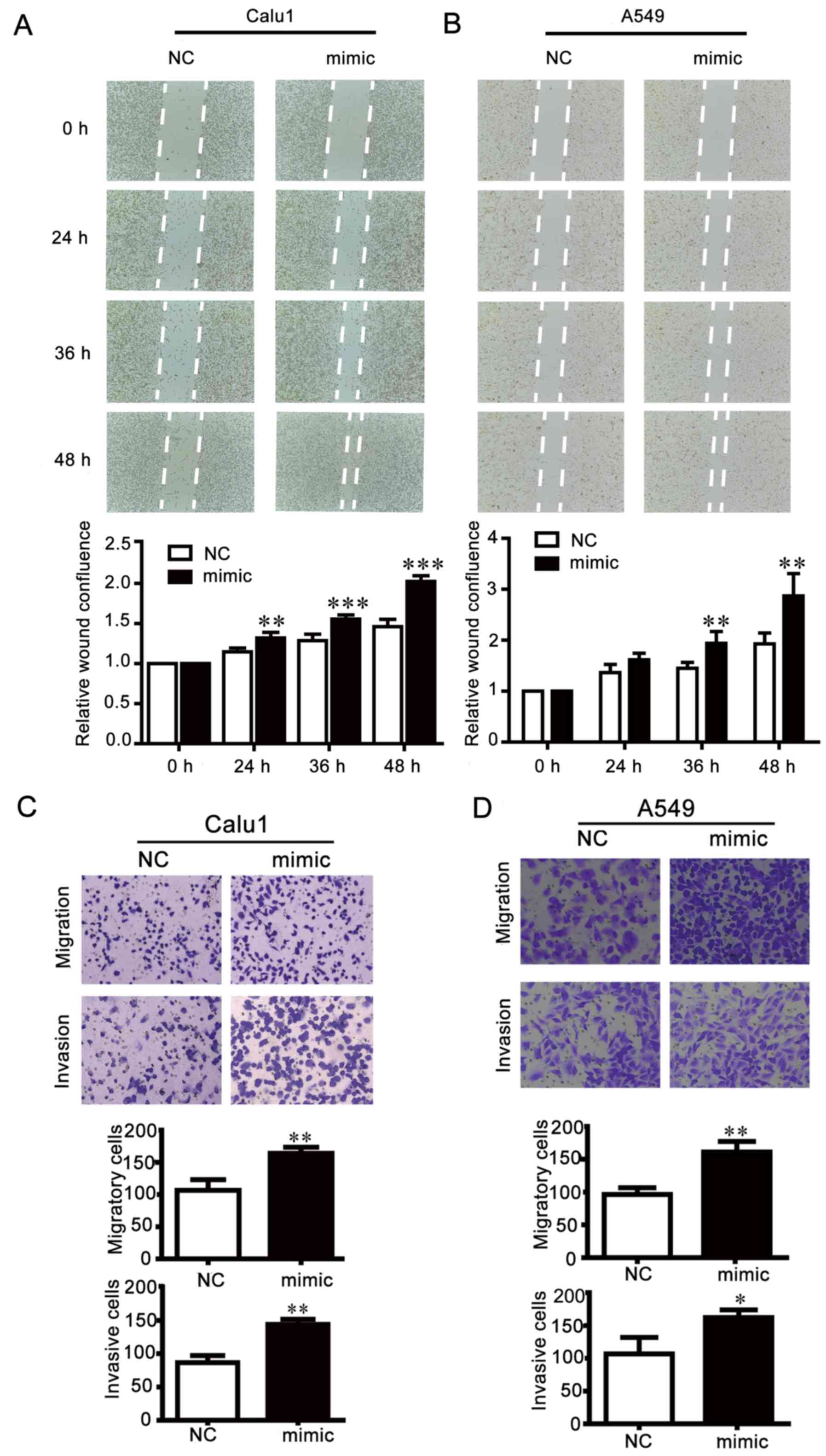
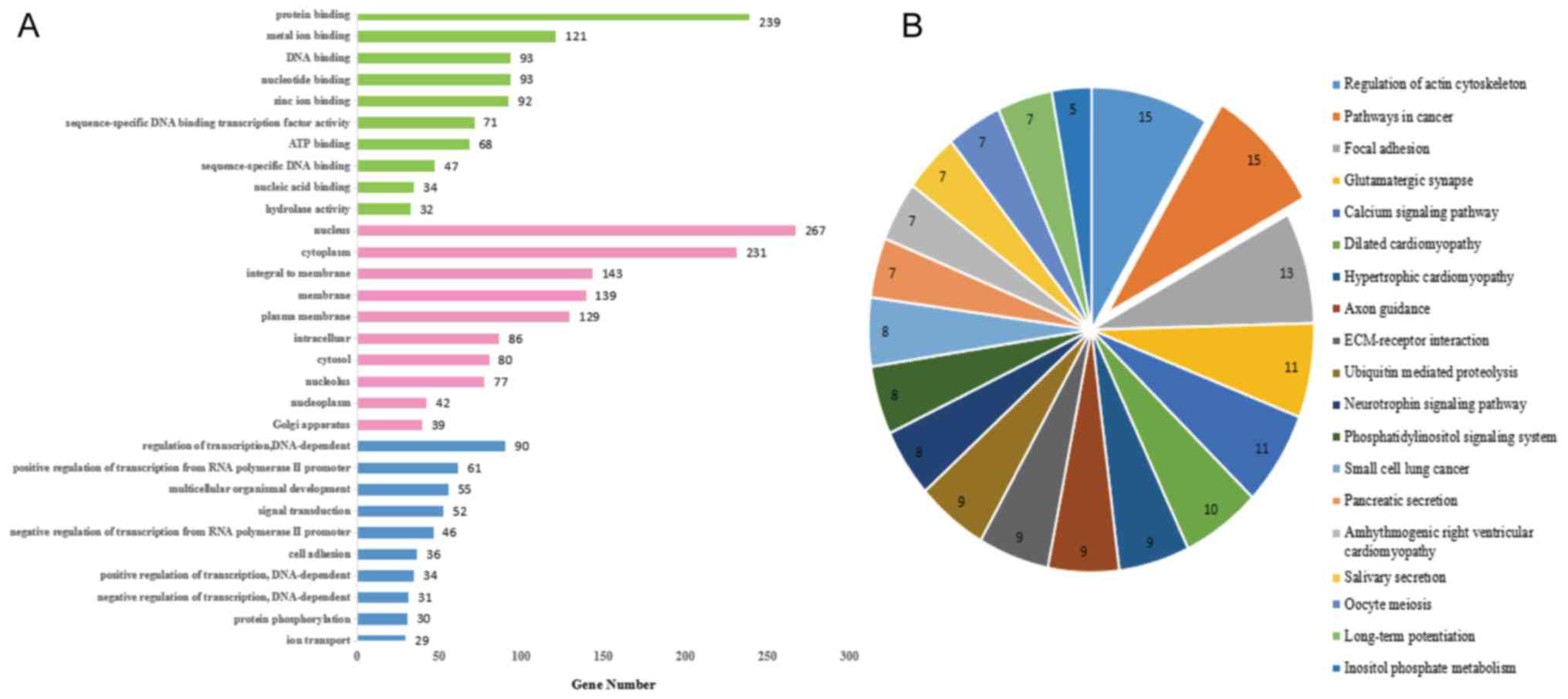
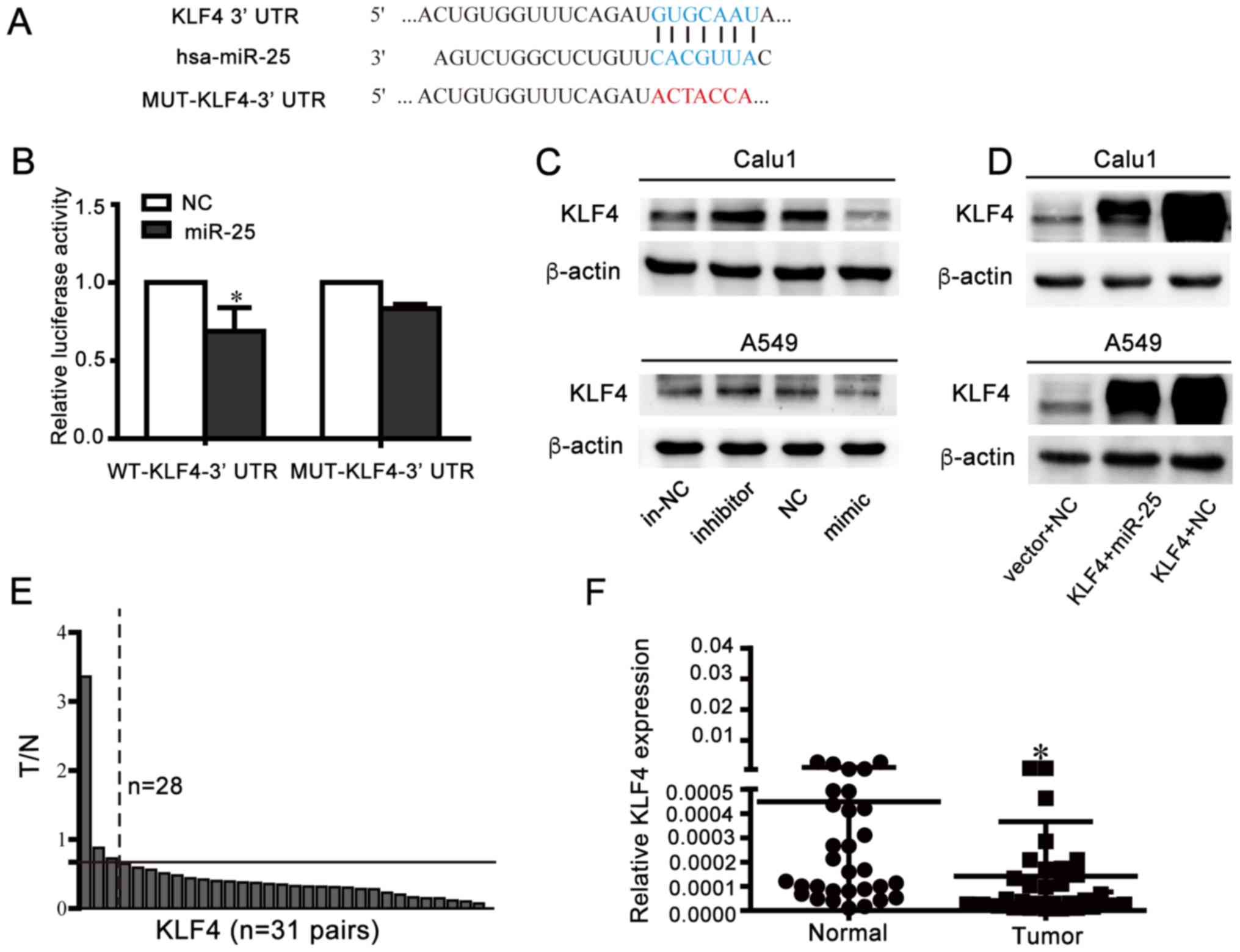
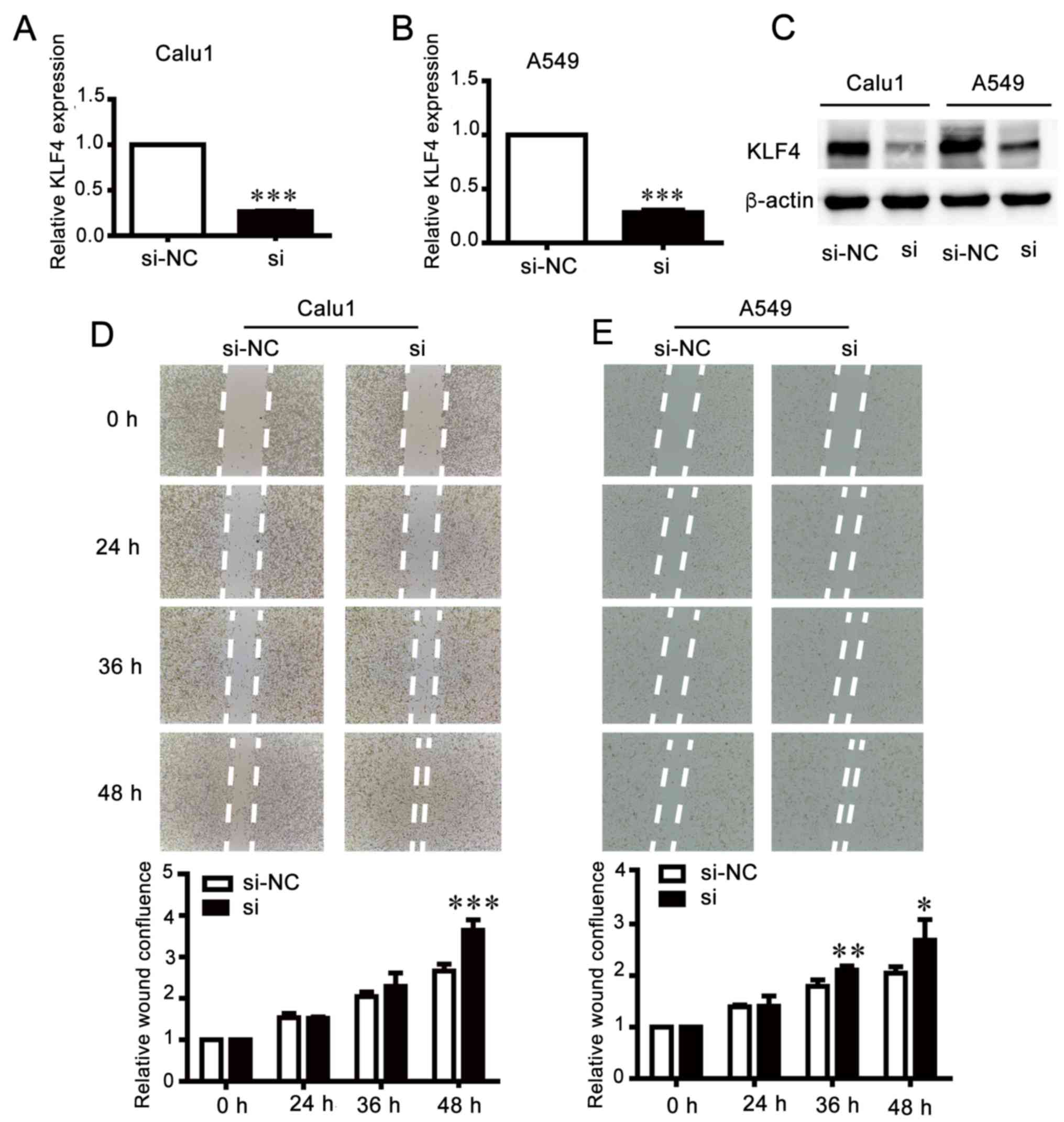
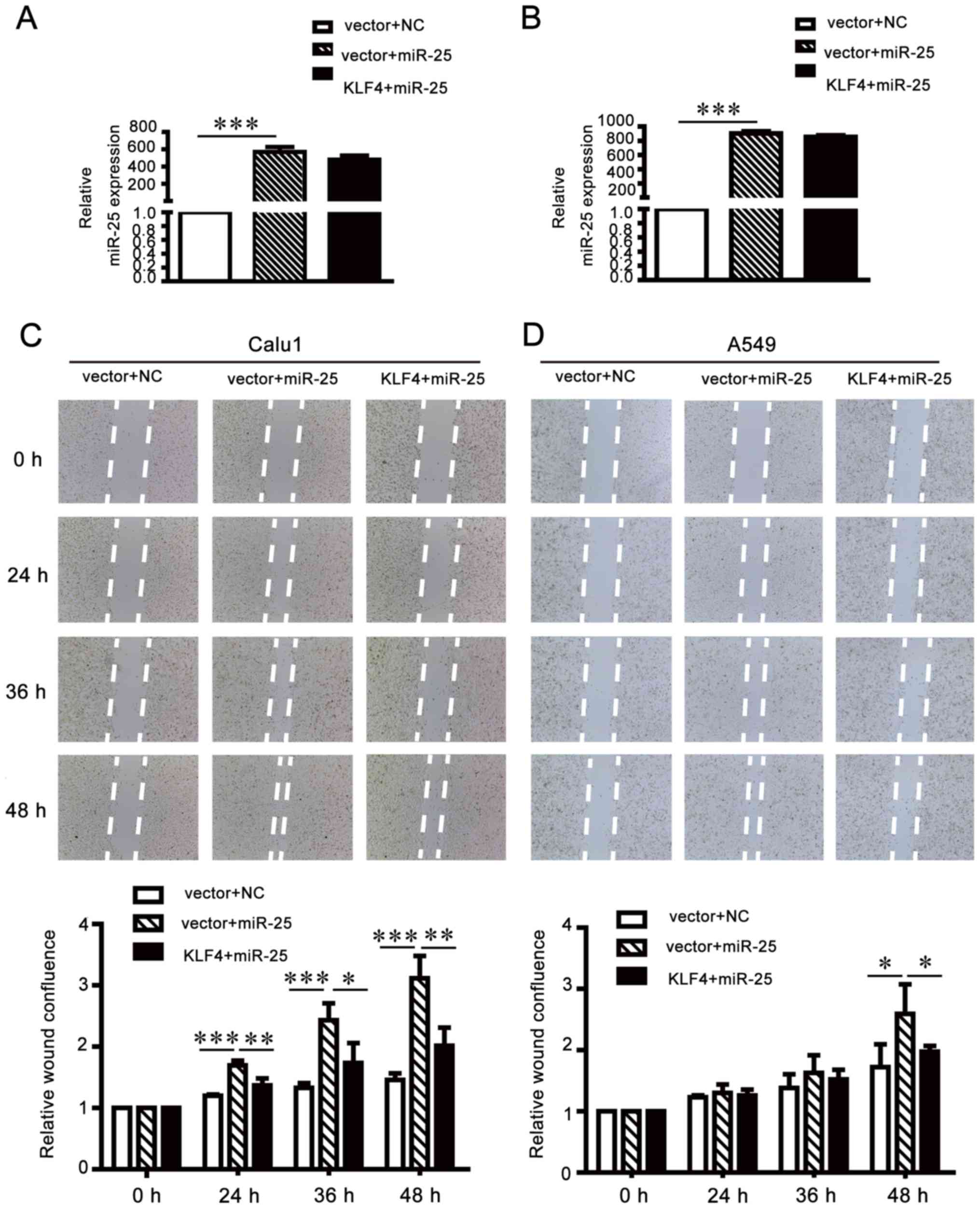
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z, Fillmore CM, Hammerman PS, Kim CF
and Wong KK: Non-small-cell lung cancers: A heterogeneous set of
diseases. Nat Rev Cancer. 14:535–546. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moreira AL and Eng J: Personalized therapy
for lung cancer. Chest. 146:1649–1657. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Preiss A, Rosenberg UB, Kienlin A, Seifert
E and Jäckle H: Molecular genetics of Kruppel, a gene required for
segmentation of the drosophila embryo. Nature. 313:27–32. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shields JM, Christy RJ and Yang VW:
Identification and characterization of a gene encoding a
gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor expressed during growth arrest. J
Biol Chem. 271:20009–20017. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pandya AY, Talley LI, Frost AR, Fitzgerald
TJ, Trivedi V, Chakravarthy M, Chhieng DC, Grizzle WE, Engler JA,
Krontiras H, et al: Nuclear localization of KLF4 is associated with
an aggressive phenotype in early-stage breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:2709–2719. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen YJ, Wu CY, Chang CC, Ma CJ, Li MC and
Chen CM: Nuclear Kruppel-like factor 4 expression is associated
with human skin squamous cell carcinoma progression and metastasis.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:777–782. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang N, Liu ZH, Ding F, Wang XQ, Zhou CN
and Wu M: Down-regulation of gut-enriched Kruppel-like factor
expression in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 8:966–970.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wei D, Gong W, Kanai M, Schlunk C, Wang L,
Yao JC, Wu TT, Huang S and Xie K: Drastic down-regulation of
Kruppel-like factor 4 expression is critical in human gastric
cancer development and progression. Cancer Res. 65:2746–2754. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei D, Kanai M, Huang S and Xie K:
Emerging role of KLF4 in human gastrointestinal cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 27:23–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li X, Li H, Zhang R and Liu J and Liu J:
MicroRNA-449a inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by
directly repressing E2F3 in gastric cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem.
35:2033–2042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang C, Ning S, Li Z, Qin X and Xu W:
miR-22 is down-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and
inhibits cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 14:1382014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q and
Yin Y: Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show
significantly different biological patterns: From functions to
targets. PLoS One. 5:pii: e13067. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xiao P, Liu W and Zhou H: miR-429 promotes
the proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells via targeting
DLC-1. Oncol Lett. 12:2163–2168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu W, Jin P, Ding C and Liu W: miR-19a/b
modulates lung cancer cells metastasis through suppression of MXD1
expression. Oncol Lett. 12:1901–1905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang WM and Liu JC: Effect and molecular
mechanism of mir-146a on proliferation of lung cancer cells by
targeting and regulating MIF gene. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 9:806–811.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang HB, Sun LC, Ling L, Cong LH and Lian
R: miR-143 suppresses the proliferation of NSCLC cells by
inhibiting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Exp Ther Med.
12:1795–1802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shi H, Ji Y, Zhang D, Liu Y and Fang P:
MicroRNA-3666-induced suppression of SIRT7 inhibits the growth of
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 36:3051–3057. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perepelyuk M, Maher C, Lakshmikuttyamma A
and Shoyele SA: Aptamer-hybrid nanoparticle bioconjugate
efficiently delivers miRNA-29b to non-small-cell lung cancer cells
and inhibits growth by downregulating essential oncoproteins. Int J
Nanomedicine. 11:3533–3544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Petrocca F, Vecchione A and Croce CM:
Emerging role of miR-106b-25/miR-17-92 clusters in the control of
transforming growth factor beta signaling. Cancer Res.
68:8191–8194. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Savita U and Karunagaran D:
MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster targets β-TRCP2, increases the expression
of Snail and enhances cell migration and invasion in H1299 (non
small cell lung cancer) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:841–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su ZX, Zhao J, Rong ZH, Geng WM, Wu YG and
Qin CK: Upregulation of microRNA-25 associates with prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 9:472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li BS, Zuo QF, Zhao YL, Xiao B, Zhuang Y,
Mao XH, Wu C, Yang SM, Zeng H, Zou QM and Guo G: MicroRNA-25
promotes gastric cancer migration, invasion and proliferation by
directly targeting transducer of ERBB2, 1 and correlates with poor
survival. Oncogene. 34:2556–2565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou J, Wang J, Wu S, Zhu S, Wang S, Zhou
H, Tian X, Tang N and Nie S: Angiopoietin-like protein 2 negatively
regulated by microRNA-25 contributes to the malignant progression
of colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Med. 34:1286–1292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu T, Chen W, Kong D, Li X, Lu H, Liu S,
Wang J, Du L, Kong Q, Huang X and Lu Z: miR-25 targets the
modulator of apoptosis 1 gene in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis.
36:925–935. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiang J, Hang JB, Che JM and Li HC: MiR-25
is up-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer and promotes cell
proliferation and motility by targeting FBXW7. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:9147–9153. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Wang J, Yang Y, Hao B, Wang R, Li
Y and Wu Q: Loss of has-miR-337-3p expression is associated with
lymph node metastasis of human gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 32:762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Zhai Y, Yu D, Cui J, Hu JF and Li
W: Valproic acid enhances iPSC induction from human bone
marrow-derived cells through the suppression of
reprogramming-induced senescence. J Cell Physiol. 231:1719–1727.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhai Y, Chen X, Yu D, Li T, Cui J, Wang G,
Hu JF and Li W: Histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid
promotes the induction of pluripotency in mouse fibroblasts by
suppressing reprogramming-induced senescence stress. Exp Cell Res.
337:61–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Patel RS, Carter G, El Bassit G, Patel AA,
Cooper DR, Murr M and Patel NA: Adipose-derived stem cells from
lean and obese humans show depot specific differences in their stem
cell markers, exosome contents and senescence: Role of protein
kinase C delta (PKCδ) in adipose stem cell niche. Stem Cell
Investig. 3:22016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xu Q, Liu M, Zhang J, Xue L, Zhang G, Hu
C, Wang Z, He S, Chen L, Ma K, et al: Overexpression of KLF4
promotes cell senescence through microRNA-203-survivin-p21 pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:60290–60302. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu T, Chen X, Zhang W, Liu J, Avdiushko R,
Napier DL, Liu AX, Neltner JM, Wang C, Cohen D and Liu C: KLF4
regulates adult lung tumor-initiating cells and represses
K-Ras-mediated lung cancer. Cell Death Differ. 23:207–215. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hu W, Jia Y, Xiao X, Lv K, Chen Y, Wang L,
Luo X, Liu T, Li W, Li Y, et al: KLF4 downregulates hTERT
expression and telomerase activity to inhibit lung carcinoma
growth. Oncotarget. 7:52870–52887. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu W, Hofstetter WL, Li H, Zhou Y, He Y,
Pataer A, Wang L, Xie K, Swisher SG and Fang B: Putative
tumor-suppressive function of Kruppel-like factor 4 in primary lung
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5688–5695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zheng B, Han M, Bernier M, Zhang XH, Meng
F, Miao SB, He M, Zhao XM and Wen JK: Kruppel-like factor 4
inhibits proliferation by platelet-derived growth factor receptor
beta-mediated, not by retinoic acid receptor alpha-mediated,
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and ERK signaling in vascular smooth
muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 284:22773–22785. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|