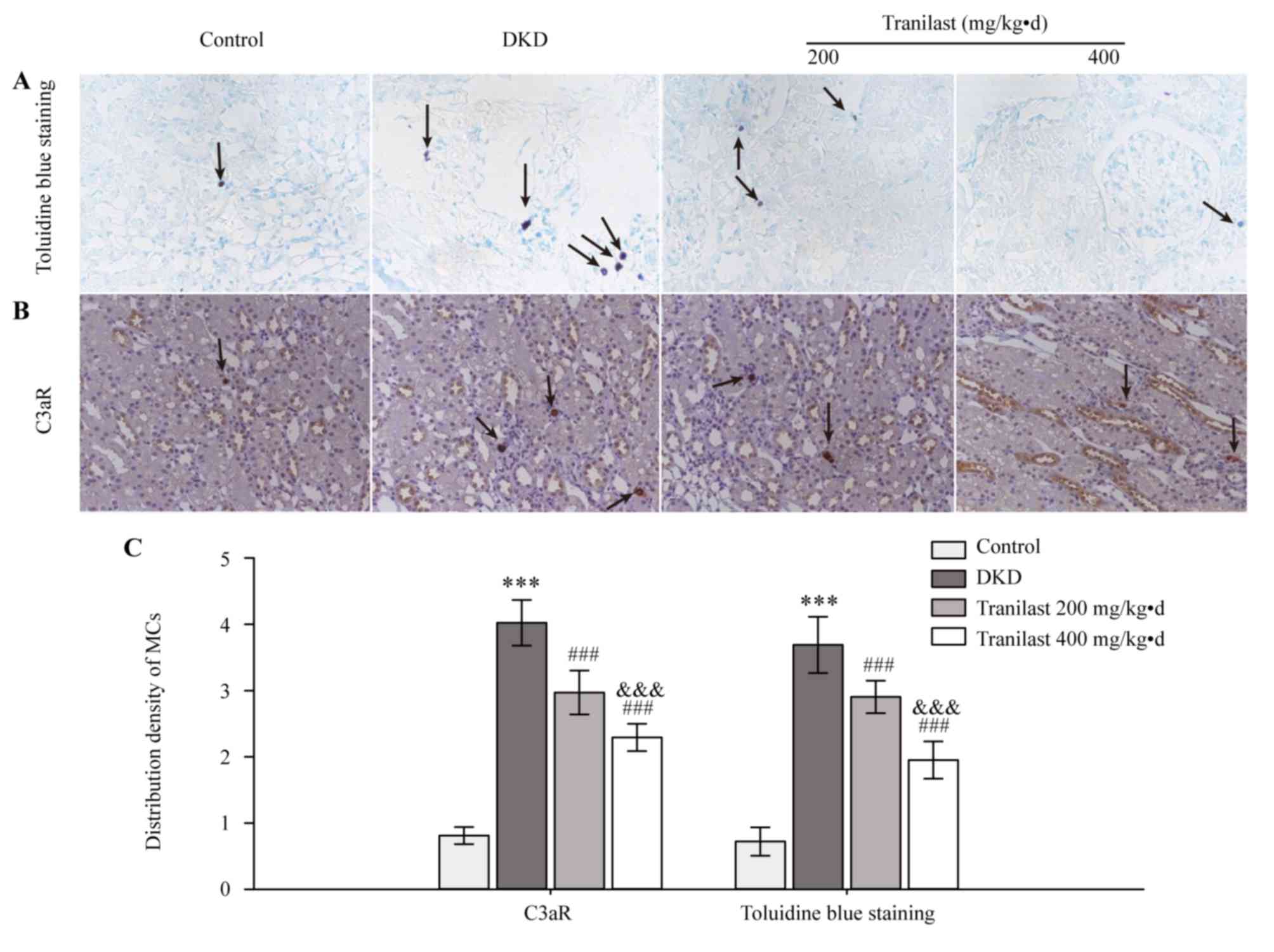
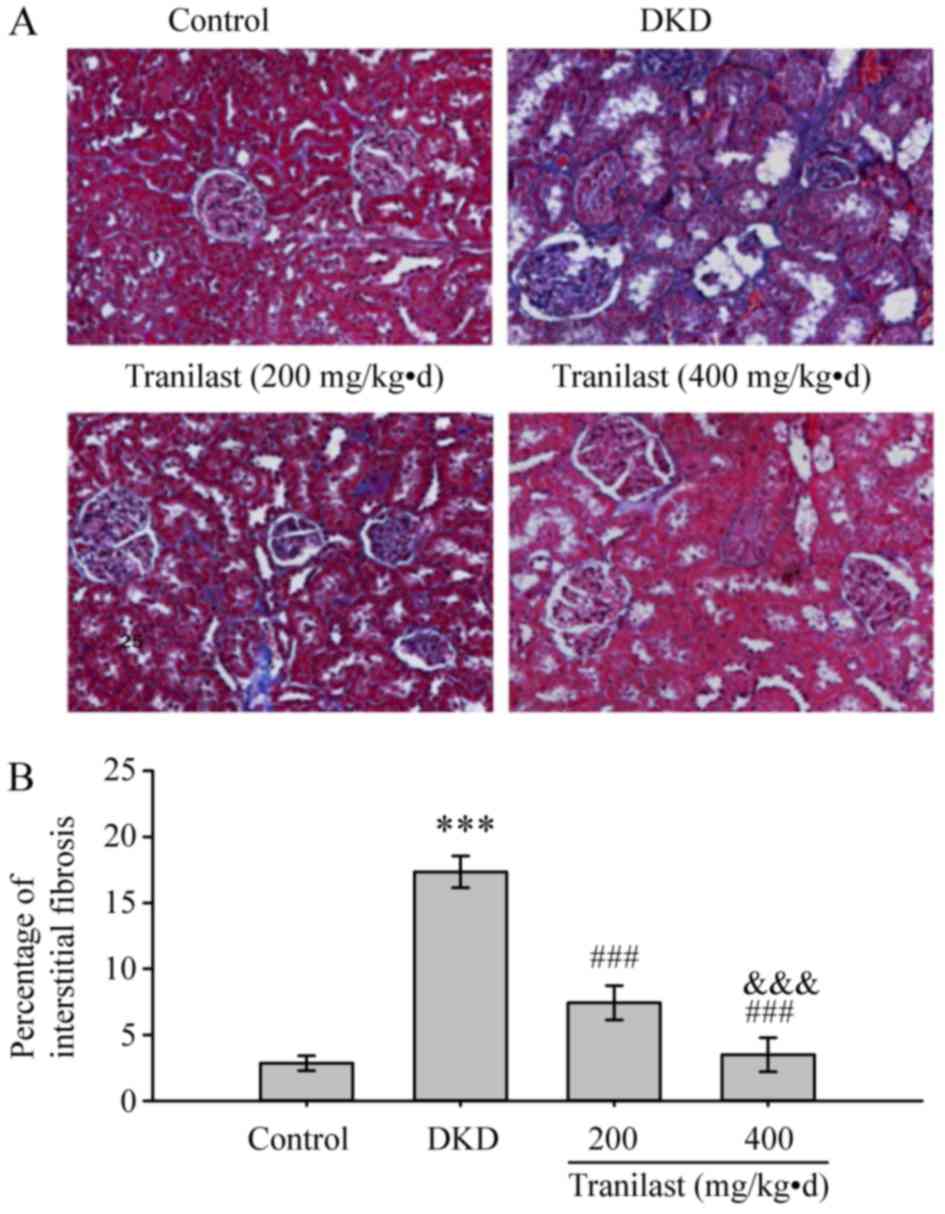
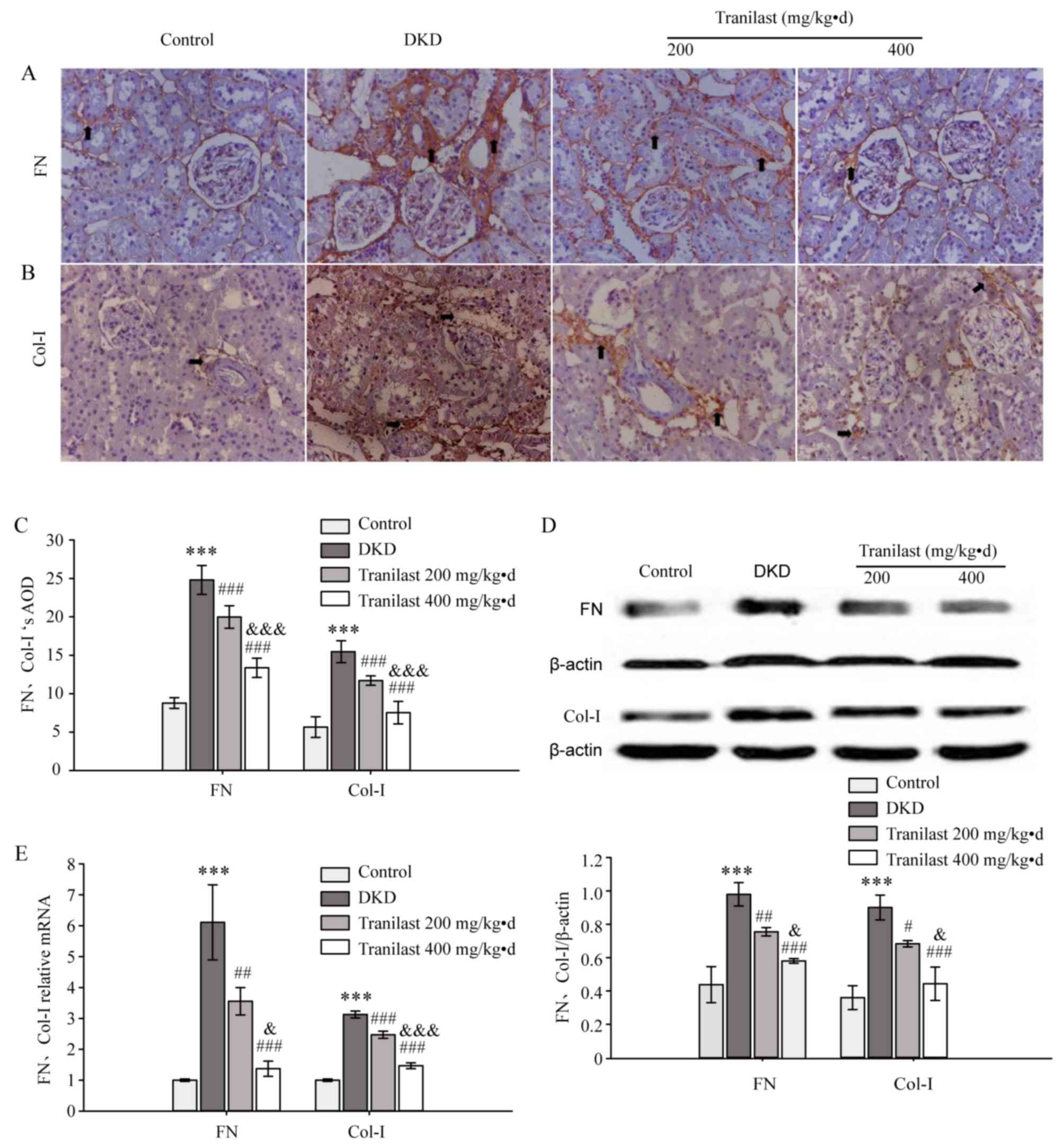
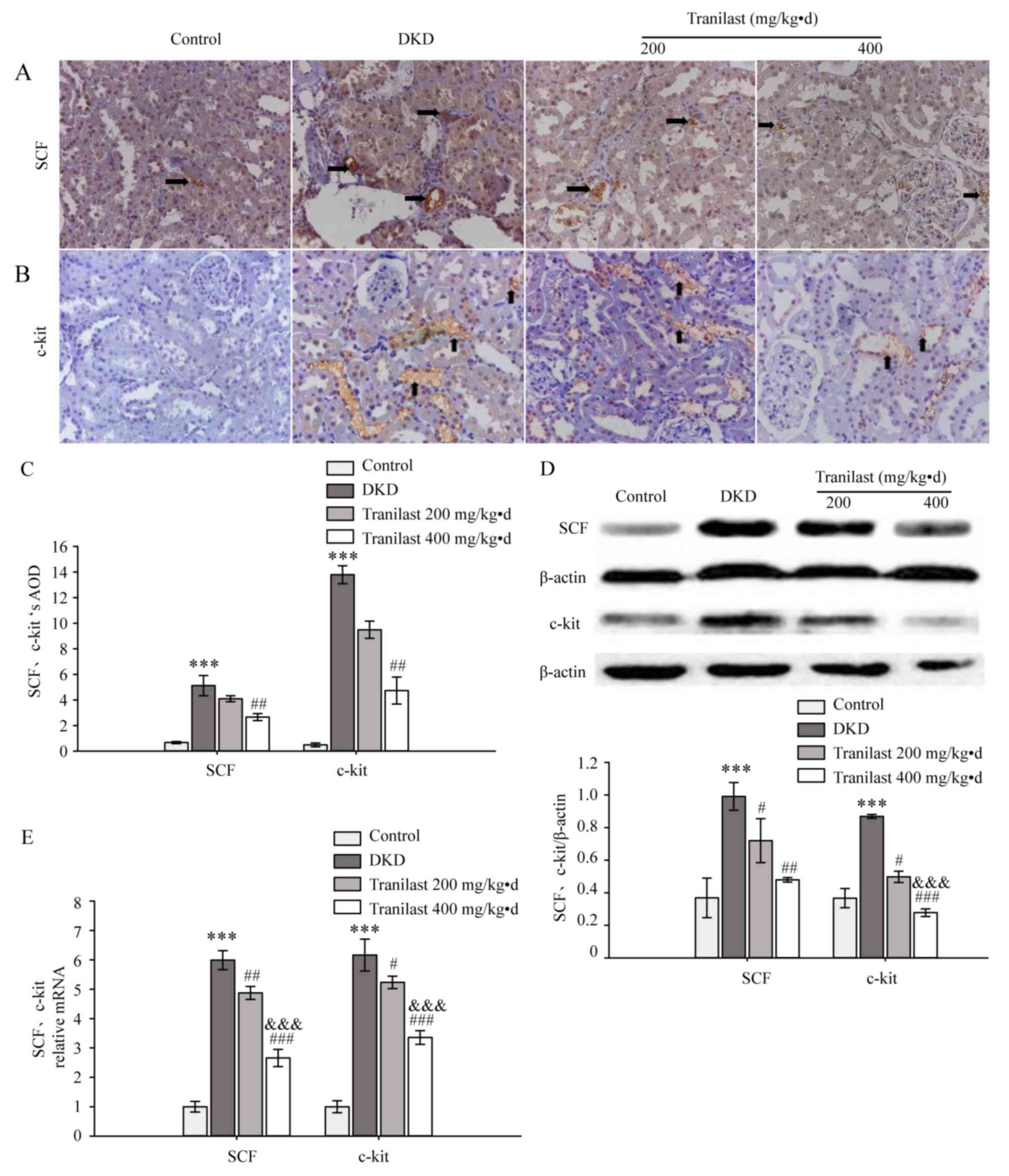
|
1
|
Liu ZH: Nephrology in China. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 9:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen
AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Haas M, de Heer
E, et al: Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:556–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Najafian B, Alpers CE and Fogo AB:
Pathology of human diabetic nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol.
170:36–47. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Elmarakby AA and Sullivan JC: Relationship
between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in diabetic
nephropathy. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:49–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moresco RN, Sangoi MB, De Carvalho JA,
Tatsch E and Bochi GV: Diabetic nephropathy: Traditional to
proteomic markers. Clin Chim Acta. 421:17–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng JM, Yao GH, Cheng Z, Wang R and Liu
ZH: Pathogenic role of mast cells in the development of diabetic
nephropathy: A study of patients at different stages of the
disease. Diabetologia. 55:801–811. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Darakhshan S and Pour AB: Tranilast: A
review of its therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Res. 91:15–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaneyama T, Kobayashi S, Aoyagi D and
Ehara T: Tranilast modulates fibrosis, epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and peritubular capillary injury in unilateral ureteral
obstruction rats. Pathology. 42:564–573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kazama I, Baba A, Endo Y, Toyama H, Ejima
Y, Matsubara M and Tachi M: Mast cell involvement in the
progression of peritoneal fibrosis in rats with chronic renal
failure. Nephrology (Carlton). 20:609–616. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
See F, Watanabe M, Kompa AR, Wang BH,
Boyle AJ, Kelly DJ, Gilbert RE and Krum H: Early and delayed
tranilast treatment reduces pathological fibrosis following
myocardial infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 22:122–132. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tao Y, Hu L, Li S, Liu Q, Wu X, Li D, Fu
P, Wei D and Luo Z: Tranilast prevents the progression of chronic
cyclosporine nephrotoxicity through regulation of transforming
growth factor β/Smad pathways. Transplant Proc. 43:pp. 1985–1988.
2011; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan SM, Zhang Y, Cox AJ, Kelly DJ and Qi
W: Tranilast attenuates the up-regulation of
thioredoxin-interacting protein and oxidative stress in an
experimental model of diabetic nephropathy. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 26:100–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y, Chen Q, Liu FY, Peng YM, Hou T, Duan
SB, Li J, Luo JH, Sun L and Ling GH: Norcantharidin attenuates
tubulointerstitial fibrosis in rat models with diabetic
nephropathy. Ren Fail. 33:233–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: A model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katz A, Caramori ML, Sisson-Ross S,
Groppoli T, Basgen JM and Mauer M: An increase in the cell
component of the cortical interstitium antedates interstitial
fibrosis in type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 61:2058–2066.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Ding J, Jiao H, Honardoust D,
Momtazi M, Shankowsky HA and Tredget EE: Human hypertrophic
scar-like nude mouse model: Characterization of the molecular and
cellular biology of the scar process. Wound Repair Regen.
19:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z,
Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY and Yang CW: Chronic kidney
disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 382:260–272.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Wang F, Wang L, Wang W, Liu B,
Liu J, Chen M, He Q, Liao Y, Yu X, et al: Prevalence of chronic
kidney disease in China: A cross-sectional survey. Lancet.
379:815–822. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Slyne J, Slattery C, McMorrow T and Ryan
MP: New developments concerning the proximal tubule in diabetic
nephropathy: In vitro models and mechanisms. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 4 30 Suppl:iv60–iv67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Eddy AA: Overview of the cellular and
molecular basis of kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 4:2–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Cellular
mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 1. Common and organ-specific
mechanisms associated with tissue fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 304:C216–C225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ribatti D and Crivellato E: Mast cell
ontogeny: An historical overview. Immunol Lett. 159:11–14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Madjene LC, Pons M, Danelli L, Claver J,
Ali L, Madera-Salcedo IK, Kassas A, Pellefigues C, Marquet F, Dadah
A, et al: Mast cells in renal inflammation and fibrosis: Lessons
learnt from animal studies. Mol Immunol. 63:86–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaczmarczyk K, Kosalka J, Soja J,
Kuzniewski M, Musial J and Okon K: Renal interstitial mast cell
counts differ across classes of proliferative lupus nephritis.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 52:218–224. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu H, Liu F, Peng Y, Liu Y, Li L, Tu X,
Cheng M, Xu X, Chen X, Ling G and Sun L: Role of mast cells, stem
cell factor and protease-activated receptor-2 in tubulointerstitial
lesions in IgA nephropathy. Inflamm Res. 59:551–559. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Zhou L, Liu F, Peng Y, Li J, Sun L,
Duan S, Ling G, Chen X, Jiang W and Xia Y: Mast cell infiltration
is involved in renal interstitial fibrosis in a rat model of
protein-overload nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press Res. 33:240–248.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taipale J, Lohi J, Saarinen J, Kovanen PT
and Keski-Oja J: Human mast cell chymase and leukocyte elastase
release latent transforming growth factor-beta 1 from the
extracellular matrix of cultured human epithelial and endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 270:4689–4696. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smrž D, Bandara G, Zhang S, Mock BA,
Beaven MA, Metcalfe DD and Gilfillan AM: A novel KIT-deficient
mouse mast cell model for the examination of human KIT-mediated
activation responses. J Immunol Methods. 390:52–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Halova I, Draberova L and Draber P: Mast
cell chemotaxis-chemoattractants and signaling pathways. Front
Immunol. 3:1192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gilfillan AM and Tkaczyk C: Integrated
signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:218–230. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Miyamoto K, Kobayashi T, Hayashi Y, Zhang
Y, Hara Y, Higashine M, Shiraishi A and Ohashi Y: Involvement of
stem cell factor and c-kit in corneal wound healing in mice. Mol
Vis. 18:1505–1515. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
El Kossi MM, Haylor JL, Johnson TS and El
Nahas AM: Stem cell factor in a rat model of serum nephrotoxic
nephritis. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 108:e1–e10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|