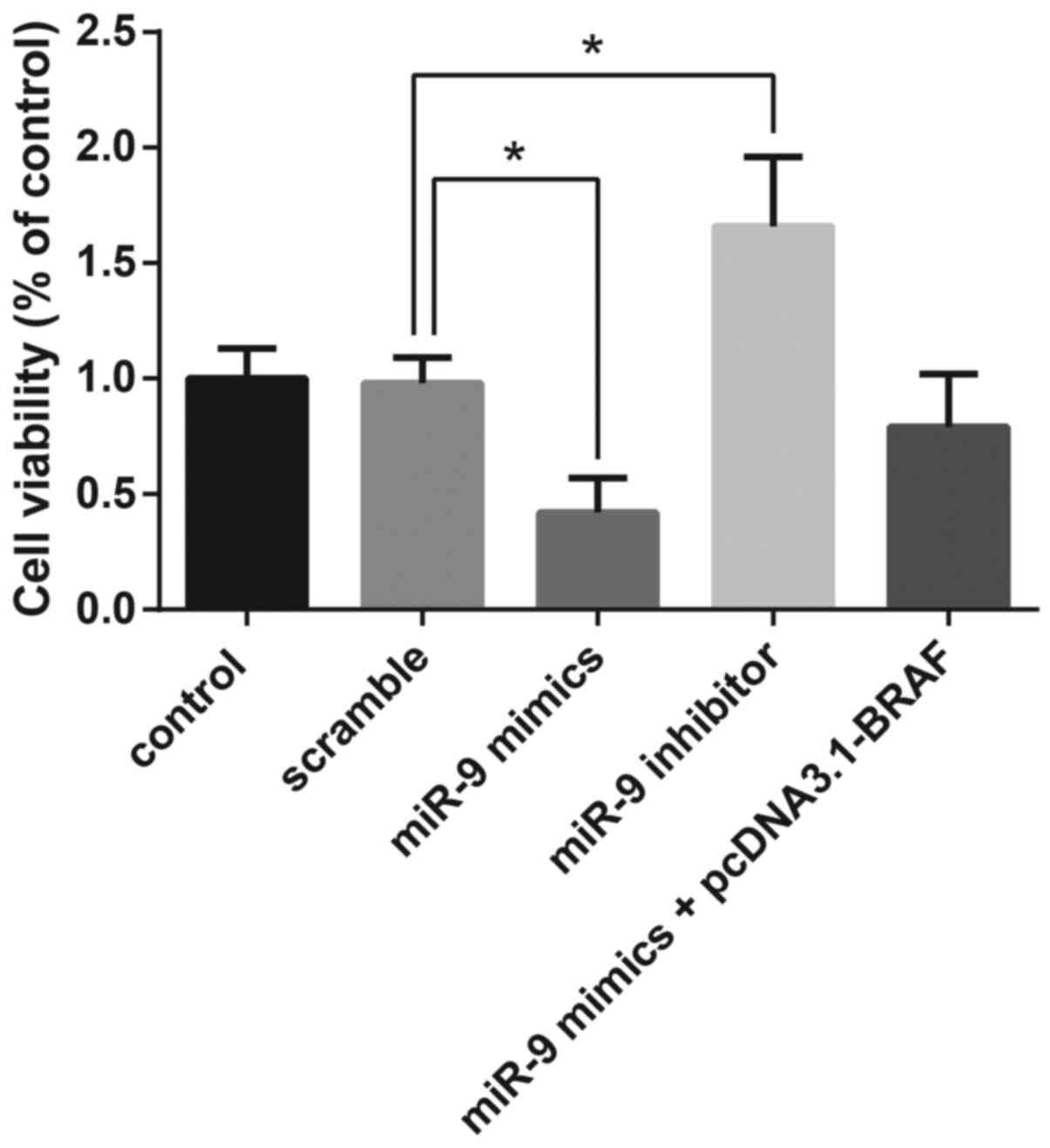
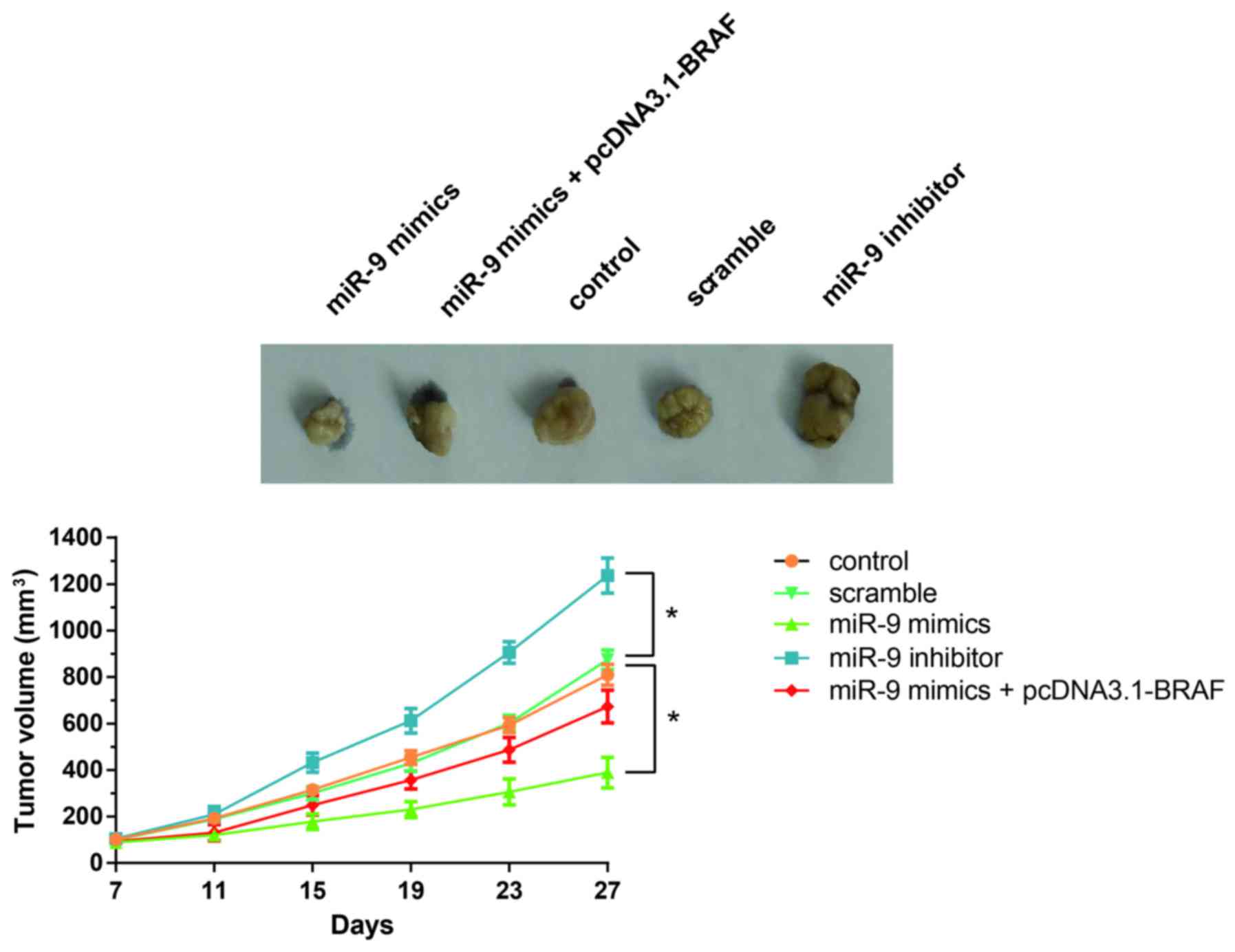
|
1
|
Pacini F: Thyroid microcarcinoma. Best
Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 26:381–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pellegriti G, Frasca F, Regalbuto C,
Squatrito S and Vigneri R: Worldwide increasing incidence of
thyroid cancer: Update on epidemiology and risk factors. J Cancer
Epidemiol. 2013:9652122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanley JP, Jackson E, Morrissey LA, Rizzo
DM, Sprague BL, Sarkar IN and Carr FE: Geospatial and temporal
analysis of thyroid cancer incidence in a rural population.
Thyroid. 25:812–822. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Magreni A, Bann DV, Schubart JR and
Goldenberg D: The effects of race and ethnicity on thyroid cancer
incidence. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 141:319–323. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zolotov S: Genetic testing in
differentiated thyroid carcinoma: Indications and clinical
implications. Rambam Maimonides Med J. 7:28–Jan;2016.doi:
10.5041/RMMJ.10236. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Griniatsos J, Tsigris C, Kanakis M,
Kaltsas G, Michail O, Dimitriou N, Argyrakopoulou G, Delladetsima
I, Kyriakou V, Syriou V, et al: Increased incidence of papillary
thyroid cancer detection among thyroidectomies in Greece between
1991 and 2006. Anticancer Res. 29:5163–5169. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hakala T, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Kholová
I, Holli K, Huhtala H and Sand J: Rising incidence of small size
papillary thyroid cancers with no change in disease-specific
survival in finnish thyroid cancer patients. Scand J Surg.
101:301–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuo EJ, Goffredo P, Sosa JA and Roman SA:
Aggressive variants of papillary thyroid microcarcinoma are
associated with extrathyroidal spread and lymph-node metastases: A
population-level analysis. Thyroid. 23:1305–1311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghossein R, Ganly I, Biagini A, Robenshtok
E, Rivera M and Tuttle RM: Prognostic factors in papillary
microcarcinoma with emphasis on histologic subtyping: A
clinicopathologic study of 148 cases. Thyroid. 24:245–253. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grant CS: Recurrence of papillary thyroid
cancer after optimized surgery. Gland Surg. 4:52–62.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Byeon HK, Ban MJ, Lee JM, Ha JG, Kim ES,
Koh YW and Choi EC: Robot-assisted Sistrunk's operation, total
thyroidectomy, and neck dissection via a transaxillary and
retroauricular (TARA) approach in papillary carcinoma arising in
thyroglossal duct cyst and thyroid gland. Ann Surg Oncol.
19:4259–4261. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lang BH, Ng SH, Lau LL, Cowling BJ, Wong
KP and Wan KY: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
prophylactic central neck dissection on short-term locoregional
recurrence in papillary thyroid carcinoma after total
thyroidectomy. Thyroid. 23:1087–1098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Macedo FI and Mittal VK: Total
thyroidectomy versus lobectomy as initial operation for small
unilateral papillary thyroid carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Surg
Oncol. 24:117–122. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Matsuzu K, Sugino K, Masudo K, Nagahama M,
Kitagawa W, Shibuya H, Ohkuwa K, Uruno T, Suzuki A, Magoshi S, et
al: Thyroid lobectomy for papillary thyroid cancer: Long-term
follow-up study of 1,088 cases. World J Surg. 38:68–79. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He Y, Lin J, Kong D, Huang M, Xu C, Kim
TK, Etheridge A, Luo Y, Ding Y and Wang K: Current state of
circulating MicroRNAs as cancer biomarkers. Clin Chem.
61:1138–1155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X, Du YL, Jin P and Ma F:
Bioinformatic analysis of cancer-related microRNAs and their target
genes. Yi Chuan. 37:855–864. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoruker EE, Terzioglu D, Teksoz S, Uslu
FE, Gezer U and Dalay N: MicroRNA expression profiles in papillary
thyroid carcinoma, benign thyroid nodules and healthy Controls. J
Cancer. 7:803–809. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Damanakis AI, Eckhardt S, Wunderlich A,
Roth S, Wissniowski TT, Bartsch DK and Di Fazio P: MicroRNAs let7
expression in thyroid cancer: Correlation with their deputed
targets HMGA2 and SLC5A5. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:1213–1220.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Czajka AA, Wójcicka A, Kubiak A, Kotlarek
M, Bakuła-Zalewska E, Koperski Ł, Wiechno W and Jażdżewski K:
Family of microRNA-146 regulates RARβ in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01519682016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cong D, He M, Chen S, Liu X and Sun H:
Expression profiles of pivotal microRNAs and targets in thyroid
papillary carcinoma: An analysis of the cancer genome atlas. Onco
Targets Ther. 8:2271–2277. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lima CR, Geraldo MV, Fuziwara CS, Kimura
ET and Santos MF: MiRNA-146b-5p upregulates migration and invasion
of different papillary thyroid carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer.
16:1082016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Minna E, Romeo P, Dugo M, De Cecco L,
Todoerti K, Pilotti S, Perrone F, Seregni E, Agnelli L, Neri A, et
al: miR-451a is underexpressed and targets AKT/mTOR pathway in
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:12731–12747. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salajegheh A, Vosgha H, Rahman Md A, Amin
M, Smith RA and Lam AK: Modulatory role of miR-205 in angiogenesis
and progression of thyroid cancer. J Mol Endocrinol. 55:183–196.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sondermann A, Andreghetto FM, Moulatlet
AC, da Silva Victor E, de Castro MG, Nunes FD, Brandão LG and
Severino P: MiR-9 and miR-21 as prognostic biomarkers for
recurrence in papillary thyroid cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis.
32:521–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gundara JS, Zhao J, Gill AJ, Lee JC,
Delbridge L, Robinson BG, McLean C, Serpell J and Sidhu SB:
Noncoding RNA blockade of autophagy is therapeutic in medullary
thyroid cancer. Cancer Med. 4:174–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma B, Shi R, Yang S, Zhou L, Qu N, Liao T,
Wang Y, Wang Y and Ji Q: DUSP4/MKP2 overexpression is associated
with BRAF(V600E) mutation and aggressive behavior of papillary
thyroid cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2255–2263. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao Q, Zhang W, Wang N, Duan H, Zhou Y,
Zhang W and Zhao D: Study on the correlation between BRAF(V600E)
mutation and lymphatic metastases in papillary thyroid cancer
staged preoperativelv as N0. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai
Ke Za Zhi. 29:2048–2052. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cordioli MI, Moraes L, Carvalheira G,
Sisdelli L, Alves MT, Delcelo R, Monte O, Longui CA, Cury AN and
Cerutti JM: AGK-BRAF gene fusion is a recurrent event in sporadic
pediatric thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Med. 5:1535–1541. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhuang G, Wu X, Jiang Z, Kasman I, Yao J,
Guan Y, Oeh J, Modrusan Z, Bais C, Sampath D and Ferrara N:
Tumour-secreted miR-9 promotes endothelial cell migration and
angiogenesis by activating the JAK-STAT pathway. EMBO J.
31:3513–3523. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:12–Aug;2015.doi: 10.7554/eLife.05005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Conzo G, Tartaglia E, Avenia N, Calò PG,
de Bellis A, Esposito K, Gambardella C, Iorio S, Pasquali D,
Santini L, et al: Role of prophylactic central compartment lymph
node dissection in clinically N0 differentiated thyroid cancer
patients: Analysis of risk factors and review of modern trends.
World J Surg Oncol. 14:1492016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chruścik A and Lam AK: Clinical
pathological impacts of microRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma: A
crucial review. Exp Mol Pathol. 99:393–398. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Min XS, Huang P, Liu X, Dong C, Jiang XL,
Yuan ZT, Mao LF and Chang S: Bioinformatics analyses of significant
prognostic risk markers for thyroid papillary carcinoma. Tumour
Biol. 36:7457–7463. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Forte S, La Rosa C, Pecce V, Rosignolo F
and Memeo L: The role of microRNAs in thyroid carcinomas.
Anticancer Res. 35:2037–2047. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schlumberger M and Sherman SI: Approach to
the patient with advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur J
Endocrinol. 166:5–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zawistowski JS, Nakamura K, Parker JS,
Granger DA, Golitz BT and Johnson GL: MicroRNA 9-3p targets β1
integrin to sensitize claudin-low breast cancer cells to MEK
inhibition. Mol Cell Biol. 33:2260–2274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ito T, Seyama T, Hayashi Y, Dohi K and
Akiyama M: Unique association of p53 mutations with
undifferentiated carcinoma of the thyroid. Nihon Rinsho.
52:1069–1074. 1994.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Falchook GS, Millward M, Hong D, Naing A,
Piha-Paul S, Waguespack SG, Cabanillas ME, Sherman SI, Ma B, Curtis
M, et al: BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib in patients with metastatic
BRAF-mutant thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 25:71–77. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rothenberg SM, McFadden DG, Palmer EL,
Daniels GH and Wirth LJ: Redifferentiation of iodine-refractory
BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic papillary thyroid cancer with
dabrafenib. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1028–1035. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fnais N, Soobiah C, Al-Qahtani K, Hamid
JS, Perrier L, Straus SE and Tricco AC: Diagnostic value of fine
needle aspiration BRAF(V600E) mutation analysis in papillary
thyroid cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Pathol.
46:1443–1454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yi W, Zhong D and Zou Q: Expression of
BRAF and its extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signal
pathway in papillary thyroid cancer. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi
Xue Ban. 37:889–894. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kandil E, Tsumagari K, Ma J, Elmageed Abd
ZY, Li X, Slakey D, Mondal D and Abdel-Mageed AB: Synergistic
inhibition of thyroid cancer by suppressing MAPK/PI3K/AKT pathways.
J Surg Res. 184:898–906. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
McCarty SK, Saji M, Zhang X, Knippler CM,
Kirschner LS, Fernandez S and Ringel MD: BRAF activates and
physically interacts with PAK to regulate cell motility. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 21:865–877. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang ZX, Liu ZQ, Jiang B, Lu XY, Ning XF,
Yuan CT and Wang AL: BRAF activated non-coding RNA (BANCR)
promoting gastric cancer cells proliferation via regulation of
NF-κB1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 465:225–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu Y, Mintz A, Shah SR, Quinones-Hinojosa
A and Hsu W: The FGFR/MEK/ERK/brachyury pathway is critical for
chordoma cell growth and survival. Carcinogenesis. 35:1491–1499.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wellbrock C and Arozarena I: The
Complexity of the ERK/MAP-kinase pathway and the treatment of
melanoma skin cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 4:332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|