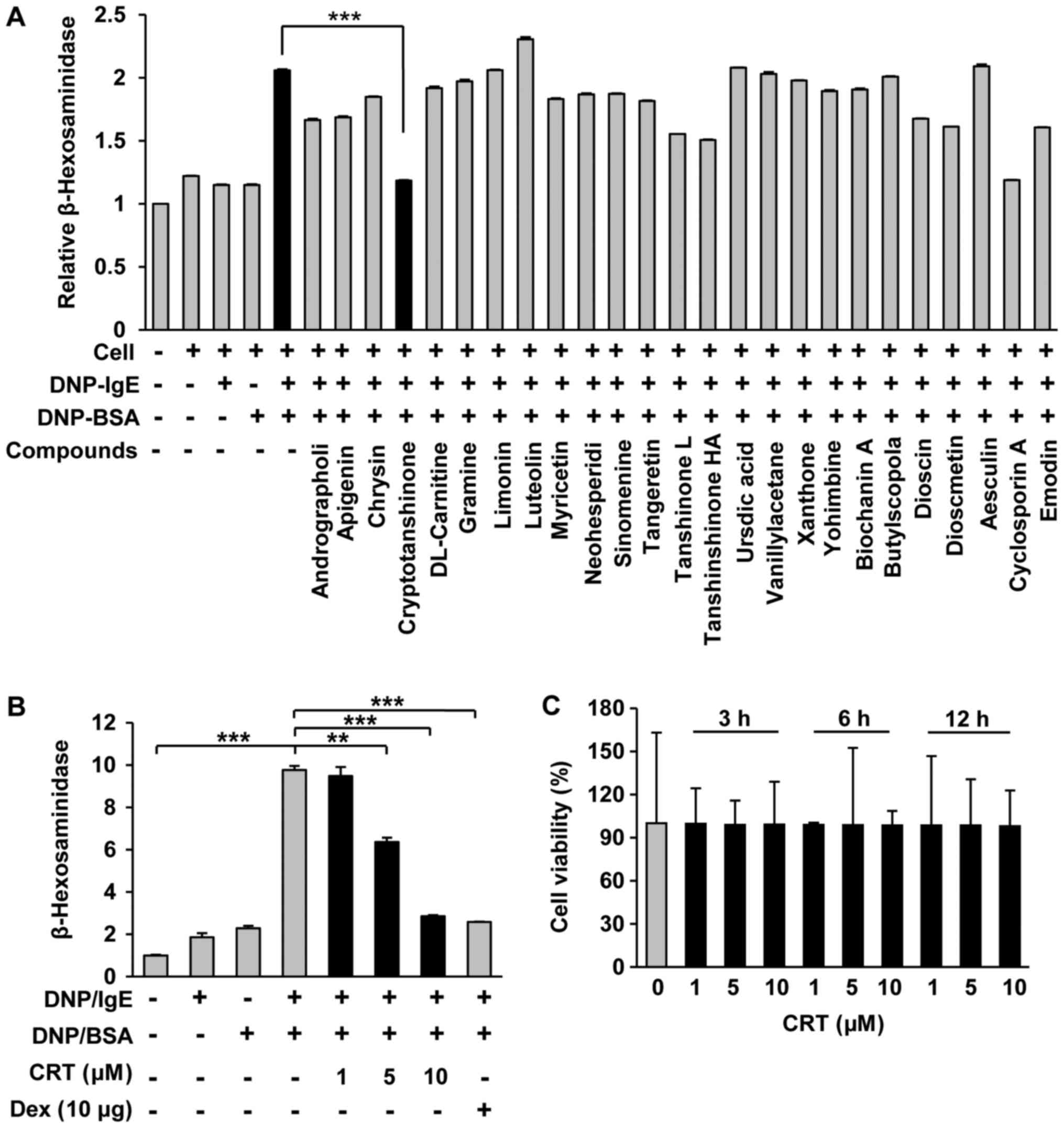
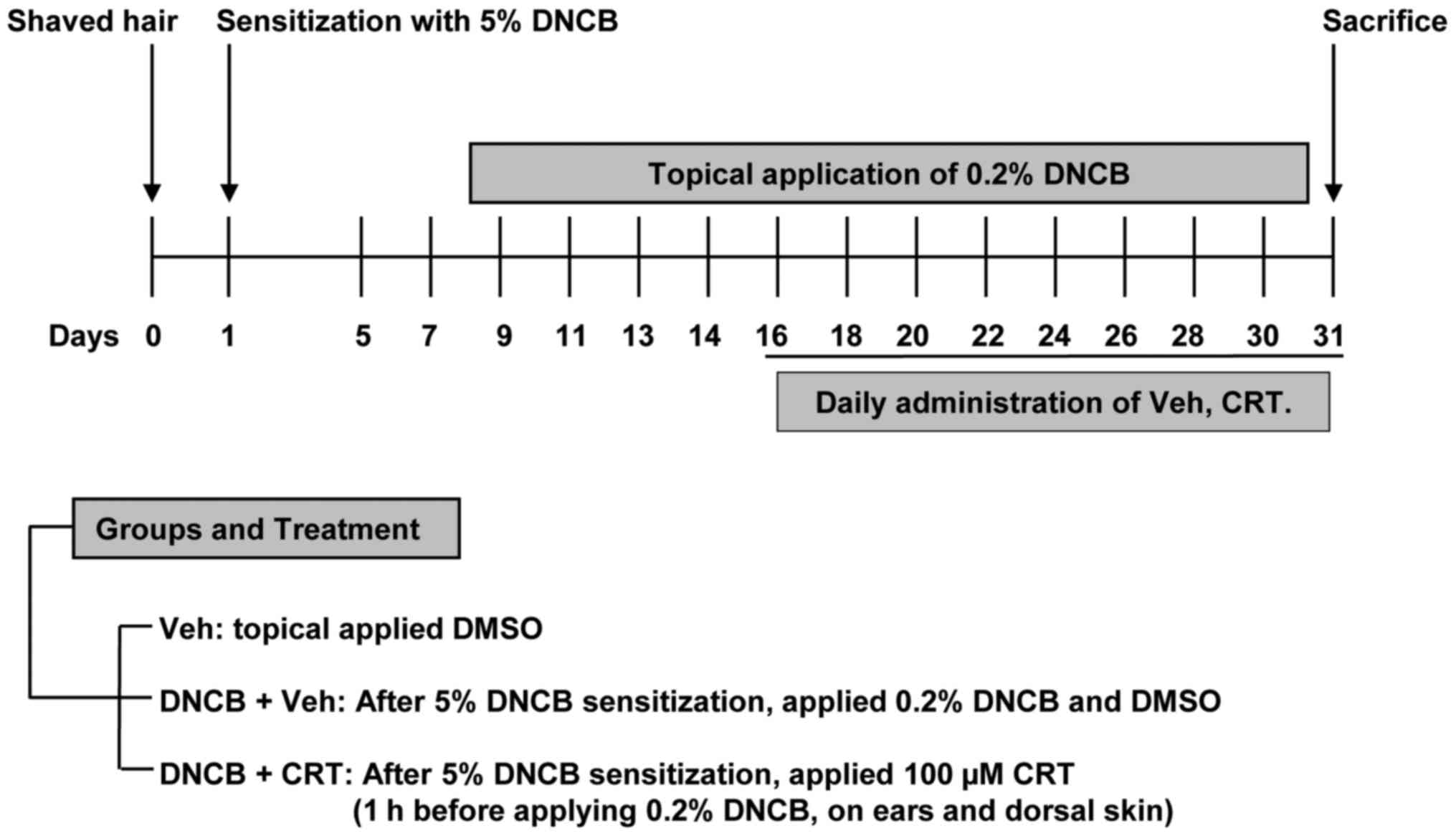
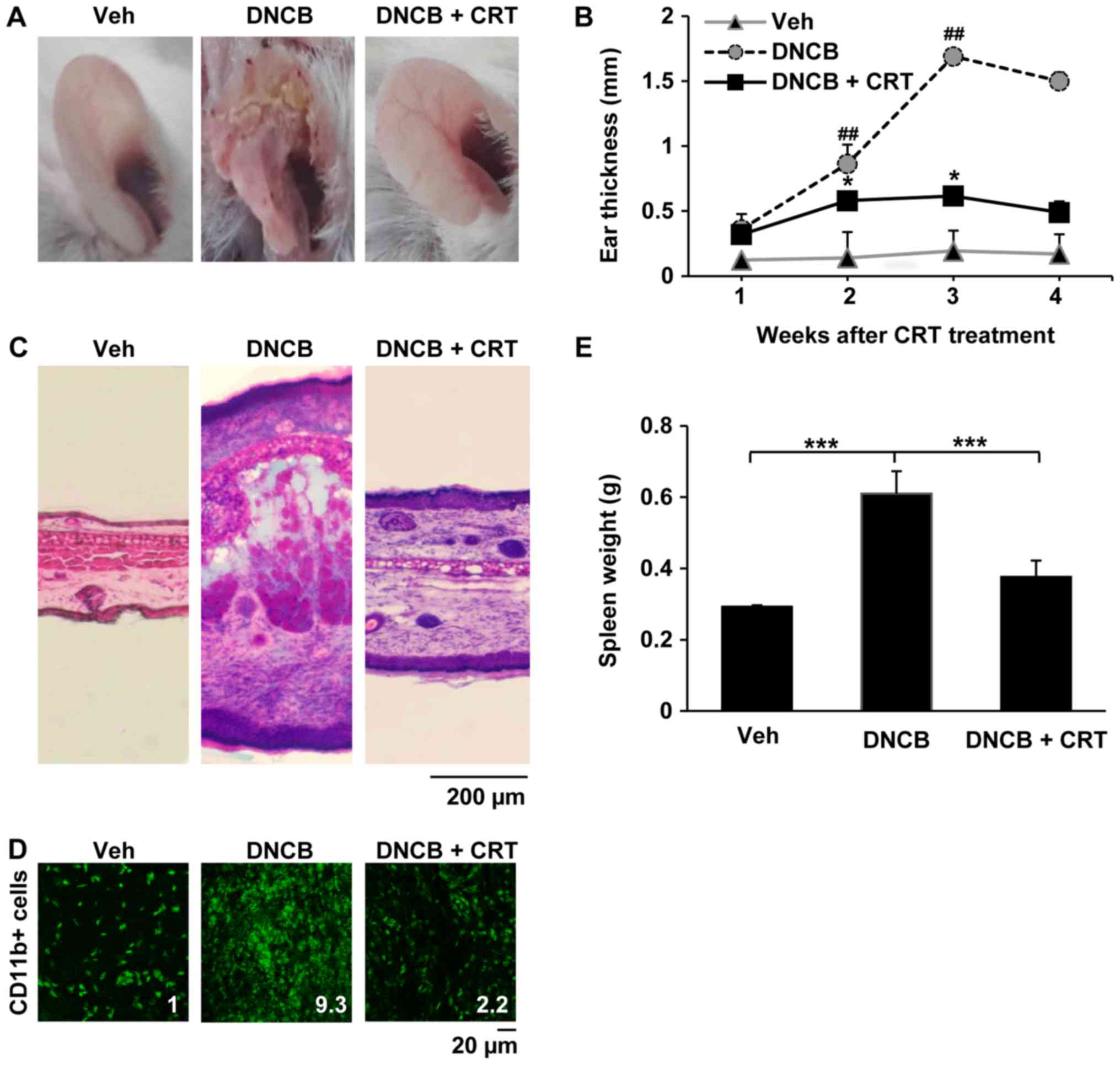
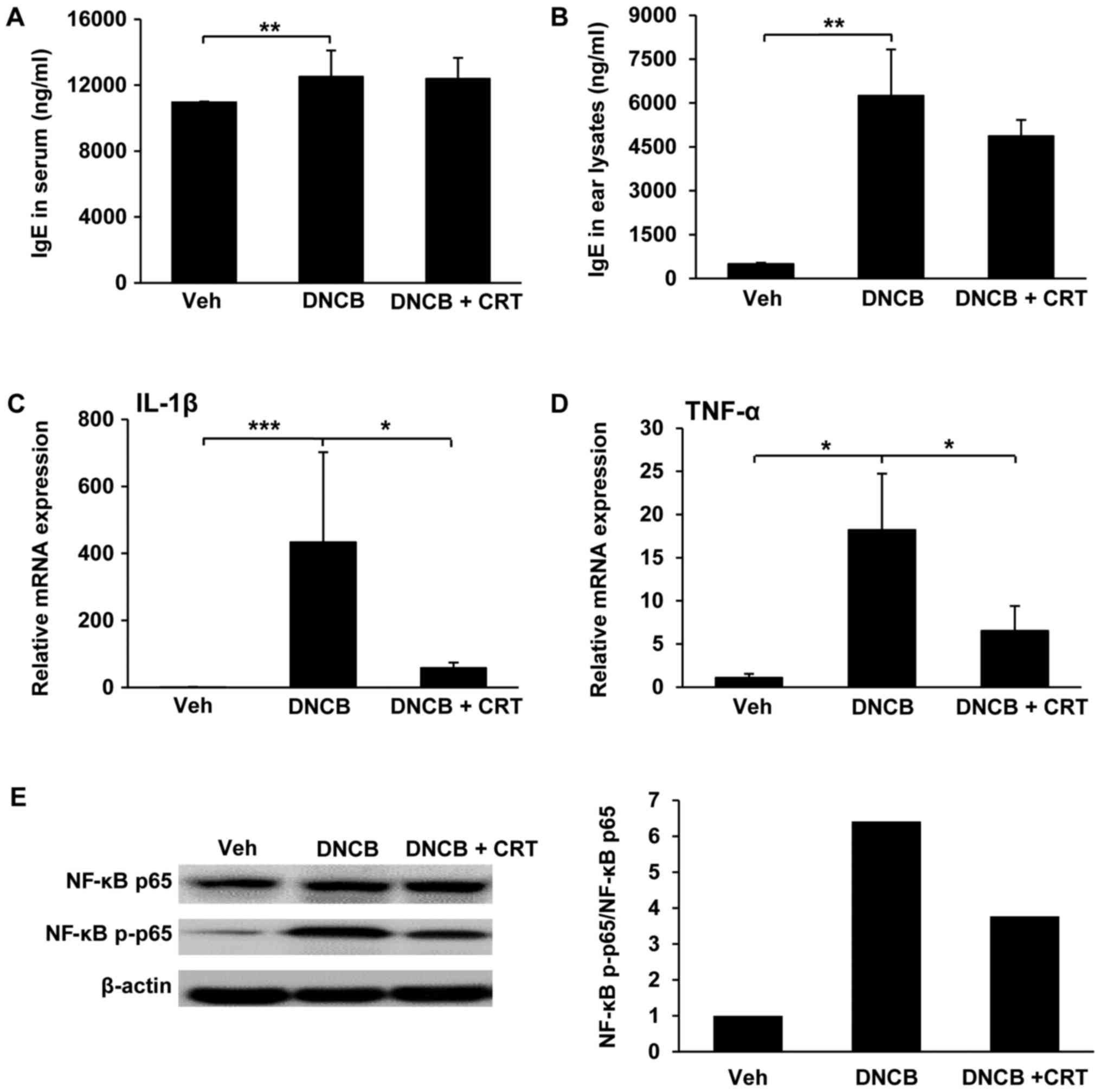
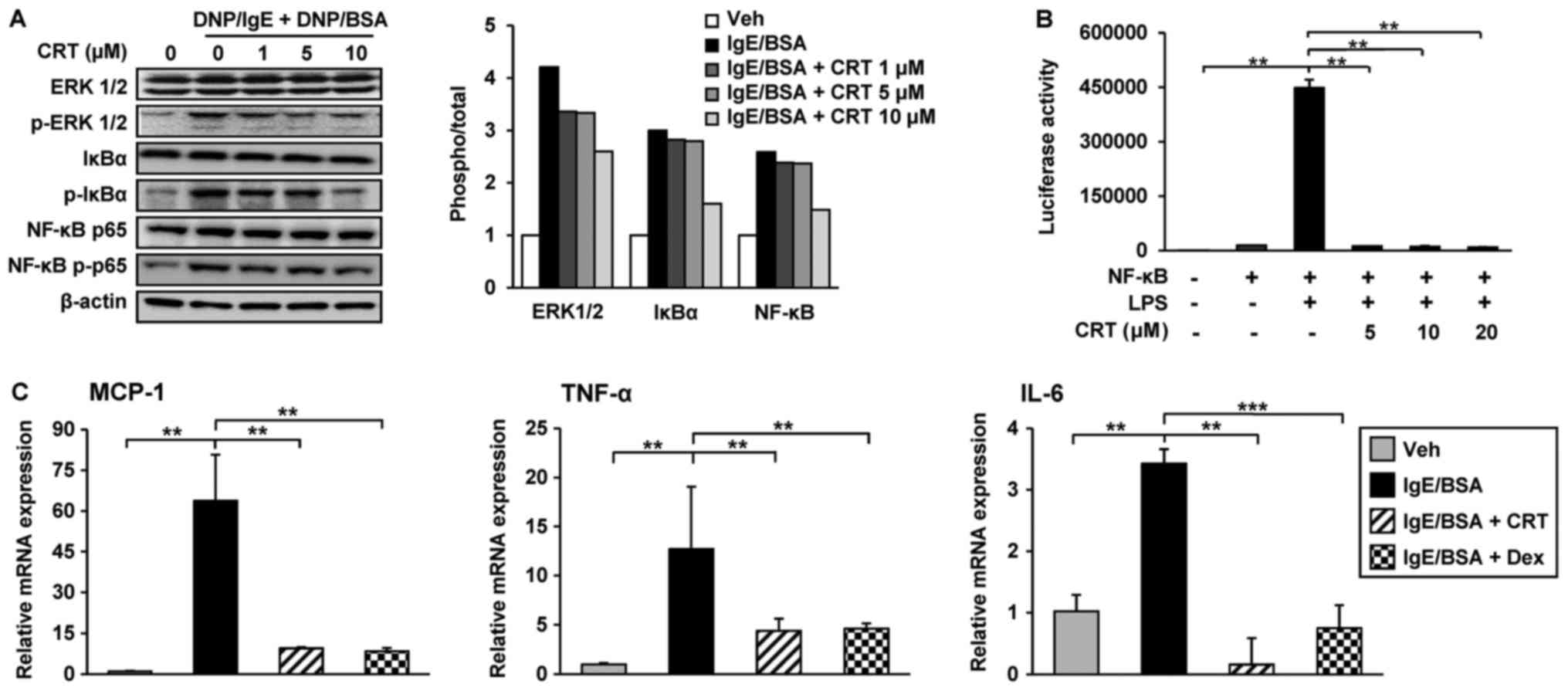
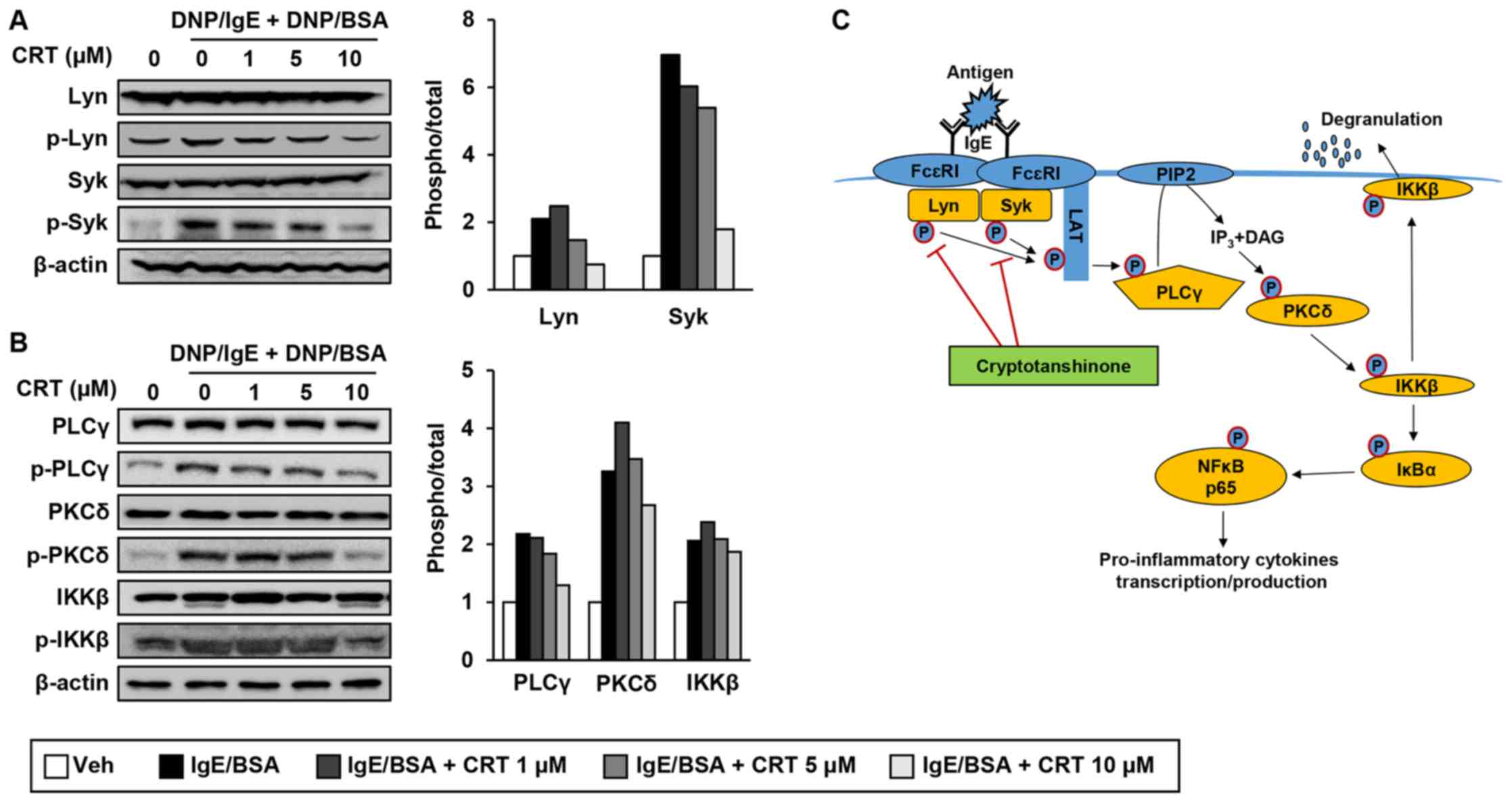
|
1
|
Park S, Lee JB and Kang S: Topical
application of Chrysanthemum indicum L. attenuates the development
of atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by suppressing serum IgE
levels, IFN-γ, and IL-4 in Nc/Nga mice. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:8219672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim SR, Choi HS, Seo HS, Ku JM, Hong SH,
Yoo HH, Shin YC and Ko SG: Oral administration of herbal mixture
extract inhibits 2,4-dinitrochlobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis
in BALB/c mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3194382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martel BC, Lovato P, Bäumer W and Olivry
T: Translational animal models of atopic dermatitis for preclinical
studies. Yale J Biol Med. 90:389–402. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee KS, Jeong ES, Heo SH, Seo JH, Jeong DG
and Choi YK: A novel model for human atopic dermatitis: Application
of repeated DNCB patch in BALB/c mice, in comparison with NC/Nga
mice. Lab Anim Res. 26:95–102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim SR, Choi HS, Seo HS, Choi YK, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Topical application of herbal mixture extract inhibits
ovalbumin- or 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5454972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shim J, Kennedy RH, Weatherly LM,
Hutchinson LM, Pelletier JH, Hashmi HN, Blais K, Velez A and Gosse
JA: Arsenic inhibits mast cell degranulation via suppression of
early tyrosine phosphorylation events. J Appl Toxicol.
36:1446–1459. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki K and Verma IM: Phosphorylation of
SNAP-23 by IkappaB kinase 2 regulates mast cell degranulation.
Cell. 134:485–495. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hepp R, Puri N, Hohenstein AC, Crawford
GL, Whiteheart SW and Roche PA: Phosphorylation of SNAP-23
regulates exocytosis from mast cells. J Biol Chem. 280:6610–6620.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park JH, Lee B, Kim HK, Kim EY, Kim JH,
Min JH, Kim S, Sohn Y and Jung HS: Peimine inhibits the production
of proinflammatory cytokines through regulation of the
phosphorylation of NF-κB and MAPKs in HMC-1 cells. Pharmacogn Mag.
13 Suppl 2:S359–S364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lian Q, Cheng Y, Zhong C and Wang F:
Inhibition of the IgE-mediated activation of RBL-2H3 cells by TIPP,
a novel thymic immunosuppressive pentapeptide. Int J Mol Sci.
16:2252–2268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi HS and Kim KM: Tanshinones inhibit
mast cell degranulation by interfering with IgE receptor-mediated
tyrosine phosphorylation of PLCgamma2 and MAPK. Planta Med.
70:178–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang BQ: Salvia miltiorrhiza: Chemical and
pharmacological review of medicinal plant. J Med Plants Res.
4:pp2813–2820. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Gao H, Sun W, Zhao J, Wu X, Lu JJ, Chen X,
Xu QM, Khan IA and Yang S: Tanshinones and diethyl blechnics with
anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activities from Salvia
miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen). Sci Rep. 6:337202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu B, Du Y, Cong L, Jia X and Yang G:
Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) compounds improve the biochemical
indices of the patients with coronary heart disease. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2016:97817152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen W and Chen G: Danshen (Salvia
miltiorrhiza Bunge): A prospective healing sage for cardiovascular
diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 23:5125–5135. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shin DS, Kim HN, Shin KD, Yoon YJ, Kim SJ,
Han DC and Kwon BM: Cryptotanshinone inhibits constitutive signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 function through
blocking the dimerization in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 69:193–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Passante E and Frankish N: The RBL-2H3
cell line: Its provenance and suitability as a model for the mast
cell. Inflamm Res. 58:737–745. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Metzger H, Alcaraz G, Hohman R, Kinet JP,
Pribluda V and Quarto R: The receptor with high affinity for
immunoglobulin E. Annu Rev Immunol. 4:419–470. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seldin DC, Adelman S, Austen KF, Stevens
RL, Hein A, Caulfield JP and Woodbury RG: Homology of the rat
basophilic leukemia cell and the rat mucosal mast cell. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 82:3871–3875. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bantz SK, Zhu Z and Zheng T: The atopic
march: Progression from atopic dermatitis to allergic rhinitis and
asthma. J Clin Cell Immunol. 5:pii: 202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Akdis CA, Akdis M, Bieber T,
Bindslev-Jensen C, Boguniewicz M, Eigenmann P, Hamid Q, Kapp A,
Leung DY, Lipozencic J, et al: Diagnosis and treatment of atopic
dermatitis in children and adults: European Academy of Allergology
and Clinical immunology/American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and
Immunology/PRACTALL Consensus Report. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
118:152–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ku JM, Hong SH, Kim HI, SEo HS, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Effects of Angelicae dahuricae Radix on 2,
4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions
in mice model. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17:982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Junghans V, Gutgesell C, Jung T and
Neumann C: Epidermal cytokines IL-1beta, TNF-alpha, and IL-12 in
patients with atopic dermatitis: Response to application of house
dust mite antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 111:1184–1188. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin G, Gao S, Cheng J, Li Y, Shan L and Hu
Z: 1β-hydroxyalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone from Inula
japonica, attenuates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by
2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in the mouse. Pharm Biol. 54:516–522.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pokharel YR, Lim SC, Kim SC, Heo TH, Choi
HK and Kang HK: Sopungyangjae-tang inhibits development of
dermatitis in Nc/Nga mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
5:173–180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gao D, Mendoza A, Lu S and Lawrence DA:
Immunomodulatory effects of Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) in BALB/c
mice. ISRN Inflamm. 2012:9540322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stone KD, Prussin C and Metcalfe DD: IgE,
mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125
2 Suppl 2:S73–S80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kawakami Y, Kitaura J, Satterthwaite AB,
Kato RM, Asai K, Hartman SE, Maeda-Yamamoto M, Lowell CA, Rawlings
DJ, Witte ON and Kawakami T: Redundant and opposing functions of
two tyrosine kinases, Btk and Lyn, in mast cell activation. J
Immunol. 165:1210–1219. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee M, Lee NY, Chung KS, Cheon SY, Lee KT
and An HJ: Roxatidine attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic
inflammation via inhibition of NF-κB and p38 MAPK activation. Sci
Rep. 7:417212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen W, Lui L, Luo Y, Odaka Y, Awate S,
Zhou H, Shen T, Zheng S, Lu Y and Huang S: Cryptotanshinone
activates p38/JNK and inhibits Erk1/2 leading to
caspase-independent cell death in tumor cells. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 5:778–787. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JH, Jeong SJ, Kwon TR, Yun SM, Jung
JH, Kim M, Lee HJ, Lee MH, Ko SG, Chen CY and Kim SH:
Cryptotanshinone enhances TNF-α-induced apoptosis in chronic
myeloid leukemia KBM-5 cells. Apoptosis. 16:696–707. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Suh SJ, Jin UH, Choi HJ, Chang HW, Son JK,
Lee SH, Jeon SJ, Son KH, Chang YC, Lee YC and Kim CH:
Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE has an inhibitory
effect on TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 production
and HASMC migration via down-regulated NF-kappaB and AP-1. Biochem
Pharmacol. 72:1680–1689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|