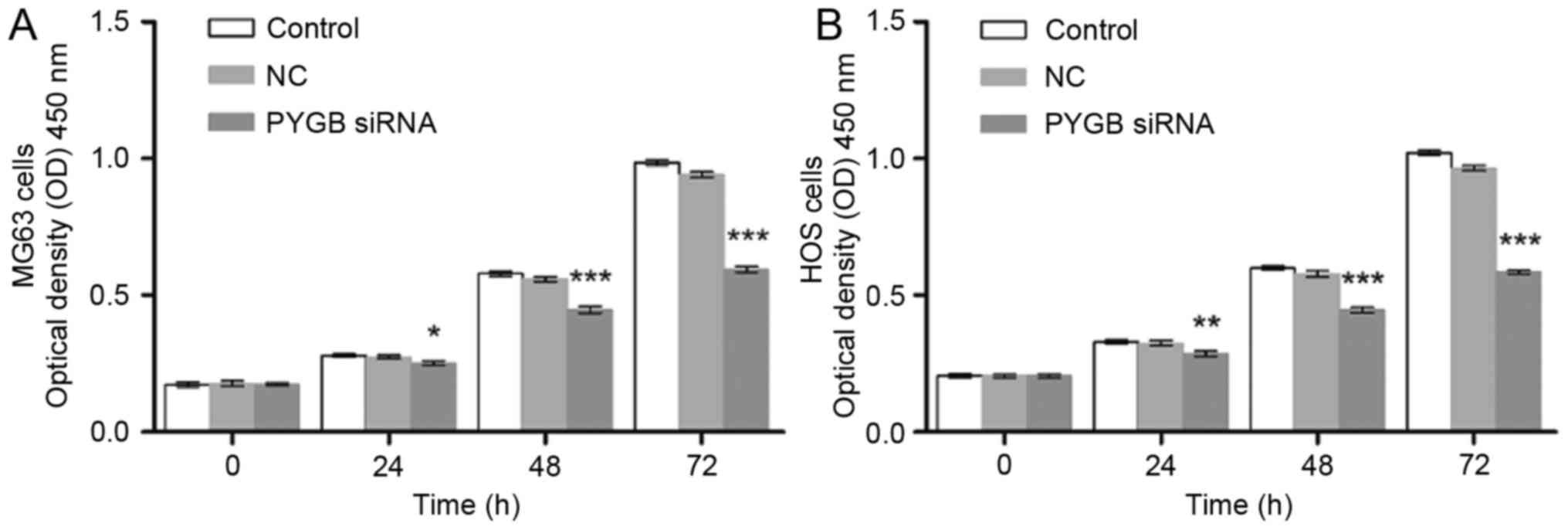
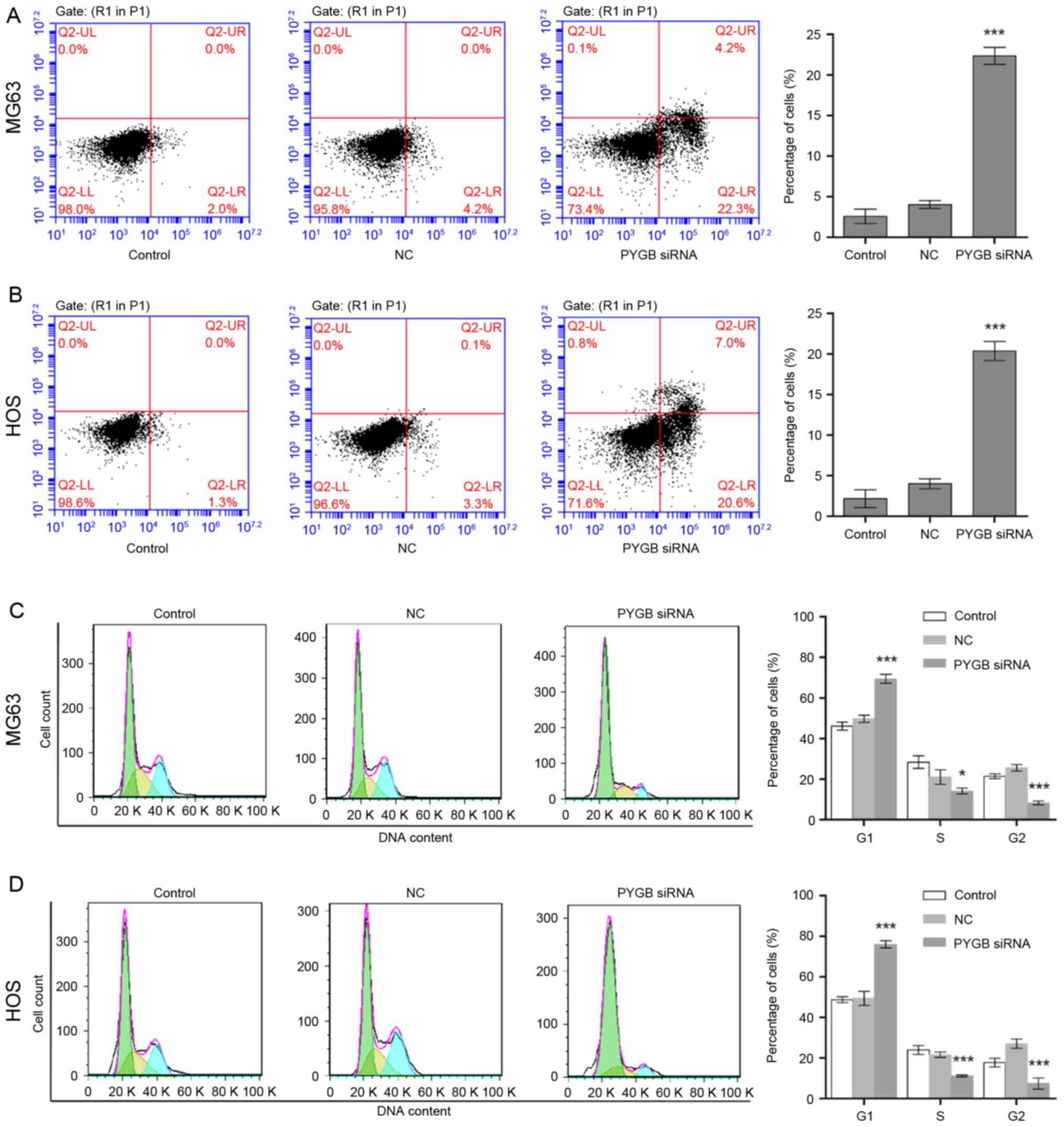
|
1
|
Anoop T, Geetha N, Babanrao SA and
Jayasree K: Primary osteosarcoma of rib mimicking lung mass with
secondary aneurysmal bone cyst formation. J Thorac Oncol.
9:738–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Do T, Renker EK and Weber MA: Simulation
of teleangiectactic osteosarcoma by aneurysmatic bone cyst.
Orthopade. 42:1067–1070. 2013.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Janevska V, Spasevska L, Samardziski M,
Nikodinovska V, Zhivadinovik J and Trajkovska E: From aneurysmal
bone cyst to telangiectatic osteosarcoma with metastasis in
inguinal lymph nodes-Case report. Med Pregl. 68:127–132. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aung L, Gorlick RG, Shi W, Thaler H,
Shorter NA, Healey JH, Huvos AG and Meyers PA: Second malignant
neoplasms in long-term survivors of osteosarcoma. Cancer.
95:1728–1734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bacci G, Ferrari C, Longhi A, Ferrari S,
Forni C, Bacchini P, Palmerini E, Briccoli A, Pignotti E,
Balladelli A and Picci P: Second malignant neoplasm in patients
with osteosarcoma of the extremities treated with adjuvant and
neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 28:774–780.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nagarajan R, Kamruzzaman A, Ness KK,
Marchese VG, Sklar C, Mertens A, Yasui Y, Robison LL and Marina N:
Twenty years of follow-up of survivors of childhood osteosarcoma: A
report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Cancer.
117:625–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jaffe N: Historical perspective of the
treatment of osteosarcoma: An interview with Dr Norman Jaffe.
Interview by Margaret pearson. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs. 15:90–94.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Longhi A, Ferrari S, Tamburini A, Luksch
R, Fagioli F, Bacci G and Ferrari C: Late effects of chemotherapy
and radiotherapy in osteosarcoma and ewing sarcoma patients: The
Italian Sarcoma Group Experience (1983–2006). Cancer.
118:5050–5059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luetke A, Meyers PA, Lewis I and Juergens
H: Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art
review. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Newgard CB, Hwang PK and Fletterick RJ:
The family of glycogen phosphorylases: Structure and function. Crit
Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 24:69–99. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Newgard CB, Littman DR, van Genderen C,
Smith M and Fletterick RJ: Human brain glycogen phosphorylase.
Cloning, sequence analysis, chromosomal mapping, tissue expression,
and comparison with the human liver and muscle isozymes. J Biol
Chem. 263:3850–3857. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Philips KB, Kurtoglu M, Leung HJ, Liu H,
Gao N, Lehrman MA, Murray TG and Lampidis TJ: Increased sensitivity
to glucose starvation correlates with downregulation of glycogen
phosphorylase isoform PYGB in tumor cell lines resistant to
2-deoxy-D-glucose. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 73:349–361. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shimada S, Maeno M, Akagi M, Hatayama I,
Sato T and Sato K: Immunohistochemical detection of glycogen
phosphorylase isoenzymes in rat and human tissues. Histochem J.
18:334–338. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barbosa AJ and Castro LP: BGP expression
in gastric epithelium and early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer.
5:123–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shimada S, Shiomori K, Honmyo U, Maeno M,
Yagi Y and Ogawa M: BGP expression in gastric biopsies may predict
the development of new lesions after local treatment for early
gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 5:130–136. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tashima S, Shimada S, Yamaguchi K, Tsuruta
J and Ogawa M: Expression of brain-type glycogen phosphorylase is a
potentially novel early biomarker in the carcinogenesis of human
colorectal carcinomas. Am J Gastroenterol. 95:255–263. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kirkin V, Joos S and Zörnig M: The role of
Bcl-2 family members in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1644:229–249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Manion MK and Hockenbery DM: Targeting
Bcl-2 related proteins in cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2 4
Suppl 1:S105–S114. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Waerner T, Alacakaptan M, Tamir I,
Oberauer R, Gal A, Brabletz T, Schreiber M, Jechlinger M and Beug
H: ILEI: A cytokine essential for EMT, tumor formation, and late
events in metastasis in epithelial cells. Cancer Cell. 10:227–239.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Halbleib JM and Nelson WJ: Cadherins in
development: Cell adhesion, sorting, and tissue morphogenesis.
Genes Dev. 20:3199–3214. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Page-McCaw A, Ewald AJ and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:221–233. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rothberg Gould BE and Bracken MB:
E-cadherin immunohistochemical expression as a prognostic factor in
infiltrating ductal carcinoma of the breast: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 100:139–148. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shibata T and Hirohashi S: E-cadherin cell
adhesion system in human cancer. Seikagaku. 78:647–656. 2006.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tycko B, Li CM and Buttyan R: The
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in Wilms tumors and prostate cancers. Curr
Mol Med. 7:479–489. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Christofori G and Semb H: The role of the
cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumour-suppressor gene.
Trends Biochem Sci. 24:73–76. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leptin M: Twist and snail as positive and
negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes
Dev. 5:1568–1576. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vesuna F, van Diest P, Chen JH and Raman
V: Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene
expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
367:235–241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|