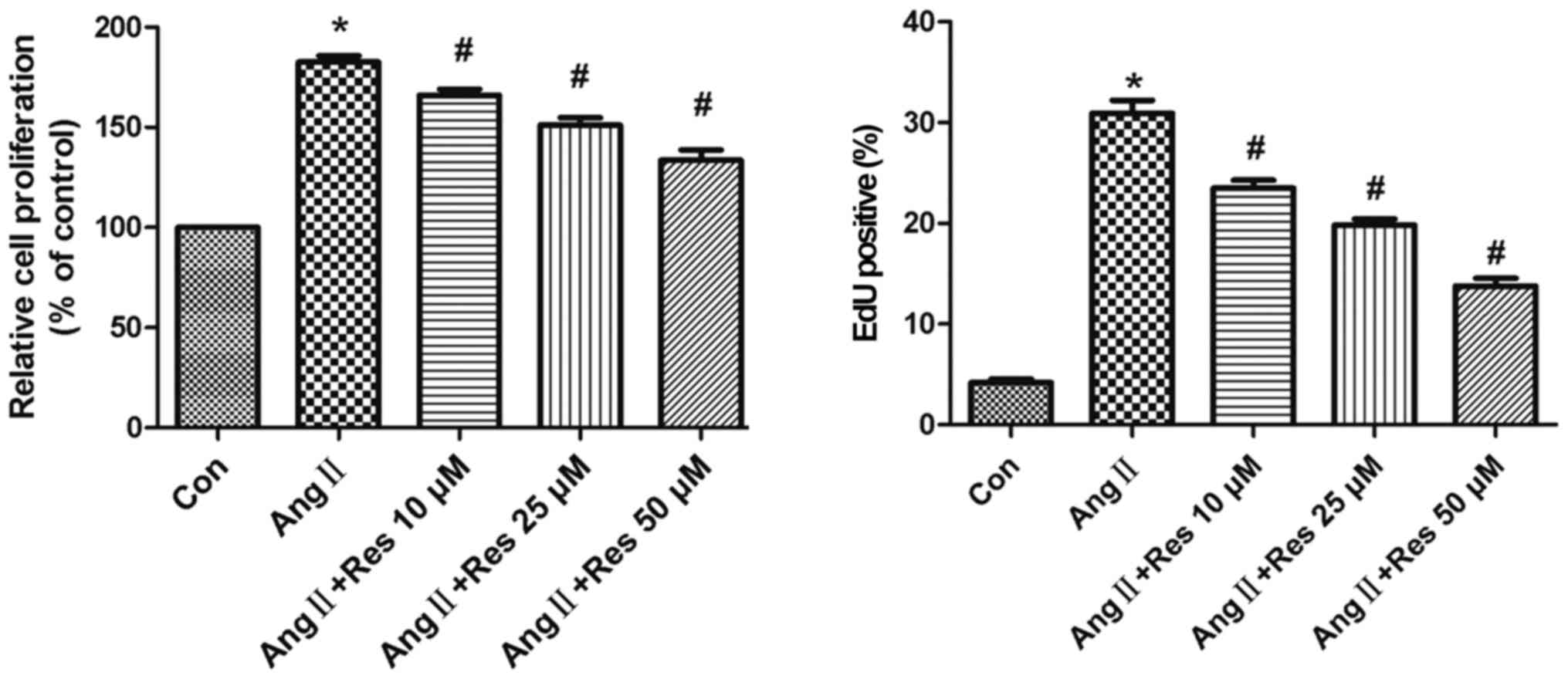
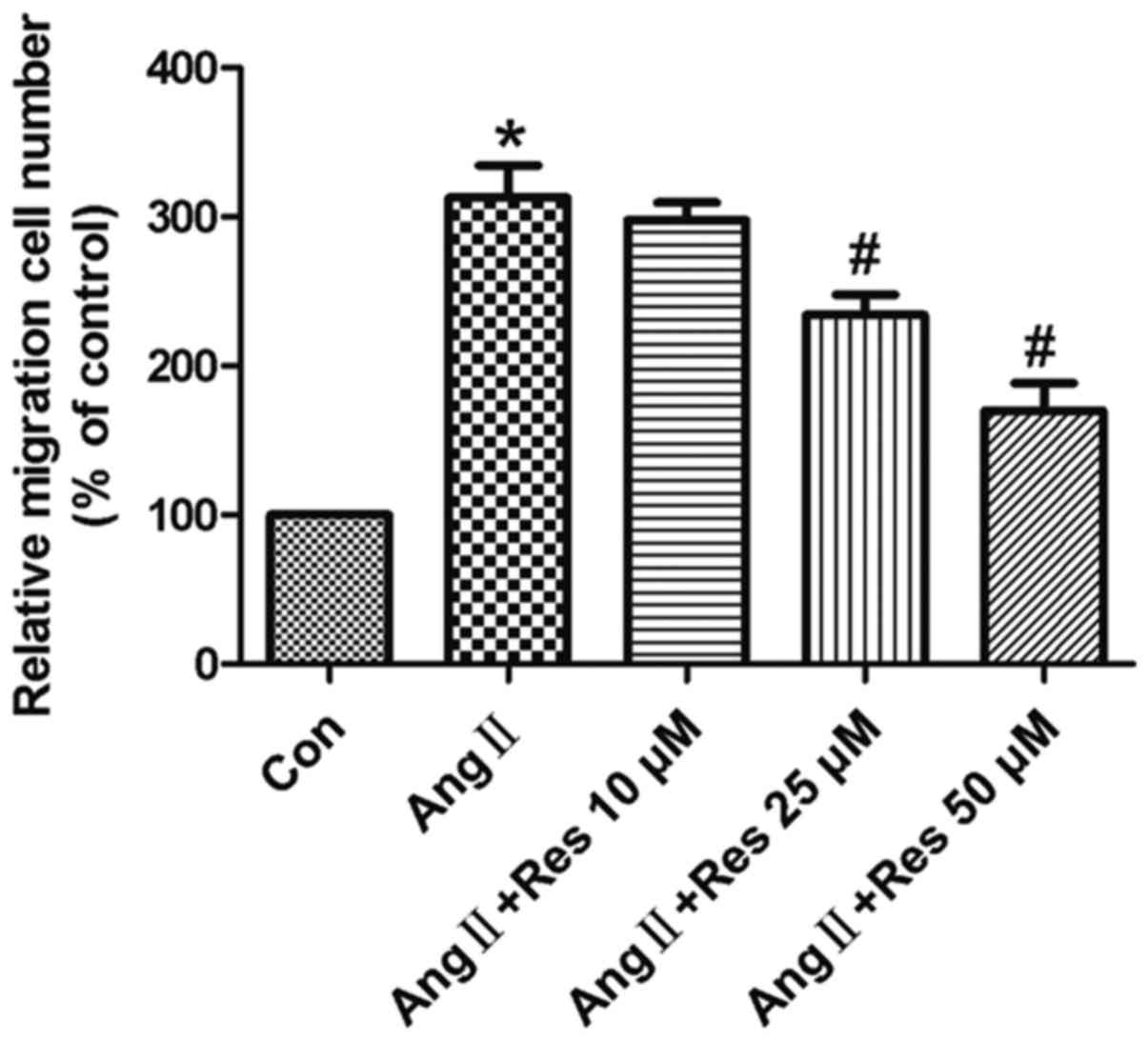
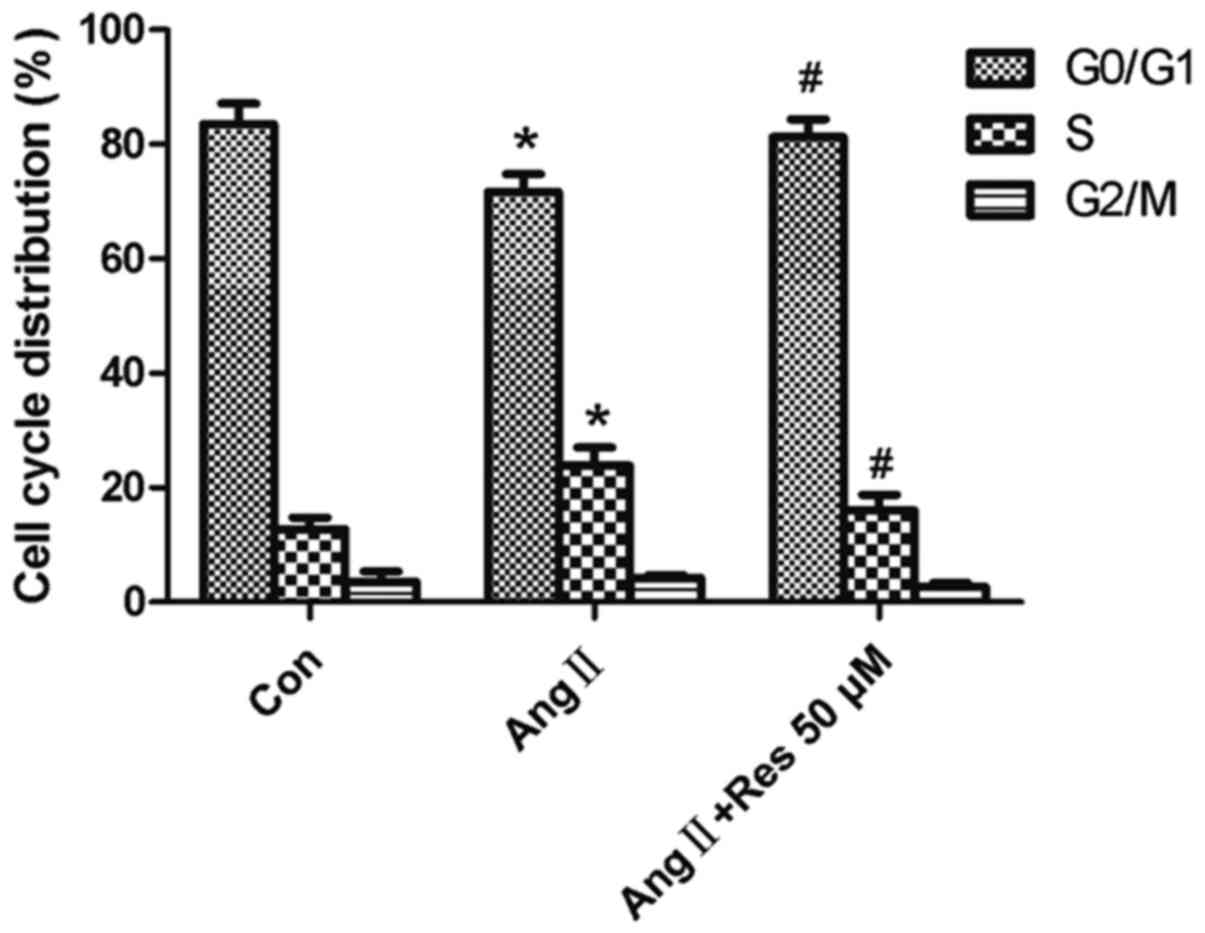
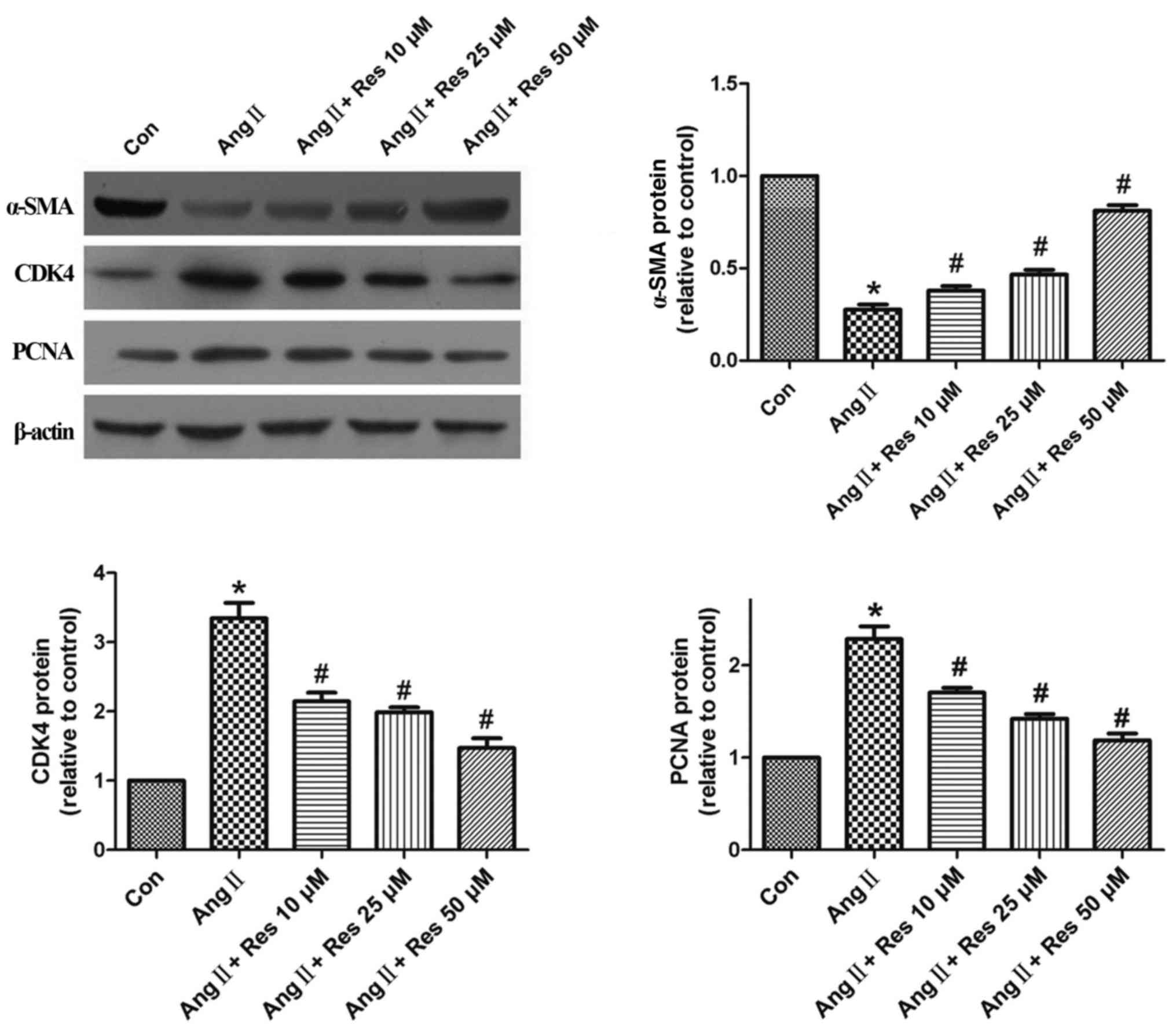
|
1
|
Sturek M and Reddy HK: New tools for
prevention of restenosis could decrease the ‘oculo-stento’ reflex.
Cardiovasc Res. 53:292–293. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Han M, Wen JK, Zheng B, Cheng Y and Zhang
C: Serum deprivation results in redifferentiation of human
umbilical vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
291:C50–C58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carrizzo A, Forte M, Damato A, Trimarco V,
Salzano F, Bartolo M, Maciag A, Puca AA and Vecchione C:
Antioxidant effects of resveratrol in cardiovascular, cerebral and
metabolic diseases. Food Chem Toxicol. 61:215–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dong HH and Ren HL: New progression in the
study of protective properties of resveratrol in anticardiovascular
disease. Bratisl Lek Listy. 105:225–229. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zordoky BN, Robertson IM and Dyck JR:
Preclinical and clinical evidence for the role of resveratrol in
the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1155–1177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ekshyyan VP, Hebert VY, Khandelwal A and
Dugas TR: Resveratrol inhibits rat aortic vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation via estrogen receptor dependent nitric oxide
production. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:83–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brito PM, Devillard R, Nègre-Salvayre A,
Almeida LM, Dinis TC, Salvayre R and Augé N: Resveratrol inhibits
the mTOR mitogenic signaling evoked by oxidized LDL in smooth
muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 205:126–134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo R, Li W, Liu B, Li S, Zhang B and Xu
Y: Resveratrol protects vascular smooth muscle cells against high
glucose-induced oxidative stress and cell proliferation in vitro.
Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 20:82–92. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang GX, Zhao XY, Meng ZX, Kern M,
Dietrich A, Chen Z, Cozacov Z, Zhou D, Okunade AL, Su X, et al: The
brown fat-enriched secreted factor Nrg4 preserves metabolic
homeostasis through attenuation of hepatic lipogenesis. Nat Med.
20:1436–1443. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang J, Chen J, Yang J, Xu CW, Pu P, Ding
JW and Jiang H: Resveratrol attenuates oxidative stress induced by
balloon injury in the rat carotid artery through actions on the
ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:230–241.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Breen DM, Dolinsky VW, Zhang H, Ghanim H,
Guo J, Mroziewicz M, Tsiani EL, Bendeck MP, Dandona P, Dyck JR, et
al: Resveratrol inhibits neointimal formation after arterial injury
through an endothelial nitric oxide synthase-dependent mechanism.
Atherosclerosis. 222:375–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fujisawa H: Regulation of the activities
of multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. J
Biochem. 129:193–199. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li H, Li W, Gupta AK, Mohler PJ, Anderson
ME and Grumbach IM: Calmodulin kinase II is required for
angiotensin II-mediated vascular smooth muscle hypertrophy. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 298:H688–H698. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
House SJ, Ginnan RG, Armstrong SE and
Singer HA: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-delta
isoform regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C2276–C2287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mercure MZ, Ginnan R and Singer HA: CaM
kinase II delta2-dependent regulation of vascular smooth muscle
cell polarization and migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
294:C1465–C1475. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li W, Li H, Sanders PN, Mohler PJ, Backs
J, Olson EN, Anderson ME and Grumbach IM: The multifunctional
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II delta (CaMKIIdelta) controls
neointima formation after carotid ligation and vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation through cell cycle regulation by p21. J
Biol Chem. 286:7990–7999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
House SJ and Singer HA: CaMKII-delta
isoform regulation of neointima formation after vascular injury.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:441–447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YH, Kim YS, Kang SS, Cho GJ and Choi
WS: Resveratrol inhibits neuronal apoptosis and elevated
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity in diabetic
mouse retina. Diabetes. 59:1825–1835. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong Q, Wu Z, Li X, Yan J, Zhao L, Yang C,
Lu J, Deng J and Chen M: Resveratrol ameliorates cardiac
dysfunction induced by pressure overload in rats via structural
protection and modulation of Ca(2+) cycling proteins. J Transl Med.
12:3232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Usui T, Morita T, Okada M and Yamawaki H:
Histone deacetylase 4 controls neointimal hyperplasia via
stimulating proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle
cells. Hypertension. 63:397–403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li C, Cai X, Sun H, Bai T, Zheng X, Zhou
XW, Chen X, Gill DL, Li J and Tang XD: The δA isoform of calmodulin
kinase II mediates pathological cardiac hypertrophy by interfering
with the HDAC4-MEF2 signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
409:125–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han M, Wen JK, Zheng B, Liu Z and Chen Y:
Blockade of integrin beta3-FAK signaling pathway activated by
osteopontin inhibits neointimal formation after balloon injury.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 16:283–290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu C, Chen J, Zhang J, Hu X, Zhou X, Lu Z
and Jiang H: Naringenin inhibits angiotensin II-induced vascular
smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration and decreases
neointimal hyperplasia in balloon injured rat carotid arteries
through suppressing oxidative stress. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:1549–1555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang J, Chen J, Xu C, Yang J, Guo Q, Hu Q
and Jiang H: Resveratrol inhibits phenotypic switching of
neointimal vascular smooth muscle cells after balloon injury
through blockade of Notch pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
63:233–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weber H, Taylor DS and Molloy CJ:
Angiotensin II induces delayed mitogenesis and cellular
proliferation in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Correlation with
the expression of specific endogenous growth factors and reversal
by suramin. J Clin Invest. 93:788–798. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kohno M, Ohmori K, Nozaki S, Mizushige K,
Yasunari K, Kano H, Minami M and Yoshikawa J: Effects of valsartan
on angiotensin II-induced migration of human coronary artery smooth
muscle cells. Hypertens Res. 23:677–681. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong X, Yu LG, Sun R, Cheng YN, Cao H,
Yang KM, Dong YN, Wu Y and Guo XL: Inhibition of PTEN expression
and activity by angiotensin II induces proliferation and migration
of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biochem. 114:174–182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zghonda N, Yoshida S, Araki M, Kusunoki M,
Mliki A, Ghorbel A and Miyazaki H: Greater effectiveness of
ε-viniferin in red wine than its monomer resveratrol for inhibiting
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 75:1259–1267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|