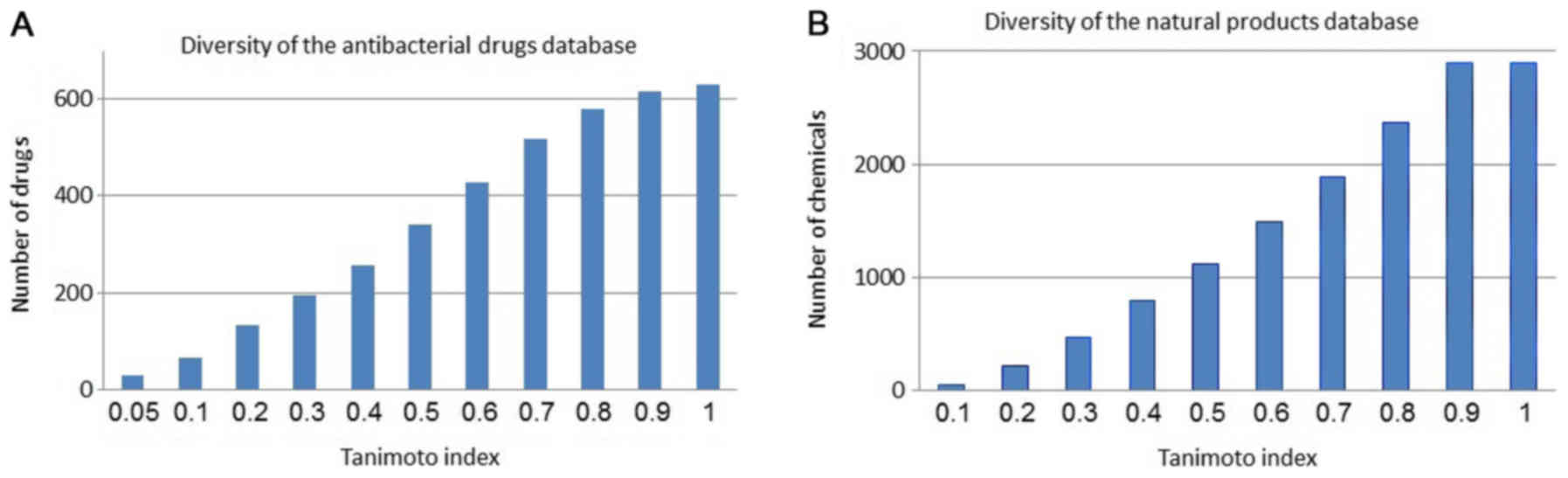
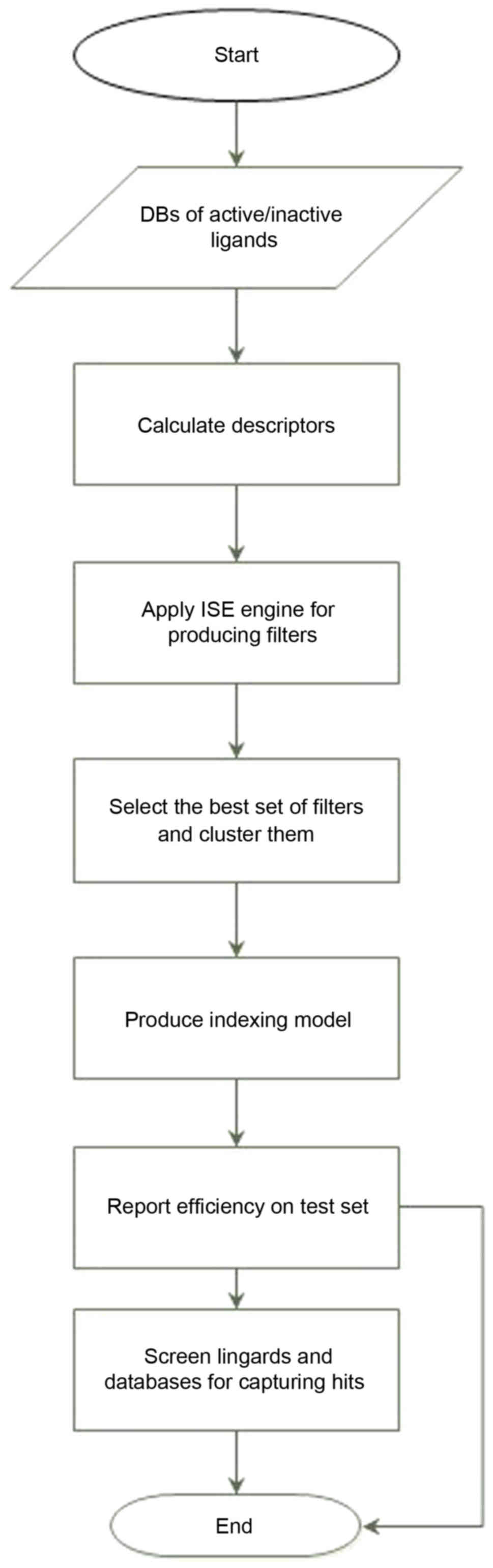
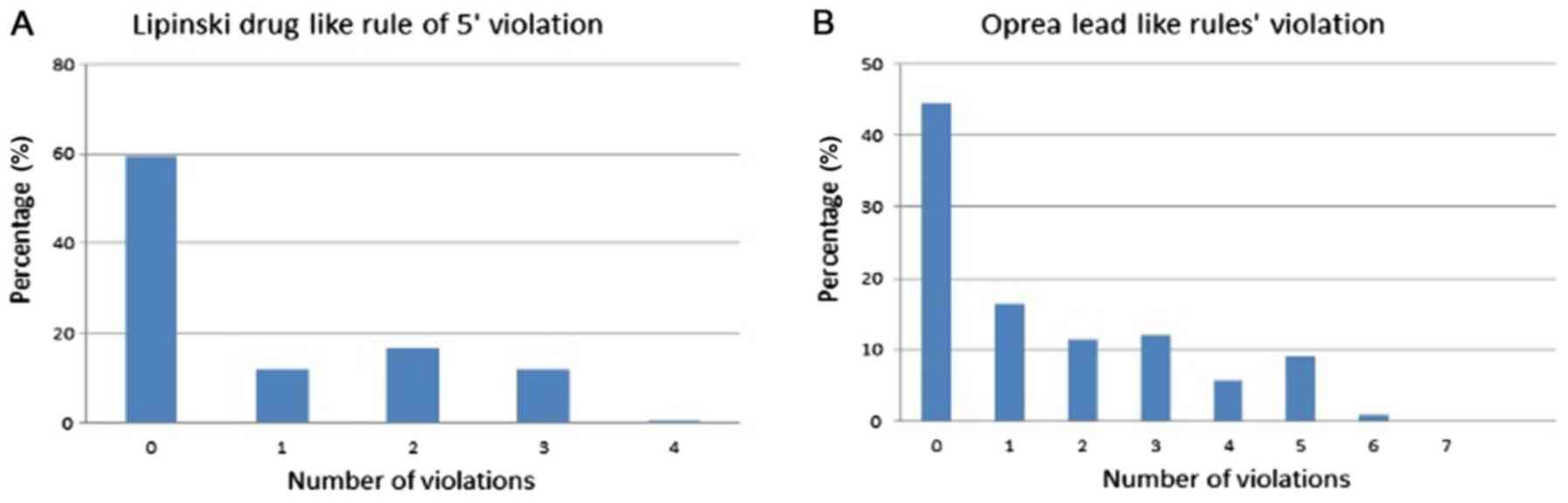
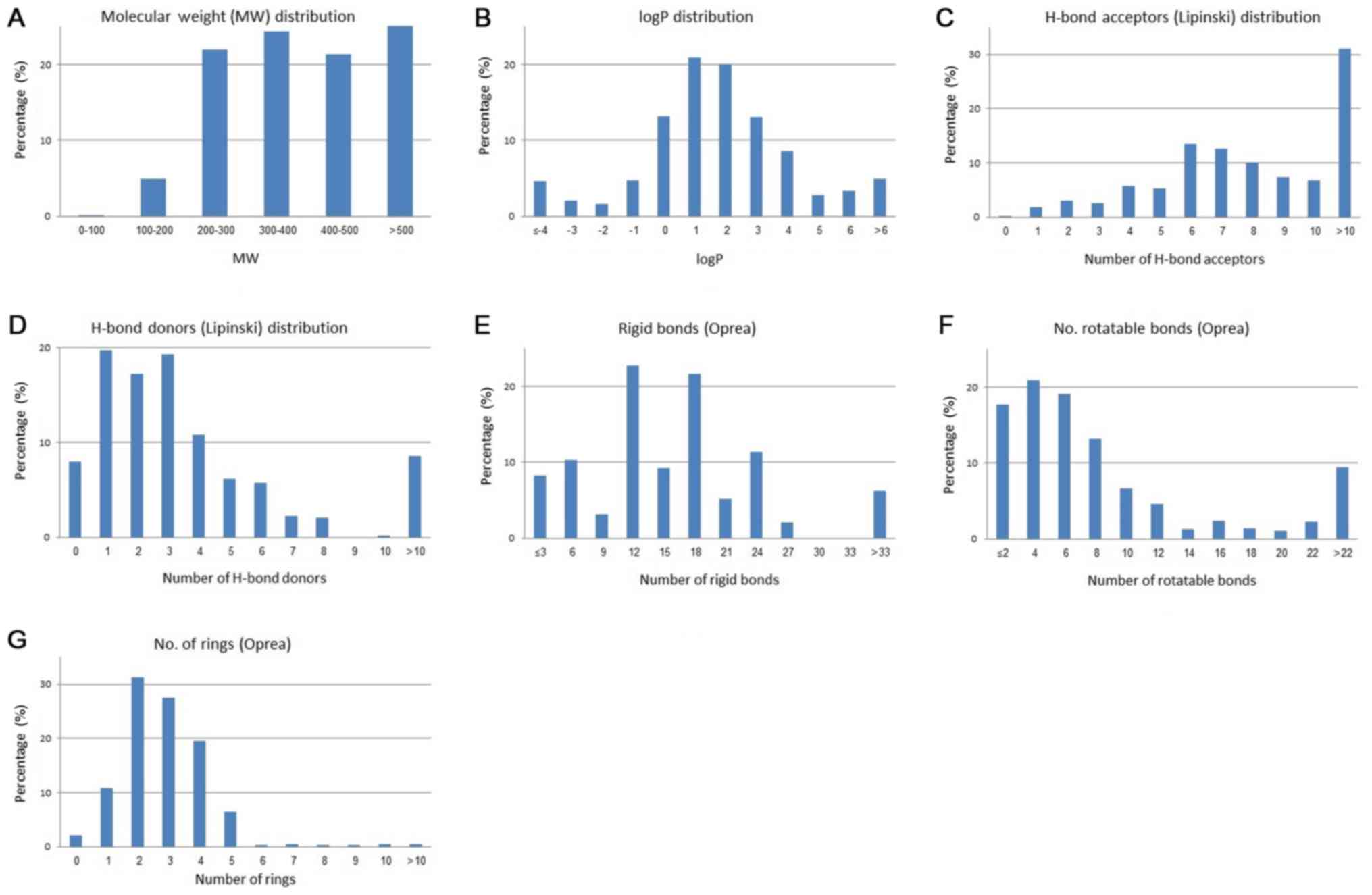
|
1
|
Alanis AJ: Resistance to antibiotics: Are
we in the post-antibiotic era? Arch Med Res. 36:697–705. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klein E, Smith DL and Laxminarayan R:
Hospitalizations and deaths caused by methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus, United States, 1999–2005. Emerg Infect Dis.
13:1840–1846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Appelbaum PC: The emergence of
vancomycin-intermediate and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 12 Suppl 1:S16–S23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Núñez-Núñez M, Navarro MD, Gkolia P,
Rajendran Babu N, Del Toro MD, Voss A, Sharland M, Sifakis F,
Tacconelli E, Rodríguez-Baño J, et al: Surveillance Systems from
Public Health Institutions and Scientific Societies for
Antimicrobial Resistance and Healthcare-Associated Infections in
Europe (SUSPIRE): Protocol for a systematic review. BMJ Open.
7:e0145382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kalesinskas P, Kačergius T, Ambrozaitis A,
Pečiulienė V and Ericson D: Reducing dental plaque formation and
caries development. A review of current methods and implications
for novel pharmaceuticals. Stomatologija. 16:44–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pitiriga V, Dimitroulia E, Saroglou G and
Tsakris A: The challenge of curbing aminoglycoside resistance: Can
antimicrobial stewardship programs play a critical role? Expert Rev
Anti Infect Ther. 15:947–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cantón R, Horcajada JP, Oliver A,
Garbajosa PR and Vila J: Inappropriate use of antibiotics in
hospitals: The complex relationship between antibiotic use and
antimicrobial resistance. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 31 Suppl
4:S3–S11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Abachi S, Lee S and Rupasinghe HP:
Molecular mechanisms of inhibition of streptococcus species by
phytochemicals. Molecules. 21:pii: E215. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mestrovic T and Ljubin-Sternak S:
Molecular mechanisms of Chlamydia trachomatis resistance to
antimicrobial drugs. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 23:656–670. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vaidya VK: Horizontal transfer of
antimicrobial resistance by extended-spectrum β lactamase-producing
enterobacteriaceae. J Lab Physicians. 3:37–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wijesekera RO: Is there an industrial
future for phytopharmaceutical drugs? An outline of UNIDO
programmes in the sector. J Ethnopharmacol. 32:217–224. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kacergius T, Abu-Lafi S, Kirkliauskiene A,
Gabe V, Adawi A, Rayan M, Qutob M, Stukas R, Utkus A, Zeidan M and
Rayan A: Inhibitory capacity of Rhus coriaria L. extract and its
major component methyl gallate on Streptococcus mutans biofilm
formation by optical profilometry: Potential applications for oral
health. Mol Med Rep. 16:949–956. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cragg GM and Newman DJ: Medicinals for the
millennia: The historical record. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 953:3–25. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Andrade-Carrera B, Clares B, Noé V,
Mallandrich M, Calpena AC, García ML and Garduño-Ramírez ML:
Cytotoxic evaluation of (2S)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-prenylflavanone
derivatives loaded PLGA nanoparticles against MiaPaCa-2 cells.
Molecules. 22:pii: E1553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zaid H, Raiyn J, Nasser A, Saad B and
Rayan A: Physicochemical properties of natural based products
versus synthetic chemicals. Open Nutraceut J. 3:194–202. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Griesenauer RH and Kinch MS: 2016 in
review: FDA approvals of new molecular entities. Drug Discov Today.
22:1593–1597. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harvey AL and Cree IA: High-throughput
screening of natural products for cancer therapy. Planta Med.
76:1080–1086. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frank A, Abu-Lafi S, Adawi A, Schwed JS,
Stark H and Rayan A: From medicinal plant extracts to defined
chemical compounds targeting the histamine H4 receptor: Curcuma
longa in the treatment of inflammation. Inflamm Res. 66:923–929.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zatsepin M, Mattes A, Rupp S, Finkelmeier
D, Basu A, Burger-Kentischer A and Goldblum A: Computational
discovery and experimental confirmation of TLR9 receptor antagonist
leads. J Chem Inf Model. 56:1835–1846. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zaid H, Raiyn J, Osman M, Falah M, Srouji
S and Rayan A: In silico modeling techniques for predicting the
tertiary structure of human H4 receptor. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 21:597–619. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pappalardo M, Rayan M, Abu-Lafi S,
Leonardi ME, Milardi D, Guccione S and Rayan A: Homology-based
modeling of rhodopsin-like family members in the inactive State:
Structural analysis and deduction of tips for modeling and
optimization. Mol Inform. 36:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shahaf N, Pappalardo M, Basile L, Guccione
S and Rayan A: How to choose the suitable template for homology
modelling of GPCRs: 5-HT7 receptor as a test case. Mol Inform.
35:414–423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Michaeli A and Rayan A: Modeling ensembles
of loop conformations by iterative stochastic elimination. Lett
Drug Design Discov. 13:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fradera X and Babaoglu K: Overview of
methods and strategies for conducting virtual small molecule
screening. Curr Protoc Chem Biol. 9:196–212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zeidan M, Rayan M, Zeidan N, Falah M and
Rayan A: Indexing natural products for their potential
anti-diabetic activity: Filtering and mapping discriminative
physicochemical properties. Molecules. 22:pii: E1563. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pappalardo M, Shachaf N, Basile L, Milardi
D, Zeidan M, Raiyn J, Guccione S and Rayan A: Sequential
application of ligand and structure based modeling approaches to
index chemicals for their hH4R antagonism. PLoS One. 9:e1093402014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rayan A, Raiyn J and Falah M: Nature is
the best source of anticancer drugs: Indexing natural products for
their anticancer bioactivity. PLoS One. 12:e01879252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rayan A, Marcus D and Goldblum A:
Predicting oral druglikeness by iterative stochastic elimination. J
Chem Inf Model. 50:437–445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Glick M, Rayan A and Goldblum A: A
stochastic algorithm for global optimization and for best
populations: A test case of side chains in proteins. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 99:703–708. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rayan A, Noy E, Chema D, Levitzki A and
Goldblum A: Stochastic algorithm for kinase homology model
construction. Curr Med Chem. 11:675–692. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rayan A, Senderowitz H and Goldblum A:
Exploring the conformational space of cyclic peptides by a
stochastic search method. J Mol Graph Model. 22:319–333. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rayan A, Falah M, Raiyn J, Da'adoosh B,
Kadan S, Zaid H and Goldblum A: Indexing molecules for their hERG
liability. Eur J Med Chem. 65:304–314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aswad M, Rayan M, Abu-Lafi S, Falah M,
Raiyn J, Abdallah Z and Rayan A: Nature is the best source of
anti-inflammatory drugs: Indexing natural products for their
anti-inflammatory bioactivity. Inflamm Res. 67:67–75. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hann MM and Oprea TI: Pursuing the
leadlikeness concept in pharmaceutical research. Curr Opin Chem
Biol. 8:255–263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dash SS and Gummadi SN: Inhibitory effect
of caffeine on growth of various bacterial strains. Res J
Microbiol. 3:457–465. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sandlie I, Solberg K and Kleppe K: The
effect of caffeine on cell growth and metabolism of thymidine in
Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 73:29–41. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Whitney AK and Weir TL: Interaction of
caffeine with the SOS response pathway in Escherichia coli. Gut
Pathog. 7:212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao QY, Hu FL, Zhu HH, Liu MQ, Li HX and
Hu F: Control effects of Ricinus communis extracts on Meloidogyne
incognita. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 22:3033–3038. 2011.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bigi MF, Torkomian VL, de Groote ST,
Hebling MJ, Bueno OC, Pagnocca FC, Fernandes JB, Vieira PC and da
Silva MF: Activity of Ricinus communis (Euphorbiaceae) and ricinine
against the leaf-cutting ant Atta sexdens rubropilosa (Hymenoptera:
Formicidae) and the symbiotic fungus Leucoagaricus gongylophorus.
Pest Manag Sci. 60:933–938. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Radonić A, Blažević I, Mastelić J, Zekić
M, Skočibušić M and Maravić A: Phytochemical analysis and
antimicrobial activity of Cardaria draba (L.) Desv. volatiles. Chem
Biodivers. 8:1170–1181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|