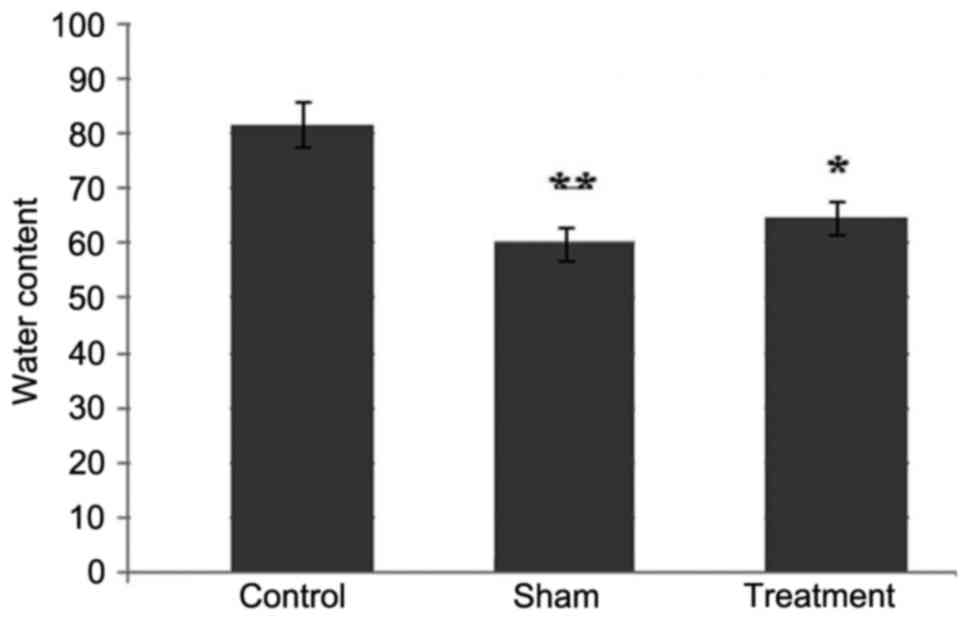
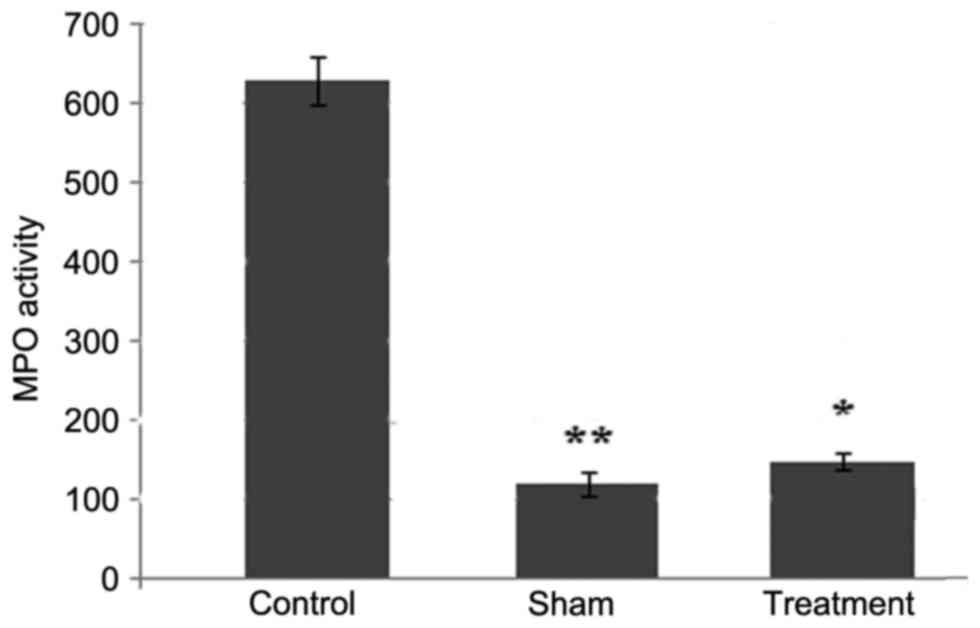
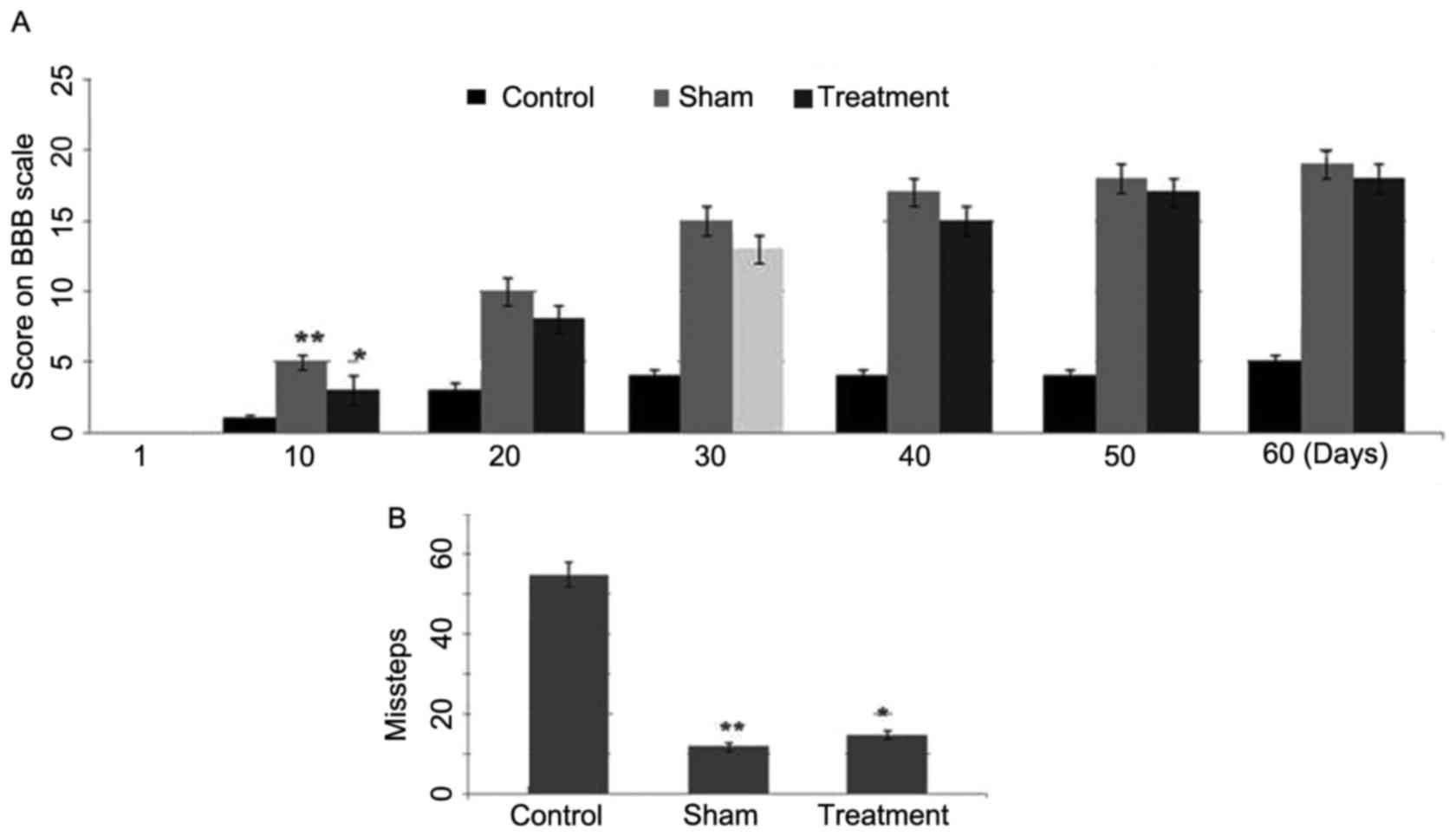
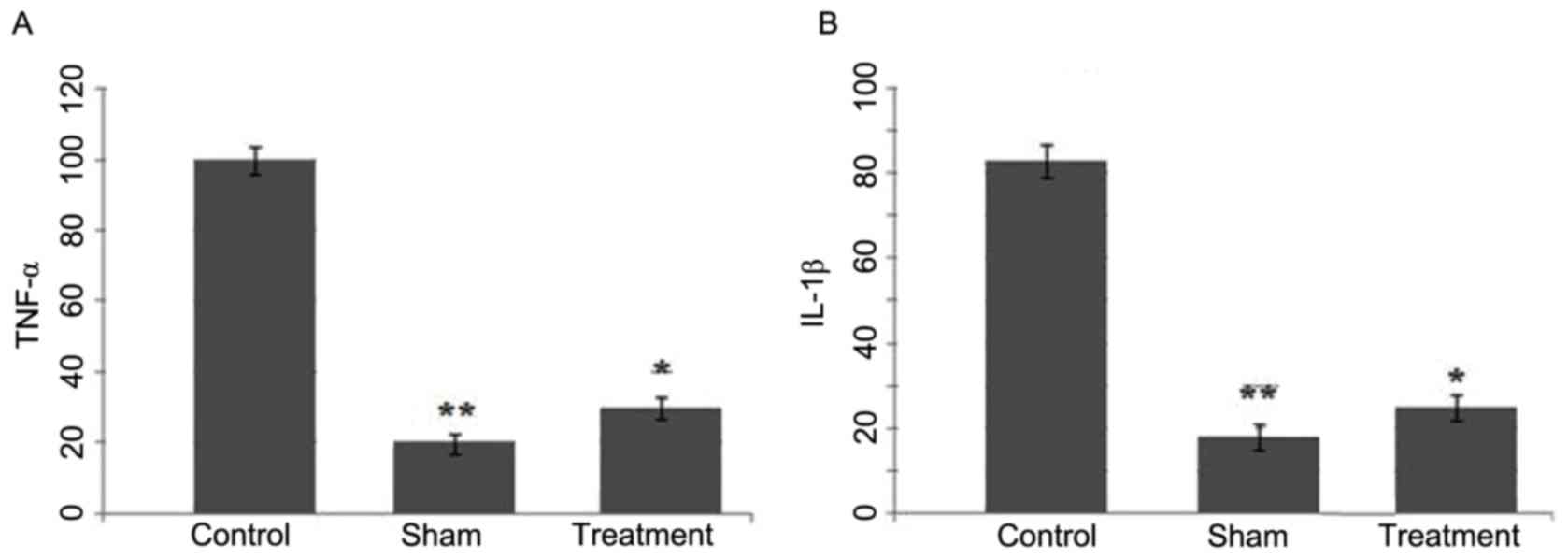
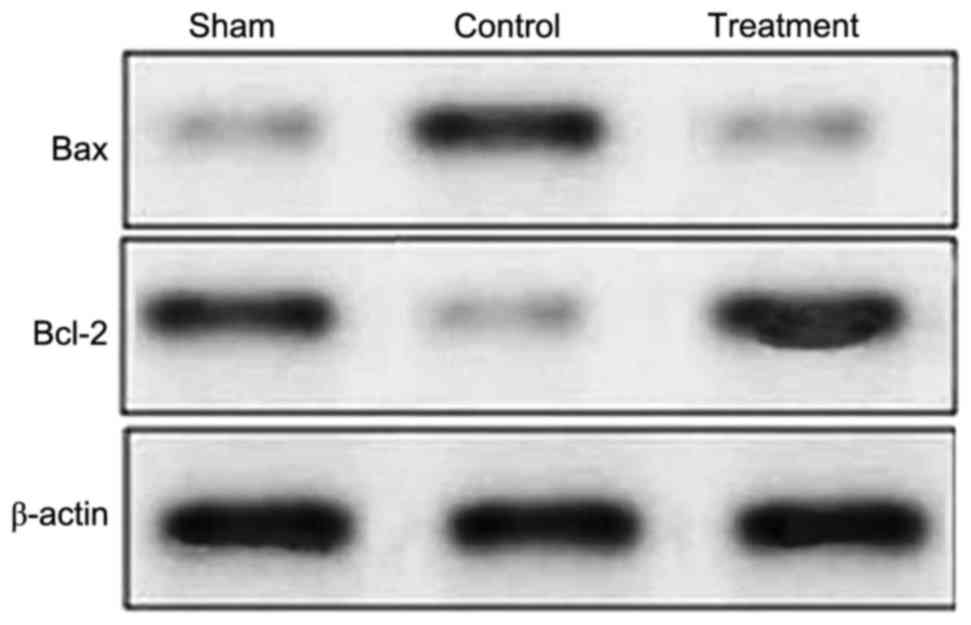
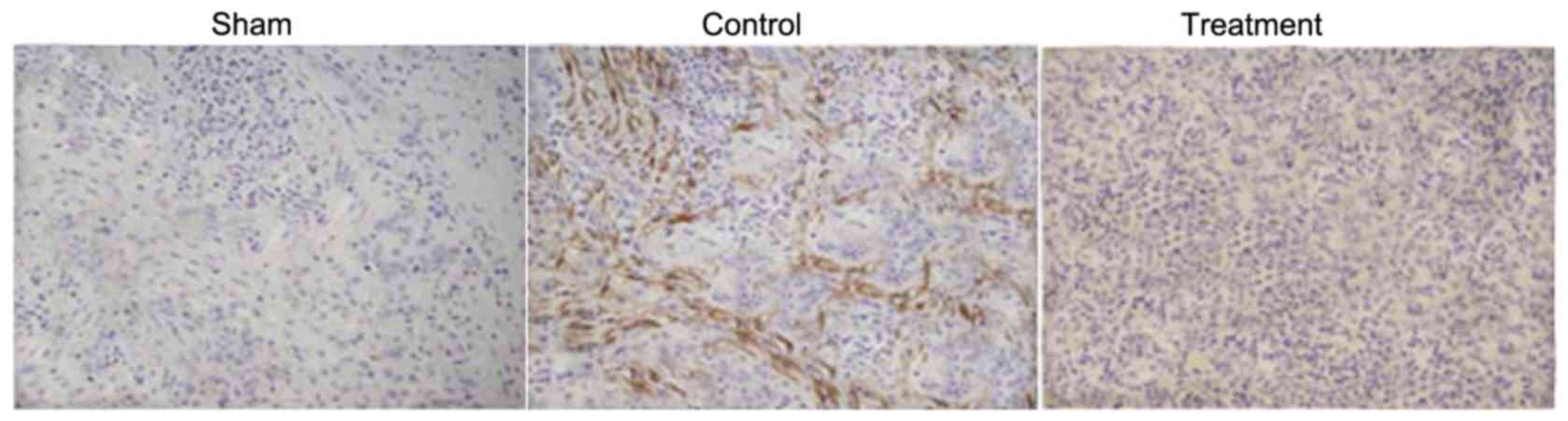
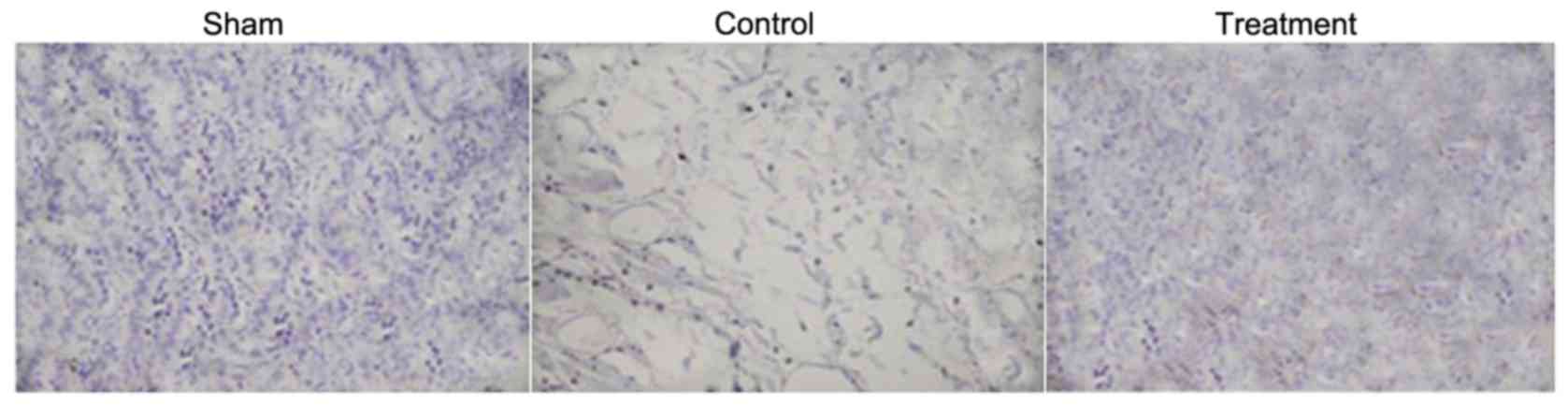
|
1
|
Schmitt C, Miranpuri GS, Dhodda VK,
Isaacson J, Vemuganti R and Resnick DK: Changes in spinal cord
injury-induced gene expression in rat are strain-dependent. Spine
J. 6:113–119. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hong Z, Chen H, Hong H, Lin L and Wang Z:
TSP-1 expression changes in diabetic rats with spinal cord injury.
Neurol Res. 31:878–882. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qiao F, Atkinson C, Kindy MS, Shunmugavel
A, Morgan BP, Song H and Tomlinson S: The alternative and terminal
pathways of complement mediate post-traumatic spinal cord
inflammation and injury. Am J Pathol. 177:3061–3070. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Beattie MS: Inflammation and apoptosis:
Linked therapeutic targets in spinal cord injury. Trends Mol Med.
10:580–583. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beck KD, Nguyen HX, Galvan MD, Salazar DL,
Woodruff TM and Anderson AJ: Quantitative analysis of cellular
inflammation after traumatic spinal cord injury: Evidence for a
multiphasic inflammatory response in the acute to chronic
environment. Brain. 133:433–447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grasso G, Sfacteria A, Meli F, Fodale V,
Buemi M and Iacopino DG: Neuroprotection by erythropoietin
administration after experimental traumatic brain injury. Brain
Res. 1182:99–105. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nisula S, Yang R, Poukkanen M, Vaara ST,
Kaukonen KM, Tallgren M, Haapio M, Tenhunen J, Korhonen AM and
Pettilä V: FINNAKI Study Group: Predictive value of urine
interleukin-18 in the evolution and outcome of acute kidney injury
in critically ill adult patients. Br J Anaesth. 114:460–468. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Zhang ZX, Lian D, Haig A,
Bhattacharjee RN and Jevnikar AM: IL-37 inhibits IL-18-induced
tubular epithelial cell expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines
and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 87:396–408.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miranda ML, Balarini MM and Bouskela E:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates the microcirculatory derangements evoked
by experimental sepsis. Anesthesiology. 122:619–630. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geloen A, Chapelier K, Cividjian A,
Dantony E, Rabilloud M, May CN and Quintin L: Clonidine and
dexmedetomidine increase the pressor response to norepinephrine in
experimental sepsis: A pilot study. Crit Care Med. 41:e431–e438.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Duan X, Li Y, Zhou C, Huang L and Dong Z:
Dexmedetomidine provides neuroprotection: Impact on
ketamine-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing rat brain. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 58:1121–1126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Turan A, Bashour CA, You J, Kirkova Y,
Kurz A, Sessler DI and Saager L: Dexmedetomidine sedation after
cardiac surgery decreases atrial arrhythmias. J Clin Anesth.
26:634–642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang ZX, Huang CY, Hua YP, Huang WQ, Deng
LH and Liu KX: Dexmedetomidine reduces intestinal and hepatic
injury after hepatectomy with inflow occlusion under general
anaesthesia: A randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth.
112:1055–1064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Si YN, Bao HG, Xu L, Wang XL, Shen Y, Wang
JS and Yang XB: Dexmedetomidine protects against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat kidney. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 18:1843–1851. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of
the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition.
National Academies Press; Washington (DC): 2011
|
|
16
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC:
Graded histological and locomotor outcomes after spinal cord
contusion using the NYU weight-drop device versus transection. Exp
Neurol. 139:244–256. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Loane DJ and Byrnes KR: Role of microglia
in neurotrauma. Neurotherapeutics. 7:366–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin Y, Sun W, Li Z, Zhang B, Cui H, Deng
L, Xie P, Xiang J and Zou J: Effects of combining
methylprednisolone with rolipram on functional recovery in adult
rats following spinal cord injury. Neurochem Int. 62:903–912. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Genovese T, Mazzon E, Crisafulli C,
Esposito E, Di Paola R, Muià C, Di Bella P, Meli R, Bramanti P and
Cuzzocrea S: Combination of dexamethasone and etanercept reduces
secondary damage in experimental spinal cord trauma. Neuroscience.
150:168–181. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McTigue DM, Tani M, Krivacic K, Chernosky
A, Kelner GS, Maciejewski D, Maki R, Ransohoff RM and Stokes BT:
Selective chemokine mRNA accumulation in the rat spinal cord after
contusion injury. J Neurosci Res. 53:368–376. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao W, Xie W, Le W, Beers DR, He Y,
Henkel JS, Simpson EP, Yen AA, Xiao Q and Appel SH: Activated
microglia initiate motor neuron injury by a nitric oxide and
glutamate-mediated mechanism. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 63:964–977.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morino T, Ogata T, Horiuchi H, Takeba J,
Okumura H, Miyazaki T and Yamamoto H: Delayed neuronal damage
related to microglia proliferation after mild spinal cord
compression injury. Neurosci Res. 46:309–318. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|