|
1
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kloosterman WP and Plasterk RH: The
diverse functions of microRNAs in animal development and disease.
Dev Cell. 11:441–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ha TY: MicroRNAs in human diseases: From
cancer to cardiovascular disease. Immune Netw. 11:135–154. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lorenzen J, Kumarswamy R, Dangwal S and
Thum T: MicroRNAs in diabetes and diabetes-associated
complications. RNA Biol. 9:820–827. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Etheridge A, Lee I, Hood L, Galas D and
Wang K: Extracellular microRNA: A new source of biomarkers. Mutat
Res. 717:85–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roth P, Wischhusen J, Happold C, Chandran
PA, Hofer S, Eisele G, Weller M and Keller A: A specific miRNA
signature in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. J
Neurochem. 118:449–457. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al Naieb ZT and Bakhiet M:
Increased oncogenic microRNA-18a expression in peripheral blood of
patients with prostate cancer: A potential role as new non-invasive
biomarker. Oncol Lett. 11:1201–1206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al-Mahroos G, Alsayed NA,
Hasan ZA, Nawaz S and Bakhiet M: Peripheral blood microRNA-15a is a
potential biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes.
Mol Med Rep. 12:7485–7490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zampetaki A, Kiechl S, Drozdov I, Willeit
P, Mayr U, Prokopi M, Mayr A, Weger S, Oberhollenzer F, Bonora E,
et al: Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial
miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ Res.
107:810–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meder B, Keller A, Vogel B, Haas J,
Sedaghat-Hamedani F, Kayyanpour E, Just S, Borries A, Rudloff J,
Leidinger P, et al: MicroRNA signatures in total peripheral blood
as novel biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Basic Res
Cardiol. 106:13–23. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al-Mahroos G, Al-Muhtaresh
HA, Sabry MA, Razzak Abdul R and Salem AH: Circulating
endothelium-enriched microRNA-126 as a potential biomarker for
coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Biomarkers. 22:268–278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shahbazian H and Rezaii I: Diabetic kidney
disease; review of the current knowledge. J Renal Inj Prev.
2:73–80. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dronavalli S, Duka I and Bakris GL: The
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol
Metab. 4:444–452. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu C, Sun L, Xiao L, Han Y, Fu X, Xiong X,
Xu X, Liu Y, Yang S, Liu F and Kanwar YS: Insight into the
mechanisms involved in the expression and regulation of
extracellular matrix proteins in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Med
Chem. 22:2858–2870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Arora MK and Singh UK: Molecular
mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: An update.
Vascul Pharmacol. 58:259–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang AS, Hathaway CK, Smithies O and
Kakoki M: Transforming growth factor-β1 and diabetic nephropathy.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 310:F689–F696. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rossing K, Christensen PK, Hovind P,
Tarnowl L, Rossing P and Parving HH: Progression of nephropathy in
type 2 diabetic patients. Kidney Int. 66:1596–1605. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
MacIsaac RJ, Tsalamandris C,
Panagiotopoulos S, Smith TJ, McNeil KJ and Jerums G:
Normoalbuminuric renal insufficiency in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes
Care. 27:195–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsalamandris C, Allen TJ, Gilbert RE,
Sinha A, Panagiotopoulos S, Cooper ME and Jerums G: Progressive
decline in renal function in diabetic patients with and without
albuminuria. Diabetes. 43:649–655. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Caramori ML, Kim Y, Huang C, Fish AJ, Rich
SS, Miller ME, Russell G and Mauer M: Cellular basis of diabetic
nephropathy: 1. Study design and renal structural-functional
relationships in patients with long-standing type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes. 51:506–513. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Najafian B, Crosson JT, Kim Y and Mauer M:
Glomerulotubular junction abnormalities are associated with
proteinuria in type 1 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17 Suppl
2:S53–S60. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Levey AS, Becker C and Inker LA:
Glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria for detection and
staging of acute and chronic kidney disease in adults: A systematic
review. JAMA. 313:837–846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Glassock RJ: Is the presence of
microalbuminuria a relevant marker of kidney disease? Curr
Hypertens Rep. 12:364–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Stehouwer CDA and Smulders YM:
Microalbuminuria and risk for cardiovascular disease: Analysis of
potential mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:2106–2111. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Silva AM, Schaan BD, Signori LU, Plentz
RD, Moreno H Jr, Bertoluci MC and Irigoyen MC: Microalbuminuria is
associated with impaired arterial and venous endothelium dependent
vasodilation in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest.
33:696–700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suarez Gonzalez ML, Thomas DB, Barisoni L
and Fornoni A: Diabetic nephropathy: Is it time yet for routine
kidney biopsy? World J Diabetes. 4:245–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alter ML, Kretschmer A, Von Websky K,
Tsuprykov O, Reichetzeder C, Simon A, Stasch JP and Hocher B: Early
urinary and plasma biomarkers for experimental diabetic
nephropathy. Clin Lab. 58:659–671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kato M and Natarajan R: MicroRNAs in
diabetic nephropathy: Functions, biomarkers, and therapeutic
targets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1353:72–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
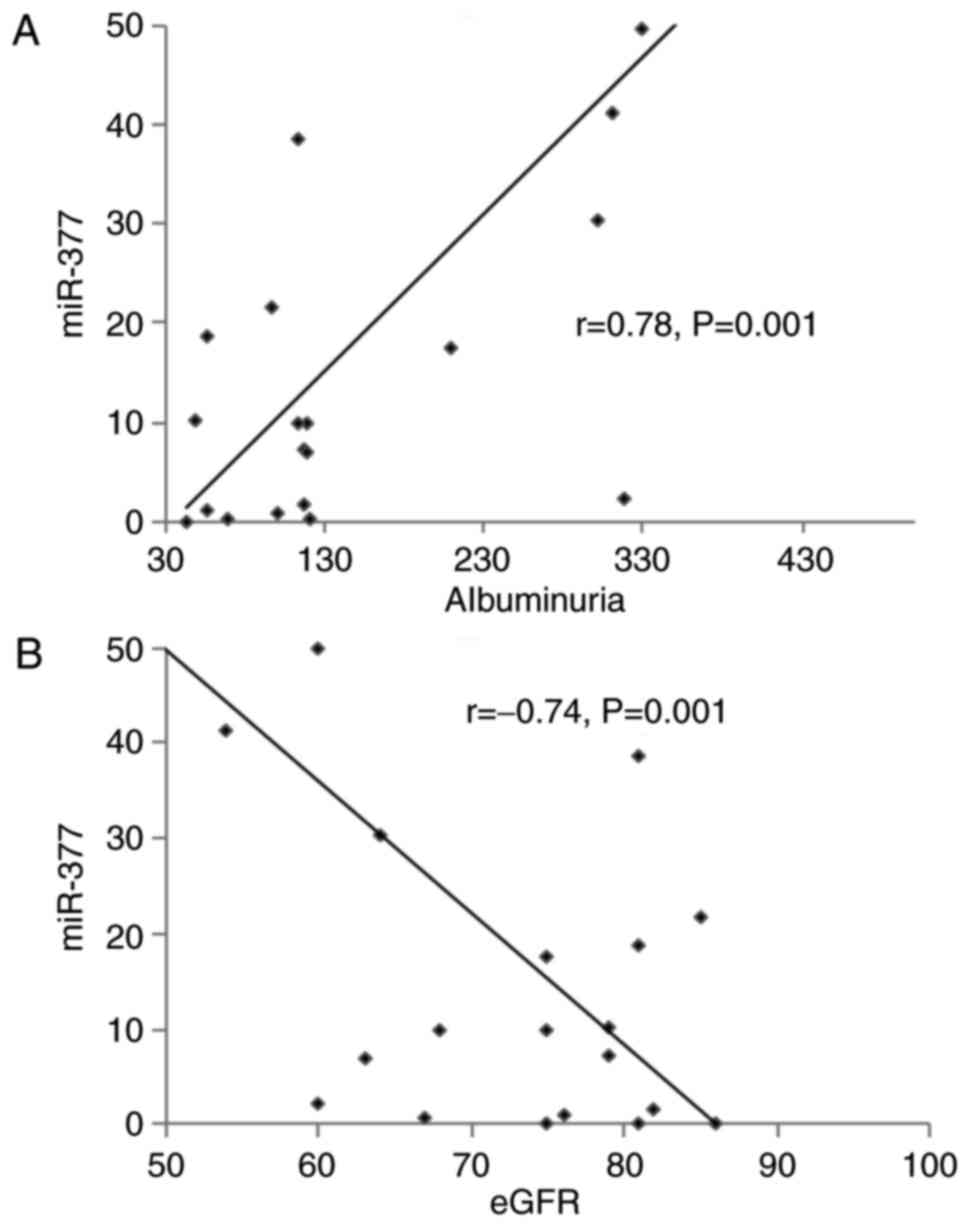
Wang Q, Wang Y, Minto AW, Wang J, Shi Q,
Li X and Quigg RJ: MicroRNA-377 is up-regulated and can lead to
increased fibronectin production in diabetic nephropathy. FASEB J.
22:4126–4135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
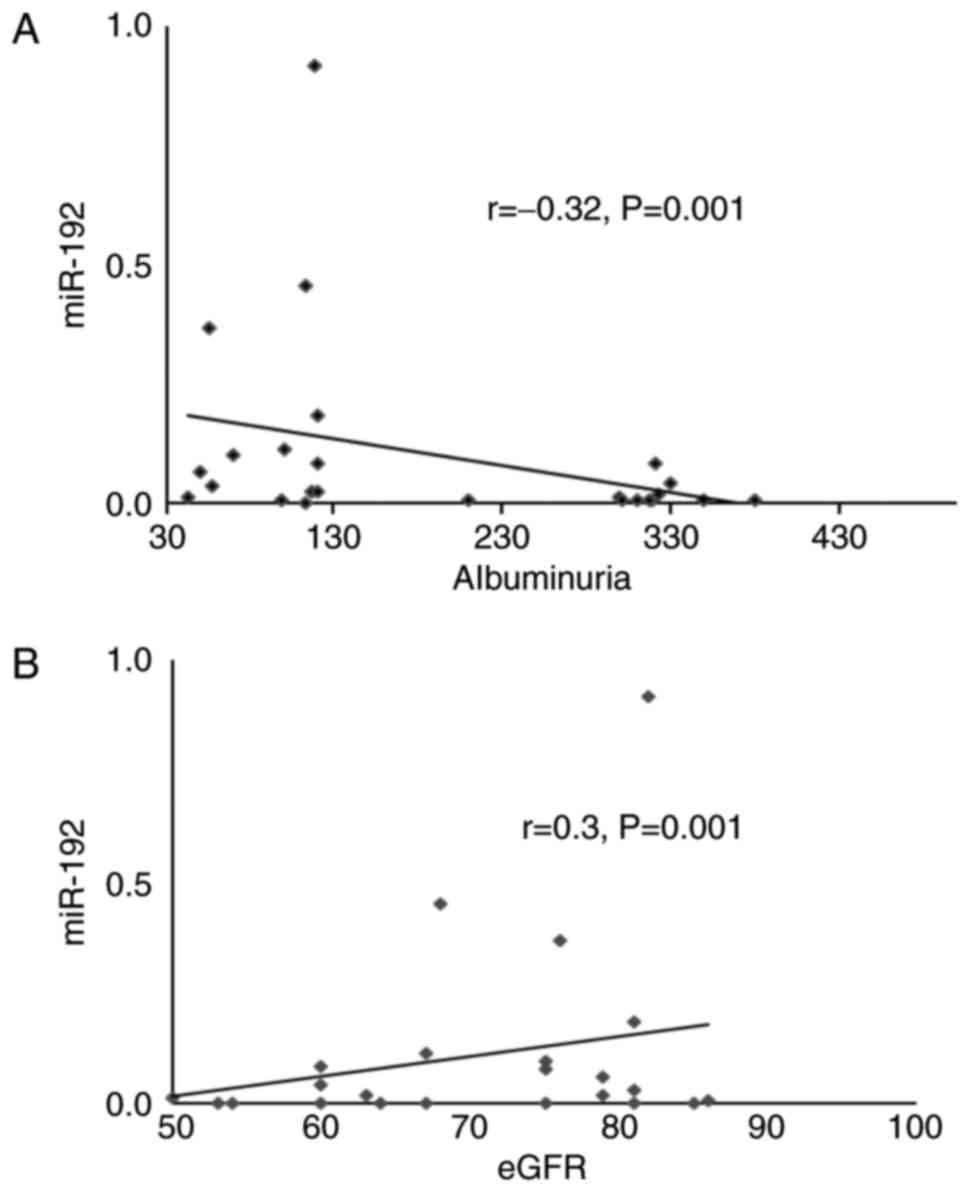
Kato M, Zhang J, Wang M, Lanting L, Yuan
H, Rossi J and Natarajan R: MicroRNA-192 in diabetic kidney
glomeruli and its function in TGF-induced collagen expression via
inhibition of E-box repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:93432–3437. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang Y, Xiao L, Li J, Kanwar YS, Liu F and
Sun L: Urine miRNAs: Potential biomarkers for monitoring
progression of early stages of diabetic nephropathy. Med
Hypotheses. 81:274–278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Simpson K, Wonnacott A, Fraser DJ and
Bowen T: MicroRNAs in diabetic nephropathy: From biomarkers to
therapy. Curr Diab Rep. 16:352016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Al-Kafaji G, Al-Mahroos G, Al-Muhtaresh
HA, Skrypnyk C, Sabry MA and Ramadan AR: Decreased expression of
circulating microRNA-126 in patients with type 2 diabetic
nephropathy: A potential blood-based biomarker. Exp Ther Med.
12:815–822. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alberti KG and Zimmet PZ: Definition,
diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes
mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med.
15:539–553. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Stoves J, Lindley EJ, Barnfield MC,
Burniston MT and Newstead CG: MDRD equation estimates of glomerular
filtration rate in potential living kidney donors and renal
transplant recipients with impaired graft function. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 17:2036–2037. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lutale JJ, Thordarson H, Abbas ZG and
Vetvik K: Microalbuminuria among type 1 and type 2 diabetic
patients of African origin in Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania. BMC Nephrol.
8:22007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Perkins BA, Ficociello LH, Silva KH,
Finkelstein DM, Warram JH and Krolewski AS: Regression of
microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 348:2285–2293.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rossing P, Hougaard P and Parving HH:
Progression of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes: Ten-year
prospective observational study. Kidney Int. 68:1446–1450. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weber JA, Baxter DH, Zhang S, Huang DY,
Huang KH, Lee MJ, Galas DJ and Wang K: The microRNA spectrum in 12
body fluids. Clin Chem. 56:1733–1741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Keller A, Leidinger P, Bauer A, Elsharawy
A, Haas J, Backes C, Wendschlag A, Giese N, Tjaden C, Werner J, et
al: Toward the blood-borne miRNome of human diseases. Nat Methods.
8:841–843. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ma X, Lu C, Lv C, Wu C and Wang Q: The
expression of miR-192 and its significance in diabetic nephropathy
patients with different urine albumin creatinine ratio. J Diabetes
Res. 2016:67894022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chien HY, Chen CY, Chiu YH, Lin YC and Li
WC: Differential microRNA profiles predict diabetic nephropathy
progression in Taiwan. Int J Med Sci. 13:457–465. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tian Z, Greene AS, Pietrusz JL, Matus IR
and Liang M: MicroRNA-target pairs in the rat kidney identified by
microRNA microarray, proteomic, and bioinformatic analysis. Genome
Res. 18:404–411. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun Y, Koo S, White N, Peralta E, Esau C,
Dean NM and Perera RJ: Development of a micro-array to detect human
and mouse microRNAs and characterization of expression in human
organs. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:e1882004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Krupa A, Jenkins R, Luo DD, Lewis A,
Phillips A and Fraser D: Loss of microRNA-192 promotes fibrogenesis
in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:438–447. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Burns
W, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Watson A, Saleem M, Goodall GJ, Twigg SM,
Cooper ME and Kantharidis P: E-cadherin expression is regulated by
miR-192/215 by a mechanism that is independent of the profibrotic
effects of transforming growth factor-β. Diabetes. 59:1794–1802.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Putta S, Lanting L, Sun G, Lawson G, Kato
M and Natarajan R: Inhibiting MicroRNA-192 ameliorates renal
fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 23:458–469.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP,
Canani LH, Caramori ML and Zelmanovitz T: Diabetic nephropathy:
Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 28:164–176.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Al-Rubeaan K, Youssef AM, Subhani SN,
Ahmad NA, Al-Sharqawi AH, Al-Mutlaq HM, David SK and AlNaqeb D:
Diabetic nephropathy and its risk factors in a society with a type
2 diabetes epidemic: A Saudi National Diabetes Registry-based
study. PLoS One. 9:e889562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jia Y, Guan M, Zheng Z, Zhang Q, Tang C,
Xu W, Xiao Z, Wang L and Xue Y: miRNAs in urine extracellular
vesicles as predictors of early-stage diabetic nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:79327652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|