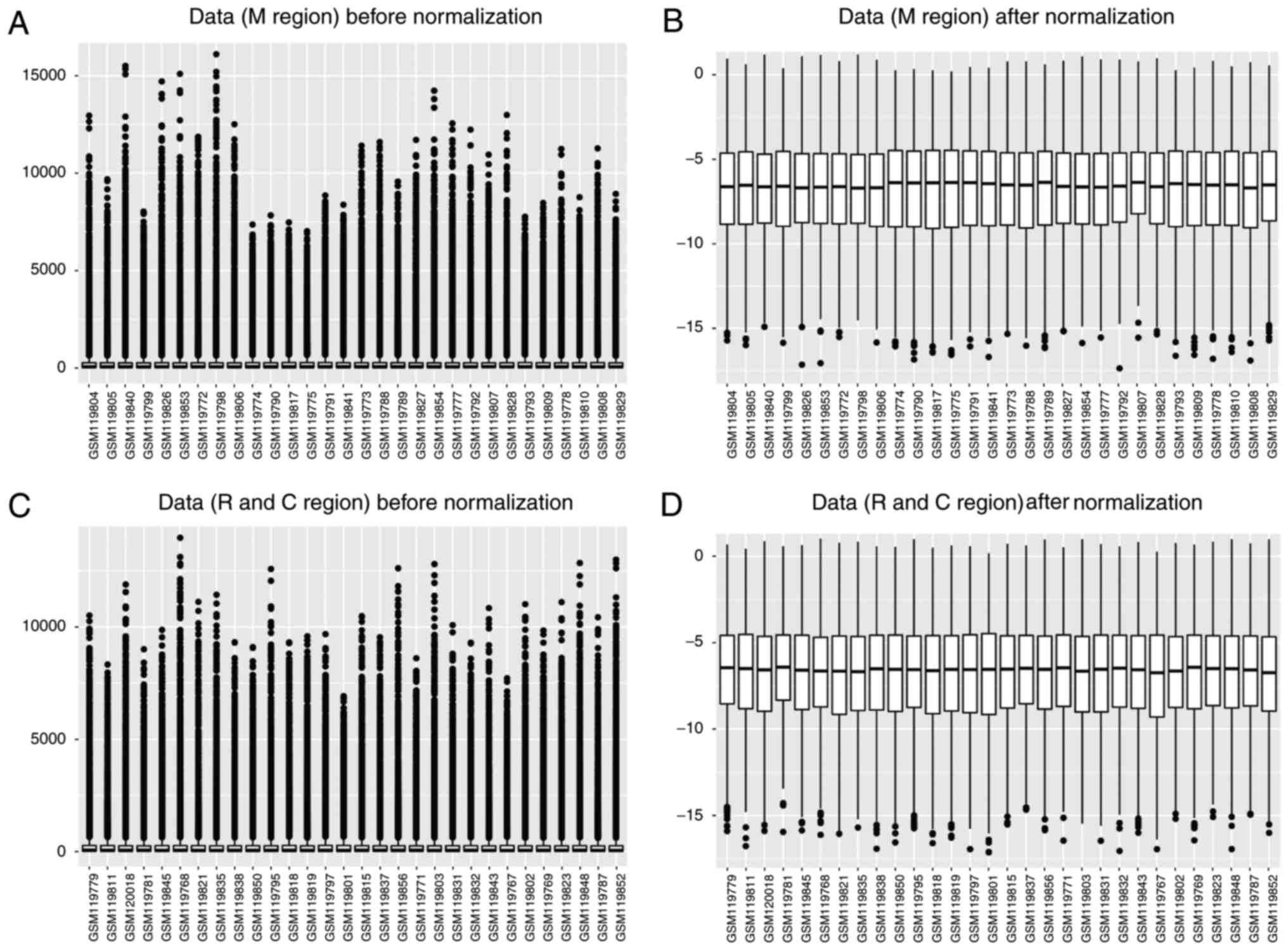
|
1
|
Ahuja CS, Wilson JR, Nori S, Kotter MRN,
Druschel C, Curt A and Fehlings MG: Traumatic spinal cord injury.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia X, Kowalski RG, Sciubba DM and
Geocadin RG: Critical care of traumatic spinal cord injury. J
Intensive Care Med. 28:12–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siddiqui AM, Khazaei M and Fehlings MG:
Translating mechanisms of neuroprotection, regeneration and repair
to treatment of spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 218:15–54.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahuja CS and Fehlings M: Concise review:
Bridging the gap: Novel neuroregenerative and neuroprotective
strategies in spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 5:914–924.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim YH, Ha KY and Kim SI: Spinal cord
injury and related clinical trials. Clin Orthop Surg. 9:1–9. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bareyre FM and Schwab ME: Inflammation,
degeneration and regeneration in the injured spinal cord: Insights
from DNA microarrays. Trends Neurosci. 26:555–563. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ydens E, Palmers I, Hendrix S and Somers
V: The next generation of biomarker research in spinal cord injury.
Mol Neurobiol. 54:1482–1499. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang W, Liu R, Xu Z, Niu X, Mao Z, Meng Q
and Cao X: Further insight into molecular mechanism underlying
thoracic spinal cord injury using bioinformatics methods. Mol Med
Rep. 12:7851–7858. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen G, Fang X and Yu M: Regulation of
gene expression in rats with spinal cord injury based on microarray
data. Mol Med Rep. 12:2465–2472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wen T, Hou J, Wang F, Zhang Y, Zhang T and
Sun T: Comparative analysis of molecular mechanism of spinal cord
injury with time based on bioinformatics data. Spinal Cord.
54:431–438. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu Z, Shen Q, Zhu L and Wei X:
Identification of pivotal genes and pathways for spinal cord injury
via bioinformatics analysis. Mol Med Rep. 16:3929–3937. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duan H, Ge W, Zhang A, Xi Y, Chen Z, Luo
D, Cheng Y, Fan KS, Horvath S, Sofroniew MV, et al: Transcriptome
analyses reveal molecular mechanisms underlying functional recovery
after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:13360–13365.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carvalho BS and Irizarry RA: A framework
for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics.
26:2363–2367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
da Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun N, Sun W, Li S, Yang J, Yang L, Quan
G, Gao X, Wang Z, Cheng X, Li Z, et al: Proteomics analysis of
cellular proteins co-immunoprecipitated with nucleoprotein of
influenza a virus (H7N9). Int J Mol Sci. 16:25982–25998. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Di Giovanni S, Knoblach SM, Brandoli C,
Aden SA, Hoffman EP and Faden AI: Gene profiling in spinal cord
injury shows role of cell cycle in neuronal death. Ann Neurol.
53:454–468. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carmel JB, Galante A, Soteropoulos P,
Tolias P, Recce M, Young W and Hart RP: Gene expression profiling
of acute spinal cord injury reveals spreading inflammatory signals
and neuron loss. Physiol Genomics. 7:201–213. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kjell J and Olson L: Rat models of spinal
cord injury: From pathology to potential therapies. Dis Model Mech.
9:1125–1137. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saghazadeh A and Rezaei N: The role of
timing in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother.
92:128–139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kinoshita T, Nakamura T, Umemoto Y, Kojima
D, Moriki T, Mitsui T, Goto M, Ishida Y and Tajima F: Increase in
interleukin-6 immediately after wheelchair basketball games in
persons with spinal cord injury: Preliminary report. Spinal Cord.
51:508–510. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu JZ, Huang JH, Xiao ZM, Li JH, Li XM and
Lu HB: Tetramethylpyrazine accelerates the function recovery of
traumatic spinal cord in rat model by attenuating inflammation. J
Neurol Sci. 324:94–99. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
David BT, Ratnayake A, Amarante MA, Reddy
NP, Dong W, Sampath S, Heary RF and Elkabes S: A toll-like receptor
9 antagonist reduces pain hypersensitivity and the inflammatory
response in spinal cord injury. Neurobiol Dis. 54:194–205. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin W, Wang J, Zhu T, Yuan B, Ni H, Jiang
J, Wang H and Liang W: Anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in
experimental spinal cord injury in rats. Inflamm Res. 63:381–387.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schroepfer GJ Jr: Sterol biosynthesis. Ann
Rev Biochem. 50:585–621. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ghayee HK and Auchus RJ: Basic concepts
and recent developments in human steroid hormone biosynthesis. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 8:289–300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elkabes S and Nicot AB: Sex steroids and
neuroprotection in spinal cord injury: A review of preclinical
investigations. Exp Neurol. 259:28–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brotfain E, Gruenbaum SE, Boyko M, Kutz R,
Zlotnik A and Klein M: Neuroprotection by estrogen and progesterone
in traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 14:641–653. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eftekharpour E, Nagakannan P, Iqbal MA and
Chen QM: Mevalonate cascade and small Rho GTPase in spinal cord
injury. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 10:141–151. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flueck JL and Perret C: Vitamin D
deficiency in individuals with a spinal cord injury: A literature
review. Spinal Cord. 55:428–434. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bauman WA, Morrison NG and Spungen AM:
Vitamin D replacement therapy in persons with spinal cord injury. J
Spinal Cord Med. 28:203–207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oleson CV, Patel PH and Wuermser LA:
Influence of season, ethnicity and chronicity on vitamin D
deficiency in traumatic spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med.
33:202–213. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Giatti S, Garcia-Segura LM and Melcangi
RC: New steps forward in the neuroactive steroid field. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 153:127–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tuem KB and Atey TM: Neuroactive steroids:
Receptor interactions and responses. Front Neurol. 8:4422017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|