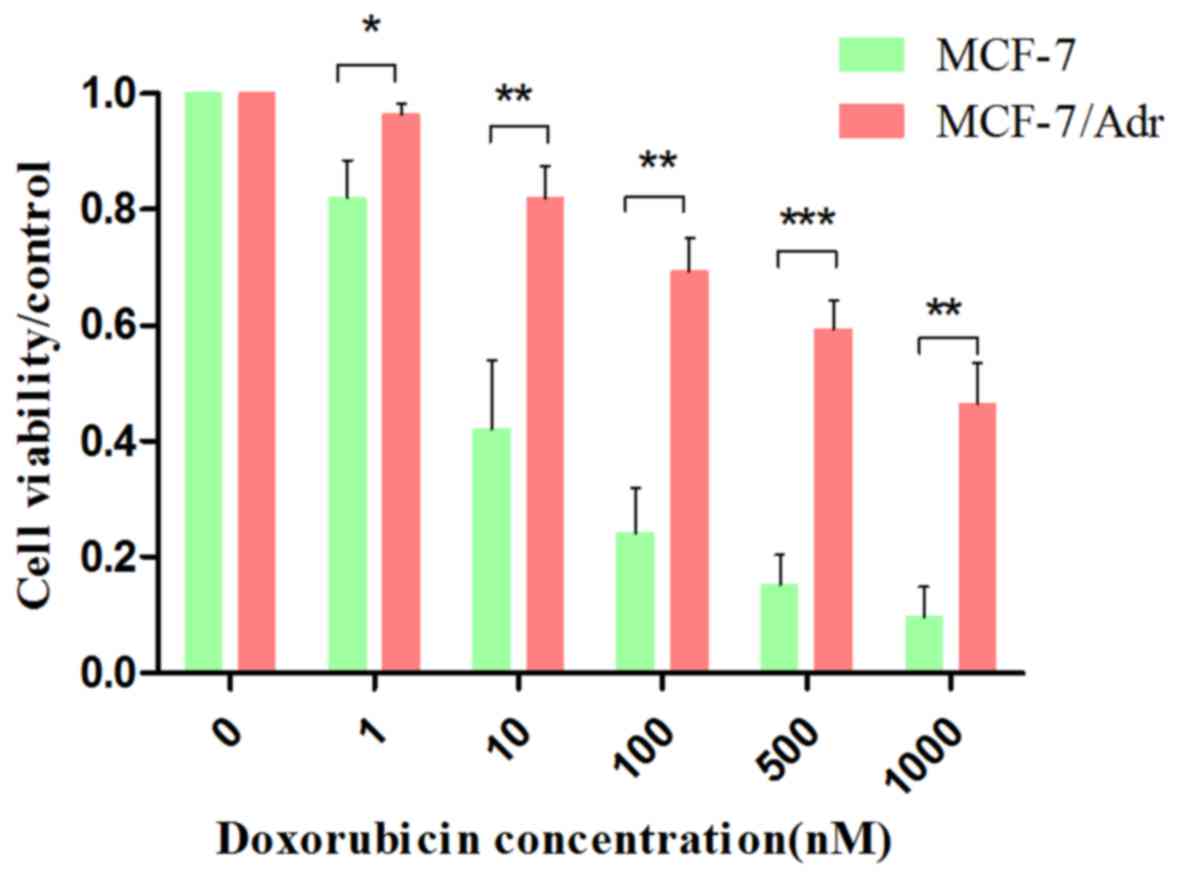
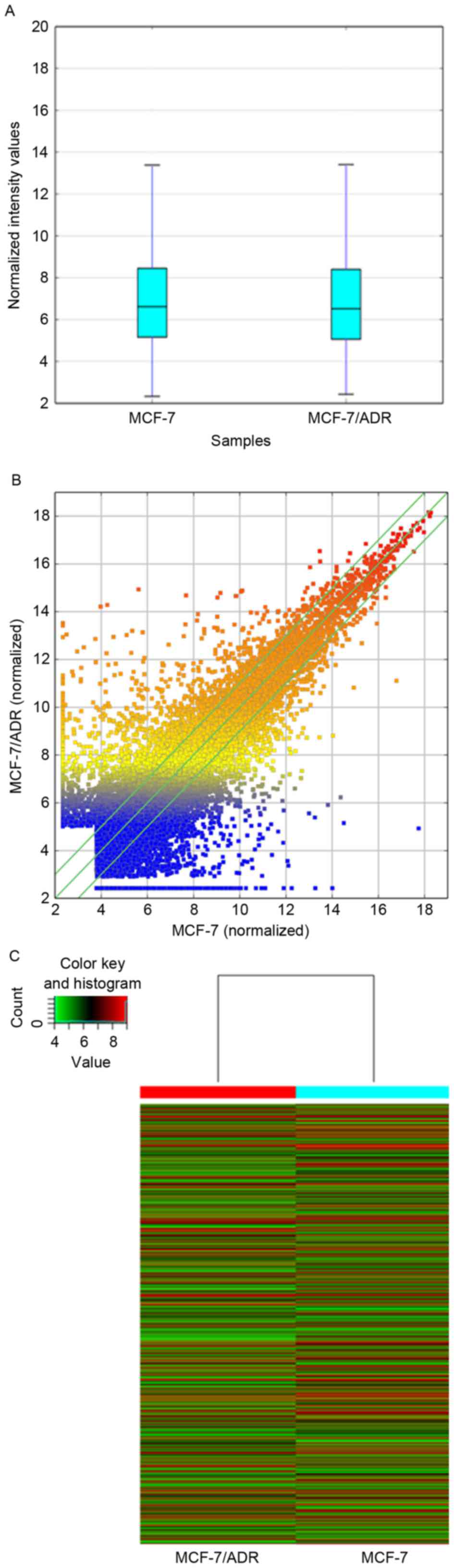
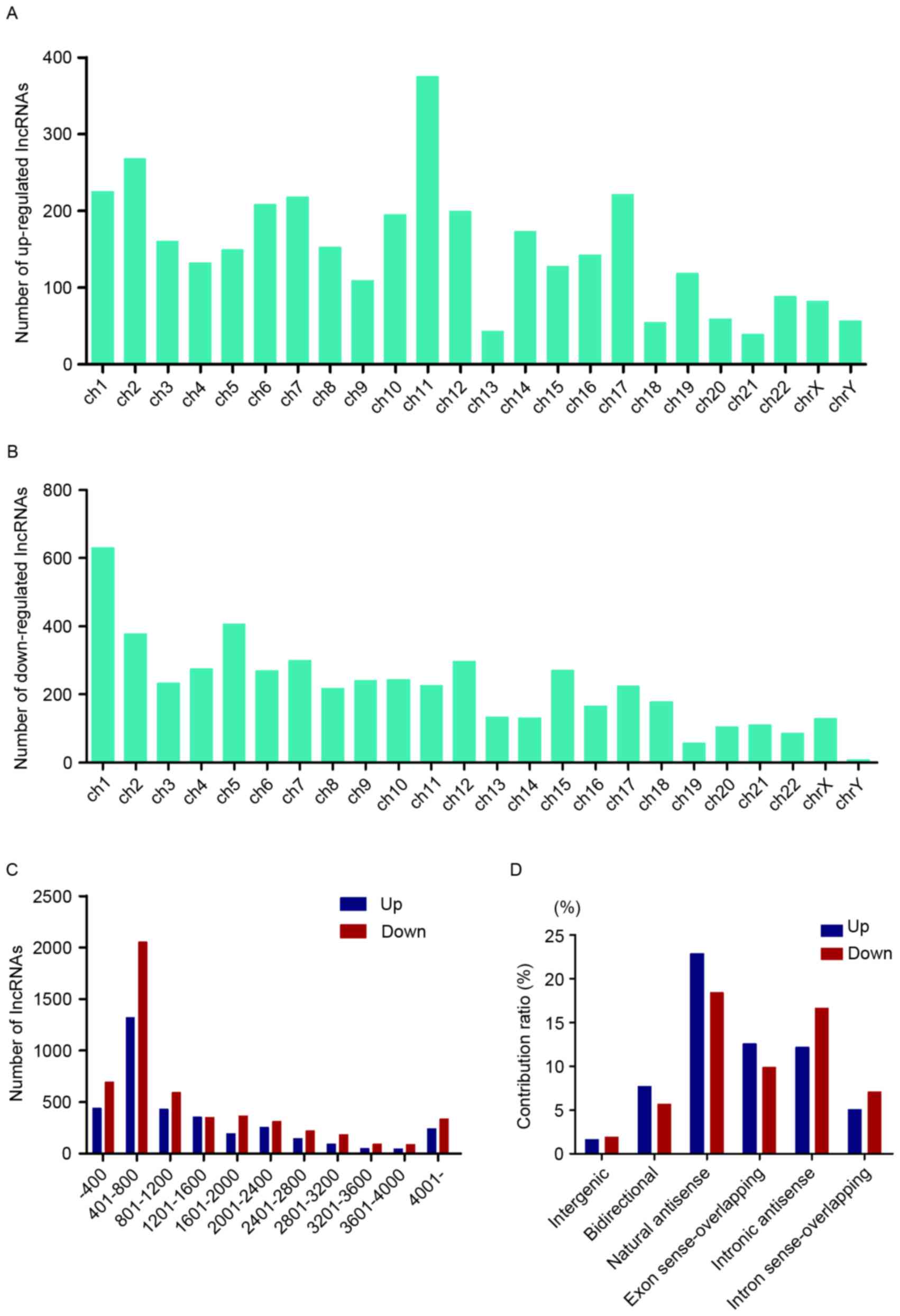
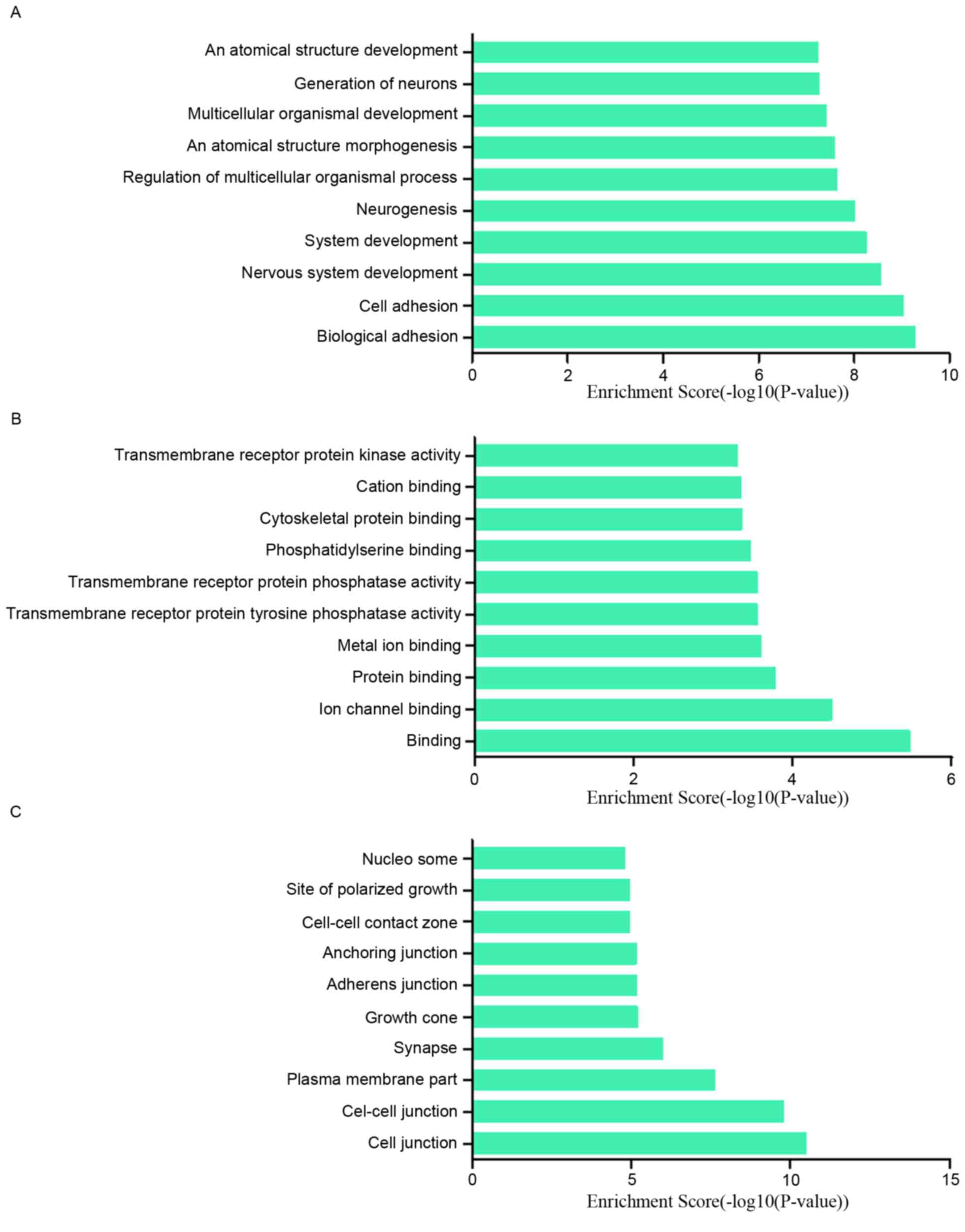
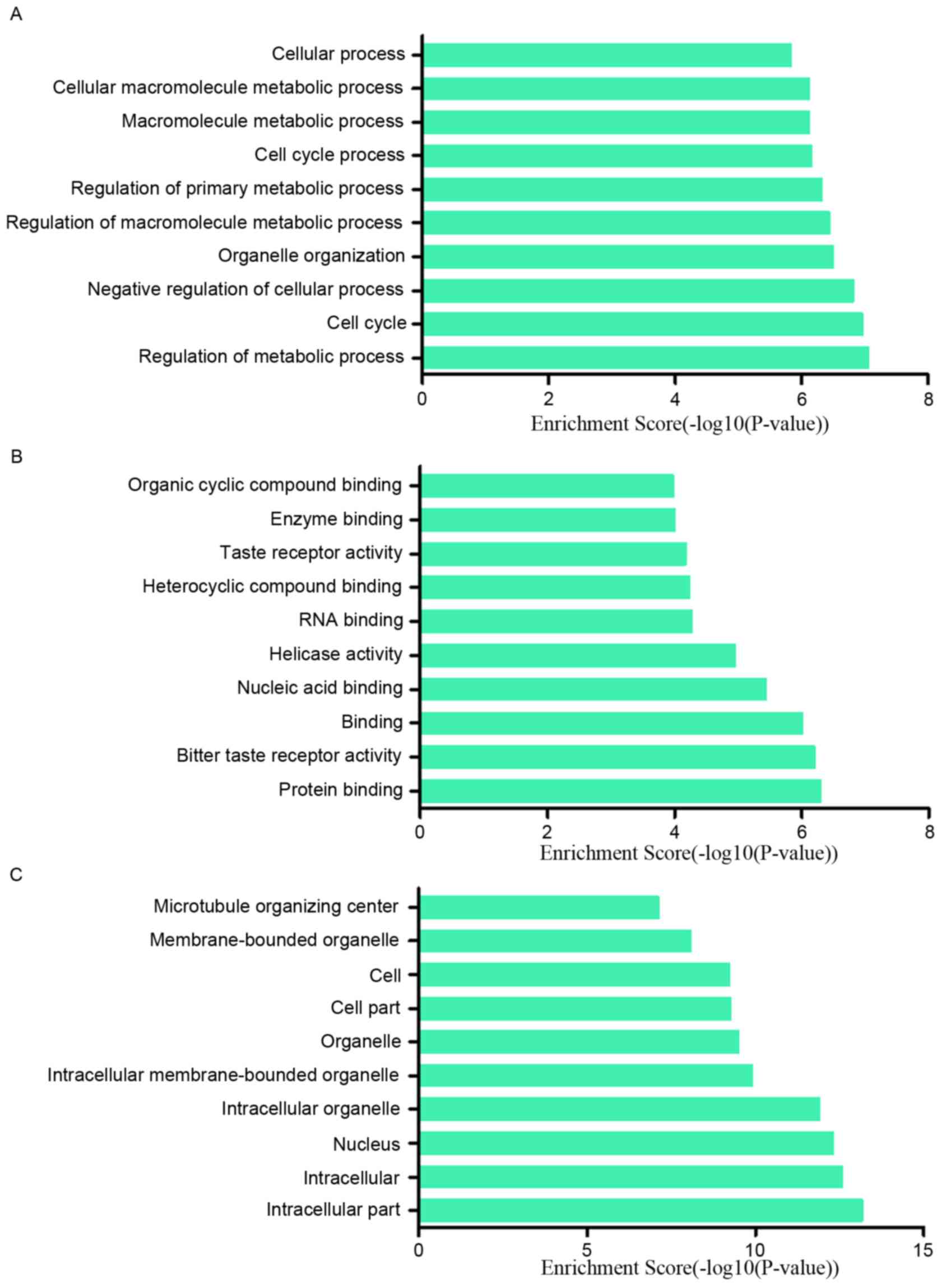
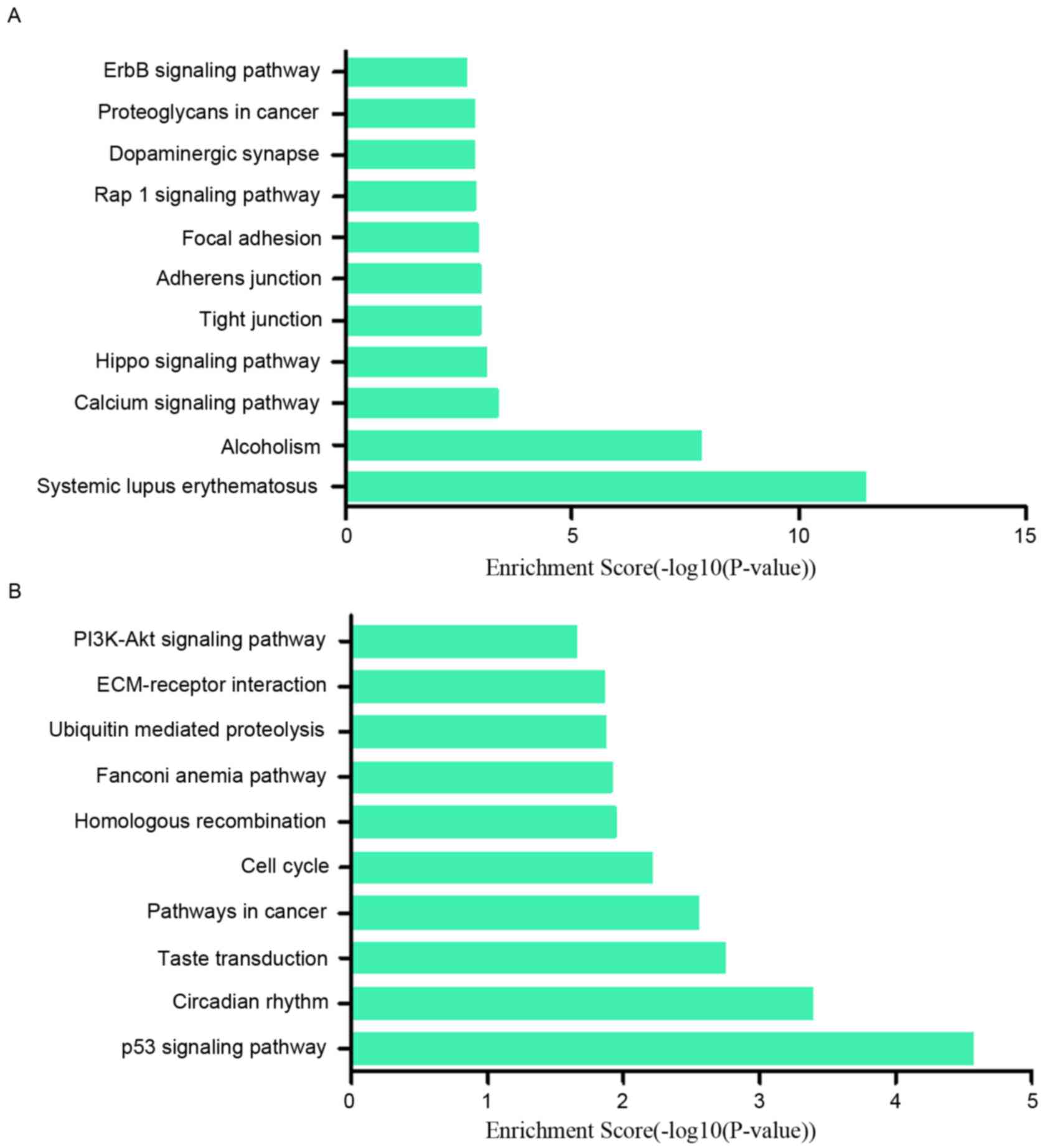
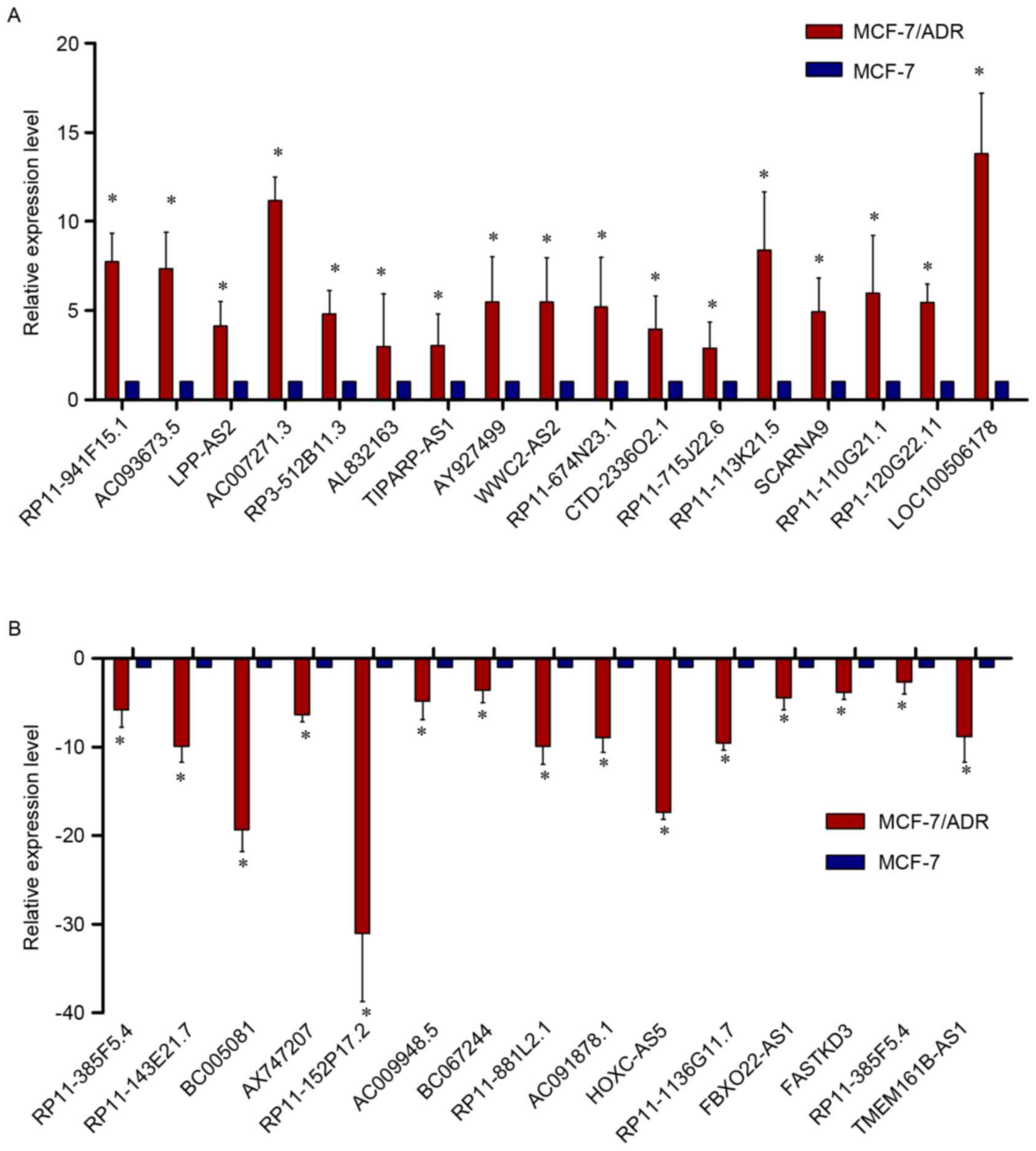
|
1
|
World Health Organization, . Cancer. Fact
sheet no. 297. https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/February.
2011
|
|
2
|
Kolonel L and Wilkens L: Migrant
studiesSchottenfeld D and Fraumeni JF Jr: Cancer epidemiology and
prevention. 3rd edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press; pp.
189–201. 2006, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis
J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Chen WQ, Shao ZM and Goss PE: Breast
cancer in China. Lancet Oncol. 15:e279–e289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lianos GD, Vlachos K, Zoras O, Katsios C,
Cho WC and Roukos DH: Potential of antibody-drug conjugates and
novel therapeutics in breast cancer management. Onco Targets Ther.
7:491–500. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E and
Chang HY: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin
domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Loewer S, Cabili MN, Guttman M, Loh YH,
Thomas K, Park IH, Garber M, Curran M, Onder T, Agarwal S, et al:
Large intergenic non-coding RNA-RoR modulates reprogramming of
human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Genet. 42:1113–1117.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hah N and Kraus WL: Hormone-regulated
transcriptomes: Lessons learned from estrogen signaling pathways in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 382:652–664. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ilott NE and Ponting CP: Predicting long
non-coding RNAs using RNA sequencing. Methods. 63:50–59. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Spizzo R, Almeida MI and Colombatti A:
Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of translational
research. Oncogene. 31:4577–4587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, French C, Lin
MF, Feldser D, Huarte M, Zuk O, Carey BW, Cassady JP, et al:
Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large
non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature. 458:223–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huarte M and Rinn JL: Large non-coding
RNAs: missing links in cancer? Hum Mol Genet. 19:R152–R161. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kogo R, Shimamura T, Mimori K, Kawahara K,
Imoto S, Sudo T, Tanaka F, Shibata K, Suzuki A, Komune S, et al:
Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates polycomb-dependent chromatin
modification and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal
cancers. Cancer Res. 71:6320–6326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sørensen KP, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Bak M,
Cold S, Burton M, Larsen MJ and Kruse TA: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in
estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 142:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prensner JR, Iyer MK, Balbin OA,
Dhanasekaran SM, Cao Q, Brenner JC, Laxman B, Asangani IA, Grasso
CS, Kominsky HD, et al: Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate
cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated
in disease progression. Nat Biotechnol. 29:742–749. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu J, Wan L, Lu K, Sun M, Pan X, Zhang P,
Lu B, Liu G and Wang Z: The long noncoding RNA MEG3 contributes to
cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01145862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, Liu J, Zhang M, Wu W,
De W, Wang Z and Wang R: The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes
to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via
downregualtion of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS One.
8:e772932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Zhao X, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Ye H,
Wang Y, Zeng J, Song Y, Gao W, et al: The long non-coding RNA
HOTTIP promotes progression and gemcitabine resistance by
regulating HOXA13 in pancreatic cancer. J Transl Med. 13:842015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi K, Yan IK, Kogure T, Haga H and
Patel T: Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of long non-coding
RNA ROR modulates chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular cancer.
FEBS Open Bio. 4:458–467. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lv J, Xia K, Xu P, Sun E, Ma J, Gao S,
Zhou Q, Zhang M, Wang F, Chen F, et al: miRNA expression patterns
in chemoresistant breast cancer tissues. Biomed Pharmacother.
68:935–942. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, . Fitzmaurice C, Dicker D, Pain A, Hamavid H,
Moradi-Lakeh M, MacIntyre MF, Allen C, Hansen G, Woodbrook R, et
al: The Global Burden of Cancer 2013. JAMA Oncol. 1:505–527. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martin HL, Smith L and Tomlinson DC:
Multidrug-resistant breast cancer: Current perspectives. Breast
Cancer (Dove Med Press). 6:1–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amiri-Kordestani L, Basseville A, Kurdziel
K, Fojo AT and Bates SE: Targeting MDR in breast and lung cancer:
Discriminating its potential importance from the failure of drug
resistance reversal studies. Drug Resist Updat. 15:50–61. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jia H, Truica CI, Wang B, Wang Y, Ren X,
Harvey HA, Song J and Yang JM: Immunotherapy for triple-negative
breast cancer: Existing challenges and exciting prospects. Drug
Resist Updat. 32:1–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan Y, Shen B, Tan M, Mu X, Qin Y, Zhang F
and Liu Y: Long non-coding RNA UCA1 increases chemoresistance of
bladder cancer cells by regulating Wnt signaling. FEBS J.
281:1750–1758. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang L, Song X, Wang X, Xie Y, Wang Z, Xu
Y, You X, Liang Z and Cao H: Circulating DNA of HOTAIR in serum is
a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
152:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gökmen-Polar Y, Vladislav IT, Neelamraju
Y, Janga SC and Badve S: Prognostic impact of HOTAIR expression is
restricted to ER-negative breast cancers. Sci Rep. 5:87652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang YL, Overstreet AM, Chen MS, Wang J,
Zhao HJ, Ho PC, Smith M and Wang SC: Combined inhibition of EGFR
and c-ABL suppresses the growth of triple-negative breast cancer
growth through inhibition of HOTAIR. Oncotarget. 6:11150–11161.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hajjari M and Salavaty A: HOTAIR: An
oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Biol
Med. 12:1–9. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Subramaniam MM, Chan JY, Yeoh KG, Quek T,
Ito K and Salto-Tellez M: Molecular pathology of RUNX3 in human
carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:315–331. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lund AH and van Lohuizen M: RUNX: A
trilogy of cancer genes. Cancer Cell. 1:213–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Levanon D, Negreanu V, Bernstein Y, Bar-Am
I, Avivi L and Groner Y: AML1, AML2 and AML3, the human members of
the runt domain gene-family: cDNA structure, expression and
chromosomal localization. Genomics. 23:425–432. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barghout SH, Zepeda N, Vincent K, Azad AK,
Xu Z, Yang C, Steed H, Postovit LM and Fu Y: RUNX3 contributes to
carboplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 138:647–655. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo C, Ding J, Yao L, Sun L, Lin T, Song
Y, Sun L and Fan D: Tumor suppressor gene Runx3 sensitizes gastric
cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drugs by downregulating Bcl-2,
MDR-1 and MRP-1. Int J Cancer. 116:155–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, Lu Q and Cai X: MicroRNA-106a
induces multidrug resistance in gastric cancer by targeting RUNX3.
FEBS Lett. 587:3069–3075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bezler M, Hengstler JG and Ullrich A:
Inhibition of doxorubicin-induced HER3-PI3K-AKT signalling enhances
apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells. Mol Oncol. 6:516–529. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gao AM, Ke ZP, Shi F, Sun GC and Chen H:
Chrysin enhances sensitivity of BEL-7402/ADM cells to doxorubicin
by suppressing PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 and ERK/Nrf2 pathway. Chem Biol
Interact. 206:100–108. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Y, Jia L, Ren D, Liu C, Gong Y, Wang N,
Zhang X and Zhao Y: Axl mediates tumor invasion and
chemosensitivity through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and is
transcriptionally regulated by slug in breast carcinoma. IUBMB
Life. 66:507–518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang XL, Lin FJ, Guo YJ, Shao ZM and Ou
ZL: Gemcitabine resistance in breast cancer cells regulated by
PI3K/AKT-mediated cellular proliferation exerts negative feedback
via the MEK/MAPK and mTOR pathways. Onco Targets Ther. 7:1033–1042.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu Y, Yu J, Wang S, Lu R, Wu J and Jiang
B: Overexpression of CD133 enhances chemoresistance to
5-fluorouracil by activating the PI3K/Akt/p70S6K pathway in gastric
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 32:2437–2444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li Y, Chen K, Li L, Li R, Zhang Z and Ren
W: Overexpression of SOX2 is involved in paclitaxel resistance of
ovarian cancer via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol. 36:9823–9828.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xiao ZM, Wang XY and Wang AM: Periostin
induces chemoresistance in colon cancer cells through activation of
the PI3K/Akt/survivin pathway. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 62:401–406.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang LH, Yin AA, Cheng JX, Huang HY, Li
XM, Zhang YQ, Han N and Zhang X: TRIM24 promotes glioma progression
and enhances chemoresistance through activation of the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Oncogene. 34:600–610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li J, Liang X and Yang X: Ursolic acid
inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in gemcitabine-resistant
human pancreatic cancer via the JNK and PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathways.
Oncol Rep. 28:501–510. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fujimoto D, Ueda Y, Hirono Y, Goi T and
Yamaguchi A: PAR1 participates in the ability of multidrug
resistance and tumorigenesis by controlling Hippo-YAP pathway.
Oncotarget. 6:34788–34799. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huo X, Zhang Q, Liu AM, Tang C, Gong Y,
Bian J, Luk JM, Xu Z and Chen J: Overexpression of Yes-associated
protein confers doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellullar
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 29:840–846. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin L, Sabnis AJ, Chan E, Olivas V, Cade
L, Pazarentzos E, Asthana S, Neel D, Yan JJ, Lu X, et al: The Hippo
effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer
therapies. Nat Genet. 47:250–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shi P, Feng J and Chen C: Hippo pathway in
mammary gland development and breast cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 47:53–59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhao Y and Yang X: The Hippo pathway in
chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Int J Cancer. 137:2767–2773.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Knappskog S, Berge EO, Chrisanthar R,
Geisler S, Staalesen V, Leirvaag B, Yndestad S, de Faveri E,
Karlsen BO, Wedge DC, et al: Concomitant inactivation of the p53-
and pRB-functional pathways predicts resistance to DNA damaging
drugs in breast cancer in vivo. Mol Oncol. 9:1553–1564. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lim SJ, Choi HG, Jeon CK and Kim SH:
Increased chemoresistance to paclitaxel in the MCF10AT series of
human breast epithelial cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 33:2023–2030.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen J, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Cui MH, Han LY,
Jia ZH, Wang L, Teng H and Miao LN: Low expression of phosphatase
and tensin homolog in clearcell renal cell carcinoma contributes to
chemoresistance through activating the Akt/HDM2 signaling pathway.
Mol Med Rep. 12:2622–2628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Weiler M, Blaes J, Pusch S, Sahm F,
Czabanka M, Luger S, Bunse L, Solecki G, Eichwald V, Jugold M, et
al: mTOR target NDRG1 confers MGMT-dependent resistance to
alkylating chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:409–414. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang L, Zhou Y, Li Y, Zhou J, Wu Y, Cui Y,
Yang G and Hong Y: Mutations of p53 and KRAS activate NF-κB to
promote chemoresistance and tumorigenesis via dysregulation of cell
cycle and suppression of apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 357:520–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF,
Pusztai L, Ravdin PM and Hortobagyi GN: The HER-2 receptor and
breast cancer: Ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and
personalized medicine. Oncologist. 14:320–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Roskoski R Jr: The ErbB/HER family of
protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol Res. 79:34–74. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, Levin WJ,
Ullrich A and McGuire WL: Human breast cancer: Correlation of
relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene.
Science. 235:177–182. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko
A, Raad Abi RF, Boon WL, Bellon JR, Wong JS, Smith BL and Harris
JR: Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor,
progesterone receptor and HER-2 is associated with local and
distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol.
26:2373–2378. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang W, Ding W, Chen Y, Feng M, Ouyang Y,
Yu Y and He Z: Up-regulation of breast cancer resistance protein
plays a role in HER2-mediated chemoresistance through PI3K/Akt and
nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathways in MCF7 breast cancer
cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:647–653. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ejlertsen B, Jensen MB, Nielsen KV,
Balslev E, Rasmussen BB, Willemoe GL, Hertel PB, Knoop AS,
Mouridsen HT and Brünner N: TIMP-1 and responsiveness to adjuvant
anthracycline-containing chemotherapy in high-risk breast cancer
patients. J Clin Oncol. 28:984–990. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Pritchard KI, Shepherd LE, O'Malley FP,
Andrulis IL, Tu D, Bramwell VH and Levine MN: National Cancer
Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group: HER2 and responsiveness
of breast cancer to adjuvant chemotherapy. N Engl J Med.
354:2103–2111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Knuefermann C, Lu Y, Liu B, Jin W, Liang
K, Wu L, Schmidt M, Mills GB, Mendelsohn J and Fan Z:
HER2/PI-3K/Akt activation leads to a multidrug resistance in human
breast adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene. 22:3205–3212. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang S, Huang X, Lee CK and Liu B:
Elevated expression of erbB3 confers paclitaxel resistance in
erbB2-overexpressing breast cancer cells via upregulation of
Survivin. Oncogene. 29:4225–4236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Coley HM: Mechanisms and strategies to
overcome chemotherapy resistance in metastatic breast cancer.
Cancer Treat Rev. 34:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|