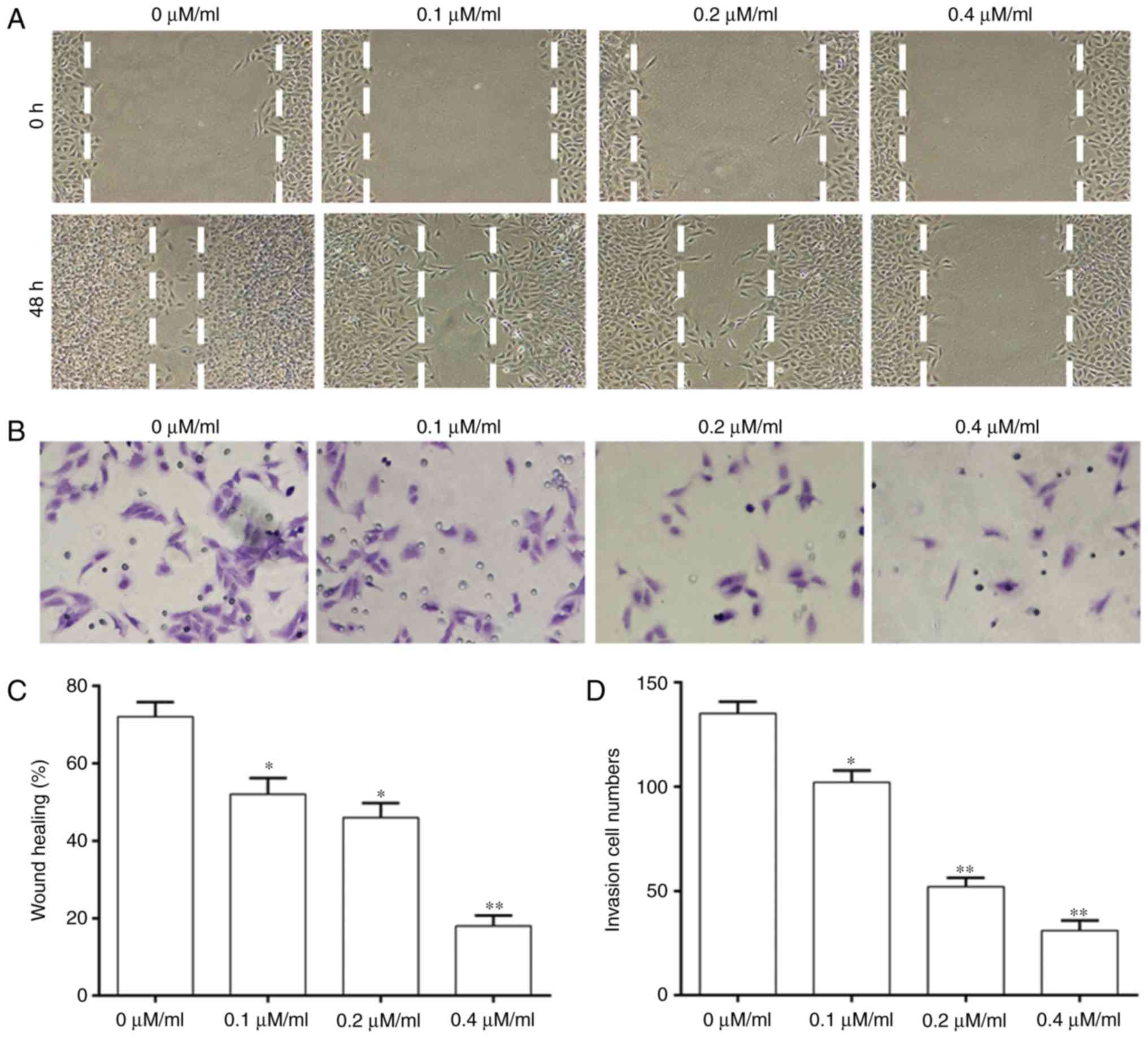
|
1
|
Hu C, Wei W, Chen X, Woodman CB, Yao Y,
Nicholls JM, Joab I, Sihota SK, Shao JY, Derkaoui KD, et al: A
global view of the oncogenic landscape in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
An integrated analysis at the genetic and expression levels. PLoS
One. 7:e410552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, Li WF, Li Y, Wei
RR, Zhang MY, Sun Y, Huang BJ, Chen M, et al: Prognostic value of a
microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A microRNA
expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:633–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sarmiento MP and Mejia MB: Preliminary
assessment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence in the
Philippines: A second look at published data from four centers.
Chin J Cancer. 33:159–164. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang HZ, Cao CN, Luo JW, Yi JL, Huang XD,
Zhang SP, Wang K, Qu Y, Xiao JP, Li SY, et al: High-risk factors of
parotid lymph node metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A
case-control study. Radiat Oncol. 11:1132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yousefi M, Bahrami T, Salmaninejad A,
Nosrati R, Ghaffari P and Ghaffari SH: Lung cancer-associated brain
metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic options. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 40:419–441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu D: Innate and adaptive immune cell
metabolism in tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1011:211–223. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He X, Guo X, Zhang H, Kong X, Yang F and
Zheng C: Mechanism of action and efficacy of LY2109761, a TGF-β
receptor inhibitor, targeting tumor microenvironment in liver
cancer after TACE. Oncotarget. 9:1130–1142. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fuxe J and Karlsson MC: TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition: A link between cancer and
inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:455–461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Grelet S, McShane A, Geslain R and Howe
PH: Pleiotropic roles of non-coding RNAs in TGF-β-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and their functions in tumor
progression. Cancers (Basel). 9:E752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ding Y, Pan Y, Liu S, Jiang F and Jiao J:
Elevation of MiR-9-3p suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via down-regulating
FN1, ITGB1 and ITGAV. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:414–424. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang T, Yin P, Zhang Z, Xu B, Che D, Dai
Z, Dong C, Jiang P, Hong H, Yang Z, et al: Deficiency of pigment
epithelium-derived factor in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
triggers the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e28382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao LJ and Tao R: Traditional chinese
medicine (TCM) therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1010:261–280. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang J, Huang F, Bai Z, Chi B, Wu J and
Chen X: Curcumol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of
colorectal cancer LoVo cell line via IGF-1R and p38 MAPK pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:19851–19867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mun SH, Kim SB, Kong R, Choi JG, Kim YC,
Shin DW, Kang OH and Kwon DY: Curcumin reverse methicillin
resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules. 19:18283–18295.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang Y, Li ZS, Jiang FS, Deng X, Yao CS
and Nie G: Effects of different ingredients of zedoary on gene
expression of HSC-T6 cells. World J Gastroenterol. 11:6780–6786.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dang YY, Li XC, Zhang QW, Li SP and Wang
YT: Preparative isolation and purification of six volatile
compounds from essential oil of Curcuma wenyujin using
high-performance centrifugal partition chromatography. J Sep Sci.
33:1658–1664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Wang Z and Chen T: Curcumol
induces apoptosis via caspases-independent mitochondrial pathway in
human lung adenocarcinoma ASTC-a-1 cells. Med Oncol. 28:307–314.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo P, Wang YW, Weng BX, Li XK, Yang SL
and Ye FQ: Synthesis, anti-tumor activity, and structure-activity
relationships of curcumol derivatives. J Asian Nat Prod Res.
16:53–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen G, Wang Y, Li M, Xu T, Wang X, Hong B
and Niu Y: Curcumol induces HSC-T6 cell death through suppression
of Bcl-2: Involvement of PI3K and NF-kappaB pathways. Eur J Pharm
Sci. 65:21–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fles R, Bos ACRK, Supriyati, Rachmawati D,
Waliyanti E, Tan IB, Haryana SM, Schmidt MK and Dewi FST: The role
of Indonesian patients' health behaviors in delaying the diagnosis
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Public Health. 17:5102017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Twu CW, Wang WY, Chen CC, Liang KL, Jiang
RS, Wu CT, Shih YT, Lin PJ, Liu YC and Lin JC: Metronomic adjuvant
chemotherapy improves treatment outcome in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
patients with postradiation persistently detectable plasma
Epstein-Barr virus deoxyribonucleic acid. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 89:21–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chee J, Loh KS, Tham I, Ho F, Wong LC, Tan
CS, Goh BC and Lim CM: Prognostic stratification of patients with
metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma using a clinical and
biochemical scoring system. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:2563–2570.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin HF, Hsieh MJ, His YT, Lo YS, Chuang
YC, Chen MK and Chien SY: Celastrol-induced apoptosis in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma is associated with the activation of the
death receptor and the mitochondrial pathway. Oncol Lett.
14:1683–1690. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng X, Zhang Q, Zeng Y, Li J, Wang L and
Ai P: Evodiamine inhibits the migration and invasion of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro via repressing MMP-2
expression. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 76:1173–1184. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Runa F, Hamalian S, Meade K, Shisgal P,
Gray PC and Kelber JA: Tumor microenvironment heterogeneity:
Challenges and opportunities. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 3:218–229. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu A, Wu K, Li J, Mo Y, Lin Y, Wang Y,
Shen X, Li S, Li L and Yang Z: Let-7a inhibits migration, invasion
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting HMGA2 in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 13:1052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taparra K, Tran PT and Zachara NE:
Hijacking the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway to promote
EMT-mediated neoplastic phenotypes. Front Oncol. 6:852016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang M, Sui C, Dai B, Shen W, Lu J and
Yang J: PEG10 is imperative for TGF-β1-induced
epithelialmesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol
Rep. 37:510–518. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Heldin CH, Vanlandewijck M and Moustakas
A: Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer. FEBS Lett. 586:1959–1970.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu JJ, Dang YY, Huang M, Xu WS, Chen XP
and Wang YT: Anti-cancer properties of terpenoids isolated from
Rhizoma Curcumae-a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 143:406–411. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|