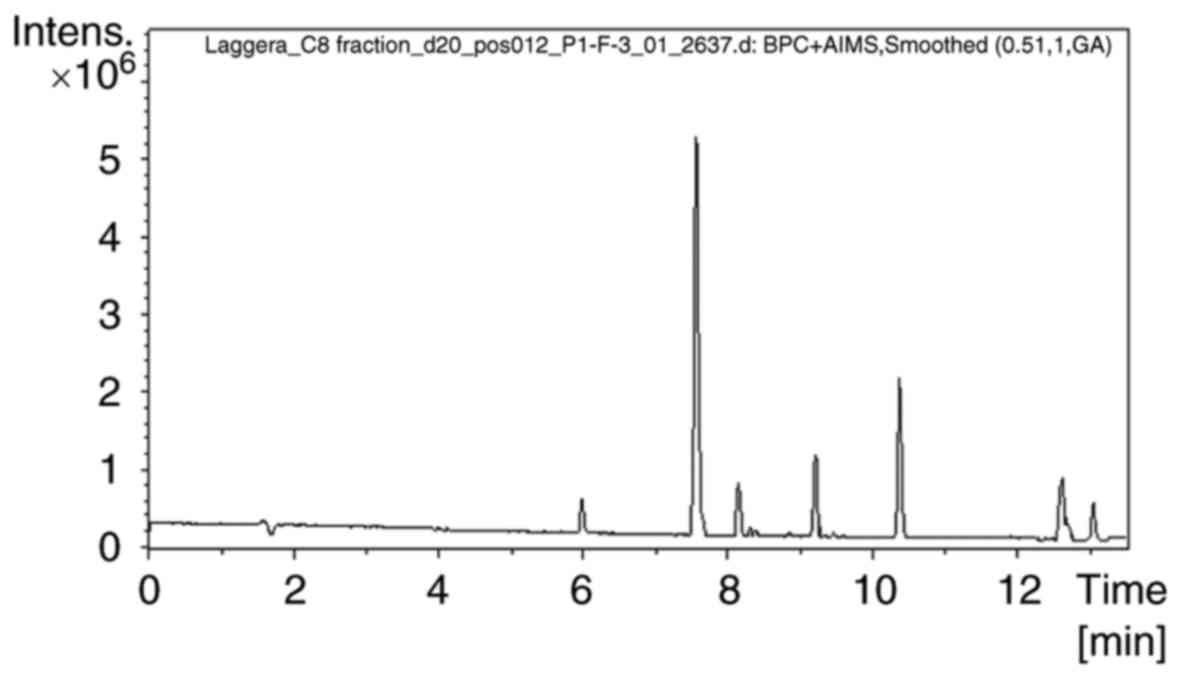
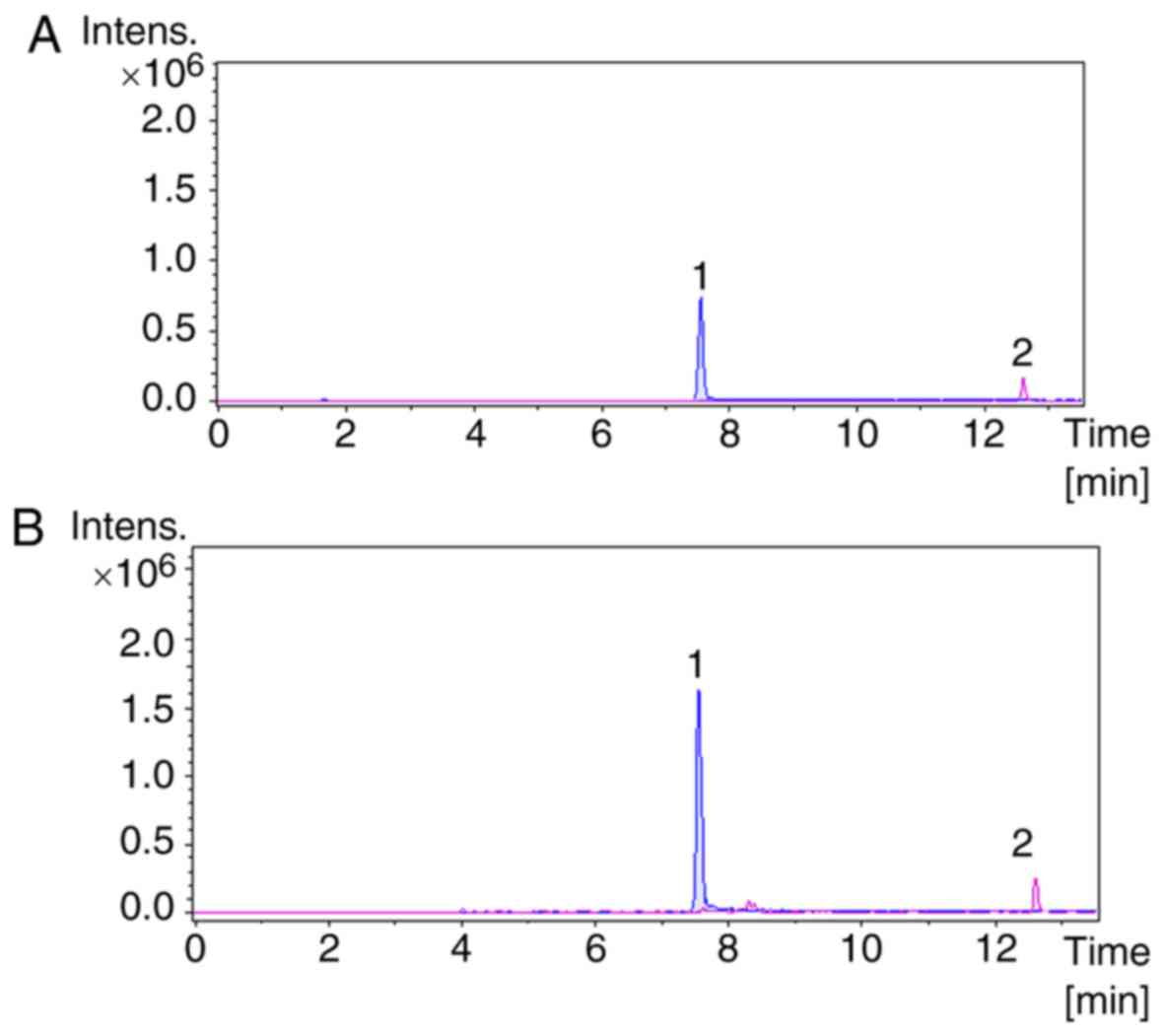
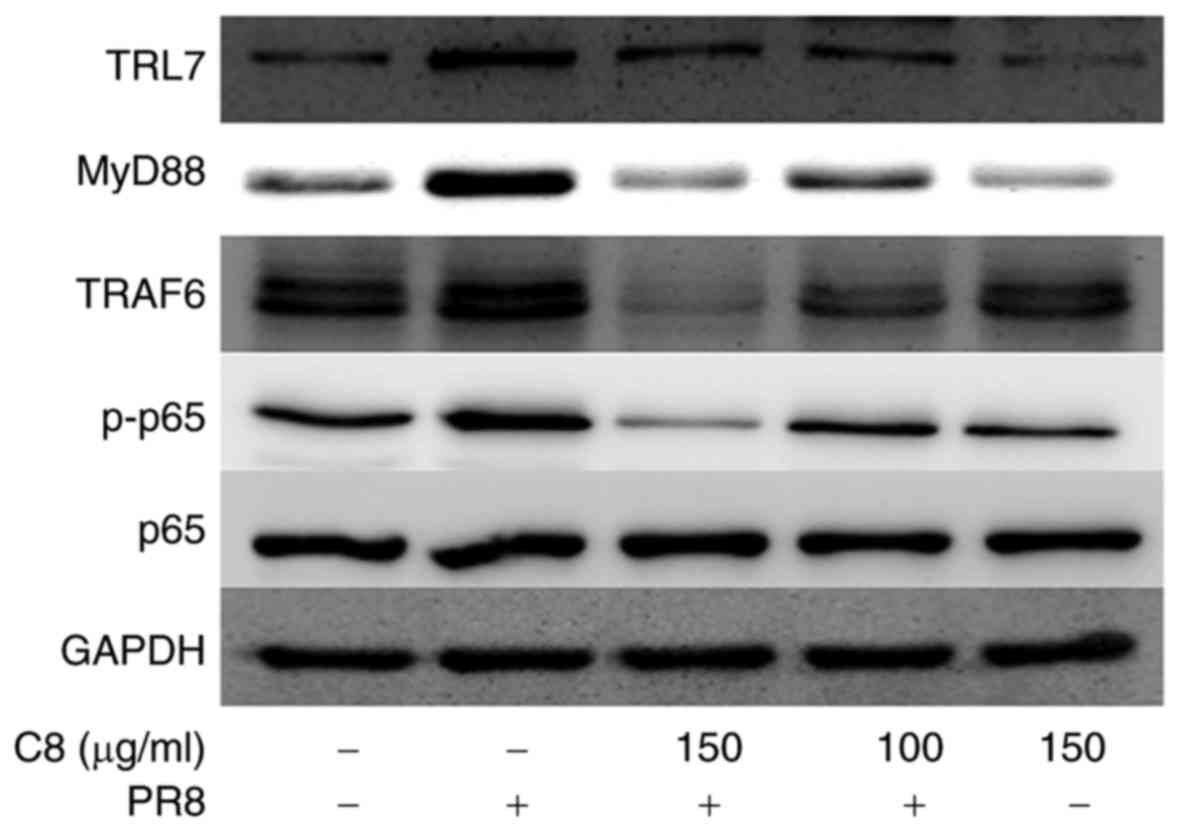
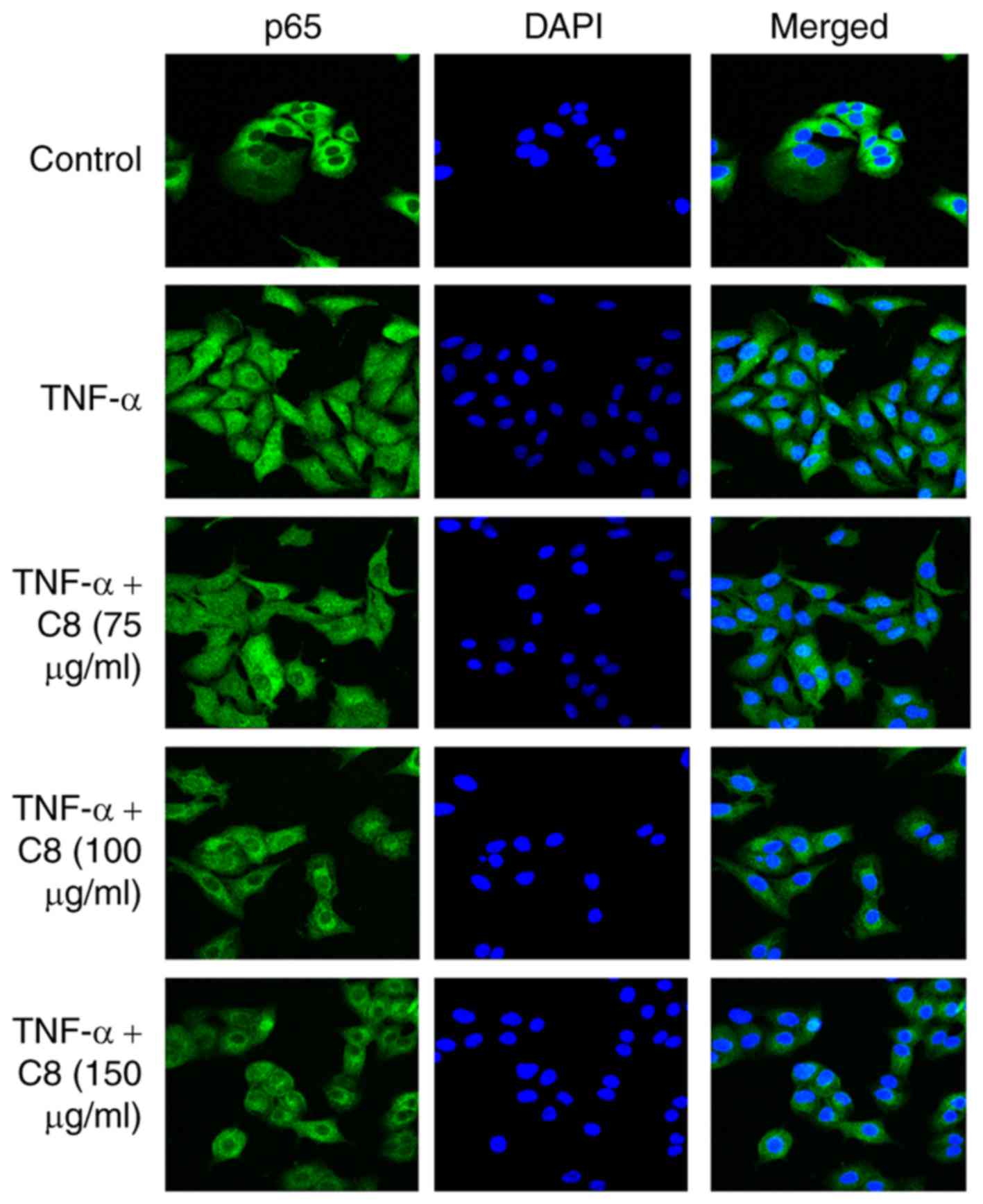
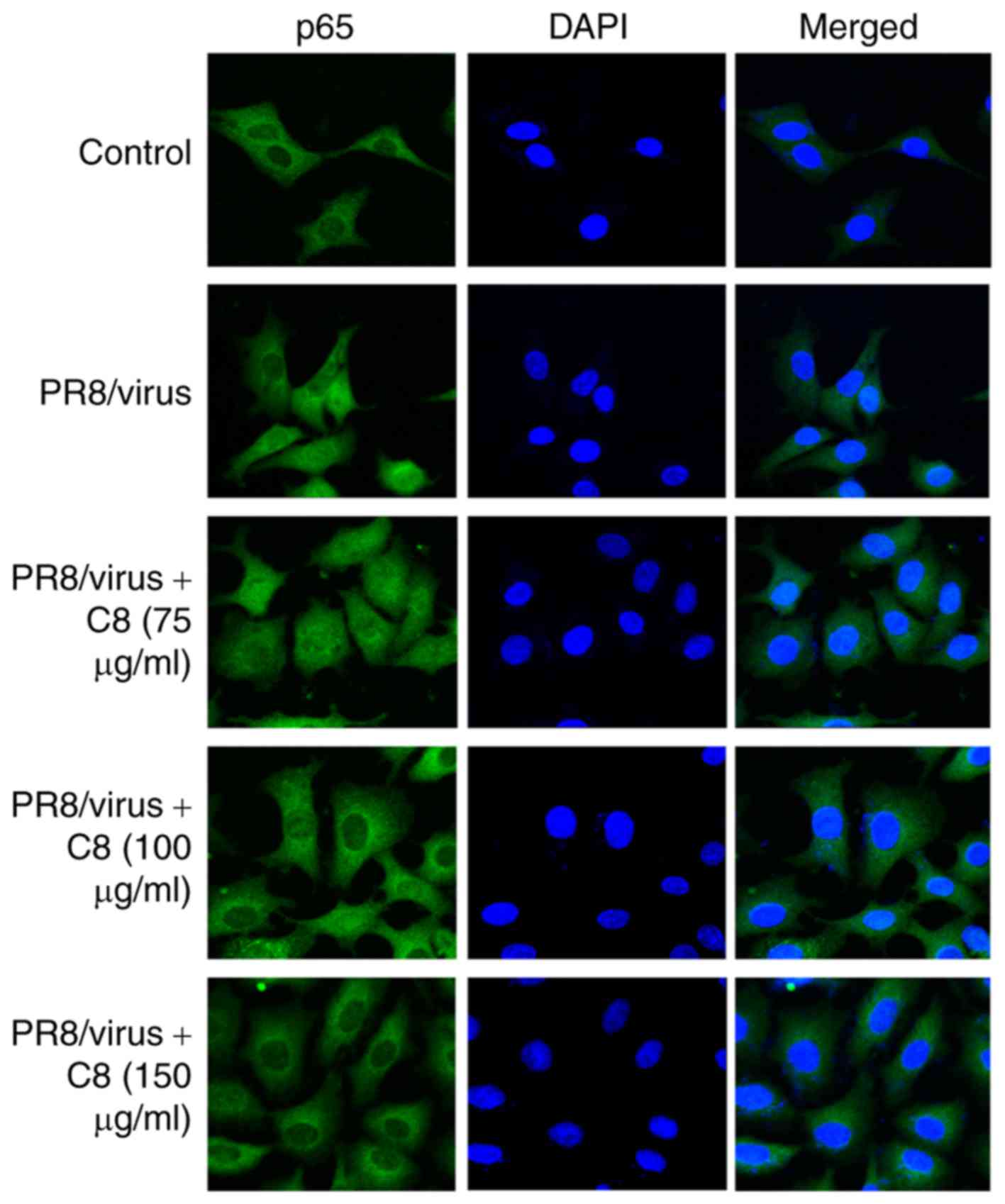
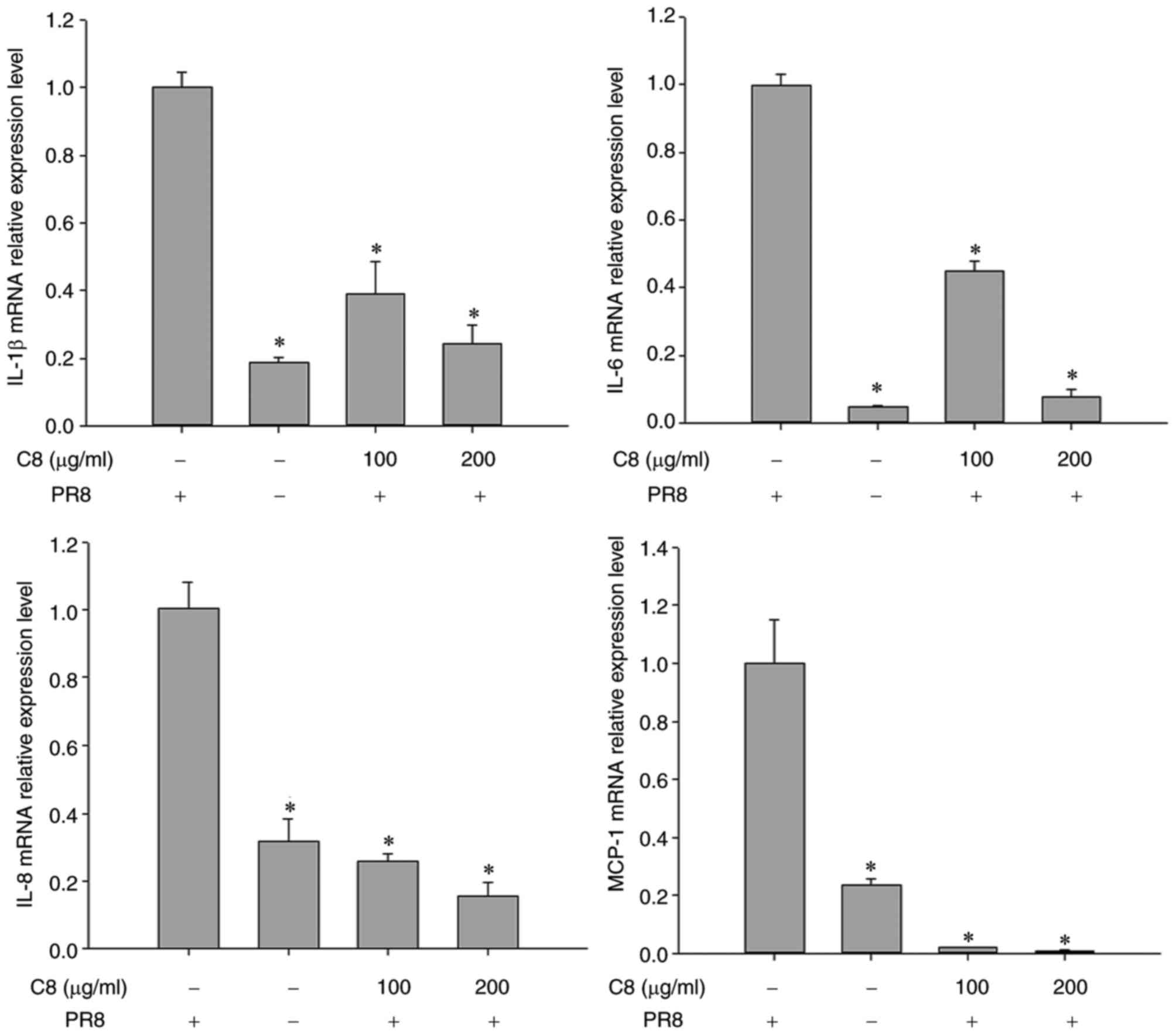
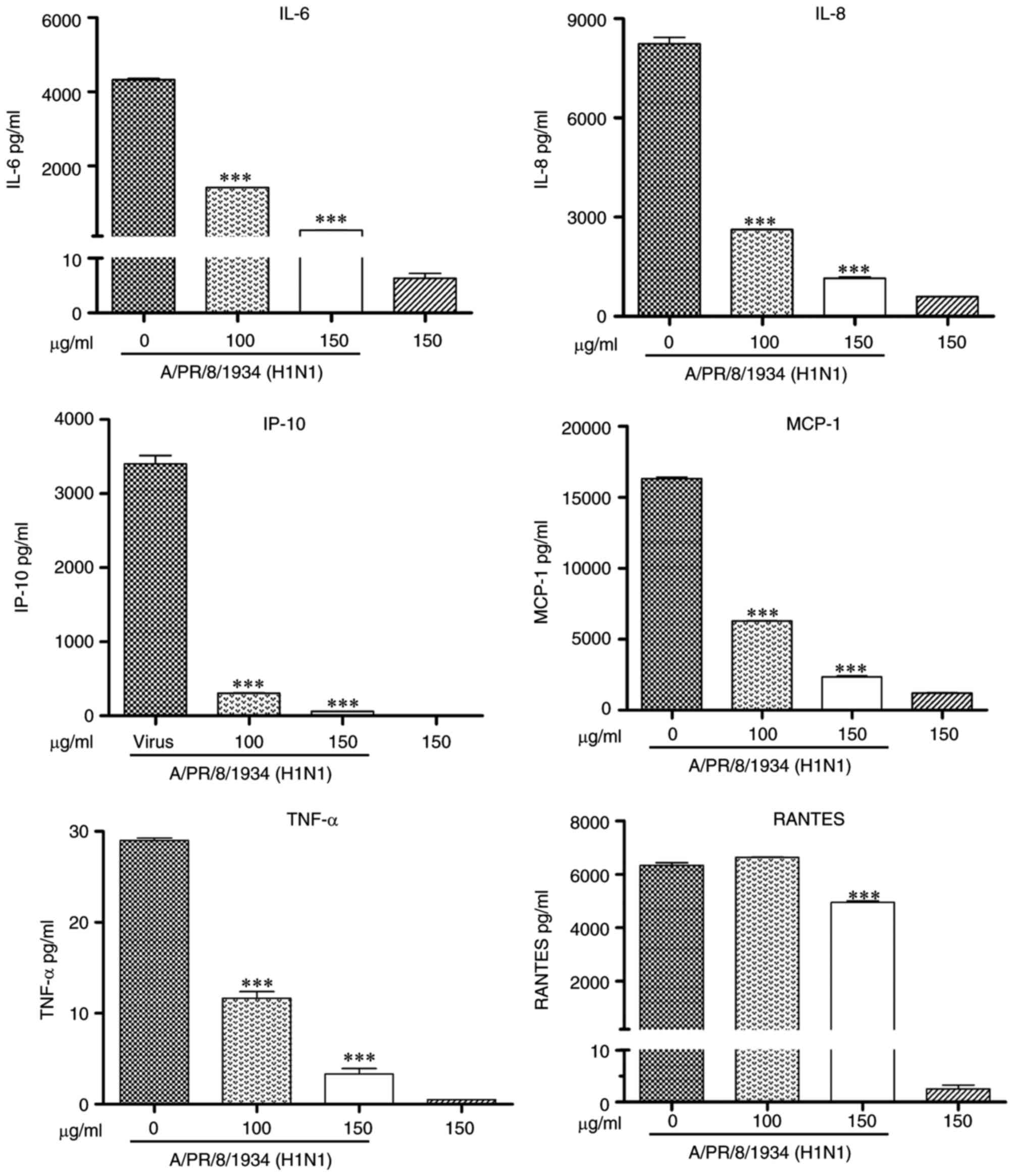
|
1
|
Marois I, Cloutier A, Meunier I, Weingartl
HM, Cantin AM and Richter MV: Inhibition of influenza virus
replication by targeting broad host cell pathways. PLoS One.
9:e1106312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saladino R, Barontini M, Crucianelli M,
Nencioni L, Sgarbanti R and Palamara AT: Current advances in
anti-influenza therapy. Curr Med Chem. 17:2101–2140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hussain M, Galvin HD, Haw TY, Nutsford AN
and Husain M: Drug resistance in influenza a virus: The
epidemiology and management. Infect Drug Resist. 10:121–134. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De Clercq E: Antiviral agents active
against influenza A viruses. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:1015–1025.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang X, Jia W, Zhao A and Wang X:
Anti-influenza agents from plants and traditional Chinese medicine.
Phytother Res. 20:335–341. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu Y, Zhou C, Li X, Song L, Wu X, Lin W,
Chen H, Bai H, Zhao J, Zhang R, et al: Evaluation of
antiinflammatory activity of the total flavonoids of Laggera
pterodonta on acute and chronic inflammation models. Phytother
Res. 20:585–590. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cao C, Liu B, Zeng C, Lu Y, Chen S, Yang
L, Li B and Li Y and Li Y: A polymethoxyflavone from Laggera
pterodonta induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant K562R cells
via activation of the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
14:1372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shi S, Huang K, Zhang Y, Zhao Y and Du Q:
Purification and identification of antiviral components from
Laggera pterodonta by high-speed counter-current
chromatography. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
859:119–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Zhou B, Lu J, Chen Q, Ti H, Huang
W, Li J, Yang Z, Jiang Z and Wang X: Inhibition of influenza virus
via a sesquiterpene fraction isolated from Laggera
pterodonta by targeting the NF-κB and p38 pathways. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 17:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Zhou B, Li C, Chen Q, Wang Y, Li Z,
Chen T, Yang C, Jiang Z, Zhong N, et al:
Lariciresinol-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside from the root of Isatis
indigotica inhibitsinfluenza A virus-induced pro-inflammatory
response. J Ethnopharmacol. 174:379–386. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reed LJ and Muench H: A simple method of
estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Hyg. 27:493–497. 1938.
|
|
12
|
Zu M, Yang F, Zhou W, Liu A, Du G and
Zheng L: In vitro anti-influenza virus and anti-inflammatory
activities of theaflavin derivatives. Antiviral Res. 94:217–224.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu W, Li R, Li X, He J, Jiang S, Liu S and
Yang J: Quercetin as an antiviral agent inhibits influenza a virus
(IAV) entry. Viruses. 8:E62016. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Uetani K, Hiroi M, Meguro T, Ogawa H,
Kamisako T, Ohmori Y and Erzurum SC: Influenza A virus abrogates
IFN-gamma response in respiratory epithelial cells bydisruption of
the Jak/Stat pathway. Eur J Immunol. 38:1559–1573. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding Y, Zeng L, Li R, Chen Q, Zhou B, Chen
Q, Cheng PL, Yutao W, Zheng J, Yang Z and Zhang F: The Chinese
prescription lianhuaqingwen capsule exerts anti-influenza
activitythrough the inhibition of viral propagation and impacts
immune function. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17:1302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mok CK, Kang SS, Chan RW, Yue PY, Mak NK,
Poon LL, Wong RN, Peiris JS and Chan MC: Anti-inflammatory and
antiviral effects of indirubin derivatives ininfluenza A (H5N1)
virus infected primary human peripheral blood-derived macrophages
and alveolar epithelial cells. Antiviral Res. 106:95–104. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramirez-Ortiz ZG, Prasad A, Griffith JW,
Pendergraft WF III, Cowley GS, Root DE, Tai M, Luster AD, El Khoury
J, Hacohen N and Means TK: The receptor TREML4 amplifies
TLR7-mediated signaling during antiviral responses and
autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 16:495–504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Neill LA, Golenbock D and Bowie AG: The
history of Toll-like receptors-redefining innate immunity. Nat Rev
Immunol. 13:453–460. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vitiello M and Galdiero M, Finamore E,
Galdiero S and Galdiero M: NF-κB as a potential therapeutic target
in microbial diseases. Mol Biosyst. 8:1108–1120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nimmerjahn F, Dudziak D, Dirmeier U, Hobom
G, Riedel A, Schlee M, Staudt LM, Rosenwald A, Behrends U, Bornkamm
GW and Mautner J: Active NF-kappaB signalling is a prerequisite for
influenza virus infection. J Gen Virol. 85:2347–2356. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pleschka S, Wolff T, Ehrhardt C, Hobom G,
Planz O, Rapp UR and Ludwig S: Influenza virus propagation is
impaired by inhibition of the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling cascade. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:301–305. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu MS, Yen HR, Chang CW, Peng TY, Hsieh
CF, Chen CJ, Lin TY and Horng JT: Mechanism of action of the
suppression of influenza virus replication by Ko-Ken Tang through
inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling
pathway and viral RNP nuclear export. J Ethnopharmacol.
134:614–623. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Holzberg M, Boergeling Y, Schräder T,
Ludwig S and Ehrhardt C: Vemurafenib limits influenza a virus
propagation by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Front
Microbiol. 8:24262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
König R, Stertz S, Zhou Y, Inoue A,
Hoffmann HH, Bhattacharyya S, Alamares JG, Tscherne DM, Ortigoza
MB, Liang Y, et al: Human host factors required for influenza virus
replication. Nature. 463:813–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Watanabe T, Watanabe S and Kawaoka Y:
Cellular networks involved in the influenza virus life cycle. Cell
Host Microbe. 7:427–439. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
La Gruta NL, Kedzierska K, Stambas J and
Doherty PC: A question of self-preservation: Immunopathology in
influenza virus infection. Immunol Cell Biol. 85:85–92. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paquette SG, Banner D, Zhao Z, Fang Y,
Huang SS, Leόn AJ, Ng DC, Almansa R, Martin-Loeches I, Ramirez P,
et al: Interleukin-6 is a potential piomarker for severe pandemic
H1N1 Influenza A infection. PLoS One. 7:e382142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Planz O: Development of cellular signaling
pathway inhibitors as new antiviral against influenza. Antiviral
Res. 98:457–468. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|