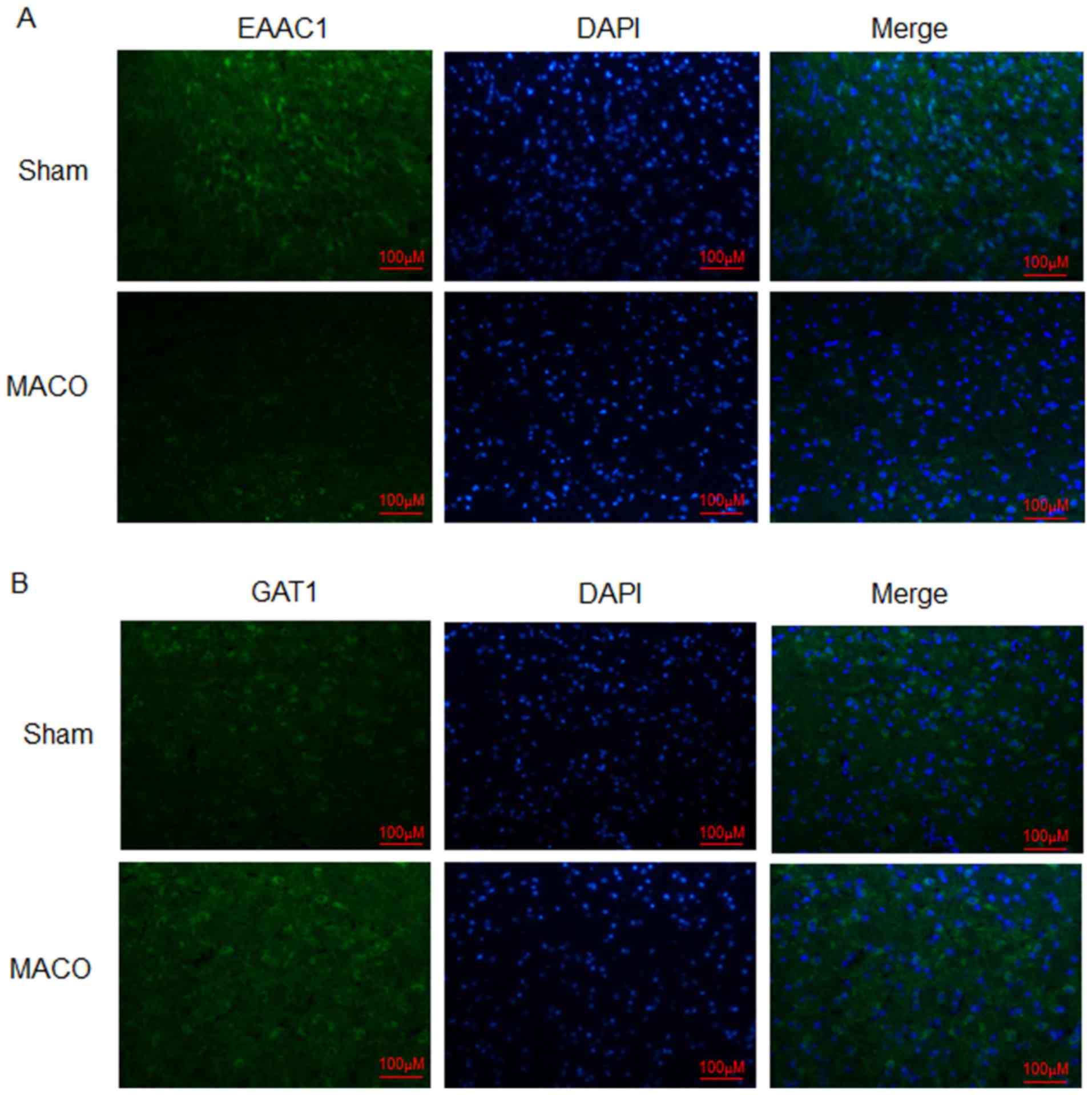
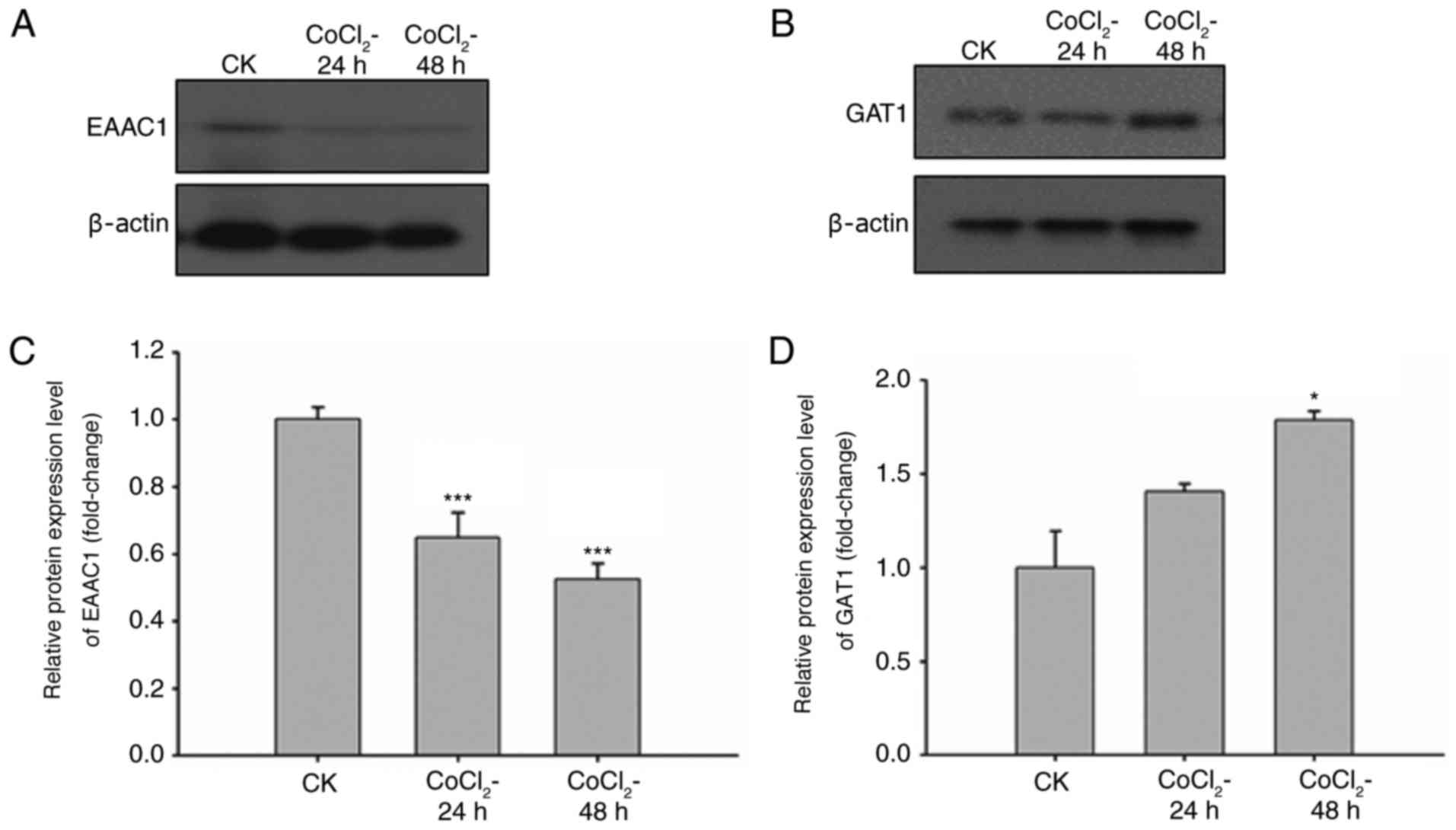
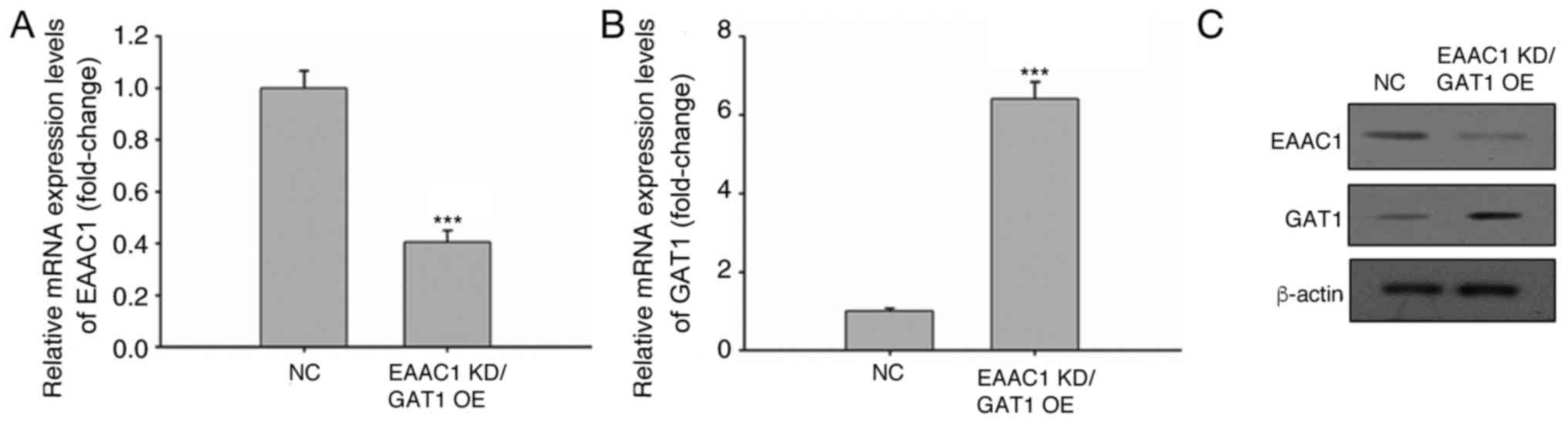
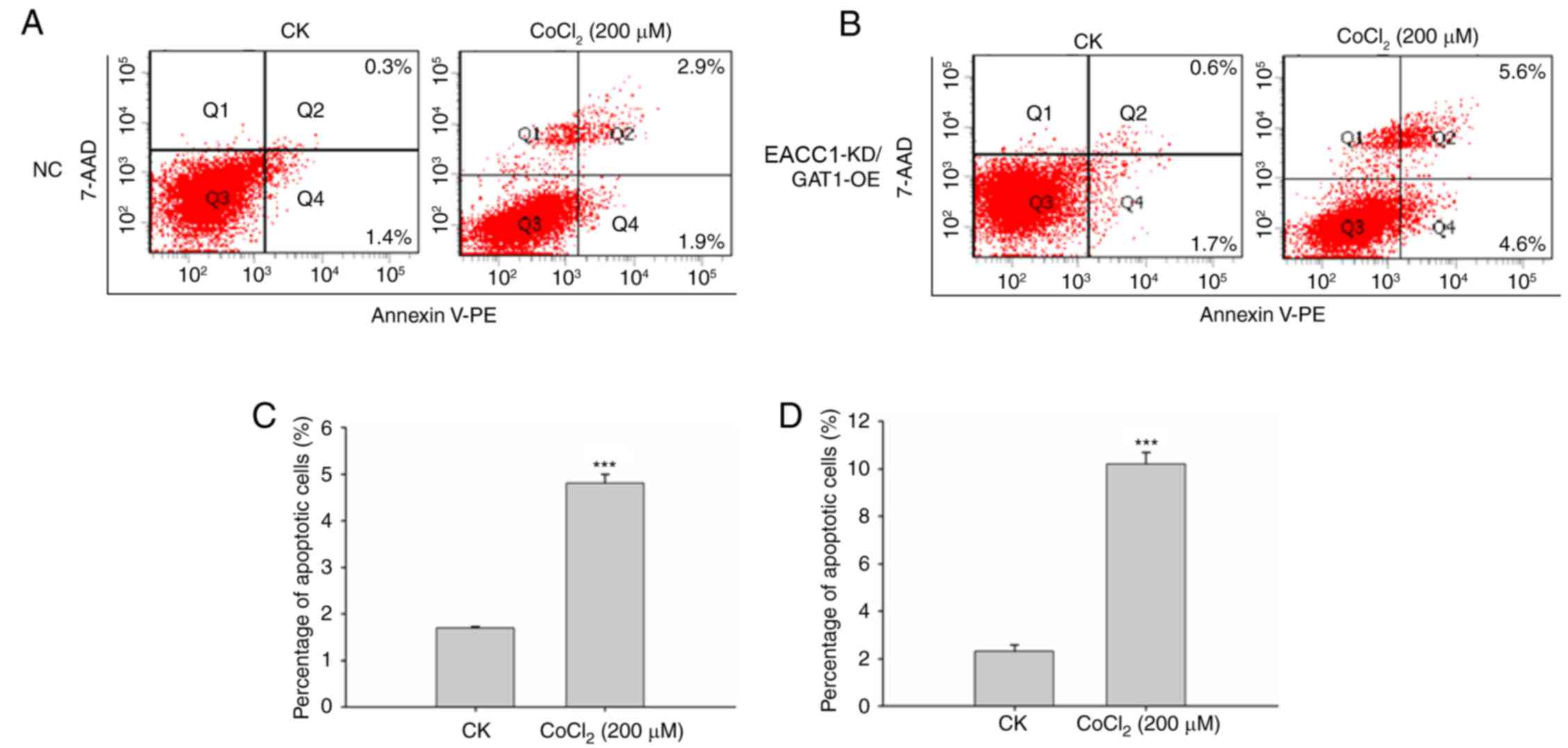
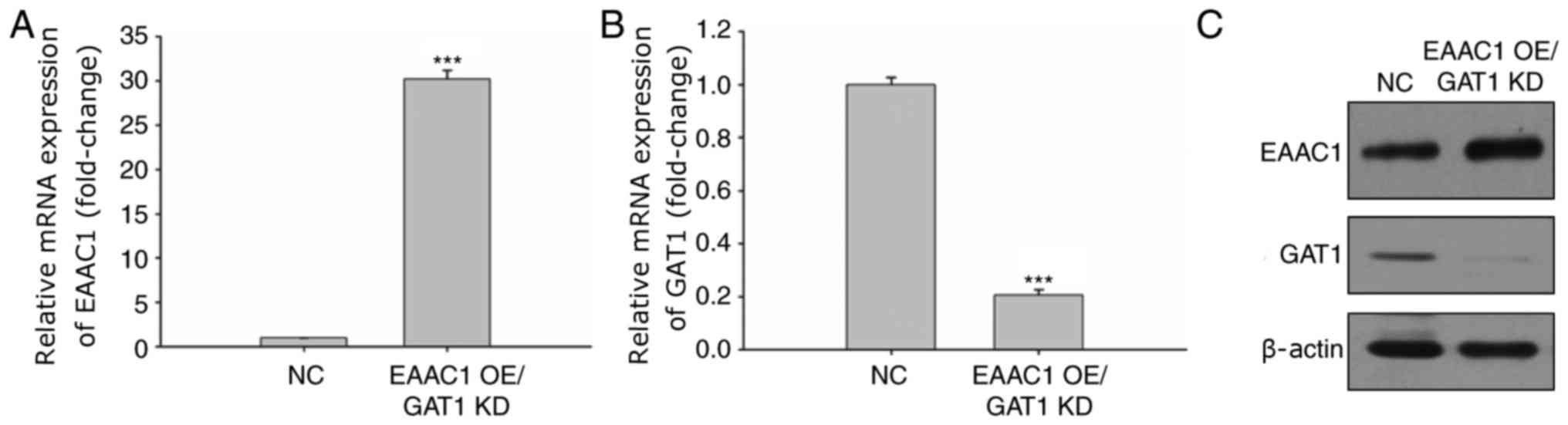
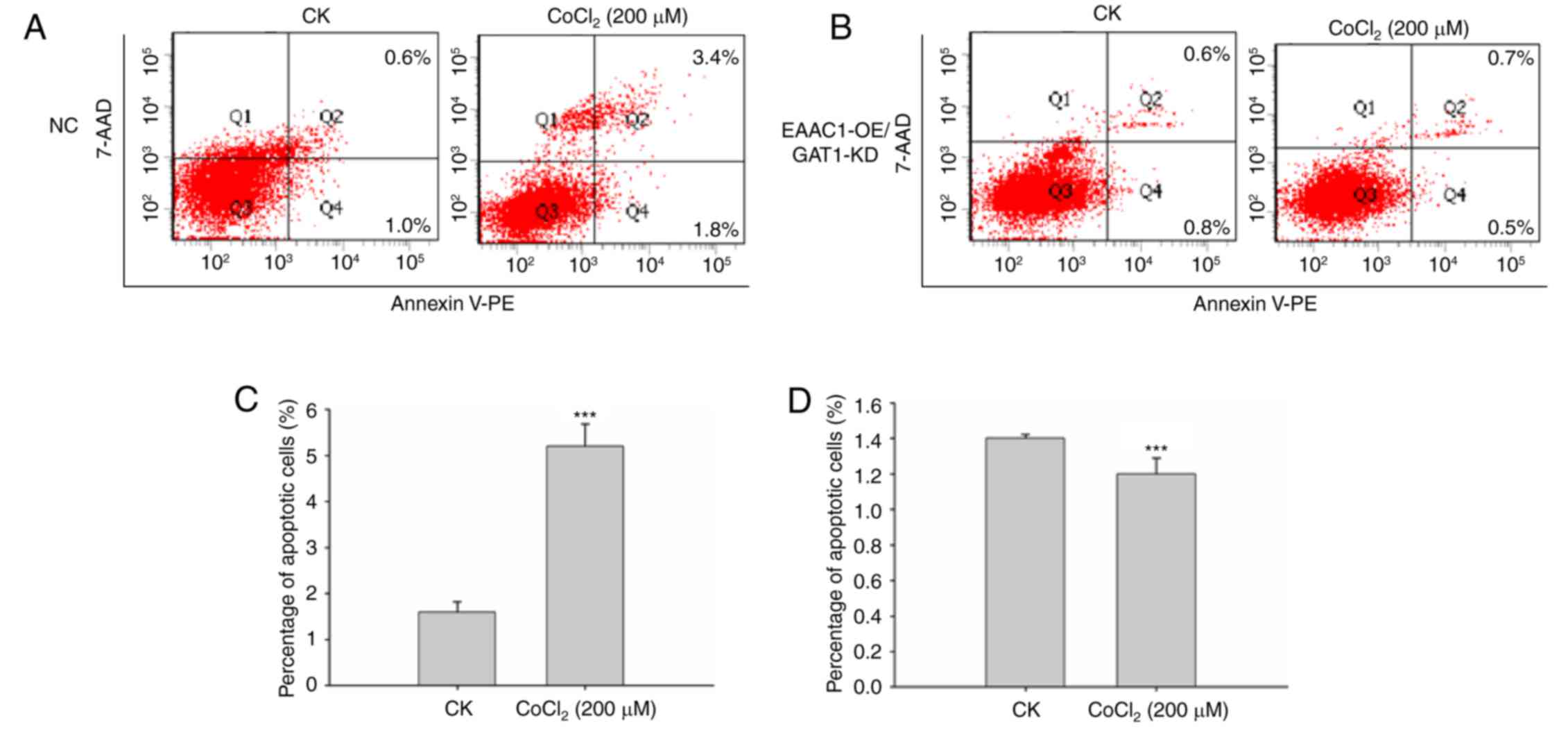
|
1
|
Choi DW and Rothman SM: The role of
glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Ann Rev
Neurosci. 13:171–182. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mwaniki MK, Atieno M, Lawn JE and Newton
CR: Long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes after intrauterine and
neonatal insults: A systematic review. Lancet. 379:445–452. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Douglas-Escobar M and Weiss MD:
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: A review for the clinician. JAMA
Pediatr. 169:397–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsumoto N, Kumamoto E, Furue H and
Yoshimura M: GABA-mediated inhibition of glutamate release during
ischemia in substantia gelatinosa of the adult rat. J Neurophysiol.
89:257–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Voytenko LP, Lushnikova IV, Savotchenko
AV, Isaeva EV, Skok MV, Lykhmus OY, Patseva MA and Skibo GG:
Hippocampal GABAergic interneurons coexpressing alpha7-nicotinic
receptors and connexin-36 are able to improve neuronal viability
under oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res. 1616:134–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Y and Danbolt NC: GABA and glutamate
transporters in brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
4:1652013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Danbolt NC: Glutamate uptake. Prog
Neurobiol. 65:1–105. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, Yamada K,
Watanabe M, Takahashi K, Iwama H, Nishikawa T, Ichihara N, Kikuchi
T, et al: Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking
the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science. 276:1699–1702. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan
WY, Chen Y and Swanson RA: Neuronal glutathione deficiency and
age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat
Neurosci. 9:119–126. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kiryu-Seo S, Gamo K, Tachibana T, Tanaka K
and Kiyama H: Unique anti-apoptotic activity of EAAC1 in injured
motor neurons. EMBO J. 25:3411–3421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Conti F, Minelli A and Melone M: GABA
transporters in the mammalian cerebral cortex: Localization,
development and pathological implications. Brain Res Brain Res Rev.
45:196–212. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pozdnyakova N, Yatsenko L, Parkhomenko N
and Himmelreich N: Perinatal hypoxia induces a long-lasting
increase in unstimulated gaba release in rat brain cortex and
hippocampus. The protective effect of pyruvate. Neurochem Int.
58:14–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Richards DA and Bowery NG: Comparative
effects of the GABA uptake inhibitors, tiagabine and NNC-711, on
extracellular GABA levels in the rat ventrolateral thalamus.
Neurochem Res. 21:135–140. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Richerson GB and Wu Y: Role of the GABA
transporter in epilepsy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 548:76–91. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smith MD, Saunders GW, Clausen RP, Frølund
B, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Larsson OM, Schousboe A, Wilcox KS and
White HS: Inhibition of the betaine-GABA transporter (mGAT2/BGT-1)
modulates spontaneous electrographic bursting in the medial
entorhinal cortex (mEC). Epilepsy Res. 79:6–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Frahm C, Siegel G, Grass S and Witte OW:
Stable expression of the vesicular GABA transporter following
photothrombotic infarct in rat brain. Neuroscience. 140:865–877.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakajima H, Kubo T, Semi Y, Itakura M,
Kuwamura M, Izawa T, Azuma YT and Takeuchi T: A rapid, targeted,
neuron-selective, in vivo knockdown following a single
intracerebroventricular injection of a novel chemically modified
siRNA in the adult rat brain. J Biotechnol. 157:326–333. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo L, Lan J, Lin Y, Guo P, Nie Q, Mao Q,
Ren L and Qiu Y: Hypoxia/ischemia up-regulates Id2 expression in
neuronal cells in vivo and in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 554:88–93.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Graham EM, Ruis KA, Hartman AL,
Northington FJ and Fox HE: A systematic review of the role of
intrapartum hypoxia-ischemia in the causation of neonatal
encephalopathy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 199:587–595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Strasser K, Lueckemann L, Kluever V,
Thavaneetharajah S, Hoeber D, Bendix I, Fandrey J, Bertsche A and
Felderhoff-Mueser U: Dose-dependent effects of levetiracetam after
hypoxia and hypothermia in the neonatal mouse brain. Brain Res.
1646:116–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murray DM, Bala P, O'Connor CM, Ryan CA,
Connolly S and Boylan GB: The predictive value of early
neurological examination in neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic
encephalopathy and neurodevelopmental outcome at 24 months. Dev Med
Child Neurol. 52:e55–e59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pettmann B and Henderson CE: Neuronal cell
death. Neuron. 20:633–647. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fu F, Wu D and Qian C: The MicroRNA-224
inhibitor prevents neuronal apoptosis via targeting spastic
paraplegia 7 after cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 59:421–429.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|