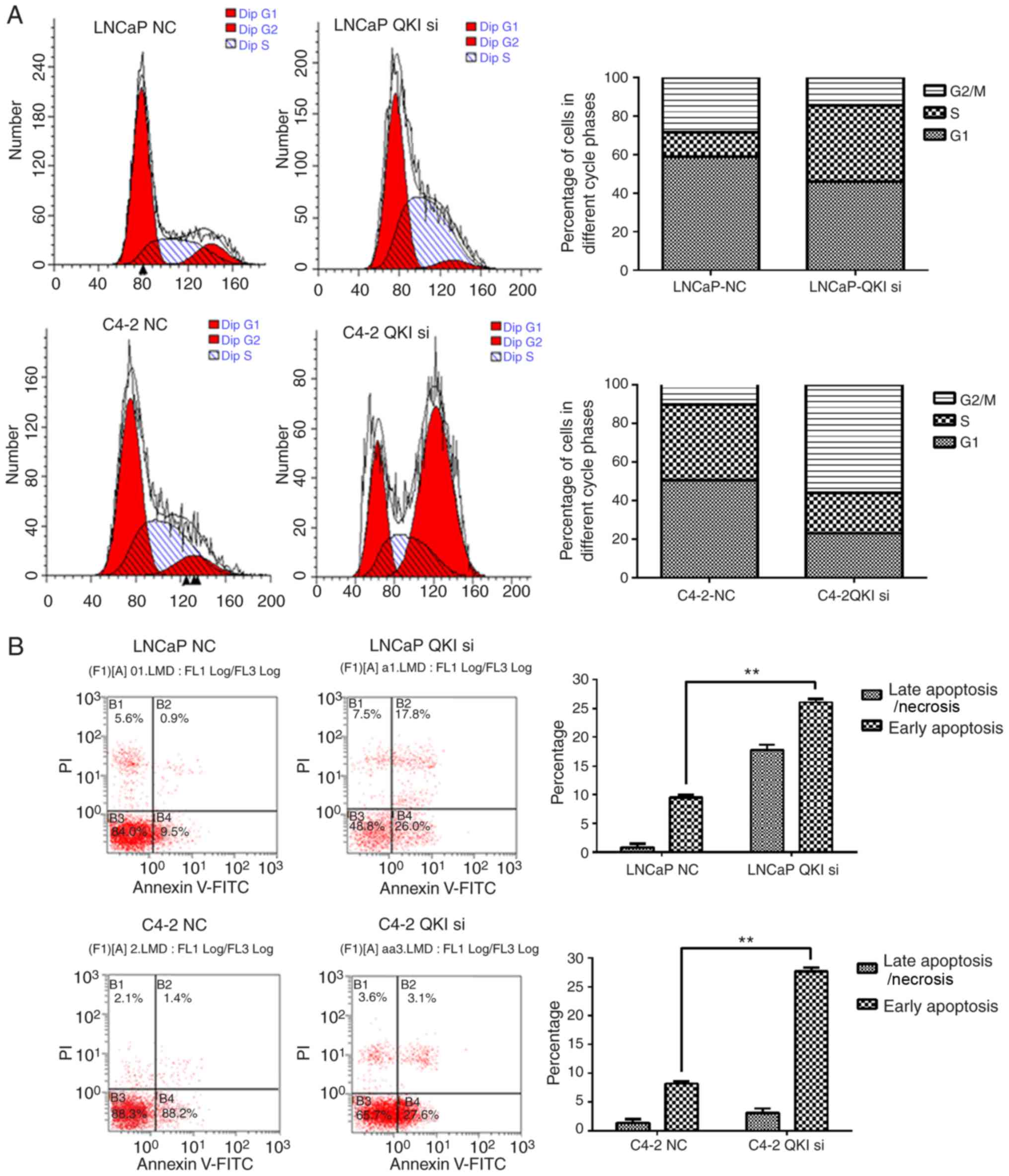
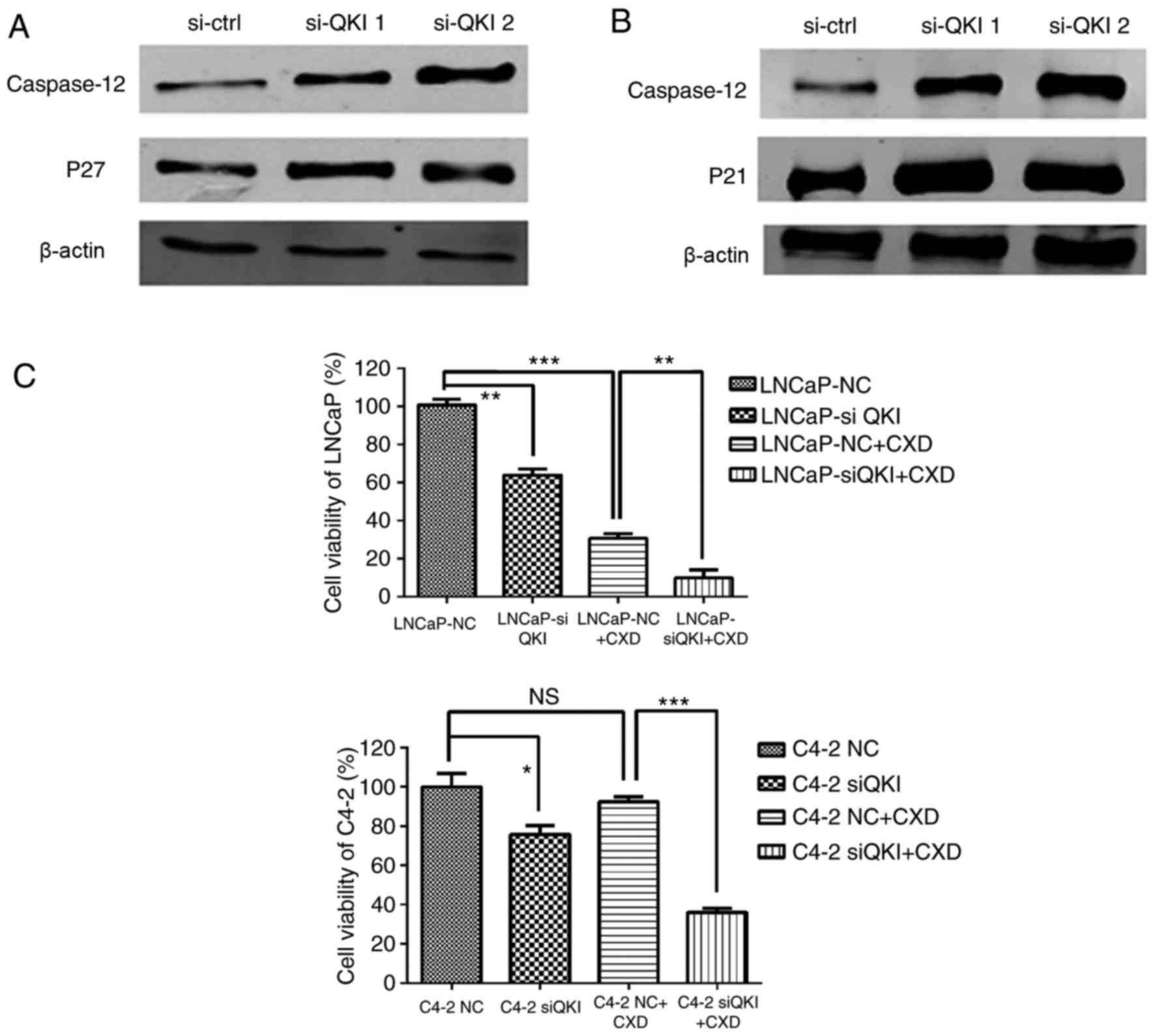
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Babu Suresh S, Joladarashi D, Jeyabal P,
Thandavarayan RA and Krishnamurthy P: RNA-stabilizing proteins as
molecular targets in cardiovascular pathologies. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 25:676–683. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feng Y and Bankston A: The star family
member QKI and cell signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol. 693:25–36. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bohnsack BL, Lai L, Northrop JL, Justice
MJ and Hirschi KK: Visceral endoderm function is regulated by
quaking and required for vascular development. Genesis. 44:93–104.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao L, Ku L, Chen Y, Xia M, LoPresti P
and Feng Y: QKI binds MAP1B mRNA and enhances MAP1B expression
during oligodendrocyte development. Mol Biol Cell. 17:4179–4186.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mulholland PJ, Fiegler H, Mazzanti C,
Gorman P, Sasieni P, Adams J, Jones TA, Babbage JW, Vatcheva R,
Ichimura K, et al: Genomic profiling identifies discrete deletions
associated with translocations in glioblastoma multiforme. Cell
Cycle. 5:783–791. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang G, Fu H, Zhang J, Lu X, Yu F, Jin L,
Bai L, Huang B, Shen L, Feng Y, et al: RNA-binding protein quaking,
a critical regulator of colon epithelial differentiation and a
suppressor of colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 138(231–240): e1–e5.
2010.
|
|
9
|
Zong FY, Fu X, Wei WJ, Luo YG, Heiner M,
Cao LJ, Fang Z, Fang R, Lu D, Ji H and Hui J: The RNA-binding
protein QKI suppresses cancer-associated aberrant splicing. PLoS
Genet. 10:e10042892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM,
Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA and
Goodall GJ: The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of
circRNAs. Cell. 160:1125–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Zhang G, Wei M, Lu X, Fu H, Feng
F, Wang S, Lu W, Wu N, Lu Z and Yuan J: The tumor suppressing
effects of QKI-5 in prostate cancer: A novel diagnostic and
prognostic protein. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:108–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu G, Sprenger C, Sun S, Epilepsia KS,
Haugk K, Zhang X, Coleman I, Nelson PS and Plymate S: AR variant
ARv567es induces carcinogenesis in a novel transgenic mouse model
of prostate cancer. Neoplasia. 15:1009–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garrido C, Paul C, Seigneuric R and
Kampinga HH: The small heat shock proteins family: The long
forgotten chaperones. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1588–1592. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaul G and Thippeswamy H: Role of heat
shock proteins in diseases and their therapeutic potential. Indian
J Microbiol. 51:124–131. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao M, Geng XP and Xiang HP: HSP90 and
SIRT3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and their effect on
invasive capability of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian
Pac J Trop Med. 8:305–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liao X, Tang S, Thrasher JB, Griebling TL
and Li B: Small-interfering RNA-induced androgen receptor silencing
leads to apoptotic cell death in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:505–515. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gillis JL, Selth LA, Centenera MM, Townley
SL, Sun S, Plymate SR, Tilley WD and Butler LM:
Constitutively-active androgen receptor variants function
independently of the HSP90 chaperone but do not confer resistance
to HSP90 inhibitors. Oncotarget. 4:691–704. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Penel N: Splicing variant of androgen
receptors (AR-V7): New paradigms. Bull Cancer. 103:711–713.
2016.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fu X and Feng Y: QKI-5 suppresses cyclin
D1 expression and proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma
cells via MAPK signalling pathway. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
44:562–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu F, Jin L, Yang G, Ji L, Wang F and Lu
Z: Post-transcriptional repression of FOXO1 by QKI results in low
levels of FOXO1 expression in breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
31:1459–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Colabufo NA, Pagliarulo V, Berardi F,
Contino M, Inglese C, Niso M, Ancona P, Albo G, Pagliarulo A and
Perrone R: Bicalutamide failure in prostate cancer treatment:
Involvement of multi drug resistance proteins. Eur J Pharmacol.
601:38–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Daniels G, Jha R, Shen Y, Logan SK and Lee
P: Androgen receptor coactivators that inhibit prostate cancer
growth. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2:62–70. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|