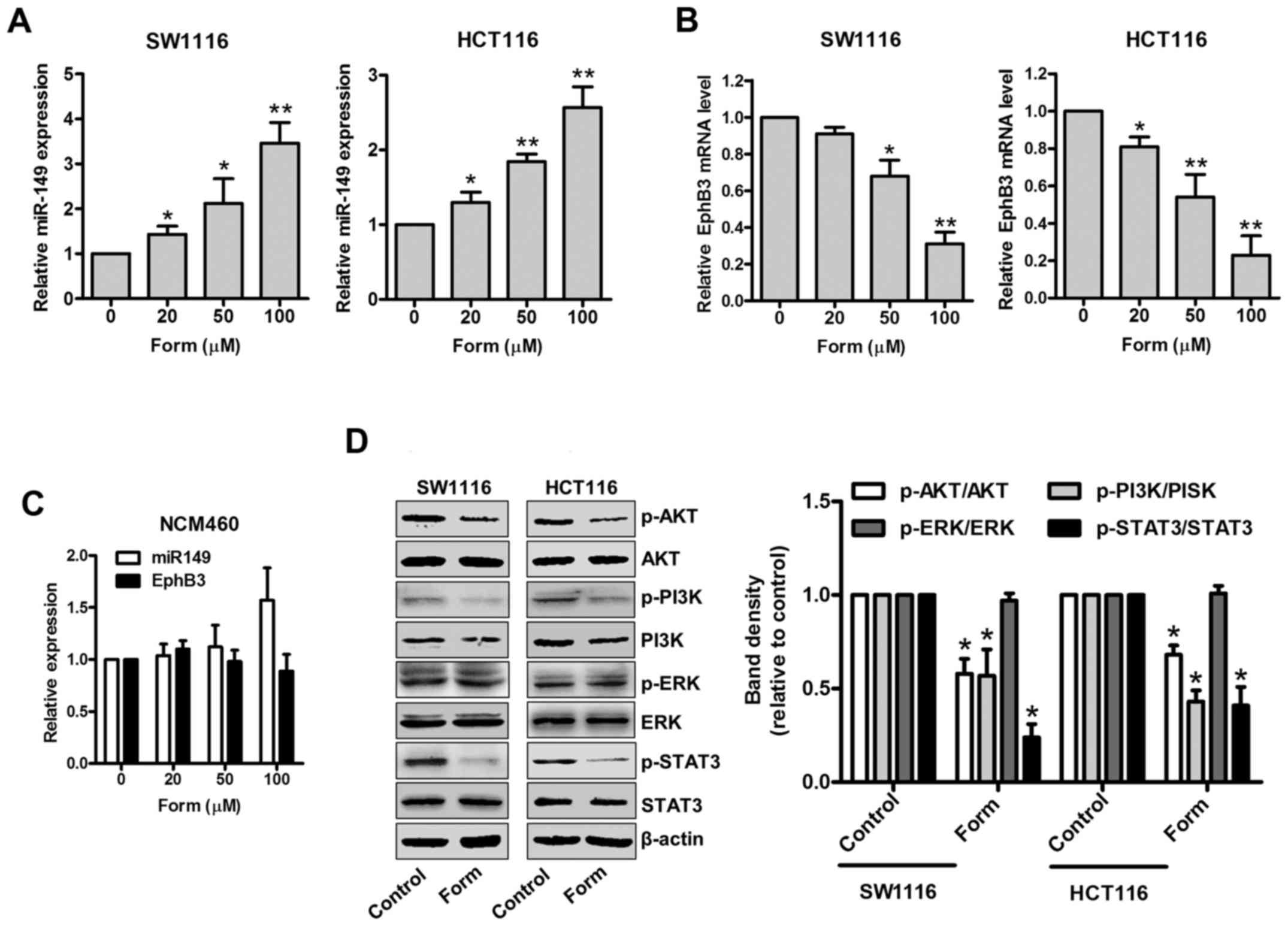
|
1
|
Bodalal Z and Bendardaf R: Coloectal
carcinoma in aSouthern Mediterranean country: The Libyan scenario.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 6:98–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Touil Y, Igoudjil W, Corvaisier M, Dessein
AF, Vandomme J, Monté D, Stechly L, Skrypek N, Langlois C, Grard G,
et al: Colon cancer cells escape 5FU chemotherapy-induced cell
death by entering stemness and quiescence associated with the
c-Yes/YAP axis. Clin Cancer Res. 20:837–846. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Misale S, Yaeger R, Hobor S, Scala E,
Janakiraman M, Liska D, Valtorta E, Schiavo R, Buscarino M,
Siravegna G, et al: Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired
resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature.
486:532–536. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin M, Zhao K, Huang Q and Shang P:
Structural features and biological activities of the
polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus. Int J Biol
Macromol. 64:257–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li T, Zhao X, Mo Z, Huang W, Yan H, Ling Z
and Ye Y: Formononetin promotes cell cycle arrest via
downregulation of Akt/Cyclin D1/CDK4 in human prostate cancer
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:1351–1358. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou R, Xu L, Ye M, Liao M, Du H and Chen
H: Formononetin inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 and
4T1 breast cancer cells by suppressing MMP-2 and MMP-9 through
PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Horm Metab Res. 46:753–760. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barbato S, Solaini G and Fabbri M:
MicroRNAs in oncogenesis and tumor suppression. Int Rev Cell Mol
Biol. 333:229–268. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu Y, Zhang X, Li Z, Yan H, Qin J and Li
T: Formononetin inhibits human bladder cancer cell proliferation
and invasiveness via regulation of miR-21 and PTEN. Food Funct.
8:1061–1066. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu W and Xiao Z: Formononetin induces
apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS by regulating the
expression of Bcl-2, Bax and MiR-375 in vitro and in vivo. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 37:933–939. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen J, Zhang X, Wang Y, Ye Y and Huang Z:
Formononetin promotes proliferation that involves a feedback loop
of microRNA-375 and estrogen receptor alpha in estrogen
receptor-positive cells. Mol Carcinog. 55:312–319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang G, Liu X, Li Y, Wang Y, Liang H, Li
K, Li L, Chen C, Sun W, Ren S, et al: EphB3-targeted regulation of
miR-149 in the migration and invasion of human colonic carcinoma
HCT116 and SW620 cells. Cancer Sci. 108:408–418. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang J, Xie M, Gao P, Ye Y, Liu Y, Zhao
Y, Luo W, Ling Z, Cao Y, Zhang S, et al: Antiproliferative effects
of formononetin on human colorectal cancer via, suppressing cell
growth in vitro, and in vivo. Process Biochem. 50:912–917. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Auyeung KK, Law PC and Ko JK: Novel
anti-angiogenic effects of formononetin in human colon cancer cells
and tumor xenograft. Oncol Rep. 28:2188–2194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen J, Zeng J, Xin M, Huang W and Chen X:
Formononetin induces cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells
via IGF1/PI3K/Akt pathways in vitro and in vivo. Horm Metab Res.
43:681–686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Begnini KR, de Leon Moura PM, Thurow H,
Schultze E, Campos VF, Rodrigues Martins F, Borsuk S, Dellagostin
OA, Savegnago L, Roesch-Ely M, et al: Brazilian red propolis
induces apoptosis-like cell death and decreases migration potential
in bladder cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:6398562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li G, Ji XD, Gao H, Zhao JS, Xu JF, Sun
ZJ, Deng YZ, Shi S, Feng YX, Zhu YQ, et al: EphB3 suppresses
non-small-cell lung cancer metastasis via a PP2A/RACK1/Akt
signalling complex. Nat Commun. 3:6672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen J and Sun L: Formononetin-induced
apoptosis by activation of Ras/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells. Horm Metab
Res. 44:943–948. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galliher AJ and Schiemann WP: Src
phosphorylates Tyr284 in TGF-beta type II receptor and regulates
TGF-beta stimulation of p38 MAPK during breast cancer cell
proliferation and invasion. Cancer Res. 67:3752–3758. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun M, Liu C, Nadiminty N, Lou W, Zhu Y,
Yang J, Evans CP, Zhou Q and Gao AC: Inhibition of Stat3 activation
by sanguinarine suppresses prostate cancer cell growth and
invasion. Prostate. 72:82–89. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ko JK, Lam FY and Cheung AP: Amelioration
of experimental colitis by Astragalus membranaceus through
anti-oxidation and inhibition of adhesion molecule synthesis. World
J Gastroenterol. 11:5787–5794. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Auyeung KK and Ko JK: Novel herbal
flavonoids promote apoptosis but differentially induce cell cycle
arrest in human colon cancer cell. Invest New Drugs. 28:1–13. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang F, Ma YL, Zhang P, Shen TY, Shi CZ,
Yang YZ, Moyer MP, Zhang HZ, Chen HQ, Liang Y and Qin HL: SP1
mediates the link between methylation of the tumour suppressor
miR-149 and outcome in colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 229:12–24.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu X, Xie T, Mao X, Xue L, Chu X and Chen
L: MicroRNA-149 increases the sensitivity of colorectal cancer
cells to 5-fluorouracil by targeting forkhead box transcription
factor FOXM1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 39:617–629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu XY, Xu H, Wu ZF, Chen C, Liu JY, Wu GN,
Yao XQ, Liu FK, Li G and Shen L: Formononetin, a novel FGFR2
inhibitor, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in
preclinical models. Oncotarget. 6:44563–44578. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nicholson KM and Anderson NG: The protein
kinase B/Akt signaling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal.
14:381–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liabakk NB, Talbot I, Smith RA, Wilkinson
K and Balkwill F: Matrix metalloprotease 2 (MMP-2) and matrix
metalloprotease 9 (MMP-9) type IV collagenases in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 56:190–196. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Timofeeva OA, Tarasova NI, Zhang X,
Chasovskikh S, Cheema AK, Wang H, Brown ML and Dritschilo A: STAT3
suppresses transcription of proapoptotic genes in cancer cells with
the involvement of its N-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:1267–1272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|