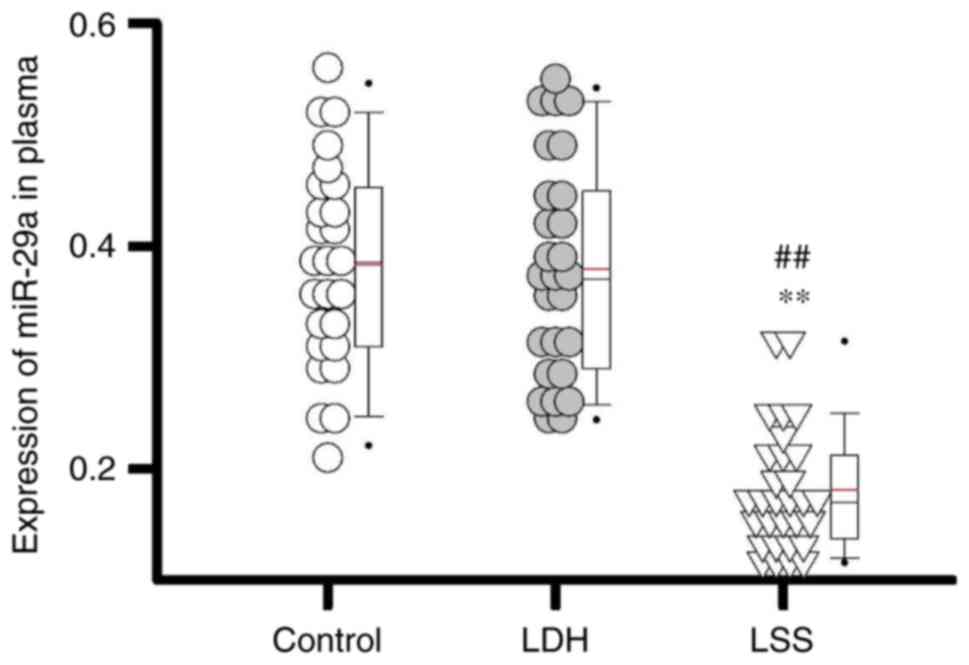
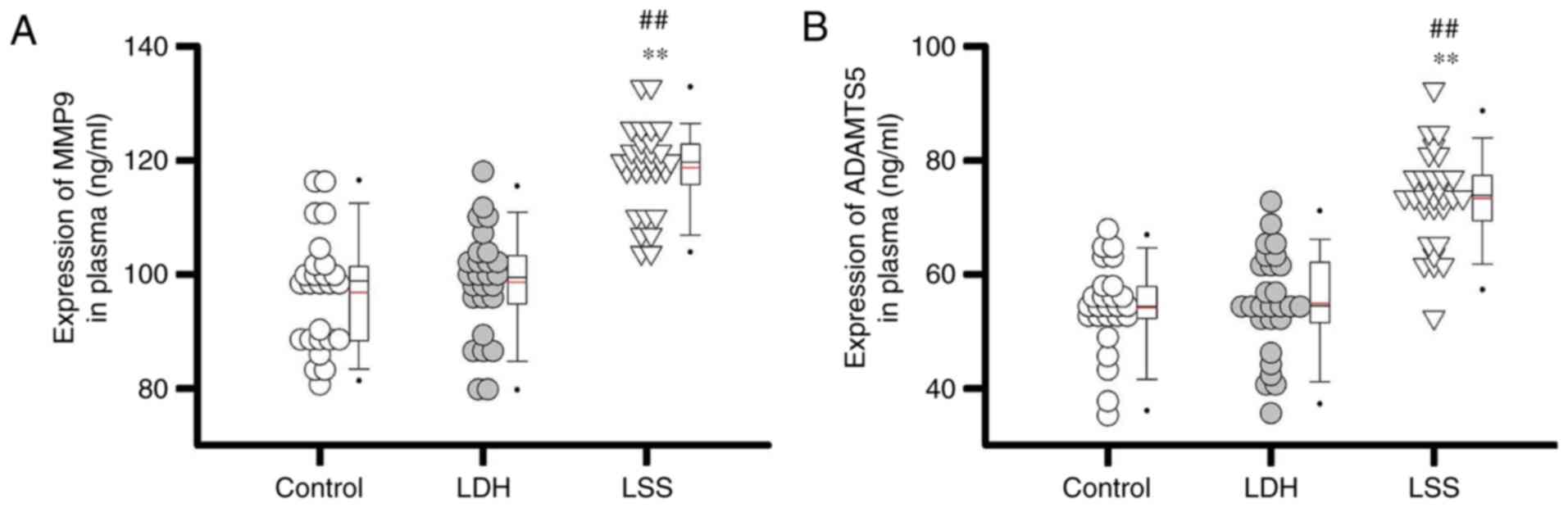
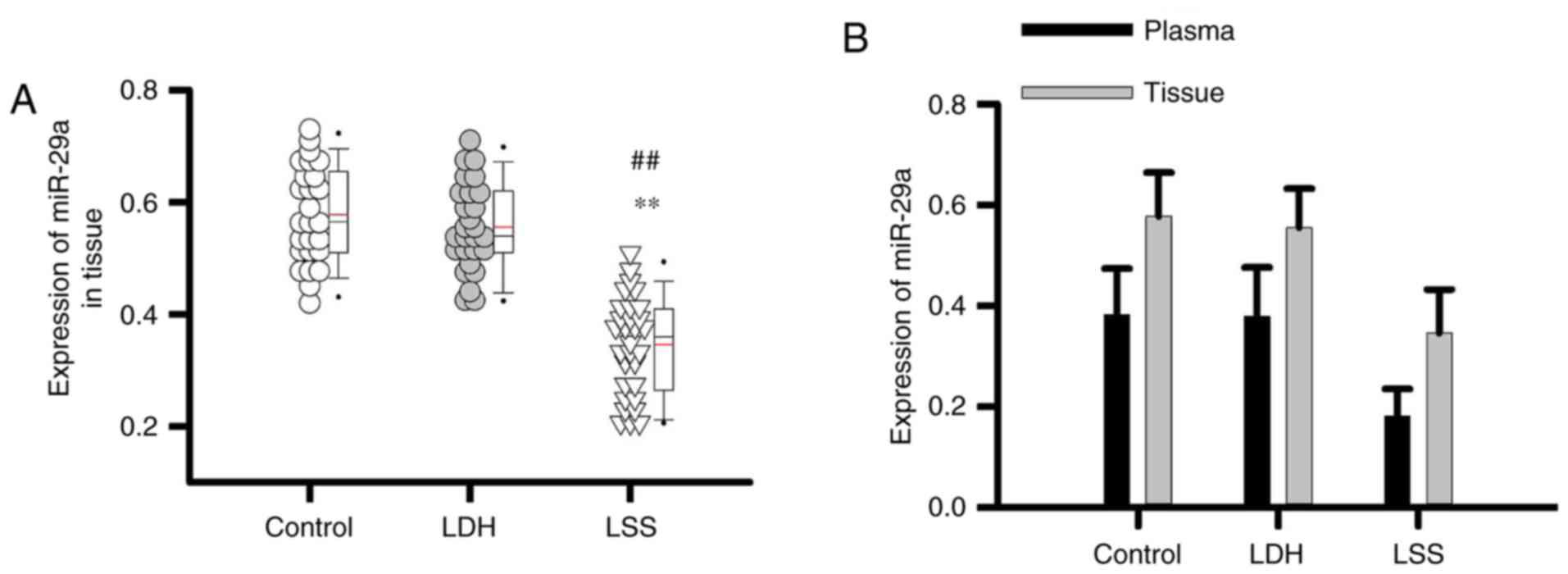
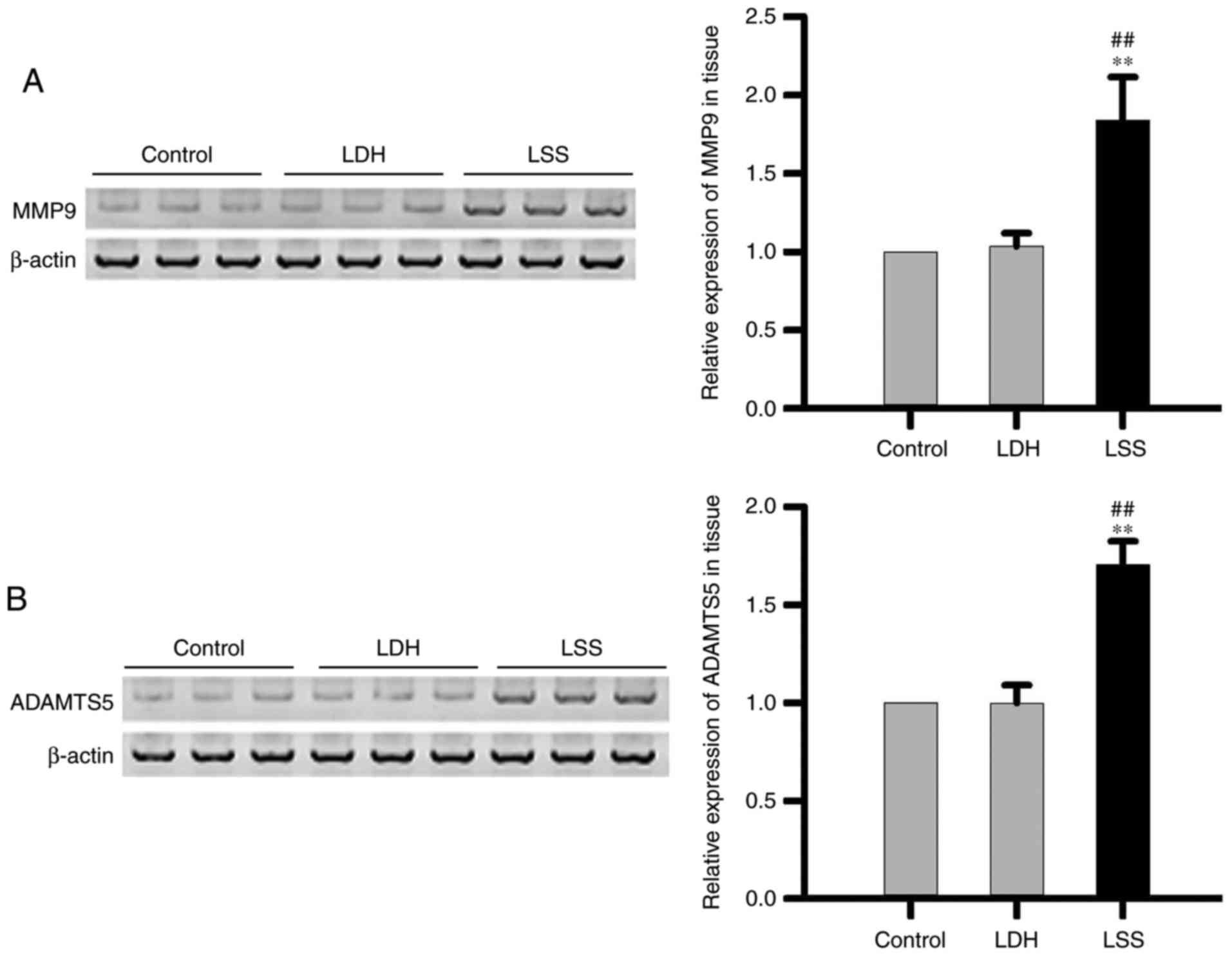
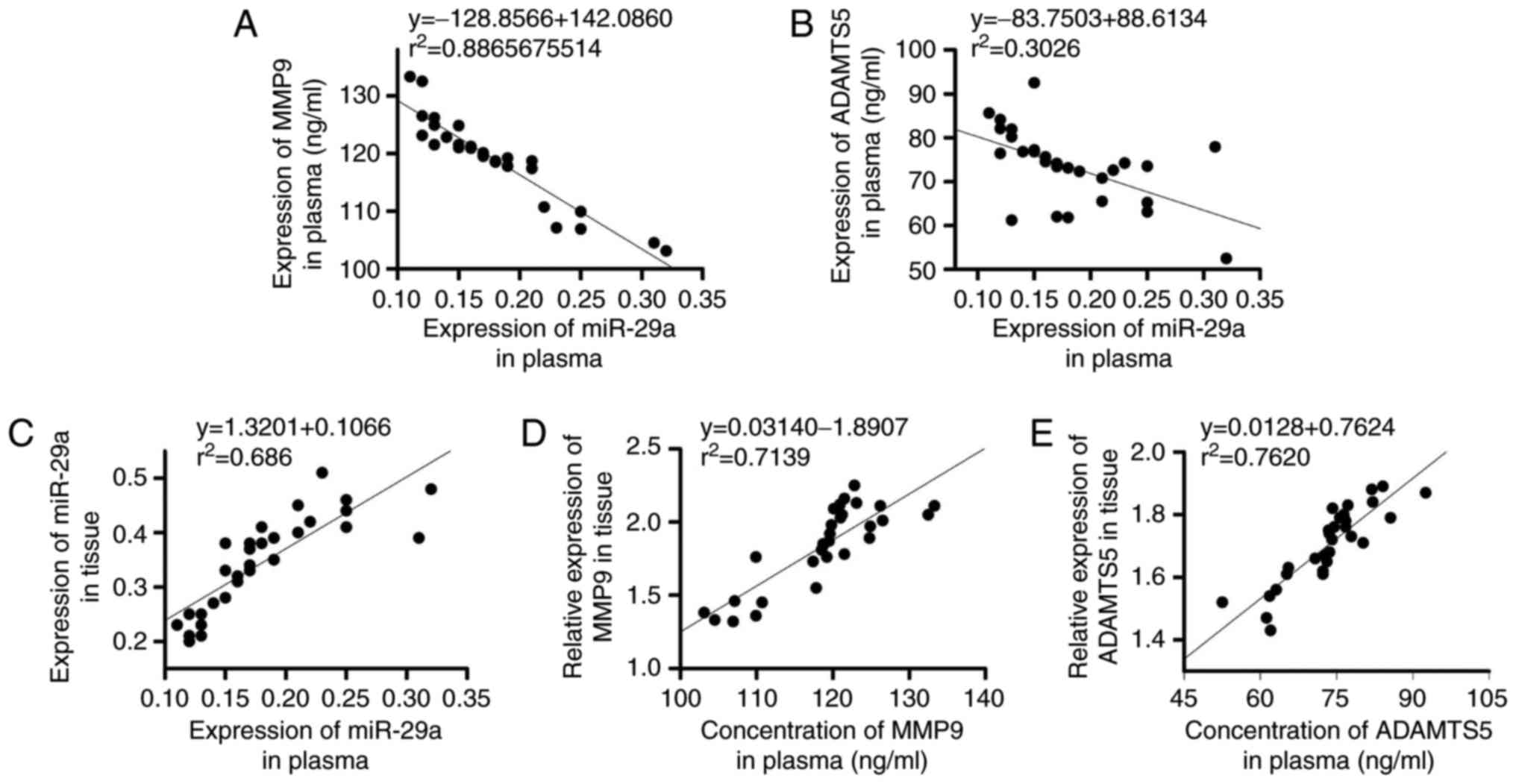
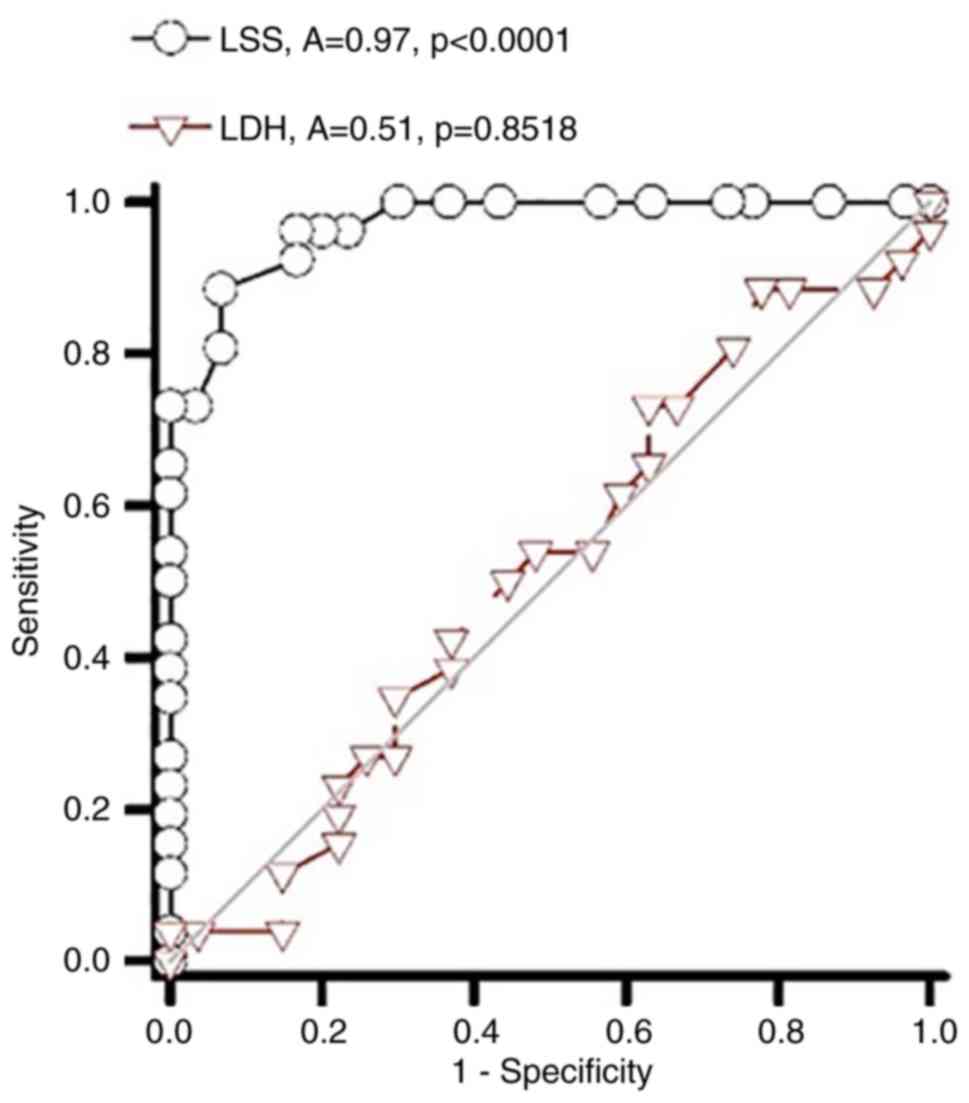
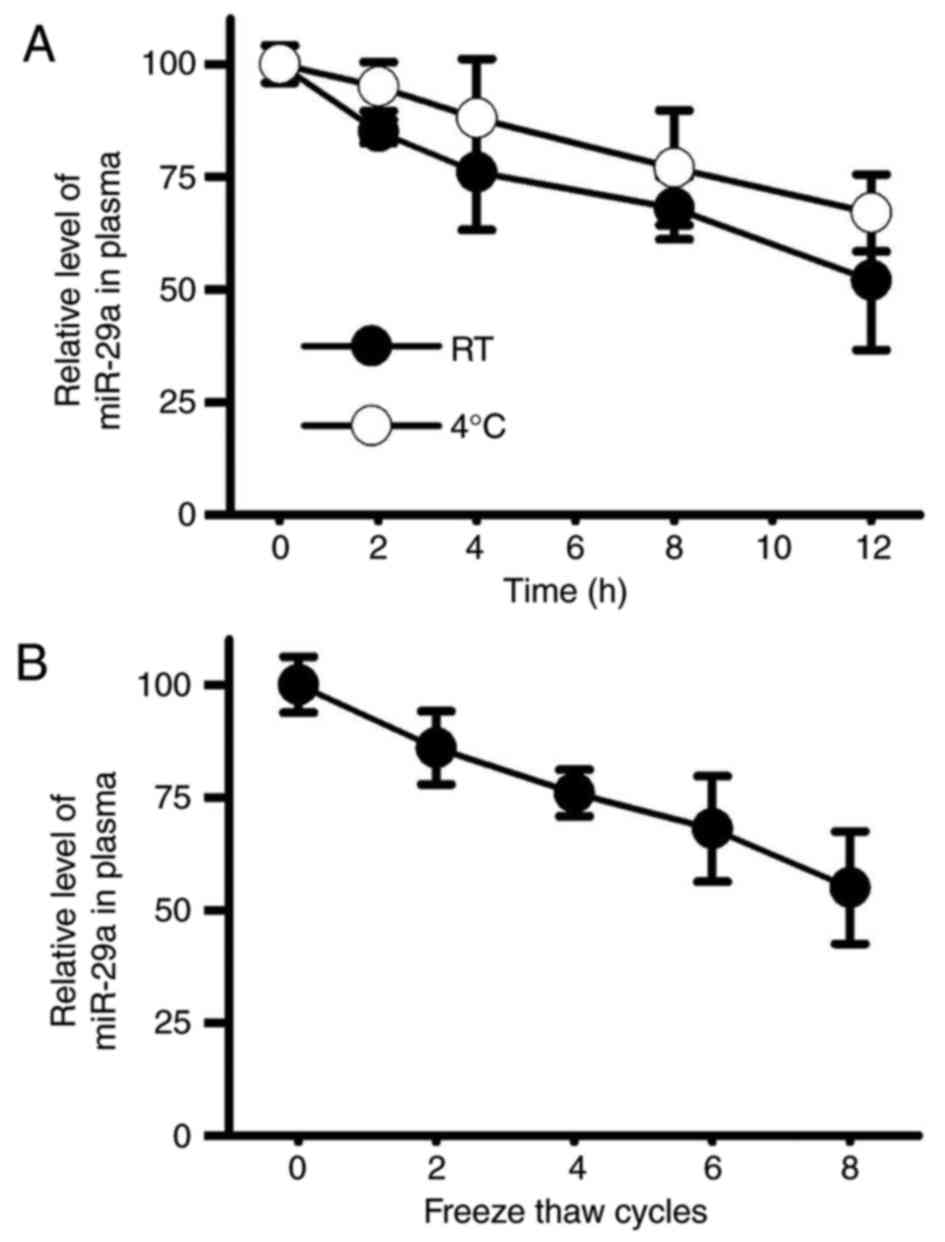
|
1
|
Kreiner DS, Shaffer WO, Baisden JL,
Gilbert TJ, Summers JT, Toton JF, Hwang SW, Mendel RC and Reitman
CA: North American Spine Society: An evidence-based clinical
guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar
spinal stenosis (update). Spine J. 13:734–743. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Backstrom KM, Whitman JM and Flynn TW:
Lumbar spinal stenosis-diagnosis and management of the aging spine.
Man Ther. 16:308–317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lucio JC, VanConia RB, DeLuzio KJ, Lehmen
JA, Rodgers JA and Rodgers W: Economics of less invasive spinal
surgery: An analysis of hospital cost differences between open and
minimally invasive instrumented spinal fusion procedures during the
perioperative period. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 5:65–74.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bressler HB, Keyes WJ, Rochon PA and
Elizabeth B: The prevalence of low back pain in the elderly: A
systematic review of the literature. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
24:1813–1819. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Schepper EI, Overdevest GM, Suri P,
Peul WC, Oei EH, Koes BW, Bierma-Zeinstra SM and Luijsterburg PA:
Diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis: An updated systematic review
of the accuracy of diagnostic tests. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
38:E469–E481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang X, Tsitsiou E, Herrick SE and
Lindsay MA: MicroRNAs and the regulation of fibrosis. FEBS J.
277:2015–2021. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shenoy A and Blelloch RH: Regulation of
microRNA function in somatic stem cell proliferation and
differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:565–576. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baumjohann D and Ansel KM:
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of T helper cell differentiation and
plasticity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:666–678. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen J, Liu Z, Zhong G, Qian L, Li Z, Qiao
Z, Chen B and Wang H: Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar
spine stenosis is associated with increased miR-155 level. Dis
Markers. 2014:7865432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu YQ, Zhang ZH, Zheng YF and Feng SQ:
MicroRNA-221 regulates hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum in lumbar
spinal stenosis by targeting TIMP-2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
41:275–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ko JY, Lee MS, Lian WS, Weng WT, Sun YC,
Chen YS and Wang FS: MicroRNA-29a counteracts synovitis in knee
osteoarthritis pathogenesis by targeting VEGF. Sci Rep. 7:35842017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han W, Han Y, Liu X and Shang X: Effect of
miR-29a inhibition on ventricular hypertrophy induced by pressure
overload. Cell Biochem Biophys. 71:821–826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Q, Yin D, Zhang Y, Yu L, Li XD, Zhou
ZJ, Zhou SL, Gao DM, Hu J, Jin C, et al: MicroRNA-29a induces loss
of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine and promotes metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma through a TET-SOCS1-MMP9 signaling axis.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e29062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Knutsson B, Sandén B, Sjödén G, Järvholm B
and Michaëlsson K: Body mass index and risk for clinical lumbar
spinal stenosis: A cohort study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
40:1451–1456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujita N, Hosogane N, Hikata T, Iwanami A,
Watanabe K, Shiono Y, Okada E, Ishikawa M, Tsuji T, Shimoda M, et
al: Potential Involvement of obesity-associated chronic
inflammation in the pathogenesis of idiopathic spinal epidural
lipomatosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:E1402–E1407. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakamura T, Okada T, Endo M, Nakamura T,
Oike Y and Mizuta H: Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes
inflammatory conditions in the ligamentum flavum in the
pathogenesis of lumbar spinal canal stenosis by activating
interleukin-6 expression. Eur Spine J. 24:2001–2009. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu SX, Li X, Hamilton JL, Chee A, Kca R,
Chen D, An HS, Kim JS, Oh CD, Ma YZ, et al: MicroRNA-146a reduces
IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc.
Gene. 555:80–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu B, Xu C, Tian Y, Shi C, Zhang Y, Deng
L, Zhou H, Cao P, Chen H and Yuan W: Inflammatory microRNA-194
and-515 attenuate the biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate during
human intervertebral disc degeneration. Oncotarget. 8:49303–49317.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Papadopoulou AS, Serneels L, Achsel T,
Mandemakers W, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Dooley J, Lau P, Ayoubi T,
Radaelli E, Spinazzi M, et al: Deficiency of the miR-29a/b-1
cluster leads to ataxic features and cerebellar alterations in
mice. Neurobiol Di. 73:275–288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ranganathan P, Ngankeu A, Zitzer NC,
Leoncini P, Yu X, Casadei L, Challagundla K, Reichenbach DK, Garman
S, Ruppert AS, et al: Serum miR-29a is upregulated in acute
graft-versus-host disease and activates dendritic cells through TLR
binding. J Immunol. 198:2500–2512. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang WJ, Yu XH, Wang C, Yang W, He WS,
Zhang SJ, Yan YG and Zhang J: MMPs and ADAMTSs in intervertebral
disc degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 448:238–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vega Brunet A, Pericay C, Moya I, Ferrer
A, Dotor E, Pisa A, Casalots À, Serra-Aracil X, Oliva JC, Ruiz A
and Saigí E: microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal
cancer: Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers.
Oncol Rep. 30:320–326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roncarati R, Anselmi Viviani C, Losi MA,
Papa L, Cavarretta E, Da Costa Martins P, Contaldi C, Jotti Saccani
G, Franzone A, Galastri L, et al: Circulating miR-29a, among other
up-regulated microRNAs, is the only biomarker for both hypertrophy
and fibrosis in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 63:920–927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|