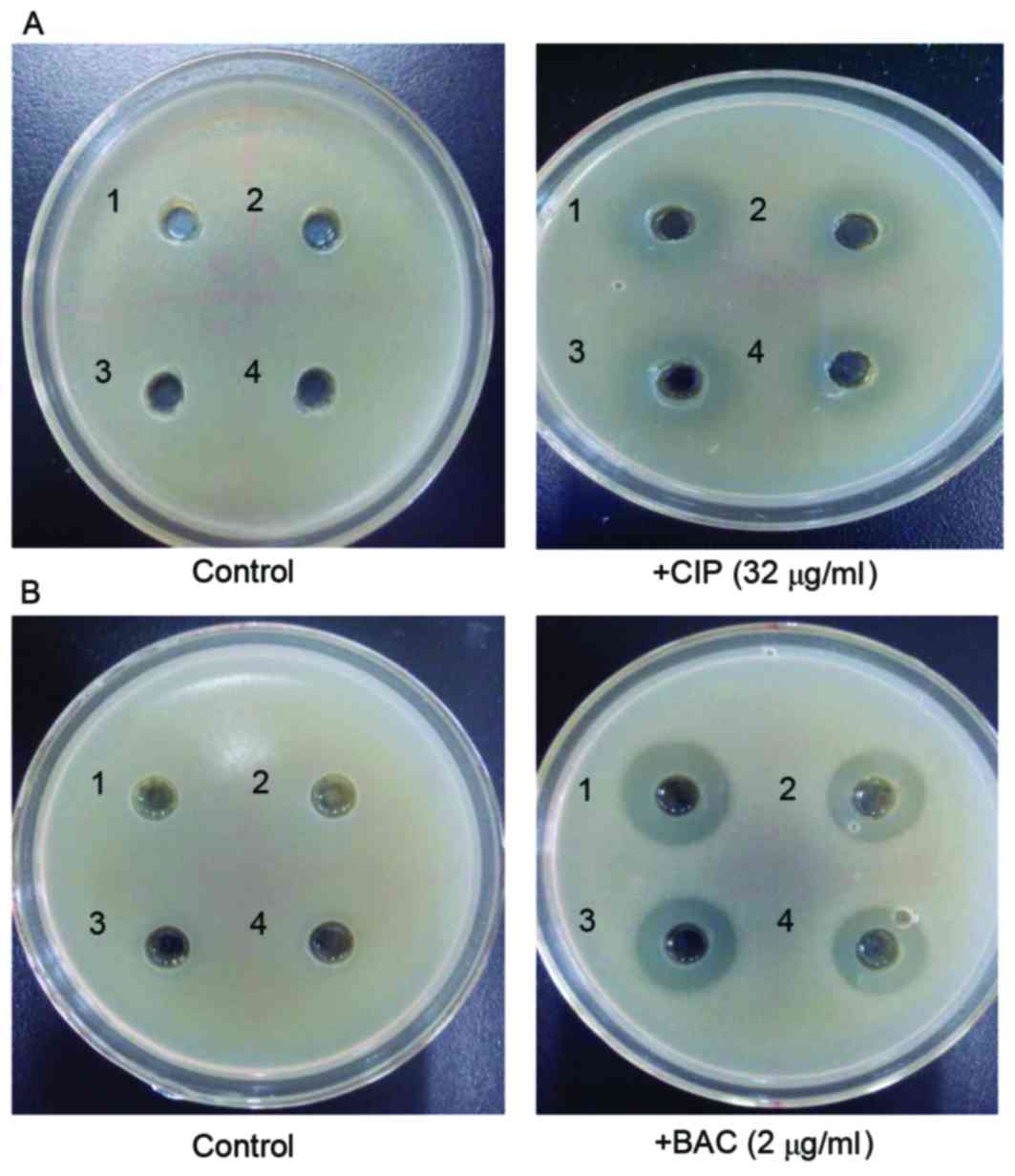
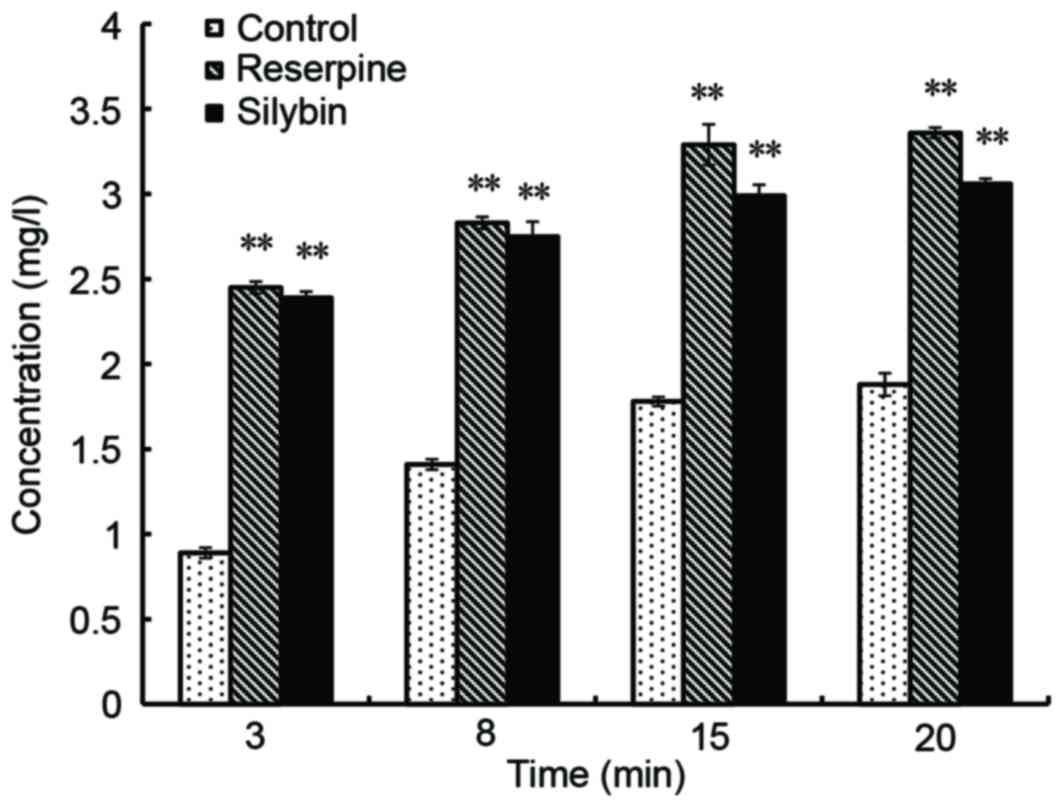
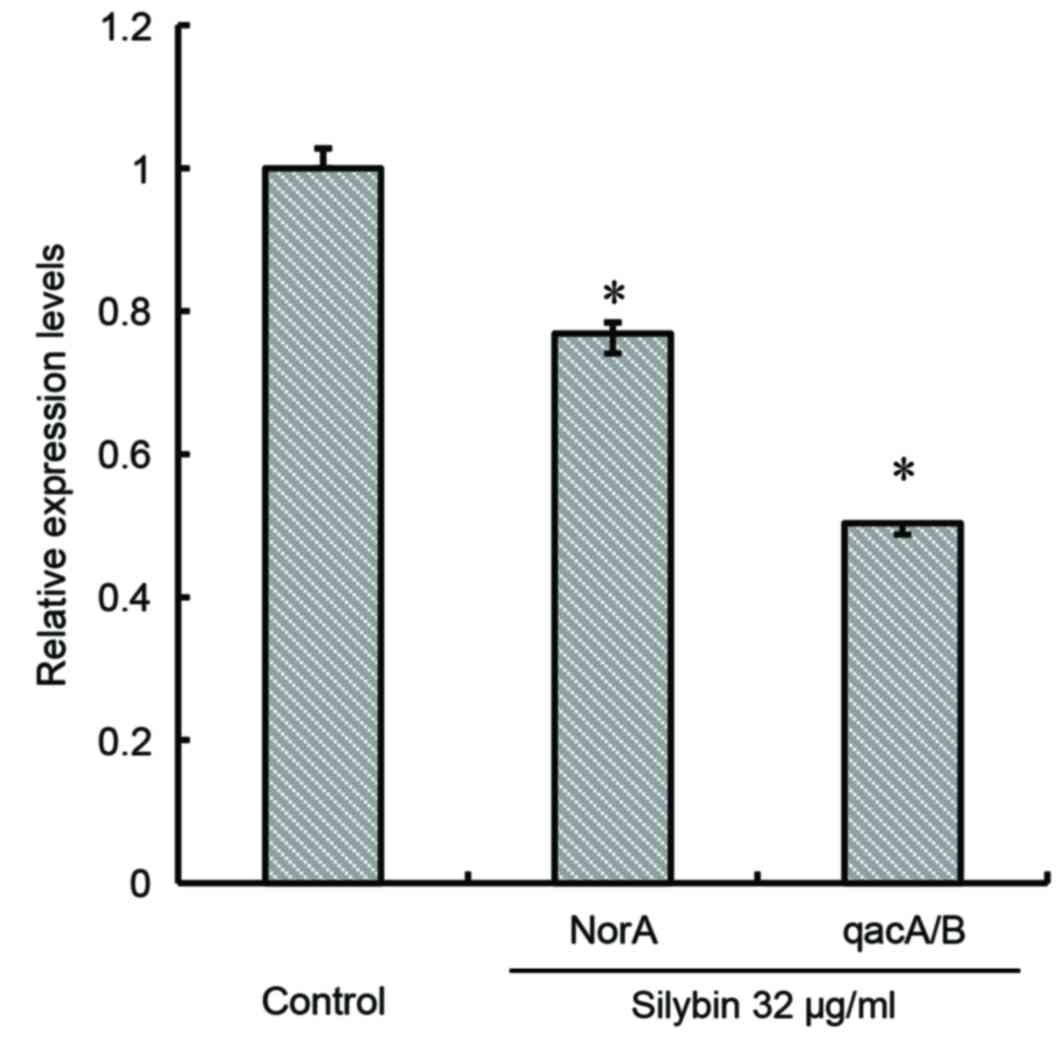
|
1
|
Zou D, Xie KM, Wang H, Chen Y and Xie M:
Inhibitory effects of biochanin A on the efflux pump of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Wei Sheng Wu
Xue Bao. 54:1204–1211. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feng M: Research progress of detection and
drug resistance of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
China Med Herald. 9:8–9. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Yu XH, Wang D and Wang R: Progress in
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chin J Clin Pharmacol.
27:306–310. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Garvev MI, Rahman MM, Gibbon S and Piddock
LJ: Medicinal plant extracts with efflux inhibitory activity
against Gram-negative bacteria. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
37:145–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dantziq AH, Law KL, Cao J and Starling JJ:
Reversal of multidrug resistance by the P-glycoprotein modulator,
LY335979 from the bench to the clinic. Curr Med Chem. 8:39–50.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gamier-Suillerot A, Marbeuf-Gueve C,
Salemo M, Loetchutinat C, Fokt I, Krawaczyk M, Kowalczyk T and
Priebe W: Analysis of drug transport kinetics in mutidrug-resistant
cells:implications for drug action. Curr Med Chem. 8:51–64. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Song ZJ, Feng X, Han WY, Ding Z, Chen AD
and Lei LC: Selection of Chinese herbal medicine Staphylococcus
aureus norA efflux pump inhibitor. J Jilin Agricultural University.
29:329–333. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Wlcek K, Koller F, Ferenci P and Stieger
B: Hepatocellular organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATPs)
and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2(MRP2) are inhibited
by silibinin. Drug Metab Dispos. 41:1522–1528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Molnár J, Engi H, Hohmann J, Molnár P,
Deli J, Wesolowska O, Michalak K and Wang Q: Reversal of multidrug
resitance by natural substances from plants. Curr Top Med Chem.
10:1757–1768. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
InstitutePerformance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility
testing; 16th informational supplement clinical and laboratory
standards lnstitnte. Wayne, PA:
|
|
11
|
Noquchi N, Hase M, Kitta M, Sasatsu M,
Dequchi K and Kono M: Antiseptics susceptibility and distribution
of antiseptic-resistance genes in Methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 172:247–253. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su LT, Liang JL, Guo XJ and Feng F:
Comparison of methods for DNA extraction in Staphylococcis aureus.
J Zhong Kai Univ Agric Eng. 24:5–19. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Wu GB, Zhou JH and Zhang J: Study on
antibacterial activity of 5 kinds of quindones in vitro. Chin J
Clin Pharmacol. 30:129–130. 2014.
|
|
14
|
Yang ZC, Yang XS and Niu YL: Screening for
and bioassay-guided isolation of bacterial efflux pump inhibitors
by control method based on double plates. Nat Prod Res Dev.
22:277–280. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen XJ, Xu XM, Niu B, Jie J, Yang Q,
Zhang YH and Zhang DC: Improving the technique to prepare plasmid
DNA from Escherichia coil on a large scale. Chin Remed Clin.
3:103–105. 2003.
|
|
17
|
Chen SB: Three kinds of Traditional
Chinese medicine (TCM) on a beta lactamase Staphylococcus aureus
plasmid elimination process. Anim Husband Vet Med. 42:81–84.
2010.
|
|
18
|
Yang CS and Liu WE: Drug resistance
mechanism of MRSA and molecular biological detection methods: A new
research progress. Chin J Nosocomiol. 17:356–358. 2007.
|
|
19
|
Costa SS, Viveiros M, Amaral L and Couto
I: Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphlococcus aureus: An update. Open
Microbiol J. 7:59–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chan BC, Ip M, Lau CB, Lui SL, Jolivalt C,
Ganem-Elbaz C, Litaudon M, Reiner NE, Gong H, See RH, et al:
Synergistic effects of baicalein with ciprofloxacin against NorA
over-expressed methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
and inhibition of MRSA Pyruvate kinase. J Ethnopharmacol.
137:767–773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaatz GW, Thyagarajan RV and Seo SM:
Effect of promoter region mutations and mgrA overexpression on
transcription of norA, which encodes a Staphylococcis aureus
multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
49:161–169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ho J and Branlev J: Prevalence of
antiseptic resistance genes qacA/B and specific sequence types of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the era of hand
hygiene. Antimicrob Chemother. 67:1549–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Noguchi N, Suwa J, Narui K, Sasatsu M, Ito
T, Hiramatsu K and Song JH: Susceptibilities to antiseptic agents
and distribution of antiseptic-resistance genes qacA/B and smr of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated in Asia during
1998 and 1999. J Med Microbiol. 54:557–565. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Su Y, Shen W and Ju LW: Progress in
Staphylococcus aureus disinfectant resistance genes. Chin J
Disinfect. 31:1084–1087. 2014.
|
|
25
|
Irizarry L, Merlin T, Rupp J and Griffith
J: Reduced susceptibility of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus to cetylpyridinium chloride and chlorhexidine. Chemotherapy.
42:248–252. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li S: Study on the epidemiological of
disinfectant-resistant gene qacA/B in MRSA and it's resistance of
disinfectant and mechanisims research (unpublished thesis). The
Fourth Military Medical University. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Hua DX and Qian YS: Progress in Bacterial
disinfectant resistance gene. Chin J Anibiot. 33:513–518. 2008.
|
|
28
|
Fan JC, Bai YN, Shi FY and Pei HB:
Drug-resistance and plasmid homology analysis of SA in medical
environment. Chin J Public Health. 24:816–817. 2008.
|