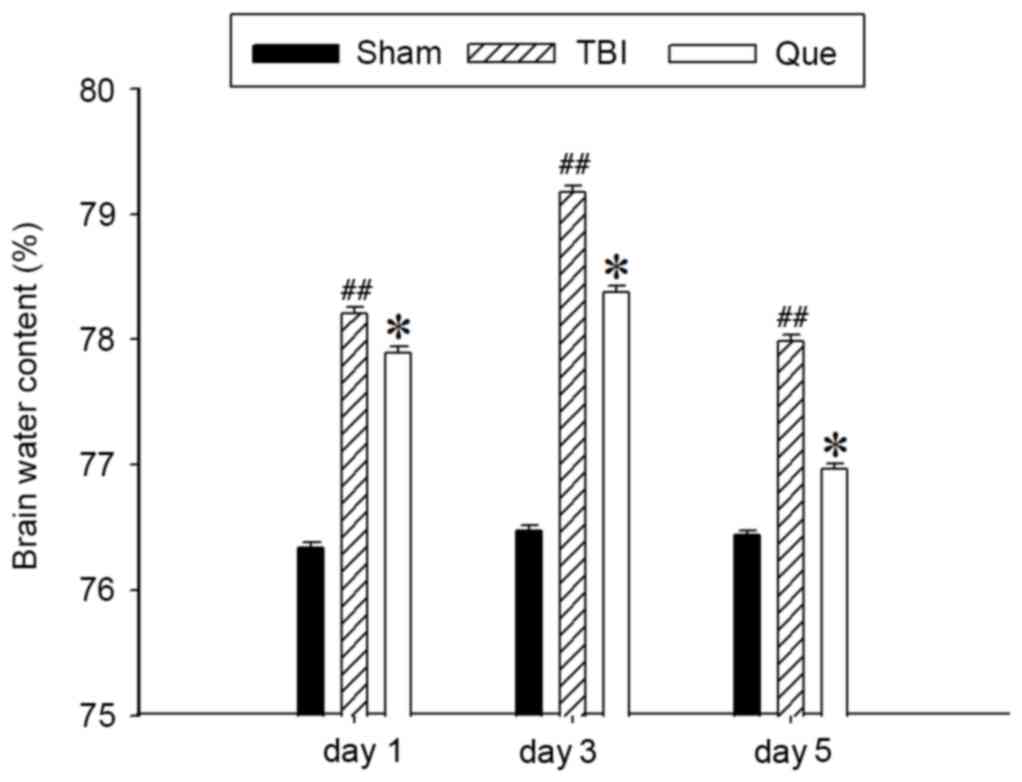
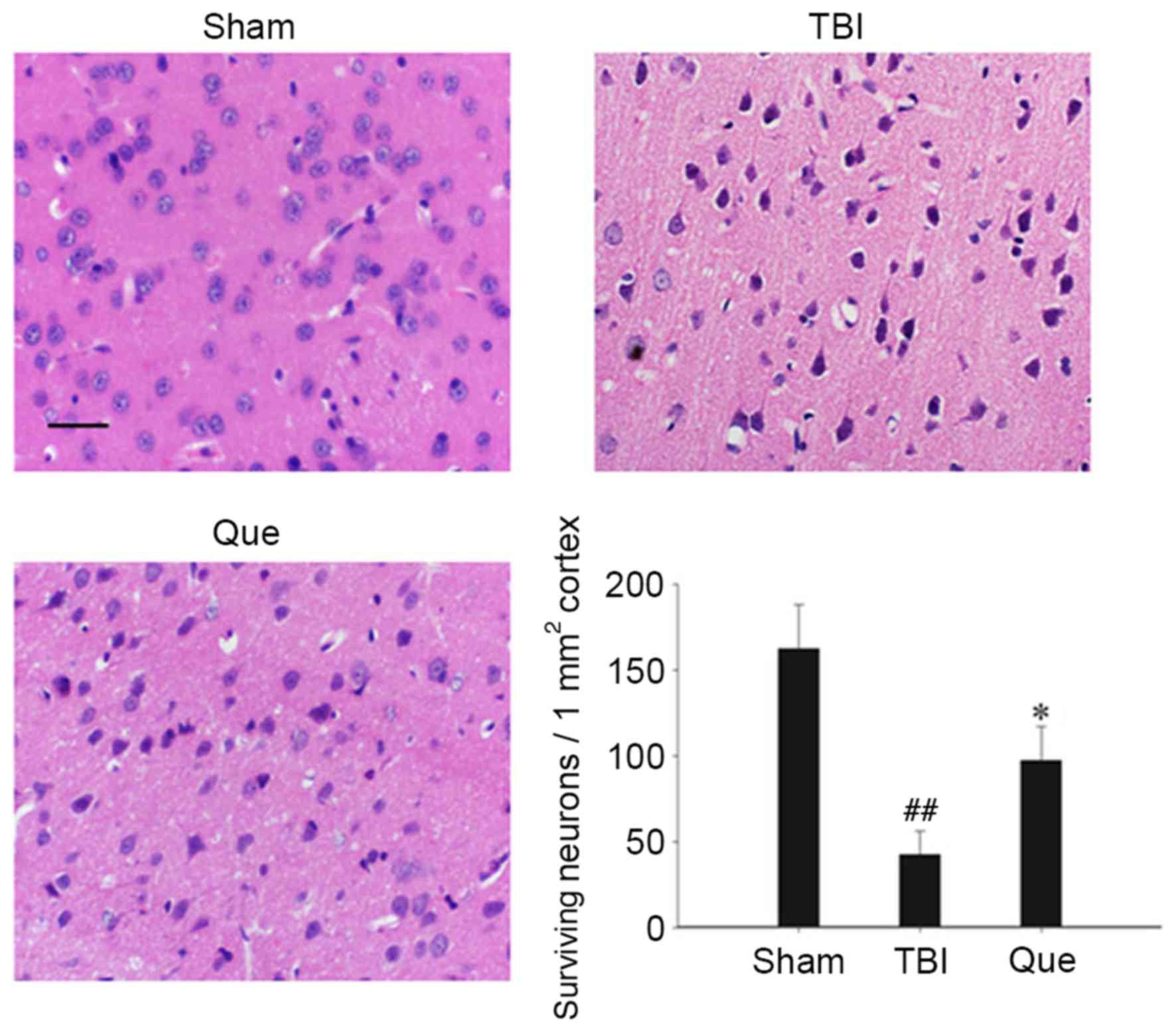
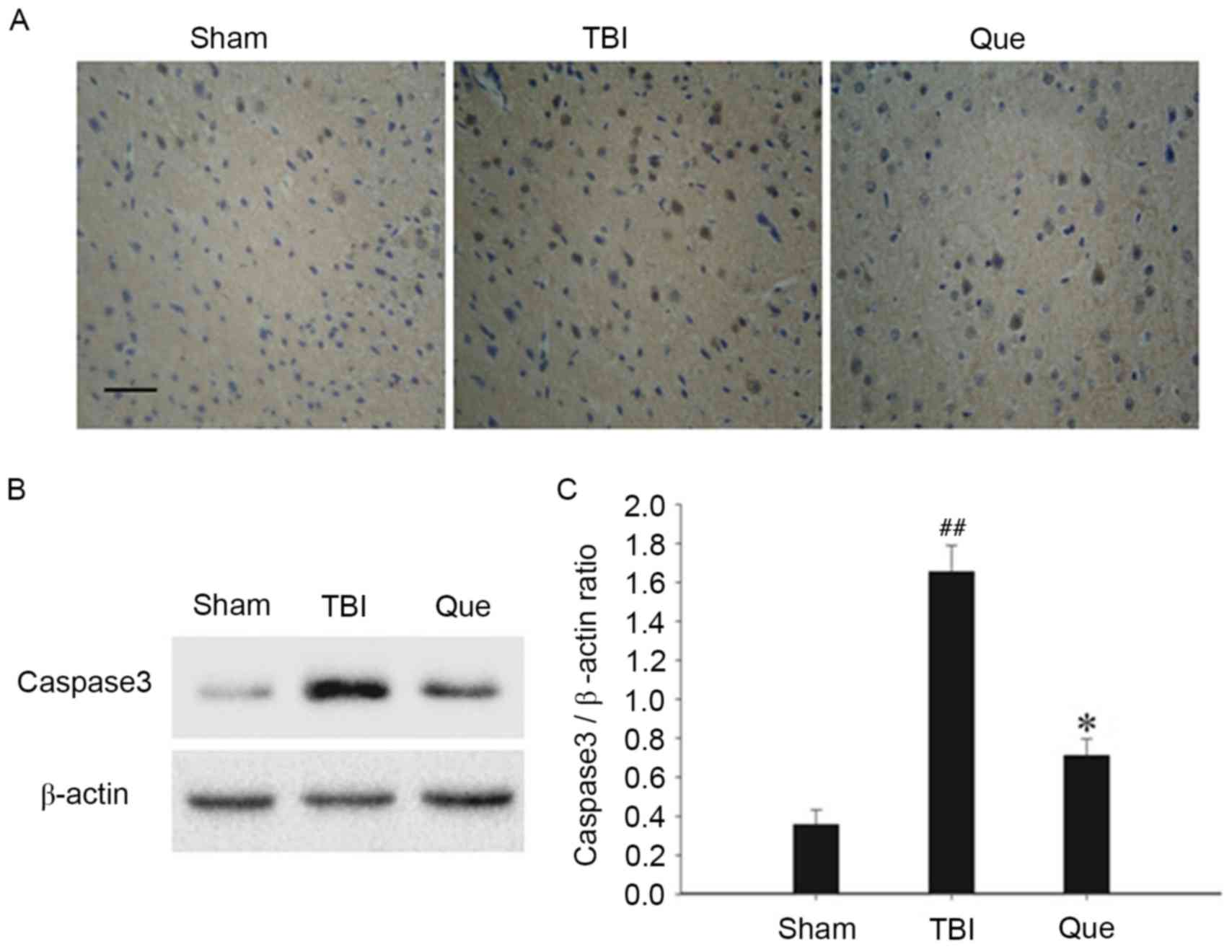
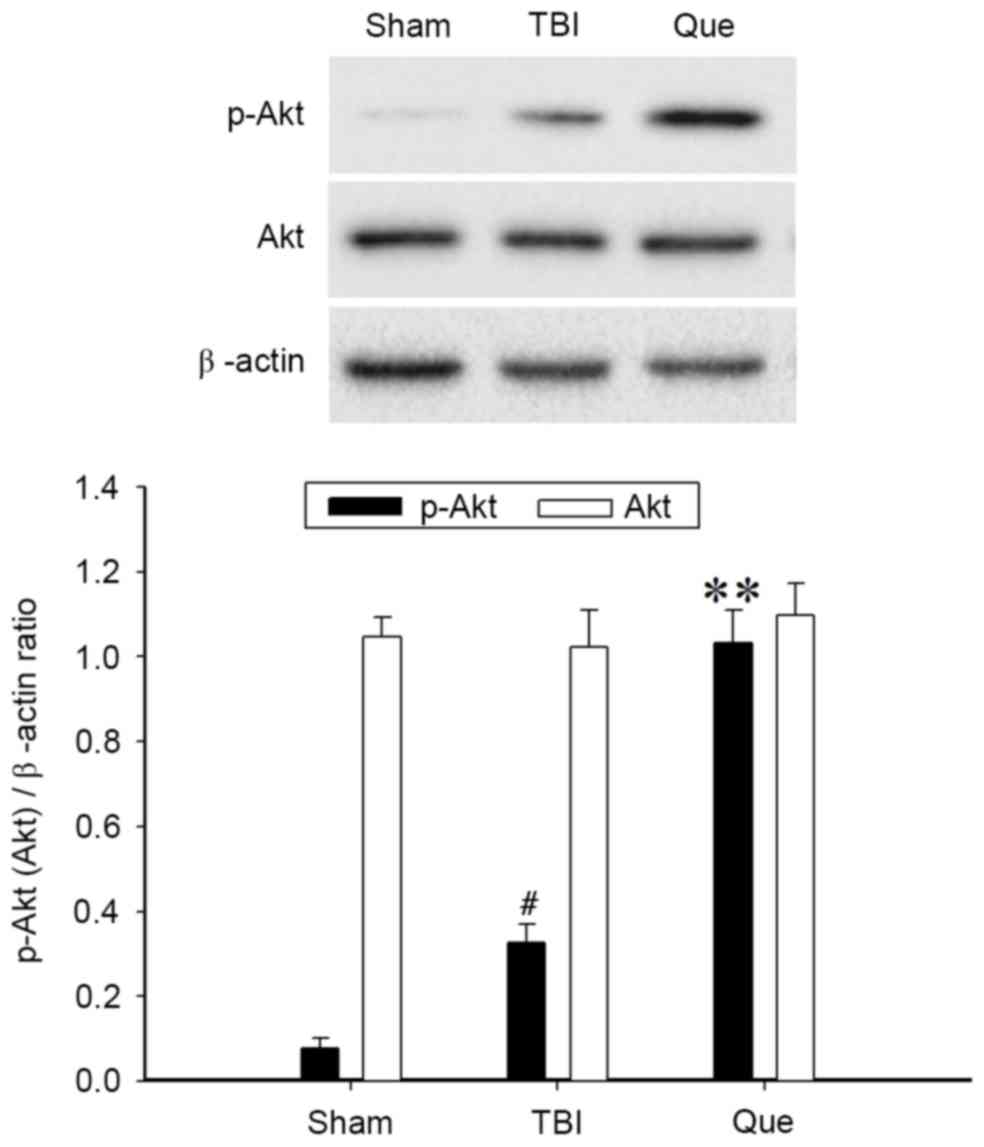
|
1
|
Ye X, Asim M and Michael C: Animal models
of traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:128–142. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carroll LJ, Cassidy JD, Cancelliere C,
Côté P, Hincapié CA, Kristman VL, Holm LW, Borg J, Nygren-de
Boussard C and Hartvigsen J: Systematic review of the prognosis
after mild traumatic brain injury in adults: Cognitive,
psychiatric, and mortality outcomes: Results of the international
collaboration on mild traumatic brain injury prognosis. Arch Phys
Med Rehabil. 95 3 Suppl:S152–S173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Verma AK and Pratap R: The biological
potential of flavones. Nat Prod Rep. 27:1571–1593. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Legault J, Perron T, Mshvildadze V,
Girard-Lalancette K, Perron S, Laprise C, Sirois P and Pichette A:
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of quercetin
7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from the leaves of Brasenia schreberi. J
Med Food. 14:1127–1134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Zhang M, Yu L, Zhao Y, He N and
Yang X: Antitumor activities of quercetin and
quercetin-5,8-disulfonate in human colon and breast cancer cell
lines. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1589–1599. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dok-Go H, Lee KH, Kim HJ, Lee EH, Lee J,
Song YS, Lee YH, Jin C, Lee YS and Cho J: Neuroprotective effects
of antioxidative flavonoids, quercetin, (+)-dihydroquercetin and
quercetin 3-methyl ether, isolated from Opuntia ficus-indica var.
saboten. Brain Res. 965:130–136. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang T, Kong B, Gu JW, Kuang YQ, Cheng L,
Yang WT, Xia X and Shu HF: Anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative roles
of quercetin after traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
34:797–804. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du G, Zhao Z, Chen Y, Li Z, Tian Y, Liu Z,
Liu B and Song J: Quercetin attenuates neuronal autophagy and
apoptosis in rat traumatic brain injury model via activation of
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurol Res. 1–8. 2016.(Epub ahead of
print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marmarou A, Foda AE, van den Brink W,
Campbell J, Kita H and Demetriadou K: A new model of diffuse brain
injury in rats. Part I: Pathophysiology and biomechanics. J
Neurosurg. 80:291–300. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Constantini S, Trembovler V,
Weinstock M and Shohami E: An experimental model of closed head
injury in mice: Pathophysiology, histopathology, and cognitive
deficits. J Neurotrauma. 13:557–568. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Donkin JJ and Vink R: Mechanisms of
cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury: Therapeutic developments.
Curr Opin Neurol. 23:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang ZJ, Cheang LC, Wang MW and Lee SM:
Quercetin exerts a neuroprotective effect through inhibition of the
iNOS/NO system and pro-inflammation gene expression in PC12 cells
and in zebrafish. Int J Mol Med. 27:195–203. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumar B, Gupta SK, Nag TC, Srivastava S,
Saxena R, Jha KA and Srinivasan BP: Retinal neuroprotective effects
of quercetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Eye Res.
125:193–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pu F, Mishima K, Irie K, Motohashi K,
Tanaka Y, Orito K, Egawa T, Kitamura Y, Egashira N, Iwasaki K and
Fujiwara M: Neuroprotective effects of quercetin and rutin on
spatial memory impairment in an 8-arm radial maze task and neuronal
death induced by repeated cerebral ischemia in rats. J Pharmacol
Sci. 104:329–334. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Silva B, Oliveira PJ, Dias A and Malva JO:
Quercetin, kaempferol and biapigenin from Hypericum perforatum are
neuroprotective against excitotoxic insults. Neurotox Res.
13:265–279. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eucker SA, Smith C, Ralston J, Friess SH
and Margulies SS: Physiological and histopathological responses
following closed rotational head injury depend on direction of head
motion. Exp Neurol. 227:79–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feng JF, Gurkoff GG, Van KC, Song M, Lowe
DA, Zhou J and Lyeth BG: NAAG peptidase inhibitor reduces cellular
damage in a model of TBI with secondary hypoxia. Brain Res.
1469:144–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Chen M,
Dixon CE, Seidberg NA, Melick J, Loeffert JE, Nathaniel PD, Jin KL
and Graham SH: Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic
brain injury in rats. J Neurochem. 74:740–753. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao RQ, Qi DS, Yu HL, Liu J, Yang LH and
Wu XX: Quercetin attenuates cell apoptosis in focal cerebral
ischemia rat brain via activation of BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurochem Res. 37:2777–2786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Yu F and Chan
PH: Akt/GSK3beta survival signaling is involved in acute brain
injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke. 37:2140–2146.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park KR, Nam D, Yun HM, Lee SG, Jang HJ,
Sethi G, Cho SK and Ahn KS: β-Caryophyllene oxide inhibits growth
and induces apoptosis through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR/S6K1
pathways and ROS-mediated MAPKs activation. Cancer Lett.
312:178–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li WX, Chen SF, Chen LP, Yang GY, Li JT,
Liu HZ and Zhu W: Thimerosal-induced apoptosis in mouse C2C12
myoblast cells occurs through suppression of the PI3K/Akt/survivin
pathway. PLoS One. 7:e490642012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan L, Tang Q, Shen D, Peng S, Zheng Q,
Guo H, Jiang M and Deng W: SOCS-1 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis via ERK1/2 pathway activation.
Inflammation. 31:180–188. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chong YH, Shin YJ, Lee EO, Kayed R, Glabe
CG and Tenner AJ: ERK1/2 activation mediates Abeta oligomer-induced
neurotoxicity via caspase-3 activation and tau cleavage in rat
organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Biol Chem.
281:20315–20325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|