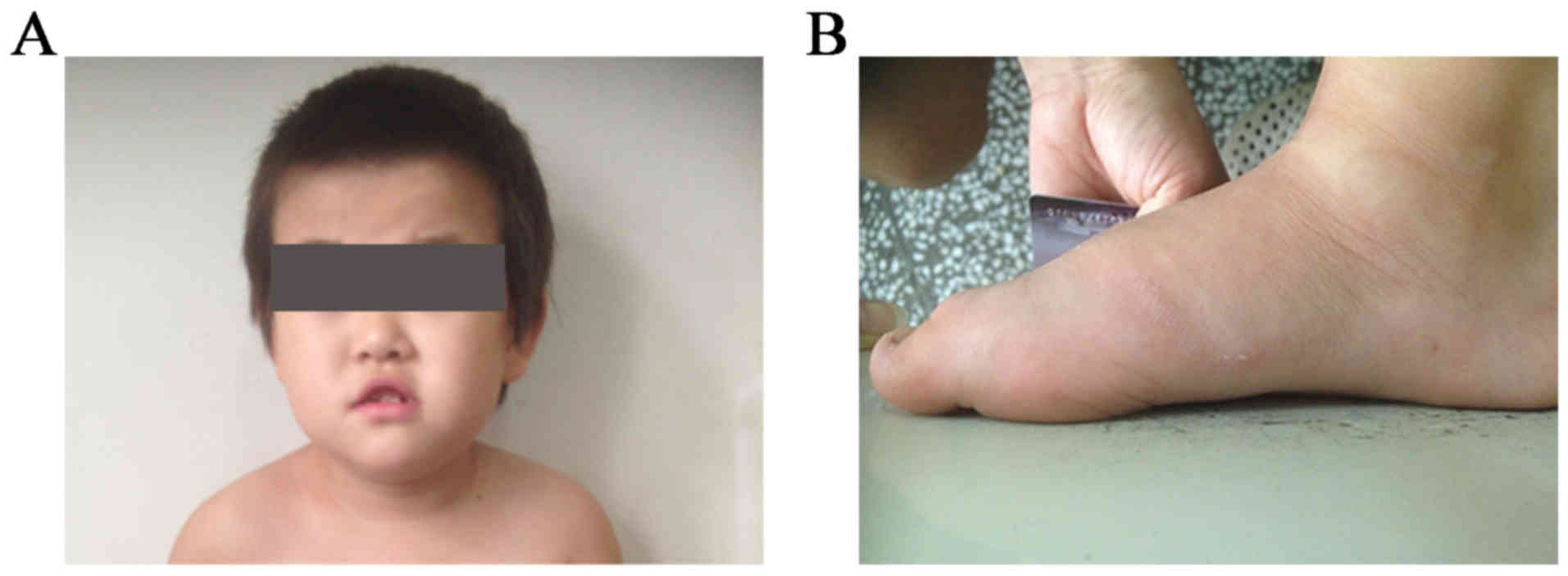
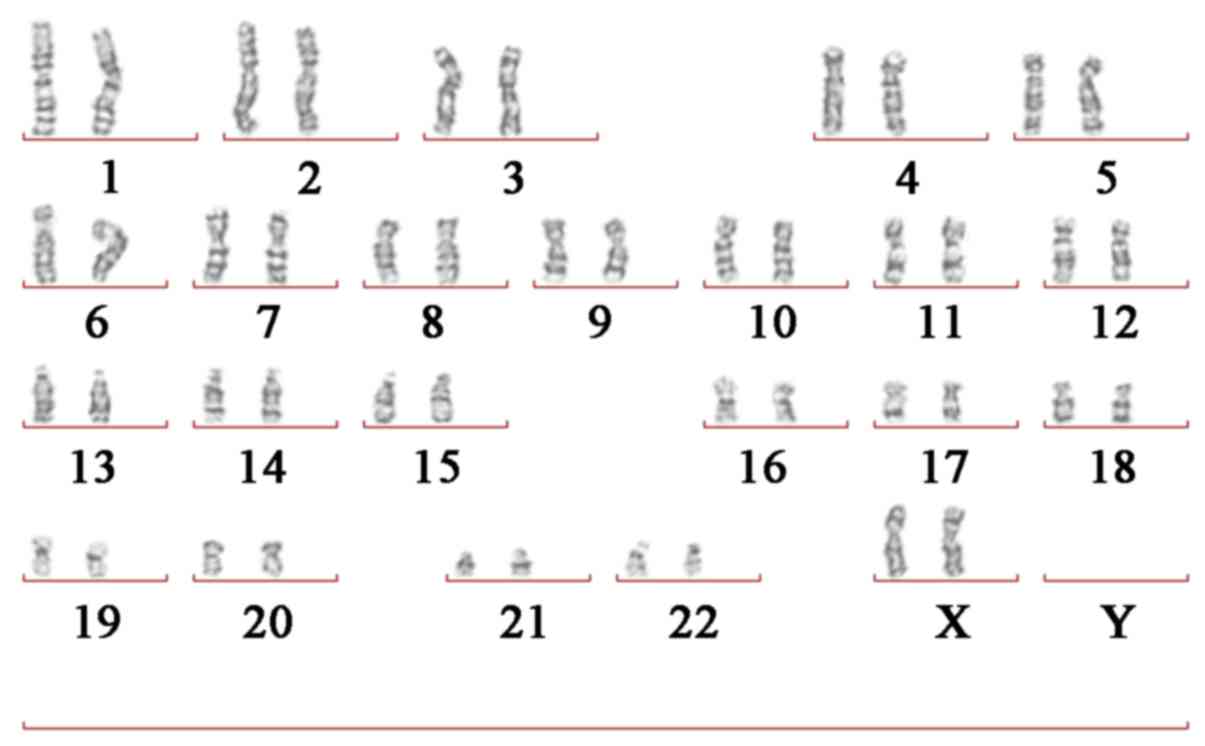
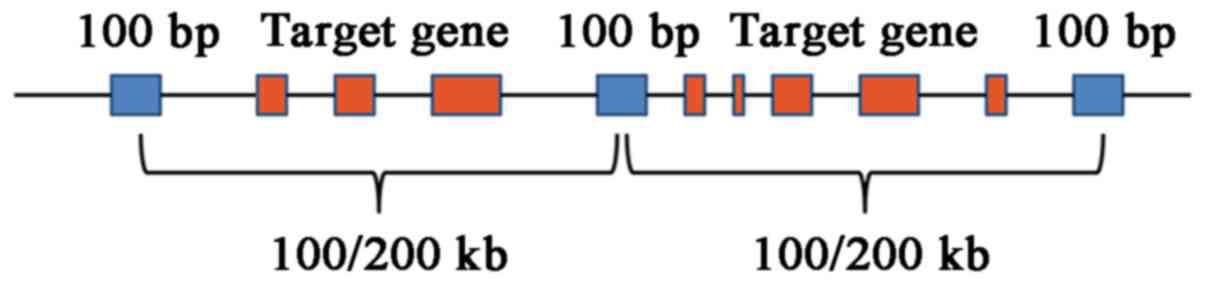
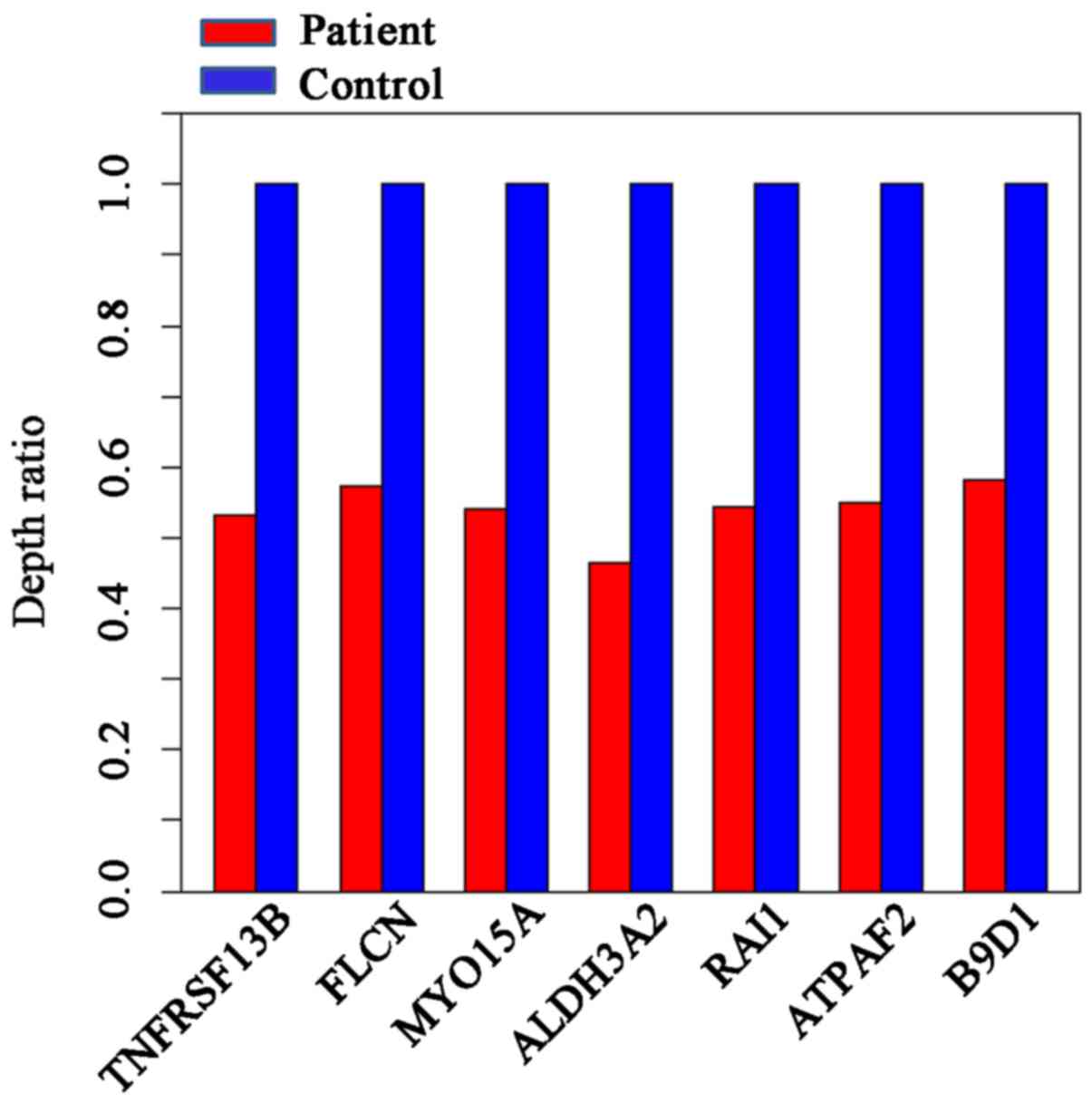
|
1
|
Daily DK, Ardinger HH and Holmes GE:
Identification and evaluation of mental retardation. Am Fam
Physician. 61(1059): 1067–1070. 2000.
|
|
2
|
Kaur A, Mahajan S and Singh JR:
Cytogenetic Profile of Individuals with Mental Retardation. Int J
Hum Genet. 3:13–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chelly J, Khelfaoui M, Francis F, Chérif B
and Bienvenu T: Genetics and pathophysiology of mental retardation.
Eur J Hum Genet. 14:701–713. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Curry CJ, Stevenson RE, Aughton D, Byrne
J, Carey JC, Cassidy S, Cunniff C, Graham JM Jr, Jones MC, Kaback
MM, et al: Evaluation of mental retardation: Recommendations of a
Consensus Conference: American College of Medical Genetics. Am J
Med Genet. 72:468–477. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Vries BB, Pfundt R, Leisink M, Koolen
DA, Vissers LE, Janssen IM, Reijmersdal Sv, Nillesen WM, Huys EH,
Leeuw Nd, et al: Diagnostic genome profiling in mental retardation.
Am J Hum Genet. 77:606–616. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pinto IP, Minasi LB, da Cruz AS, de Melo
AV, da Cruz E, Cunha DM, Pereira RR, Ribeiro CL, da Silva CC, de
Melo E Silva D and da Cruz AD: A non-syndromic intellectual
disability associated with a de novo microdeletion at 7q and 18p,
microduplication at Xp, and 18q partial trisomy detected using
chromosomal microarray analysis approach. Mol Cytogenet. 7:442014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tucker T, Zahir FR, Griffith M, Delaney A,
Chai D, Tsang E, Lemyre E, Dobrzeniecka S, Marra M, Eydoux P, et
al: Single exon-resolution targeted chromosomal microarray analysis
of known and candidate intellectual disability genes. Eur J Hum
Genet. 22:792–800. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Martinez F, Caro-Llopis A, Roselló M,
Oltra S, Mayo S, Monfort S and Orellana C: High diagnostic yield of
syndromic intellectual disability by targeted next-generation
sequencing. J Med Genet. 54:87–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morgan A, Gandin I, Belcaro C, Palumbo P,
Palumbo O, Biamino E, Dal Col V, Laurini E, Pricl S, Bosco P, et
al: Target sequencing approach intended to discover new mutations
in non-syndromic intellectual disability. Mutat Res. 781:32–36.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ehmke N, Karge S, Buchmann J, Korinth D,
Horn D, Reis O and Häßler F: A de novo nonsense mutation in ZBTB18
plus a de novo 15q13.3 microdeletion in a 6-year-old female. Am J
Med Genet A. 173:1251–1256. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Wei X, Kong X, Guo X, Sun Y, Man J,
Du L, Zhu H, Qu Z, Tian P, et al: Targeted next-generation
sequencing for clinical diagnosis of 561 mendelian diseases. PLoS
One. 10:e01336362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith AC, McGavran L, Robinson J,
Waldstein G, Macfarlane J, Zonona J, Reiss J, Lahr M, Allen L and
Magenis E: Interstitial deletion of (17)(p11.2p11.2) in nine
patients. Am J Med Genet. 24:393–414. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Girirajan S, Elsas LJ II, Devriendt K and
Elsea SH: RAI1 variations in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients
without 17p11.2 deletions. J Med Genet. 42:820–828. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Elsea SH and Girirajan S: Smith-Magenis
syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 16:412–421. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Slager RE, Newton TL, Vlangos CN, Finucane
B and Elsea SH: Mutations in RAI1 associated with Smith-Magenis
syndrome. Nat Genet. 33:466–468. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seabright M: A rapid banding technique for
human chromosomes. Lancet. 2:971–972. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Magi A, Tattini L, Pippucci T, Torricelli
F and Benelli M: Read count approach for DNA copy number variants
detection. Bioinformatics. 28:470–478. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bragin E, Chatzimichali EA, Wright CF,
Hurles ME, Firth HV, Bevan AP and Swaminathan GJ: DECIPHER:
Database for the interpretation of phenotype-linked plausibly
pathogenic sequence and copy-number variation. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:(Database issue). D993–D1000. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Chen S, Xie W, Vogel I, Choy KW,
Chen F, Christensen R, Zhang C, Ge H, Jiang H, et al: PSCC:
Sensitive and reliable population-scale copy number variation
detection method based on low coverage sequencing. PLoS One.
9:e850962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Röthlisberger B and Kotzot D: Recurrence
risk in de novo structural chromosomal rearrangements. Am J Med
Genet A. 143A:1708–1714. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilton SD, Chandler DC, Kakulas BA and
Laing NG: Identification of a point mutation and germinal mosaicism
in a Duchenne muscular dystrophy family. Hum Mutat. 3:133–140.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Slavin TP, Lazebnik N, Clark DM,
Vengoechea J, Cohen L, Kaur M, Konczal L, Crowe CA, Corteville JE,
Nowaczyk MJ, et al: Germline mosaicism in Cornelia de Lange
syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 158A:1481–1485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bermúdez-López C, García-de Teresa B,
González-del Angel A and Alcántara-Ortigoza MA: Germinal mosaicism
in a sample of families with Duchenne/Becker muscular dystrophy
with partial deletions in the DMD gene. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.
18:93–97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyagawa M, Nishio SY, Hattori M, Takumi Y
and Usami S: Germinal mosaicism in a family with BO syndrome. Ann
Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 124 Suppl 1:118S–122S. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sánchez J, Fernández R, Madruga M,
Bernabeu-Wittel J, Antiñolo G and Borrego S: Somatic and germ-line
mosaicism of deletion 15q11.2-q13 in a mother of dyzigotic twins
with Angelman syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 164A:370–376. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|