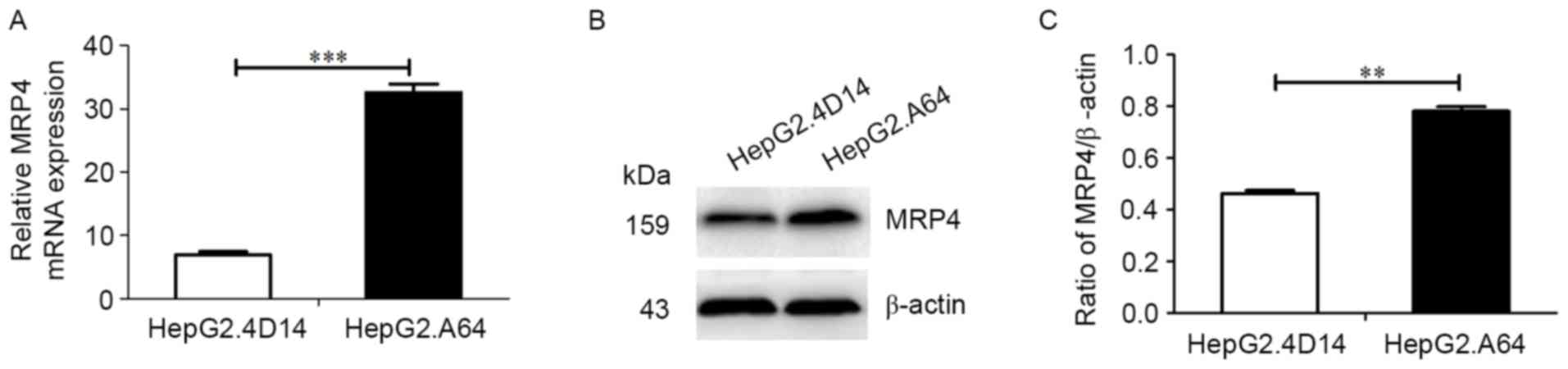
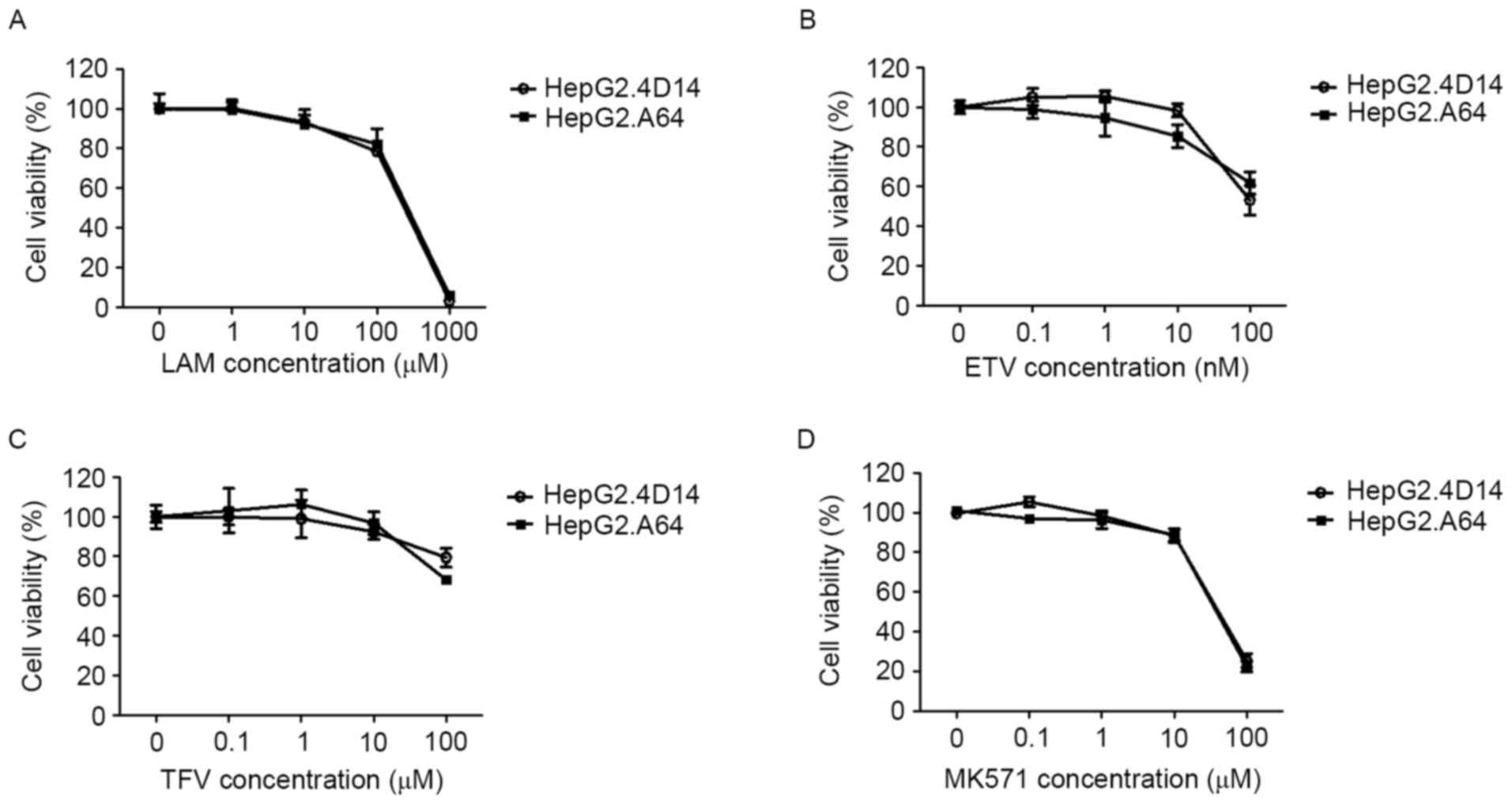
|
1
|
Schuetz JD, Connelly MC, Sun D, Paibir SG,
Flynn PM, Srinivas RV, Kumar A and Fridland A: MRP4: A previously
unidentified factor in resistance to nucleoside-based antiviral
drugs. Nat Med. 5:1048–1051. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sodani K, Patel A, Kathawala RJ and Chen
ZS: Multidrug resistance associated proteins in multidrug
resistance. Chin J Cancer. 31:58–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Imaoka T, Kusuhara H, Adachi M, Schuetz
JD, Takeuchi K and Sugiyama Y: Functional involvement of multidrug
resistance-associated protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) in the renal
elimination of the antiviral drugs adefovir and tenofovir. Mol
Pharmacol. 71:619–627. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fukuda Y, Takenaka K, Sparreboom A,
Cheepala SB, Wu CP, Ekins S, Ambudkar SV and Schuetz JD: Human
immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors interact with ATP
binding cassette transporter 4/multidrug resistance protein 4: A
basis for unanticipated enhanced cytotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol.
84:361–371. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wen J, Luo J, Huang W, Tang J, Zhou H and
Zhang W: The pharmacological and physiological role of
multidrug-resistant protein 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 354:358–375.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takenaka K, Morgan JA, Scheffer GL, Adachi
M, Stewart CF, Sun D, Leggas M, Ejendal KF, Hrycyna CA and Schuetz
JD: Substrate overlap between Mrp4 and Abcg2/Bcrp affects purine
analogue drug cytotoxicity and tissue distribution. Cancer Res.
67:6965–6972. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ray AS, Cihlar T, Robinson KL, Tong L,
Vela JE, Fuller MD, Wieman LM, Eisenberg EJ and Rhodes GR:
Mechanism of active renal tubular efflux of tenofovir. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 50:3297–3304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mu L, Liu X, Li S, Tang F and Yu P:
Determination of intracellular concentrations of nucleoside
analogues and their phosphorylated metabolites. J Mol Pharm Org
Process Res. 2:1122014.doi: 10.4172/2329-9053.1000112.
|
|
9
|
Bushman LR, Kiser JJ, Rower JE, Klein B,
Zheng JH, Ray ML and Anderson PL: Determination of nucleoside
analog mono-, di-, and tri-phosphates in cellular matrix by solid
phase extraction and ultra-sensitive LC-MS/MS detection. J Pharm
Biomed Anal. 56:390–401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang D, Fu Y, Gale JP, Aubry AF and
Arnold ME: A sensitive method for the determination of entecavir at
picogram per milliliter level in human plasma by solid phase
extraction and high-pH LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 49:1027–1033.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Liu Y, Liu W, et al: Establishment
of three hepatoma cell lines stably replicating wild-type,
entecavir-resistant or multidrug-resistant genotype C hepatitis B
viruses. Hepatology. 54:1082A. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Liu W, Song H, Chen Q, Xu C, Zhang W, Liu
Y, Wang B, Xu D, Lu M, Yang D and Zheng X: Multidrug resistance
protein 4 is a critical protein associated with the antiviral
efficacy of nucleos(t)ide analogues. Liver Int. 36:1284–1294. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fu X, Tan D, Dou X, Chen J and Wu J: A
multi-center clinical study comparing Sansure Magb and CAP/CTM HBV
tests in the quantitative detection of HBV DNA. J Infect Dev
Ctries. 10:755–761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
U.S. Department of Health and Human
Services: Guidance for industry, . Bioanalytical method validation.
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidance/ucm070107.pdfDecember
2–2015
|
|
16
|
Hendrix CW, Chen BA, Guddera V, Hoesley C,
Justman J, Nakabiito C, Salata R, Soto-Torres L, Patterson K,
Minnis AM, et al: MTN-001: Randomized pharmacokinetic cross-over
study comparing tenofovir vaginal gel and oral tablets in vaginal
tissue and other compartments. PLoS One. 8:e550132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Thompson CG, Cohen MS and Kashuba AD:
Antiretroviral pharmacology in mucosal tissues. J Acquir Immune
Defic Syndr. 63 Suppl 2:S240–S247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Delaney WE IV, Ray AS, Yang H, Qi X, Xiong
S, Zhu Y and Miller MD: Intracellular metabolism and in vitro
activity of tenofovir against hepatitis B virus. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 50:2471–2477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Wang R, Piotrowski M, Zhang H and
Leach KL: Intracellular concentrations determine the cytotoxicity
of adefovir, cidofovir and tenofovir. Toxicol In Vitro. 29:251–258.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trufelli H, Palma P, Famiglini G and
Cappiello A: An overview of matrix effects in liquid
chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev. 30:491–509.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gosetti F, Chiuminatto U, Zampieri D,
Mazzucco E, Robotti E, Calabrese G, Gennaro MC and Marengo E:
Determination of perfluorochemicals in biological, environmental
and food samples by an automated on-line solid phase extraction
ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass
spectrometry method. J Chromatogr A. 1217:7864–7872. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Challa BR, Awen BZ, Chandu BR and
Rihanaparveen S: LC-ESI-MS/MS method for the quantification of
entecavir in human plasma and its application to bioequivalence
study. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 879:769–776.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao FJ, Tang H, Zhang QH, Yang J, Davey
AK and Wang JP: Salting-out homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction
approach applied in sample pre-processing for the quantitative
determination of entecavir in human plasma by LC-MS. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 881-882:119–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zacharis CK and Tzanavaras PD:
Determination of bisphosphonate active pharmaceutical ingredients
in pharmaceuticals and biological material: A review of analytical
methods. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 48:483–496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oeckl P and Ferger B: Simultaneous
LC-MS/MS analysis of the biomarkers cAMP and cGMP in plasma, CSF
and brain tissue. J Neurosci Methods. 203:338–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Losa R, Sierra MI, Gion MO, Esteban E and
Buesa JM: Simultaneous determination of gemcitabine di- and
triphosphate in human blood mononuclear and cancer cells by RP-HPLC
and UV detection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
840:44–49. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang J, Bathena SP, Csanaky IL and
Alnouti Y: Simultaneous characterization of bile acids and their
sulfate metabolites in mouse liver, plasma, bile, and urine using
LC-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 55:1111–1119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bobeldijk I, Hekman M, de Vries-van der
Weij J, Coulier L, Ramaker R, Kleemann R, Kooistra T, Rubingh C,
Freidig A and Verheij E: Quantitative profiling of bile acids in
biofluids and tissues based on accurate mass high resolution
LC-FT-MS: Compound class targeting in a metabolomics workflow. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 871:306–313. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schuetz JD, Connelly MC, Sun D, Paibir SG,
Flynn PM, Srinivas RV, Kumar A and Fridland A: MRP4: A previously
unidentified factor in resistance to nucleoside-based antiviral
drugs. Nat Med. 5:1048–1051. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rius M, Thon WF, Keppler D and Nies AT:
Prostanoid transport by multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4)
localized in tissues of the human urogenital tract. J Urol.
174:2409–2414. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rius M, Nies AT, Hummel-Eisenbeiss J,
Jedlitschky G and Keppler D: Cotransport of reduced glutathione
with bile salts by MRP4 (ABCC4) localized to the basolateral
hepatocyte membrane. Hepatology. 38:374–384. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sauna ZE, Nandigama K and Ambudkar SV:
Multidrug resistance protein 4 (ABCC4)-mediated ATP hydrolysis:
Effect of transport substrates and characterization of the
post-hydrolysis transition state. J Biol Chem. 279:48855–48864.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zelcer N, Reid G, Wielinga P, Kuil A, van
der Heijden I, Schuetz JD and Borst P: Steroid and bile acid
conjugates are substrates of human multidrug-resistance protein
(MRP) 4 (ATP-binding cassette C4). Biochem J. 371:361–367. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|