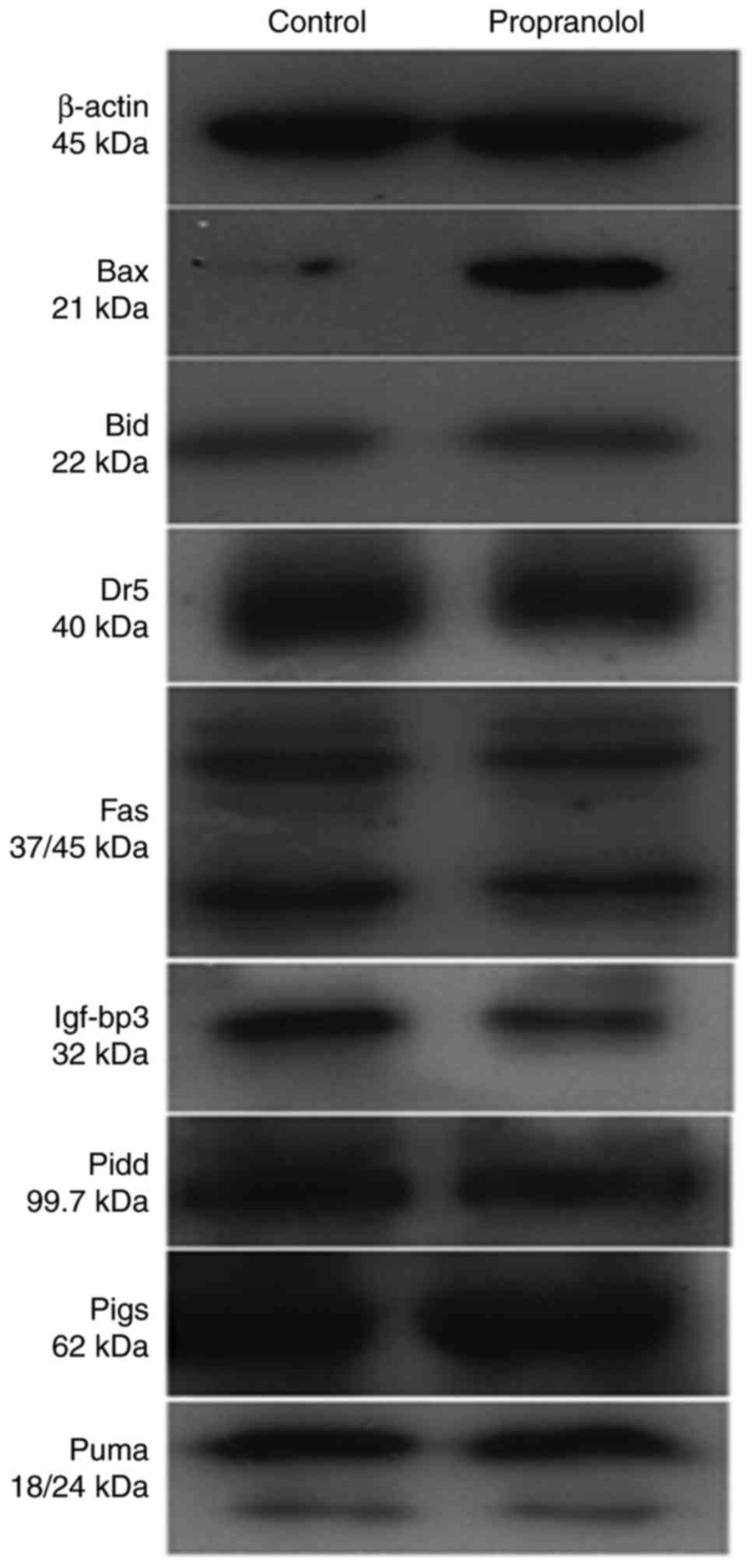
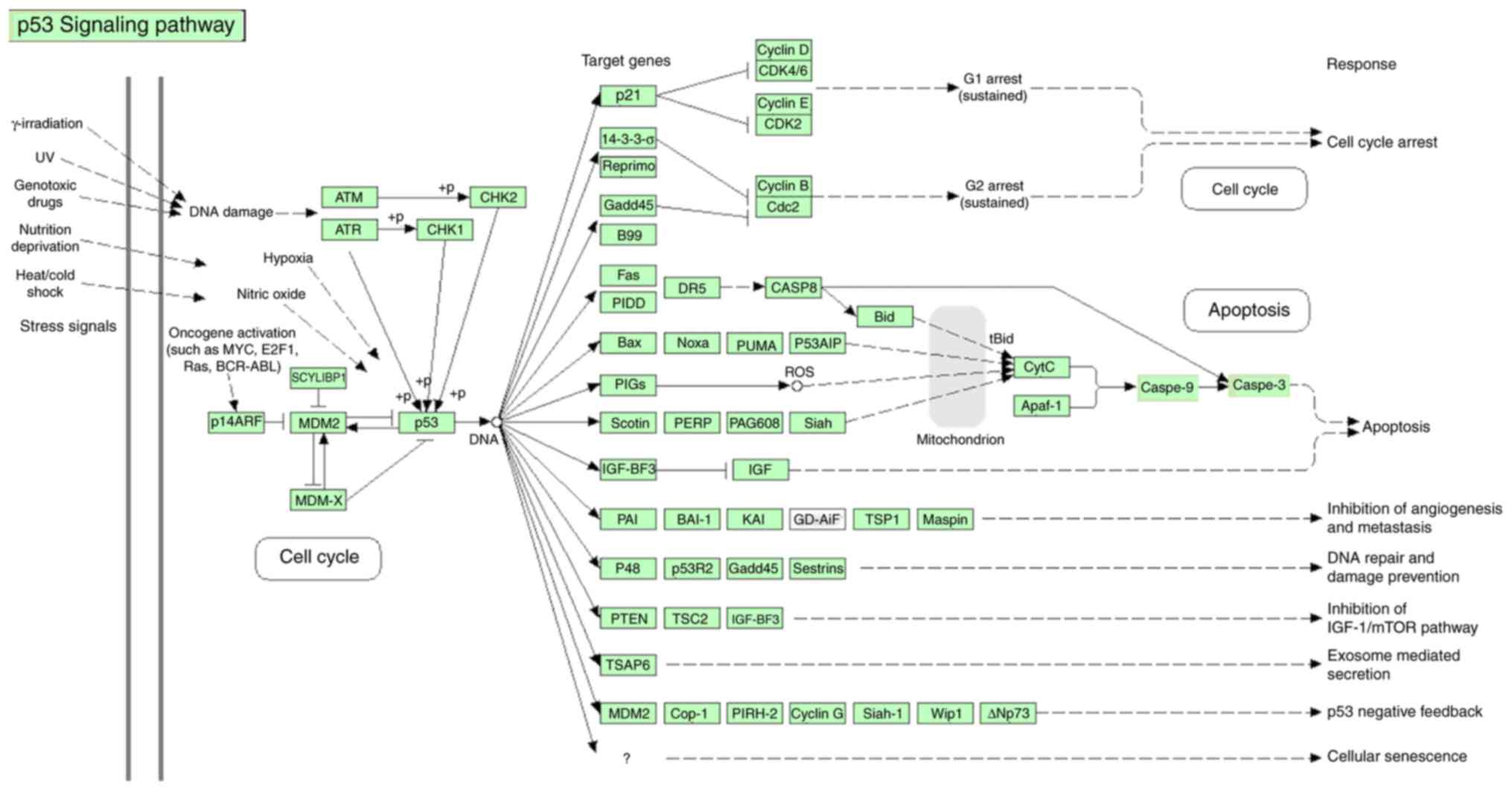
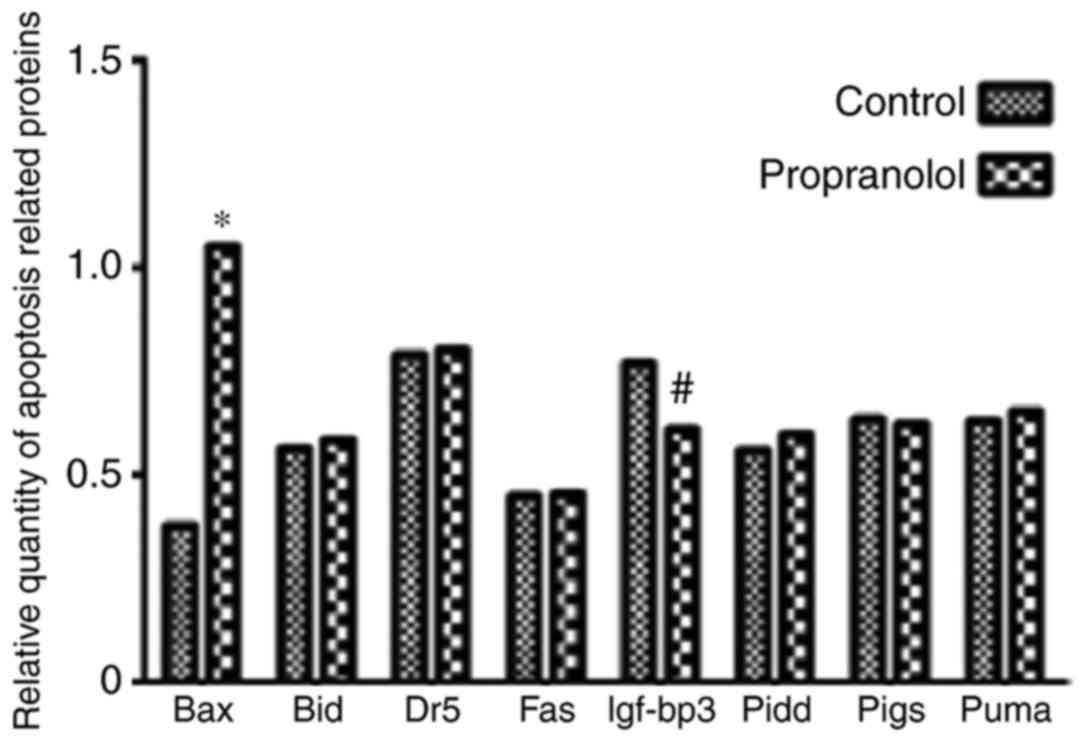
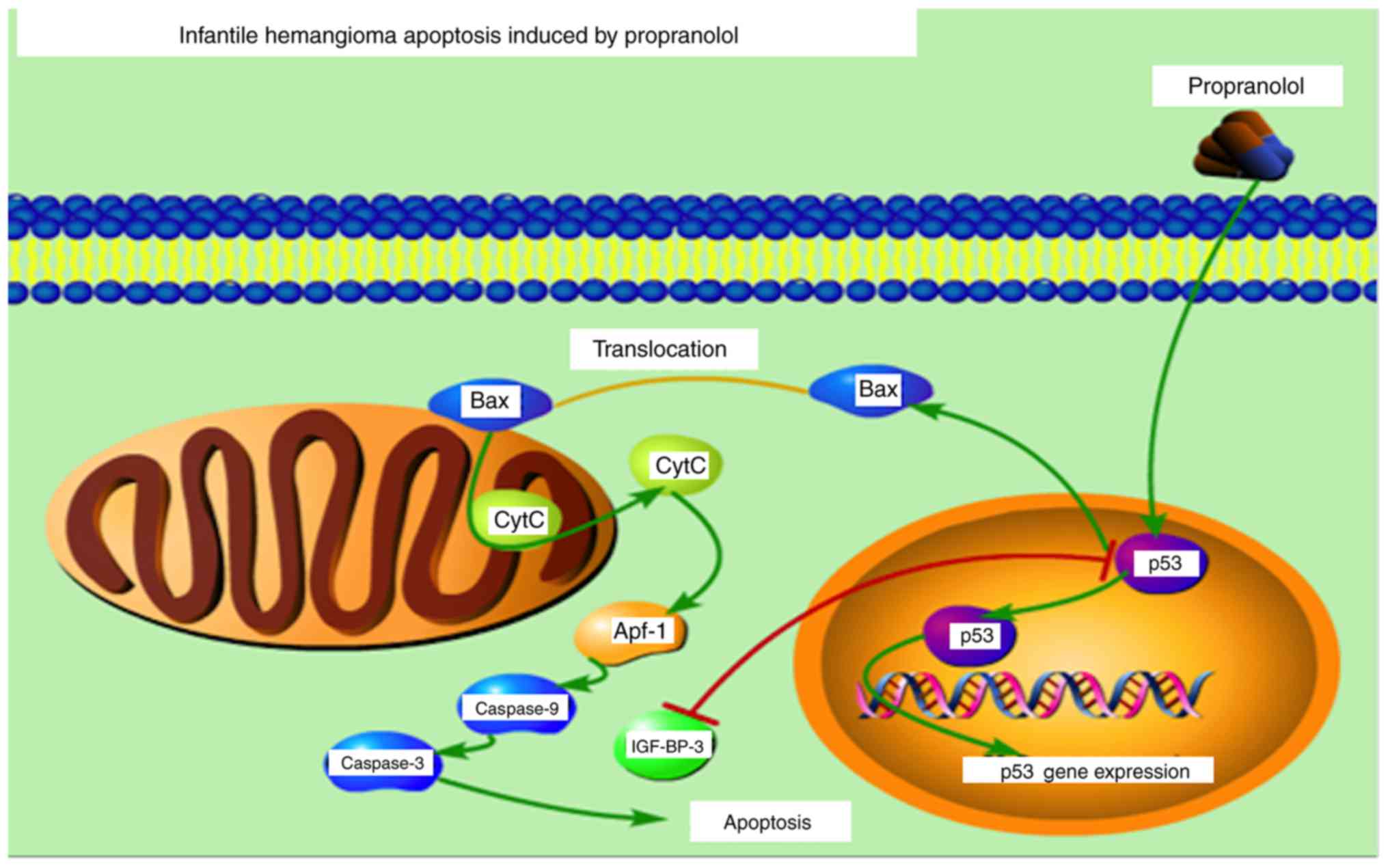
|
1
|
Starkey E and Shahidullah H: Propranolol
for infantile haemangiomas: A review. Arch Dis Child. 96:890–893.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Drolet BA, Swanson EA and Frieden IJ:
Hemangioma Investigator Group: Infantile hemangiomas: An emerging
health issue linked to an increased rate of low birth weight
infants. J Pediatr. 153(712–715): 715.e12008.
|
|
3
|
Greenberger S and Bischoff J: Infantile
hemangioma-mechanism(s) of drug action on a vascular tumor. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0064602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bowers RE, Graham EA and Tomlinson KM: The
natural history of the strawberry nevus. Arch Dermatol. 82:667–680.
1960. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Léauté-Labrèze C and Taïeb A: Efficacy of
beta-blockers in infantile capillary haemangiomas: The
physiopathological significance and therapeutic consequences. Ann
Dermatol Venereol. 135:860–862. 2008.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zimmermann AP, Wiegand S, Werner JA and
Eivazi B: Propranolol therapy for infantile haemangiomas: Review of
the literature. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 74:338–342. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schwartz RA, Sidor MI, Musumeci ML, Lin RL
and Micali G: Infantile haemangiomas: A challenge in paediatric
dermatology. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 24:631–638. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Buckmiller LM, Munson PD, Dyamenahalli U,
Dai Y and Richter GT: Propranolol for infantile hemangiomas: Early
experience at a tertiary vascular anomalies center. Laryngoscope.
120:676–681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Léauté-Labrèze C, de la Roque Dumas E,
Hubiche T, Boralevi F, Thambo JB and Taïeb A: Propranolol for
severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 358:2649–2651. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Handgretinger R: How an accidental
discovery paved the way for the treatment of complicated infantile
haemangiomas. Acta Paediatr. 103:896–897. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Manunza F, Syed S, Laguda B, Linward J,
Kennedy H, Gholam K, Glover M, Giardini A and Harper JI:
Propranolol for complicated infantile haemangiomas: A case series
of 30 infants. Br J Dermatol. 162:466–468. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Missoi TG, Lueder GT, Gilbertson K and
Bayliss SJ: Oral propranolol for treatment of periocular infantile
hemangiomas. Arch Ophthalmol. 129:899–903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moodley ST, Hudson DA, Adams S and Adams
KG: Shouldn't propranolol be used to treat all haemangiomas?
Aesthetic Plast Surg. 39:963–967. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schiestl C, Neuhaus K, Zoller S, Subotic
U, Forster-Kuebler I, Michels R, Balmer C and Weibel L: Efficacy
and safety of propranolol as first-line treatment for infantile
hemangiomas. Eur J Pediatr. 170:493–501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vercellino N, Romanini MV, Pelegrini M,
Rimini A, Occella C and Dalmonte P: The use of propranolol for
complicated infantile hemangiomas. Int J Dermatol. 52:1140–1146.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Storch CH and Hoeger PH: Propranolol for
infantile haemangiomas: Insights into the molecular mechanisms of
action. Br J Dermatol. 163:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lawley LP, Siegfried E and Todd JL:
Propranolol treatment for hemangioma of infancy: Risks and
recommendations. Pediatr Dermatol. 26:610–614. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang D, Ma Q, Shen S and Hu H: Inhibition
of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by propranolol occurs
through apoptosis induction: The study of beta-adrenoceptor
antagonist's anticancer effect in pancreatic cancer cell. Pancreas.
38:94–100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Phillips JD, Zhang H, Wei T and Richter
GT: Expression of β-adrenergic receptor subtypes in proliferative,
involuted, and propranolol-responsive infantile hemangiomas. JAMA
Facial Plast Surg. 19:102–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caporali A, Martello A, Miscianinov V,
Maselli D, Vono R and Spinetti G: Contribution of pericyte
paracrine regulation of the endothelium to angiogenesis. Pharmacol
Ther. 171:56–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mancini AJ and Smoller BR: Proliferation
and apoptosis within juvenile capillary hemangiomas. Am J
Dermatopathol. 18:505–514. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong XY, Guo LL, Wei F, Li JF, Jiang ML,
Li GM, Zhao YD and Chen H: Some characteristics and functional
properties of rapeseed protein prepared by ultrasonication,
ultrafiltration and isoelectric precipitation. J Sci Food Agric.
91:1488–1498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ahogo CK, Ezzedine K, Prey S, Colona V,
Diallo A, Boralevi F, Taïeb A and Léauté-Labrèze C: Factors
associated with the relapse of infantile haemangiomas in children
treated with oral propranolol. Br J Dermatol. 169:1252–1256. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tu JB, Li QY, Jiang F, Hu XY, Ma RZ, Dong
Q, Zhang H, Pattar P and Li SX: Pingyangmycin stimulates apoptosis
in human hemangioma-derived endothelial cells through activation of
the p53 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 10:301–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ye S, Zhao XY, Hu XG, Li T, Xu QR, Yang
HM, Huang DS and Yang L: TP53 and RET may serve as biomarkers of
prognostic evaluation and targeted therapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 37:2215–2226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Homo sapiens tumor protein p53 (TP53),
transcript variant 1, mRNA-Nucleotide-NCBI. 2017.
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Peart MJ and Prives C: Stxbp4
regulates DeltaNp63 stability by suppression of RACK1-dependent
degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 29:3953–3963. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong A, Hardy KL, Kitajewski AM, Shawber
CJ, Kitajewski JK and Wu JK: Propranolol accelerates adipogenesis
in hemangioma stem cells and causes apoptosis of hemangioma
endothelial cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 130:1012–1021. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ji Y, Li K, Xiao X, Zheng S, Xu T and Chen
S: Effects of propranolol on the proliferation and apoptosis of
hemangioma-derived endothelial cells. J Pediatr Surg. 47:2216–2223.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weibel ER and Palade GE: New cytoplasmic
components in arterial endothelia. J Cell Biol. 23:101–112. 1964.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
da Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Frieden IJ, Eichenfield LF, Esterly NB,
Geronemus R and Mallory SB: Guidelines of care for hemangiomas of
infancy. American Academy of Dermatology Guidelines/Outcomes
Committee. J Am Acad Dermatol. 37:631–637. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Haimowitz JE: Guidelines of care:
Hemangiomas of infancy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 39:6621998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lakshmi Chandrasekar K, Sankarapandiyan S
and Mohanarangam Pulivadula VS: Intramuscular haemangioma with
diagnostic challenge: A cause for strange pain in the masseter
muscle. Case Rep Dent. 2014:2858342014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cho JK, Cha W and Sung MW: Intramuscular
hemangioma in the anterior scalene muscle diagnosed by core needle
biopsy. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 8:298–301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Apfelberg DB, Maser MR and Lash H: Argon
laser treatment of cutaneous vascular abnormalities: Progress
report. Ann Plast Surg. 1:14–18. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Edgerton MT: The treatment of hemangiomas:
with special reference to the role of steroid therapy. Ann Surg.
183:517–532. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kveton JF and Pillsbury HC: Conservative
treatment of infantile subglottic hemangioma with corticosteroids.
Arch Otolaryngol. 108:117–119. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Léauté-Labrèze C, Hoeger P,
Mazereeuw-Hautier J, Guibaud L, Baselga E, Posiunas G, Phillips RJ,
Caceres H, Gutierrez Lopez JC, Ballona R, et al: A randomized,
controlled trial of oral propranolol in infantile hemangioma. N
Engl J Med. 372:735–746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Drolet BA, Frommelt PC, Chamlin SL,
Haggstrom A, Bauman NM, Chiu YE, Chun RH, Garzon MC, Holland KE,
Liberman L, et al: Initiation and use of propranolol for infantile
hemangioma: Report of a consensus conference. Pediatrics.
131:128–140. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin TT and He YJ: The advance of
β-blockers in the treatment of infantile hemangiomas. Zhonghua Yan
Ke Za Zhi. 49:1138–1144. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kum JJ and Khan ZA: Propranolol inhibits
growth of hemangioma-initiating cells but does not induce
apoptosis. Pediatr Res. 75:381–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Munabi NC, England RW, Edwards AK,
Kitajewski AA, Tan QK, Weinstein A, Kung JE, Wilcox M, Kitajewski
JK, Shawber CJ and Wu JK: Propranolol targets hemangioma stem cells
via cAMP and mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation. Stem
Cells Transl Med. 5:45–55. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
El-Gibaly AM, Scheuer C, Menger MD and
Vollmar B: Improvement of rat liver graft quality by
pifithrin-alpha-mediated inhibition of hepatocyte necrapoptosis.
Hepatology. 39:1553–1562. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Leker RR, Aharonowiz M, Greig NH and
Ovadia H: The role of p53-induced apoptosis in cerebral ischemia:
effects of the p53 inhibitor pifithrin alpha. Exp Neurol.
187:478–486. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Murphy PJ, Galigniana MD, Morishima Y,
Harrell JM, Kwok RP, Ljungman M and Pratt WB: Pifithrin-alpha
inhibits p53 signaling after interaction of the tumor suppressor
protein with hsp90 and its nuclear translocation. J Biol Chem.
279:30195–30201. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Longobardi L, Torello M, Buckway C, O'Rear
L, Horton WA, Hwa V, Roberts CT Jr, Chiarelli F, Rosenfeld RG and
Spagnoli A: A novel insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-independent
role for IGF binding protein-3 in mesenchymal chondroprogenitor
cell apoptosis. Endocrinology. 144:1695–1702. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ali O, Cohen P and Lee KW: Epidemiology
and biology of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
(IGFBP-3) as an anti-cancer molecule. Horm Metab Res. 35:726–733.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Grimberg A, Liu B, Bannerman P, El-Deiry
WS and Cohen P: IGFBP-3 mediates p53-induced apoptosis during serum
starvation. Int J Oncol. 21:327–335. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fernandez-Pineda I, Williams R,
Ortega-Laureano L and Jones R: Cardiovascular drugs in the
treatment of infantile hemangioma. World J Cardiol. 8:74–80. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Tian Y, Xu DP, Tong S, Xi SL, Liu ZM and
Wang XK: Oral propranolol for the treatment of infantile
hemangiomas in the post-proliferative phase: A-single center
retrospective study of 31 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg.
74:1623–1629. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|