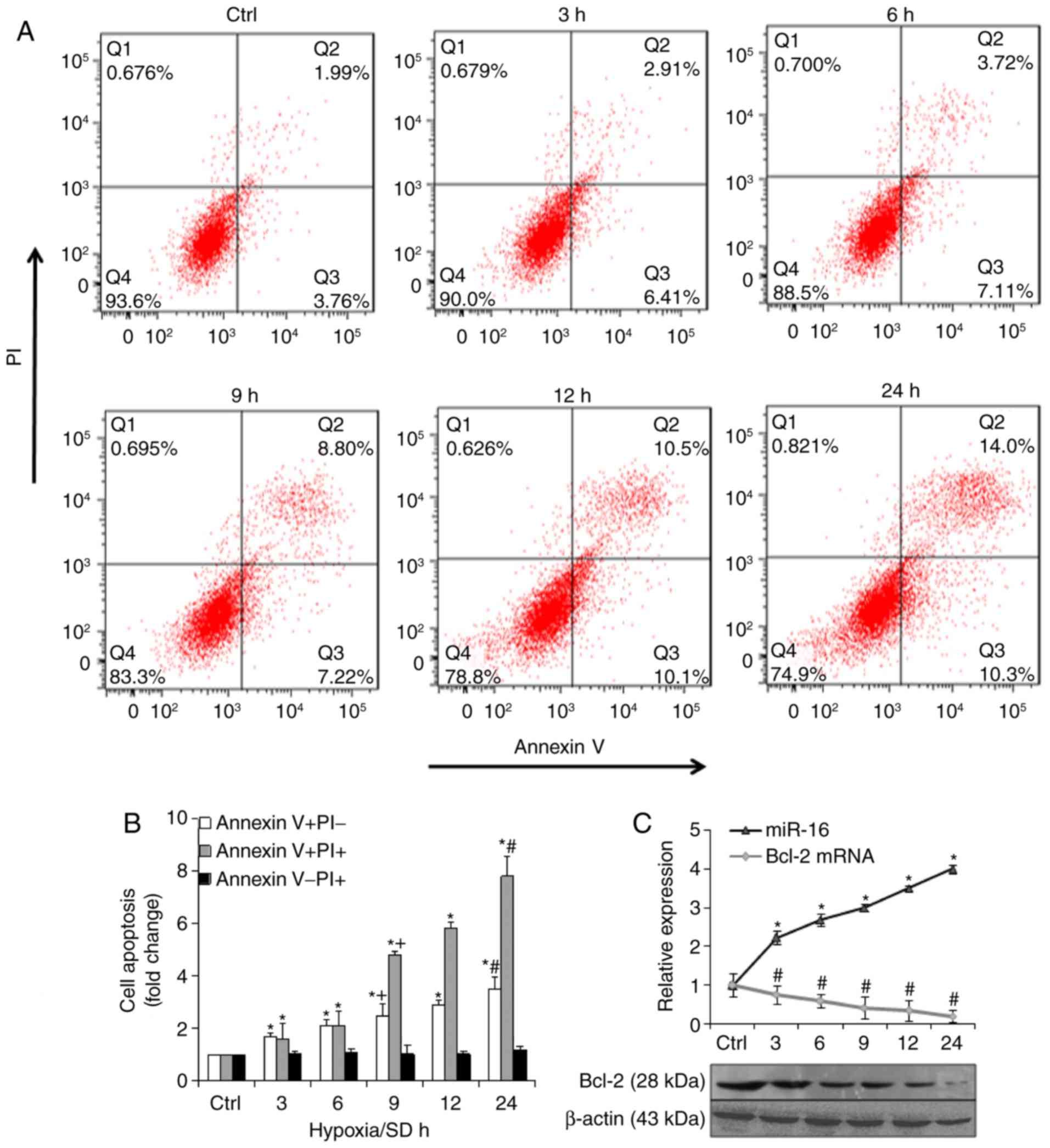
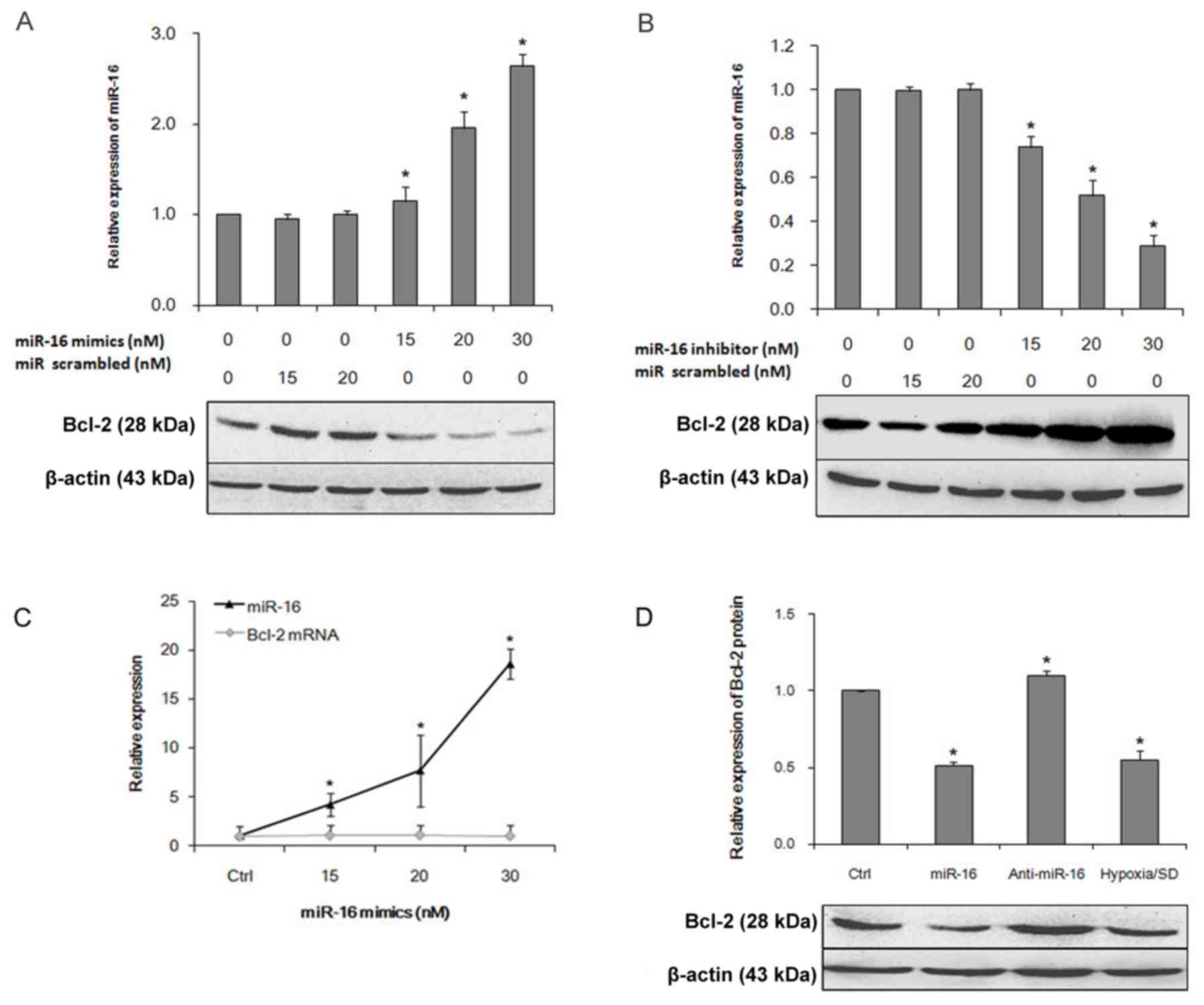
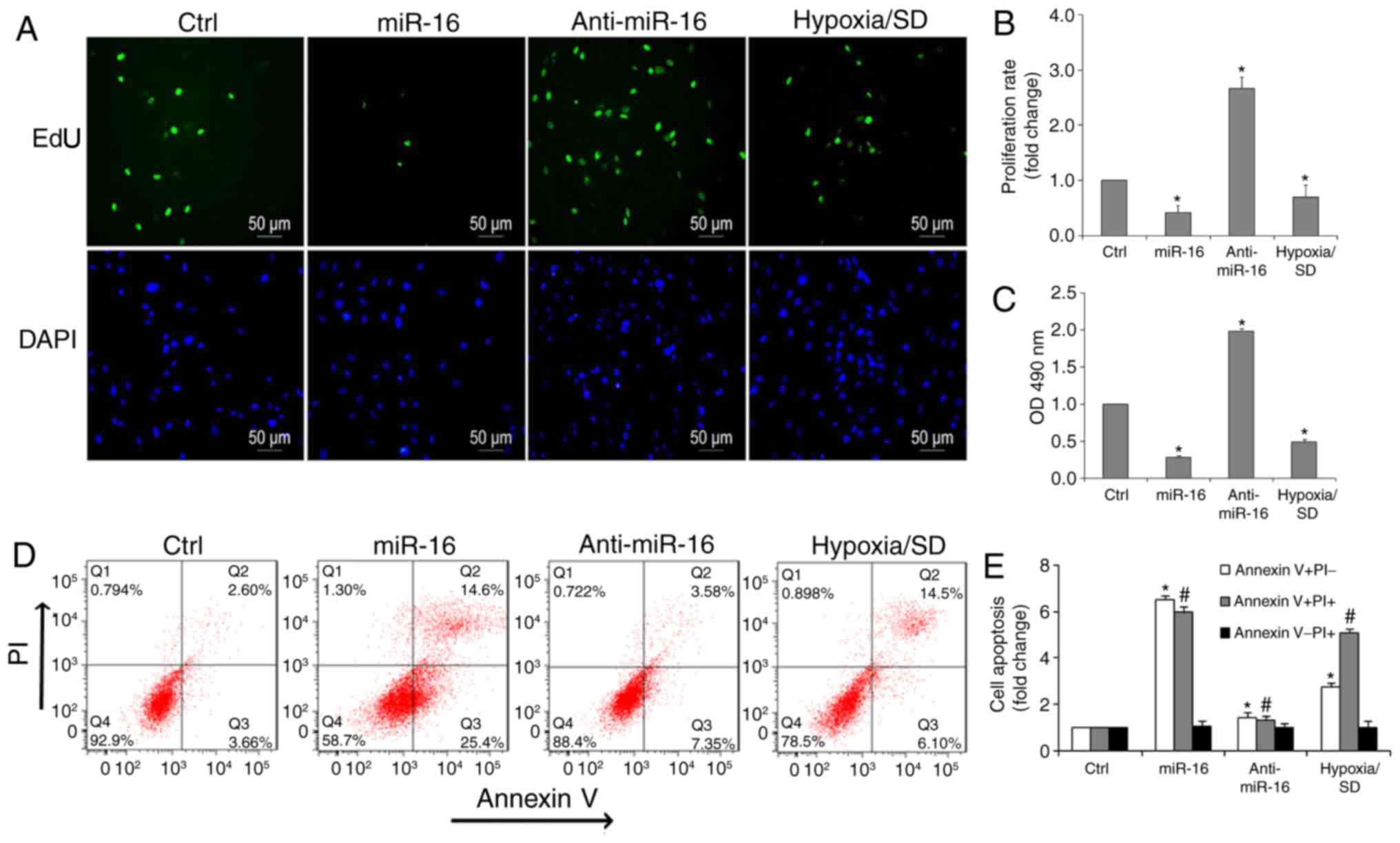
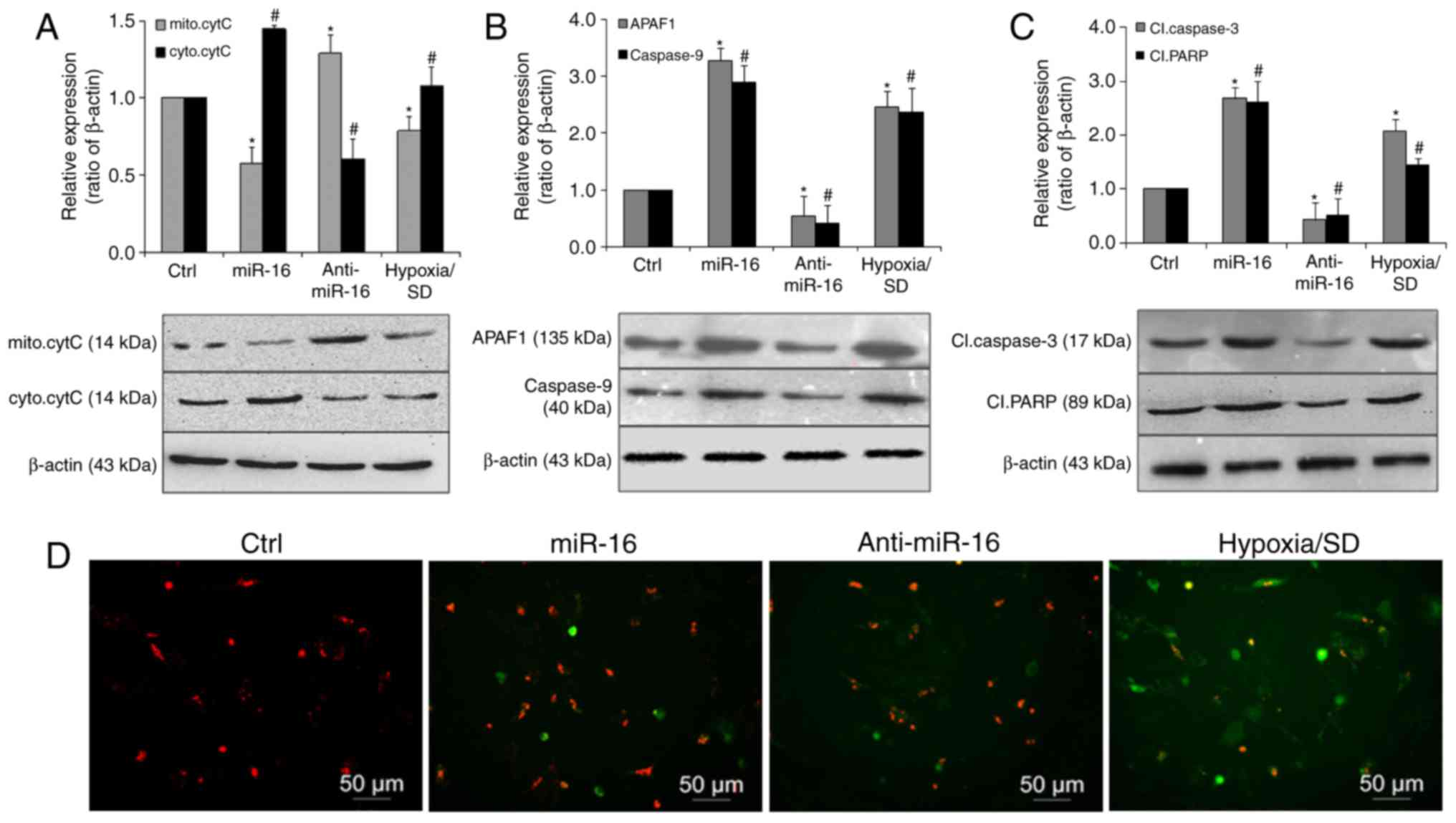
|
1
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Small EM and Olson EN: Pervasive roles of
microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature. 469:336–342. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Afzal MR, Samanta A, Shah ZI, Jeevanantham
V, Abdel-Latif A, Zuba-Surma EK and Dawn B: Adult bone marrow cell
therapy for ischemic heart disease: Evidence and insights from
randomized controlled trials. Circ Res. 117:558–575. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Strauer BE and Steinhoff G: 10 years of
intracoronary and intramyocardial bone marrow stem cell therapy of
the heart: from the methodological origin to clinical practice. J
Am Coll Cardiol. 58:1095–1104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li W, Ma N, Ong LL, Nesselmann C, Klopsch
C, Ladilov Y, Furlani D, Piechaczek C, Moebius JM, Lützow K, et al:
Bcl-2 Engineered MSCs Inhibited Apoptosis and Improved Heart
Function. Stem Cells. 25:2118–2127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stamm C, Westphal B, Kleine HD, Petzsch M,
Kittner C, Klinge H, Schümichen C, Nienaber CA, Freund M and
Steinhoff G: Autologousbone-marrow stem-cell transplantation for
myocardial regeneration. Lancet. 361:45–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Menasché P, Hagège AA, Vilquin JT, Desnos
M, Abergel E, Pouzet B, Bel A, Sarateanu S, Scorsin M, Schwartz K,
et al: Autologous skeletal myoblast transplantation for severe
postinfarction left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol.
41:1078–1083. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Leistner DM, Fischer-Rasokat U, Honold J,
Seeger FH, Schächinger V, Lehmann R, Martin H, Burck I, Urbich C,
Dimmeler S, et al: Transplantation of progenitor cells and
regeneration enhancement in acute myocardial infarction
(TOPCARE-AMI): Final 5-year results suggest long-term safety and
efficacy. Clin Res Cardiol. 100:925–934. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Toma C, Pittenger MF, Cahill KS, Byrne BJ
and Kessler PD: Human mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to a
cardiomyocyte phenotype in the adult murine heart. Circulation.
105:93–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD, Dib N,
Strumpf RK, Schulman SP, Gerstenblith G, DeMaria AN, Denktas AE,
Gammon RS, et al: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem
cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 54:2277–2286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carè A, Catalucci D, Felicetti F, Bonci D,
Addario A, Gallo P, Bang ML, Segnalini P, Gu Y, Dalton ND, et al:
MicroRNA-133 controls cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med. 13:613–618.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ and
Parker R: Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and
siRNAs. Genes Dev. 20:515–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Davis JA, Saunders SJ, Mann M and Backofen
R: Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet.
37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Calin RI GA and Croce CM: miR-15a and
miR-16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives.
Cell Death Differ. 17:215–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Rooij E, Marshall WS and Olson EN:
Toward MicroRNA-based therapeutics for heart disease: The sense in
antisense. Circ Res. 103:919–928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bandi N, Zbinden S, Gugger M, Arnold M,
Kocher V, Hasan L, Kappeler A, Brunner T and Vassella E: miR-15a
and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a
Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5553–5559. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV,
Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, et
al: miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo CJ, Pan Q, Li DG, Sun H and Liu BW:
miR-15b and miR-16 are implicated in activation of the rat hepatic
stellate cell: An essential role for apoptosis. J Hepatol.
50:766–778. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun
S, Hong L, Liu J and Fan D: miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug
resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 123:372–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of Apoptosis by
Bcl-2: Release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science.
275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release ofcytochrome c from mitochondria: A
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu W, Chen J, Cong X, Hu S and Chen X:
Hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 24:416–425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Du W, Liu W, Liu F, Zhang
L, Zhang M, Hou M, Liu K, Zhang S and Yu B: Wnt1 inhibits hydrogen
peroxide-induced apoptosis in mouse cardiac stem cells. PLoS One.
8:e588832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(t)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1311. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu WH, Liu JJ, Wu J, Zhang LL, Liu F, Yin
L, Zhang MM and Yu B: Novel mechanism of inhibition of dendritic
cells maturation by mesenchymal stem cells via interleukin −10 and
the JAK1/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. PLoS One. 8:e554872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han D, Huang W, Li X, Gao L, Su T, Li X,
Ma S, Liu T, Li C, Chen J, et al: Melatonin facilitates
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to repair the murine
infarcted heart via the SIRT1 signaling pathway. J Pineal Res.
60:178–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barwari T, Joshi A and Mayr M: MicroRNAs
in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 68:2577–2584. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yan X, Liang H, Deng T, Zhu K, Zhang S,
Wang N, Jiang X, Wang X, Liu R, Zen K, et al: The identification of
novel targets of miR-16 and characterization of their biological
functions in cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 12:922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Thompson B, Leleu X,
Azab AK, Azab F, Runnels J, Jia X, Ngo HT, Melhem MR, et al:
MicroRNAs 15a and 16 regulate tumor proliferation in multiple
myeloma. Blood. 113:6669–6680. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu JL, Jiang L, Lin QX, Deng CY, Mai LP,
Zhu JN, Li XH, Yu XY, Lin SG and Shan ZX: MicroRNA 16 enhances
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in a
cardiac niche toward myogenic phenotypes in vitro. Life Sci.
90:1020–1026. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|