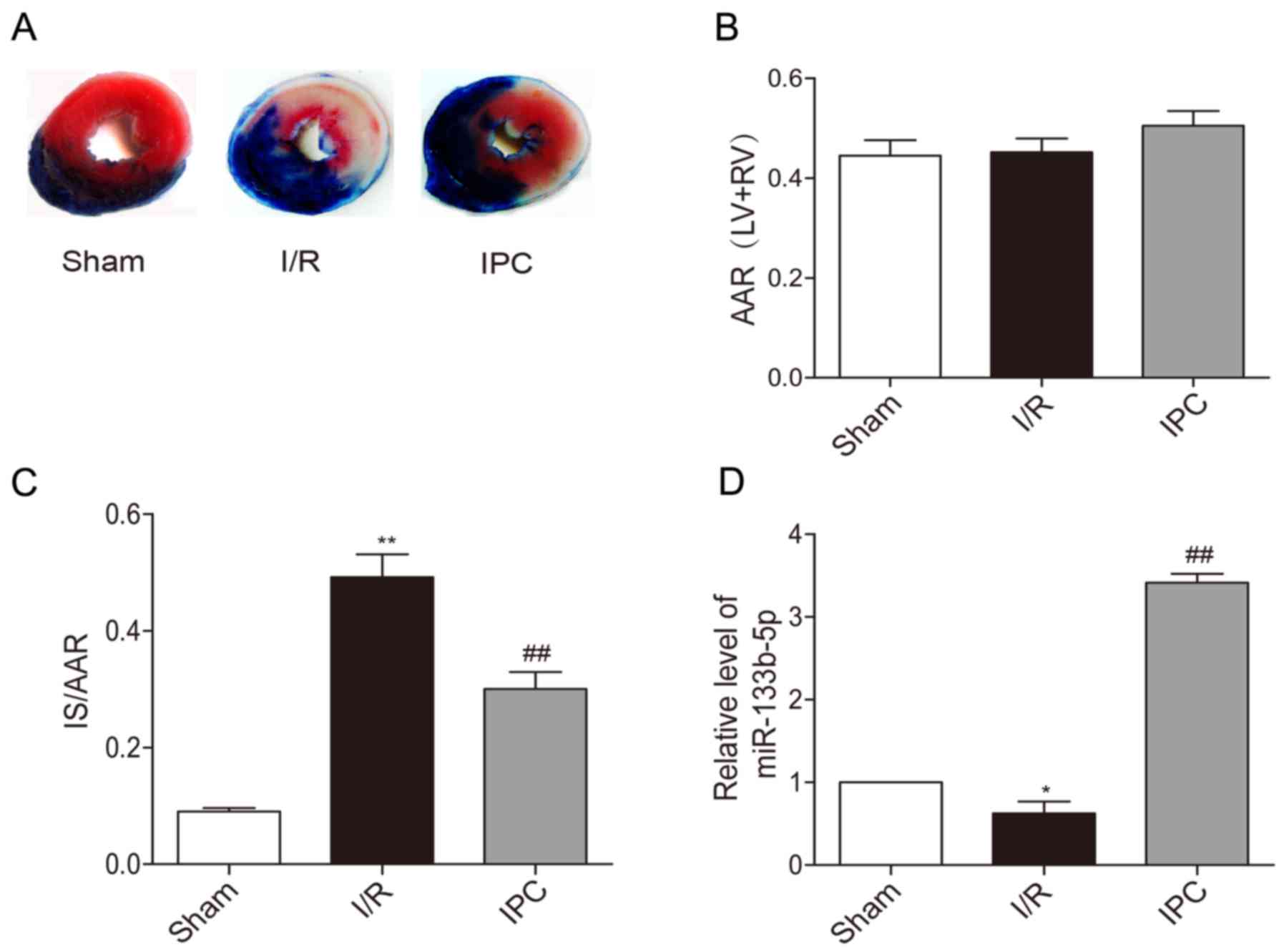
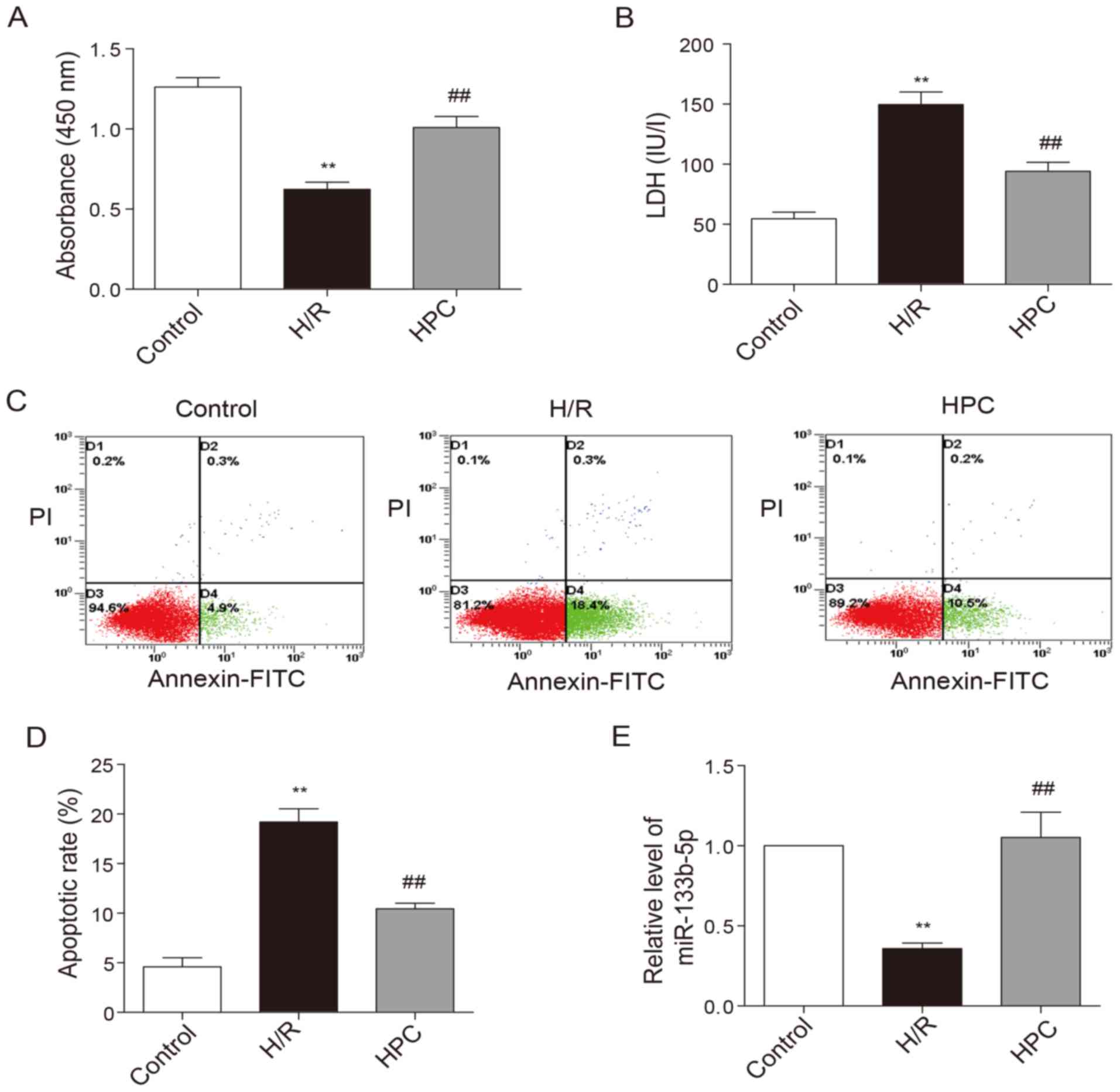
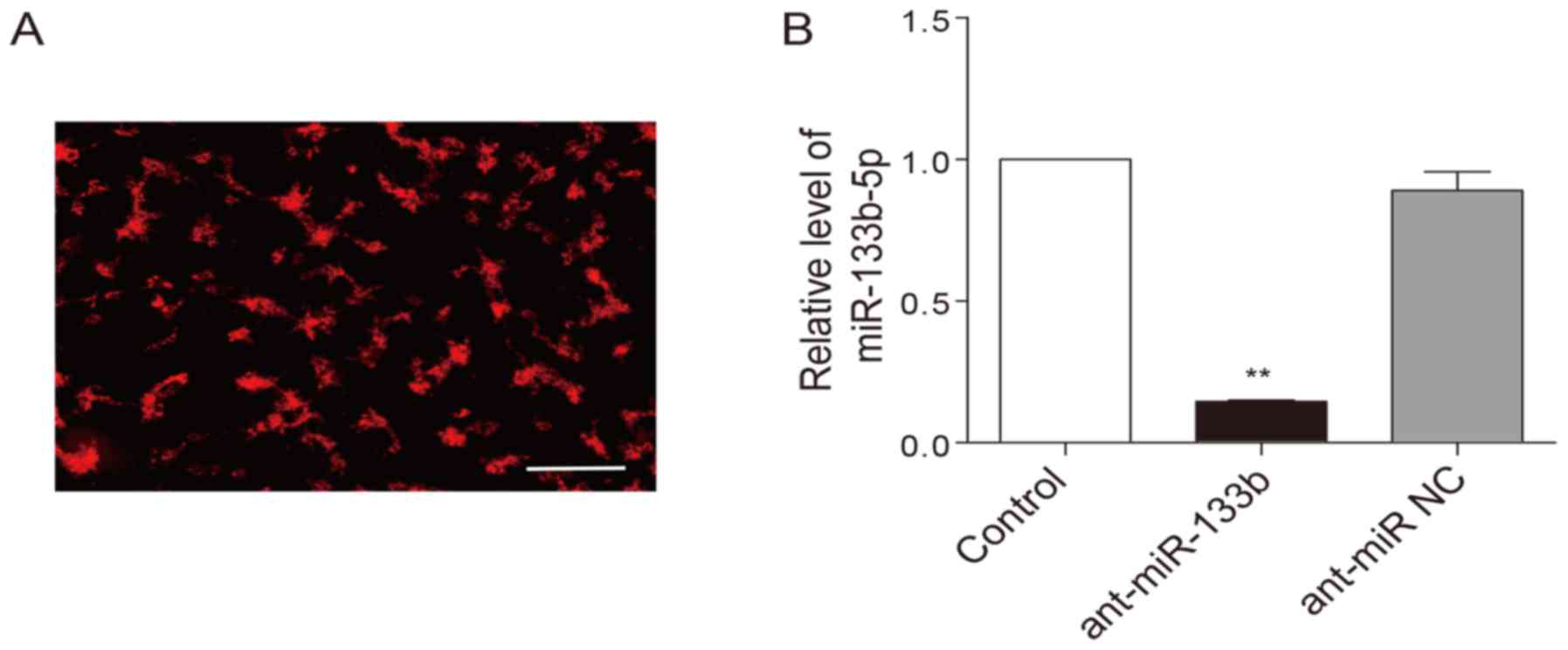
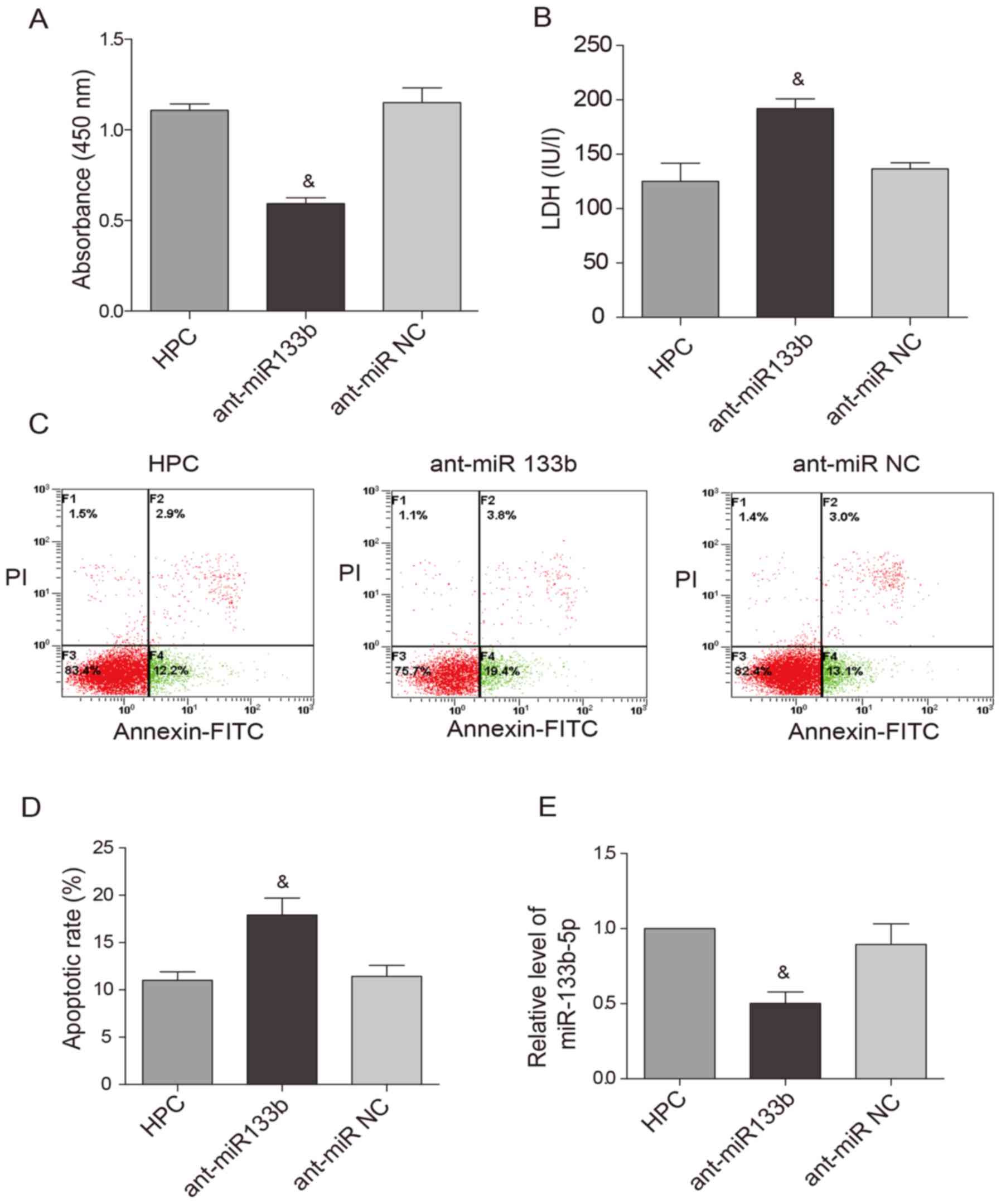
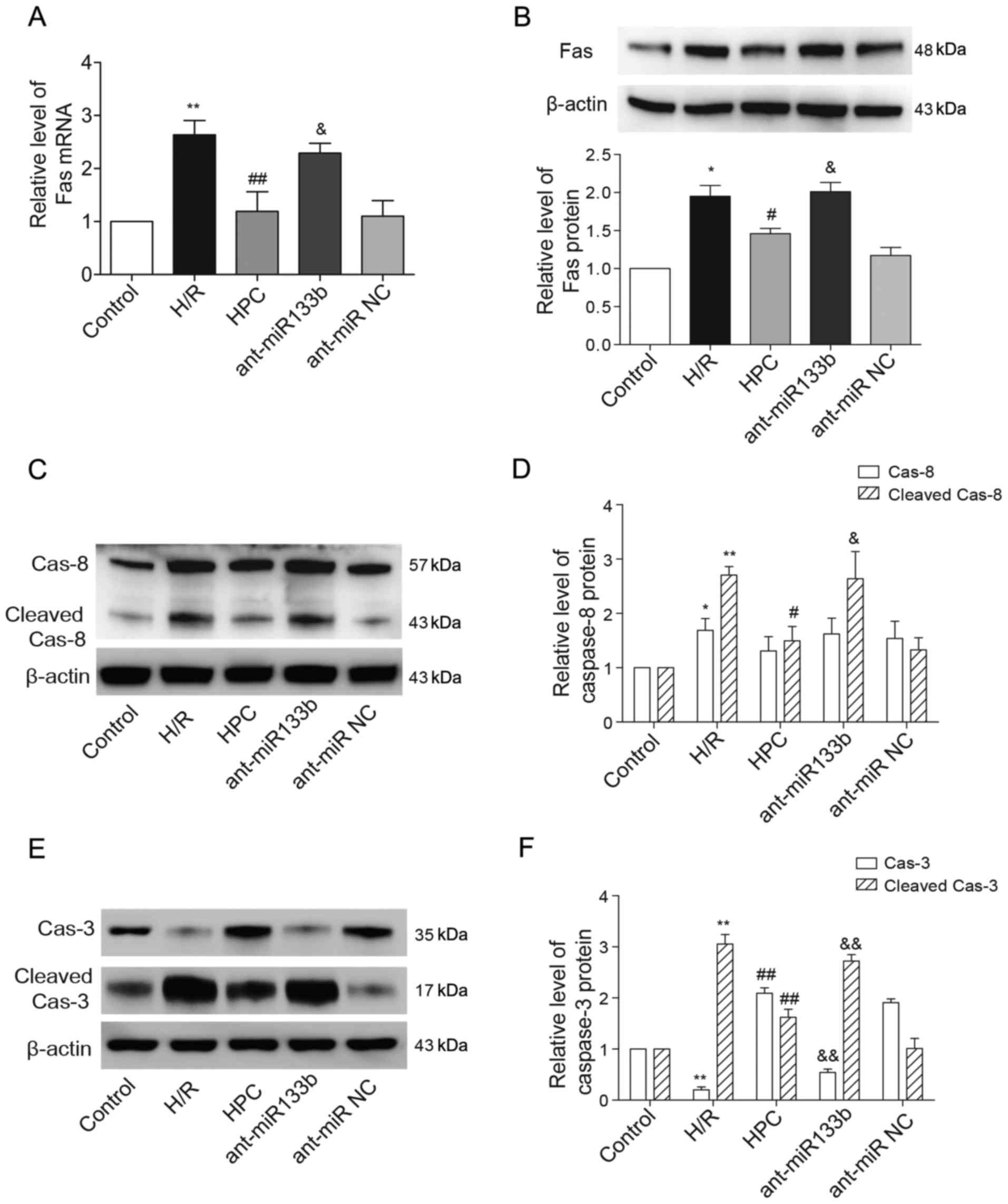
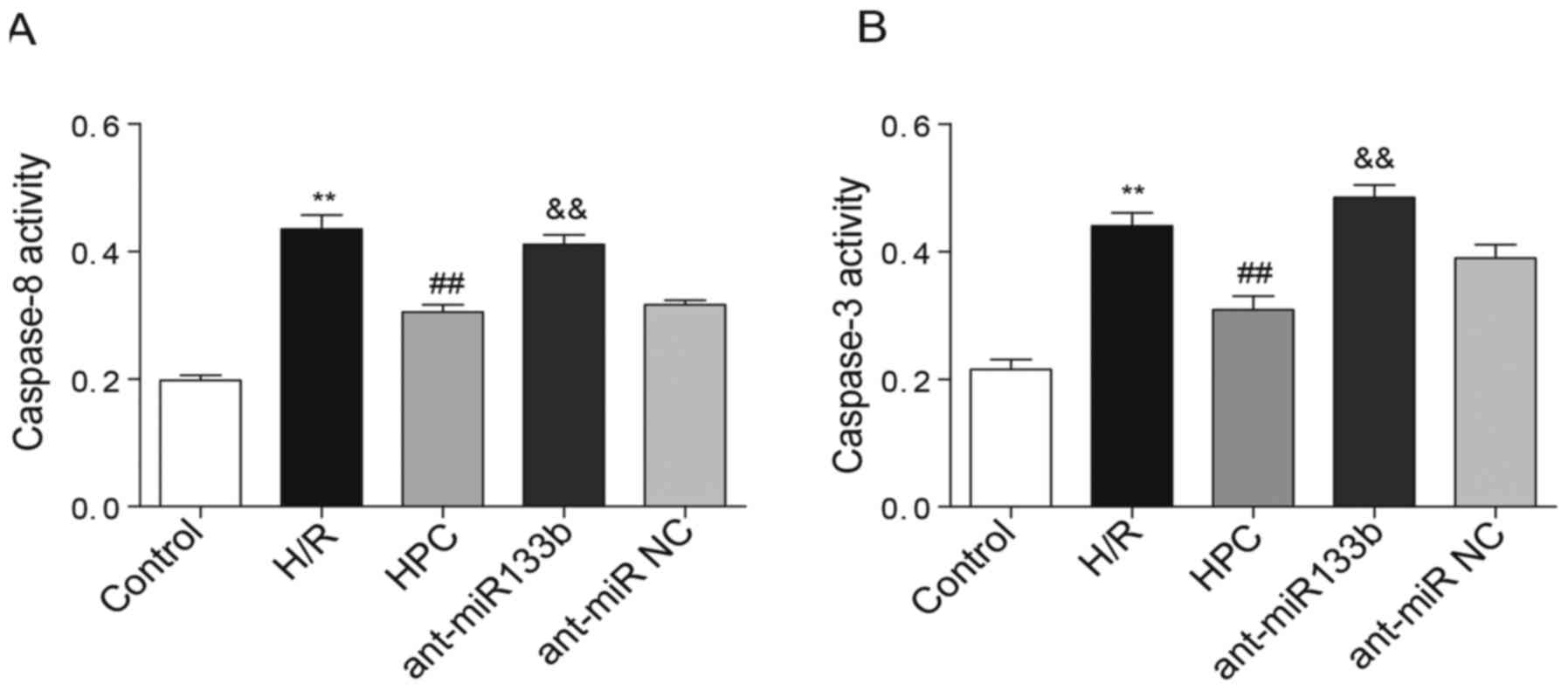
|
1
|
Arslan F, Smeets MB, O'Neill LA, Keogh B,
McGuirk P, Timmers L, Tersteeg C, Hoefer IE, Doevendans PA,
Pasterkamp G and de Kleijn DP: Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury is mediated by leukocytic toll-like receptor-2 and reduced
by systemic administration of a novel anti-toll-like receptor-2
antibody. Circulation. 121:80–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gong D, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Gu H, Jiang Q
and Hu S: Aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 activation during cardioplegic
arrest enhances the cardioprotection against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 12:350–358. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verges S, Chacaroun S, Godin-Ribuot D and
Baillieul S: Hypoxic conditioning as a new therapeutic modality.
Front Pediatr. 3:582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barrington JH, Chrismas BCR, Gibson OR,
Tuttle J, Pegrum J, Govilkar S, Kabir C, Giannakakis N, Rayan F,
Okasheh Z, et al: Hypoxic air inhalation and ischemia interventions
both elicit preconditioning which attenuate subsequent cellular
stress In vivo following blood flow occlusion and
reperfusion. Front Physiol. 8:5602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Das DK and Maulik N: Cardiac genomic
response following preconditioning stimulus. Cardiovasc Res.
70:254–263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Turer AT and Hill JA: Pathogenesis of
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy.
Am J Cardiol. 106:360–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hoole SP, Heck PM, Sharples L, Khan SN,
Duehmke R, Densem CG, Clarke SC, Shapiro LM, Schofield PM,
O'Sullivan M and Dutka DP: Cardiac remote ischemic preconditioning
in coronary stenting (CRISP stent) study: A prospective, randomized
control trial. Circulation. 119:820–827. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krol J, Loedige I and Filipowicz W: The
widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay.
Nat Rev Genet. 11:597–610. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gagan J, Dey BK, Layer R, Yan Z and Dutta
A: MicroRNA-378 targets the myogenic repressor MyoR during myoblast
differentiation. J Biol Chem. 286:19431–19438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng S, Cong S, Zhang X, Bao X, Wang W, Li
H, Wang Z, Wang G, Xu J, Du B, et al: MicroRNA-192 targeting
retinoblastoma 1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell
apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:6669–6678.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carè A, Catalucci D, Felicetti F, Bonci D,
Addario A, Gallo P, Bang ML, Segnalini P, Gu Y, Dalton ND, et al:
MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med. 13:613–618.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song XW, Li Q, Lin L, Wang XC, Li DF, Wang
GK, Ren AJ, Wang YR, Qin YW, Yuan WJ and Jing Q: MicroRNAs are
dynamically regulated in hypertrophic hearts, and miR-199a is
essential for the maintenance of cell size in cardiomyocytes. J
Cell Physiol. 225:437–443. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thum T, Galuppo P, Wolf C, Fiedler J,
Kneitz S, van Laake LW, Doevendans PA, Mummery CL, Borlak J,
Haverich A, et al: MicroRNAs in the human heart: A clue to fetal
gene reprogramming in heart failure. Circulation. 116:258–267.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dong S, Cheng Y, Yang J, Li J, Liu X, Wang
X, Wang D, Krall TJ, Delphin ES and Zhang C: MicroRNA expression
signature and the role of microRNA-21 in the early phase of acute
myocardial infarction. J Biol Chem. 284:29514–29525. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qian L, Van Laake LW, Huang Y, Liu S,
Wendland MF and Srivastava D: miR-24 inhibits apoptosis and
represses Bim in mouse cardiomyocytes. J Exp Med. 208:549–560.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Zhang X, Ren XP, Chen J, Liu H,
Yang J, Medvedovic M, Hu Z and Fan GC: MicroRNA-494 targeting both
proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Circulation.
122:1308–1318. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wystub K, Besser J, Bachmann A, Boettger T
and Braun T: miR-1/133a clusters cooperatively specify the
cardiomyogenic lineage by adjustment of myocardin levels during
embryonic heart development. PLoS Genet. 9:e10037932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
He B, Xiao J, Ren AJ, Zhang YF, Zhang H,
Chen M, Xie B, Gao XG and Wang YW: Role of miR-1 and miR-133a in
myocardial ischemic postconditioning. J Biomed Sci. 18:222011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li AY, Yang Q and Yang K: miR-133a
mediates the hypoxia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting TAGLN2
expression in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Irwin MG and Wong TM:
Remifentanil preconditioning protects against ischemic injury in
the intact rat heart. Anesthesiology. 101:918–923. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suh JH, Choi E, Cha MJ, Song BW, Ham O,
Lee SY, Yoon C, Lee CY, Park JH, Lee SH and Hwang KC: Up-regulation
of miR-26a promotes apoptosis of hypoxic rat neonatal
cardiomyocytes by repressing GSK-3β protein expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 423:404–410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakamura T, Kuroi M, Fujiwara Y, Warashina
S, Sato Y and Harashima H: Small-sized, stable lipid nanoparticle
for the efficient delivery of siRNA to human immune cell lines. Sci
Rep. 6:378492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He SF, Zhu HJ, Han ZY, Wu H, Jin SY, Irwin
MG and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-133b-5p is involved in cardioprotection of
morphine preconditioning in rat cardiomyocytes by targeting fas.
Can J Cardiol. 32:996–1007. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Louch WE, Sheehan KA and Wolska BM:
Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:288–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Weiss JB, Eisenhardt SU, Stark GB, Bode C,
Moser M and Grundmann S: MicroRNAs in ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Am J Cardiovasc Dis. 2:237–247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
D'Alessandra Y, Devanna P, Limana F,
Straino S, Di Carlo A, Brambilla PG, Rubino M, Carena MC,
Spazzafumo L, De Simone M, et al: Circulating microRNAs are new and
sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J.
31:2765–2773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cortez-Dias N, Costa MC, Carrilho-Ferreira
P, Silva D, Jorge C, Calisto C, Pessoa T, Robalo Martins S, de
Sousa JC, da Silva PC, et al: Circulating miR-122-5p/miR-133b ratio
is a specific early prognostic biomarker in acute myocardial
infarction. Circ J. 80:2183–2191. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boštjančič E, Jerše M, Glavač D and Zidar
N: miR-1, miR-133a/b, and miR-208a in human fetal hearts correlate
to the apoptotic and proliferation markers. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:211–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bostjancic E, Zidar N, Stajer D and Glavac
D: MicroRNAs miR-1, miR-133a, miR-133b and miR-208 are dysregulated
in human myocardial infarction. Cardiology. 115:163–169. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sucharov C, Bristow MR and Port JD: miRNA
expression in the failing human heart: Functional correlates. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 45:185–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu HJ, Han ZY, He SF, Jin SY, Xu SJ, Fang
XD and Zhang Y: Specific MicroRNAs comparisons in hypoxia and
morphine preconditioning against hypoxia-reoxgenation injury with
and without heart failure. Life Sci. 170:82–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yin C, Salloum FN and Kukreja RC: A novel
role of microRNA in late preconditioning: Upregulation of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase and heat shock protein 70. Circ
Res. 104:572–575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou W, Bi X, Gao G and Sun L: miRNA-133b
and miRNA-135a induce apoptosis via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling
pathway in human renal carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:722–729. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pan JY, Sun CC, Bi ZY, Chen ZL, Li SJ, Li
QQ, Wang YX, Bi YY and Li DJ: miR-206/133b Cluster: A weapon
against lung cancer? Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 8:442–449. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ying B, Huang H, Li H, Song M, Wu S and
Ying H: Procaine inhibits proliferation and migration and promotes
cell apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells by upregulation of
microRNA-133b. Oncol Res. 25:1463–1470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia C, Cai Y, Lin Y, Guan R, Xiao G and
Yang J: MiR-133b-5p regulates the expression of the heat shock
protein 70 during rat neuronal cell apoptosis induced by the gp120
V3 loop peptide. J Med Virol. 88:437–447. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang L, Li X, Zhou Y, Shi H, Xu C, He H,
Wang S, Xiong X, Zhang Y, Du Z, et al: Downregulation of miR-133
via MAPK/ERK signaling pathway involved in nicotine-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol.
387:197–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jeremias I, Kupatt C, Martin-Villalba A,
Habazettl H, Schenkel J, Boekstegers P and Debatin KM: Involvement
of CD95/Apo1/Fas in cell death after myocardial ischemia.
Circulation. 102:915–920. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee P, Sata M, Lefer DJ, Factor SM, Walsh
K and Kitsis RN: Fas pathway is a critical mediator of cardiac
myocyte death and MI during ischemia-reperfusion in vivo. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 284:H456–H463. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kantari C and Walczak H: Caspase-8 and
bid: Caught in the act between death receptors and mitochondria.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:558–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Engels IH, Stepczynska A, Stroh C, Lauber
K, Berg C, Schwenzer R, Wajant H, Jänicke RU, Porter AG, Belka C,
et al: Caspase-8/FLICE functions as an executioner caspase in
anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Oncogene. 19:4563–4573. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|