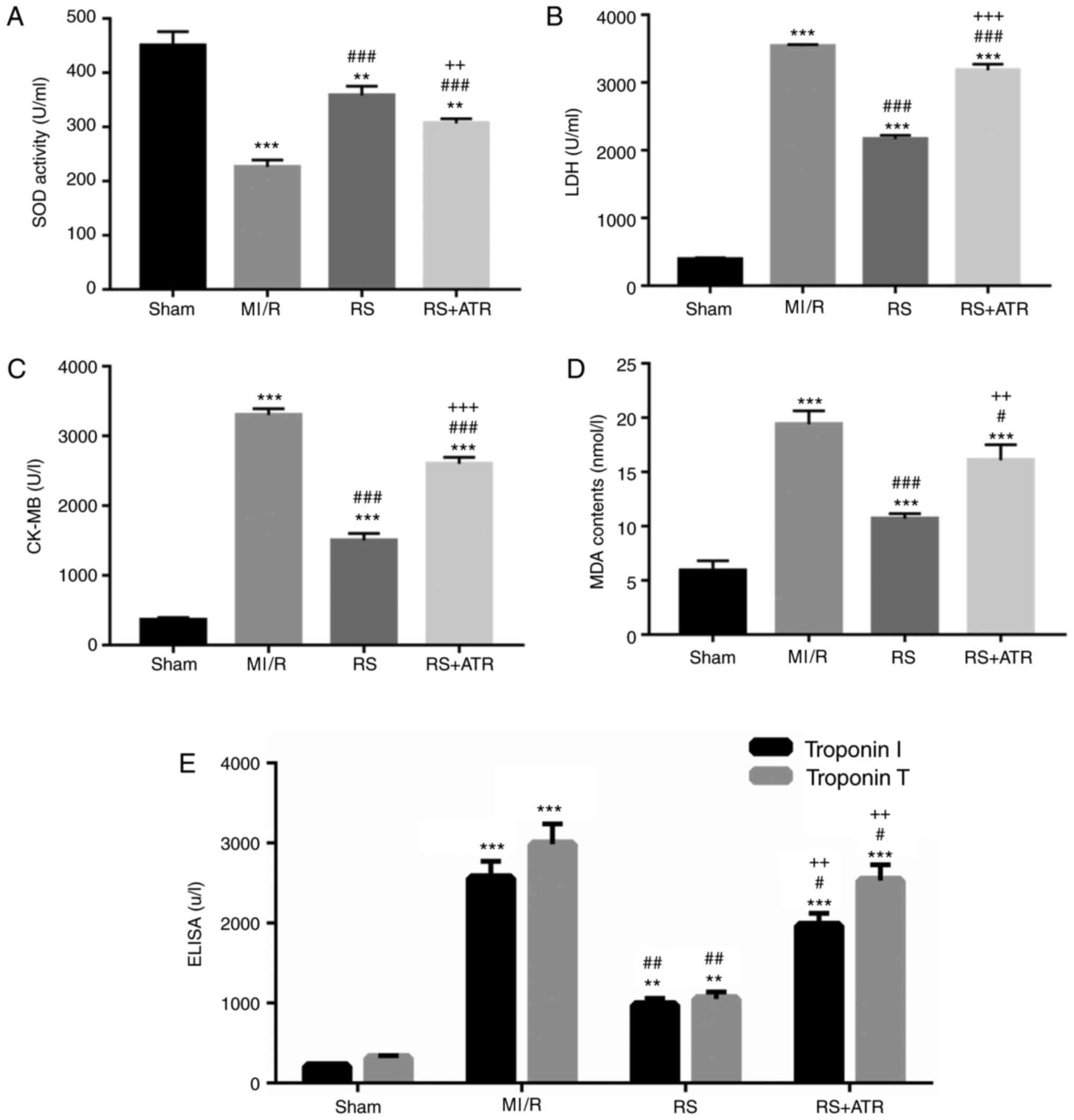
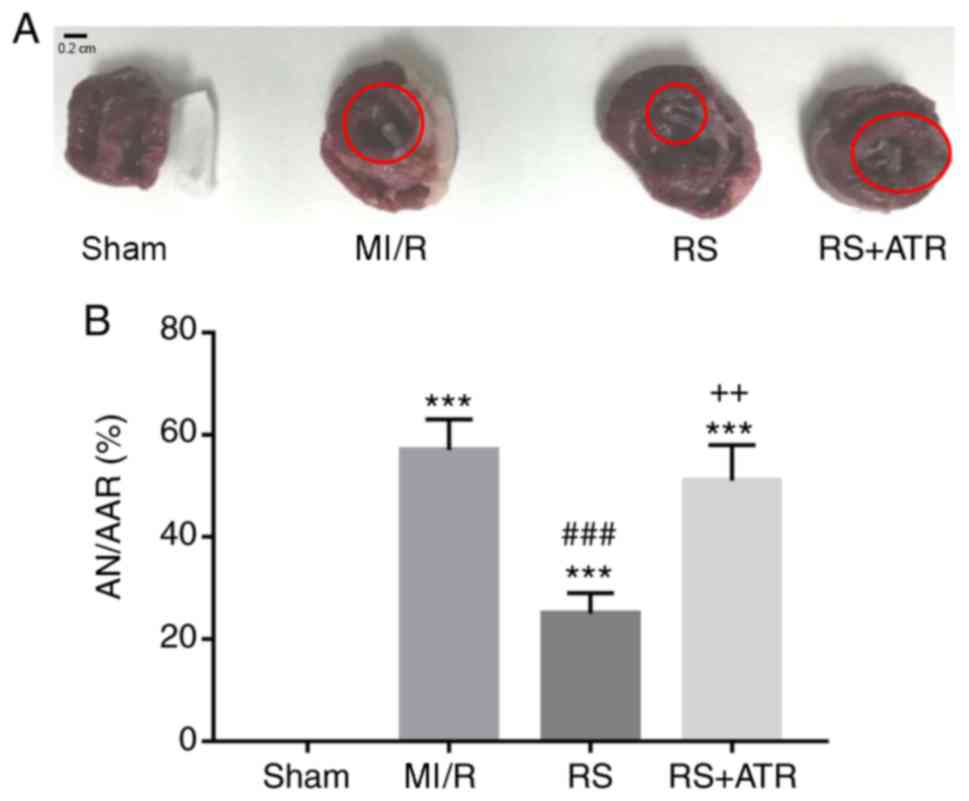
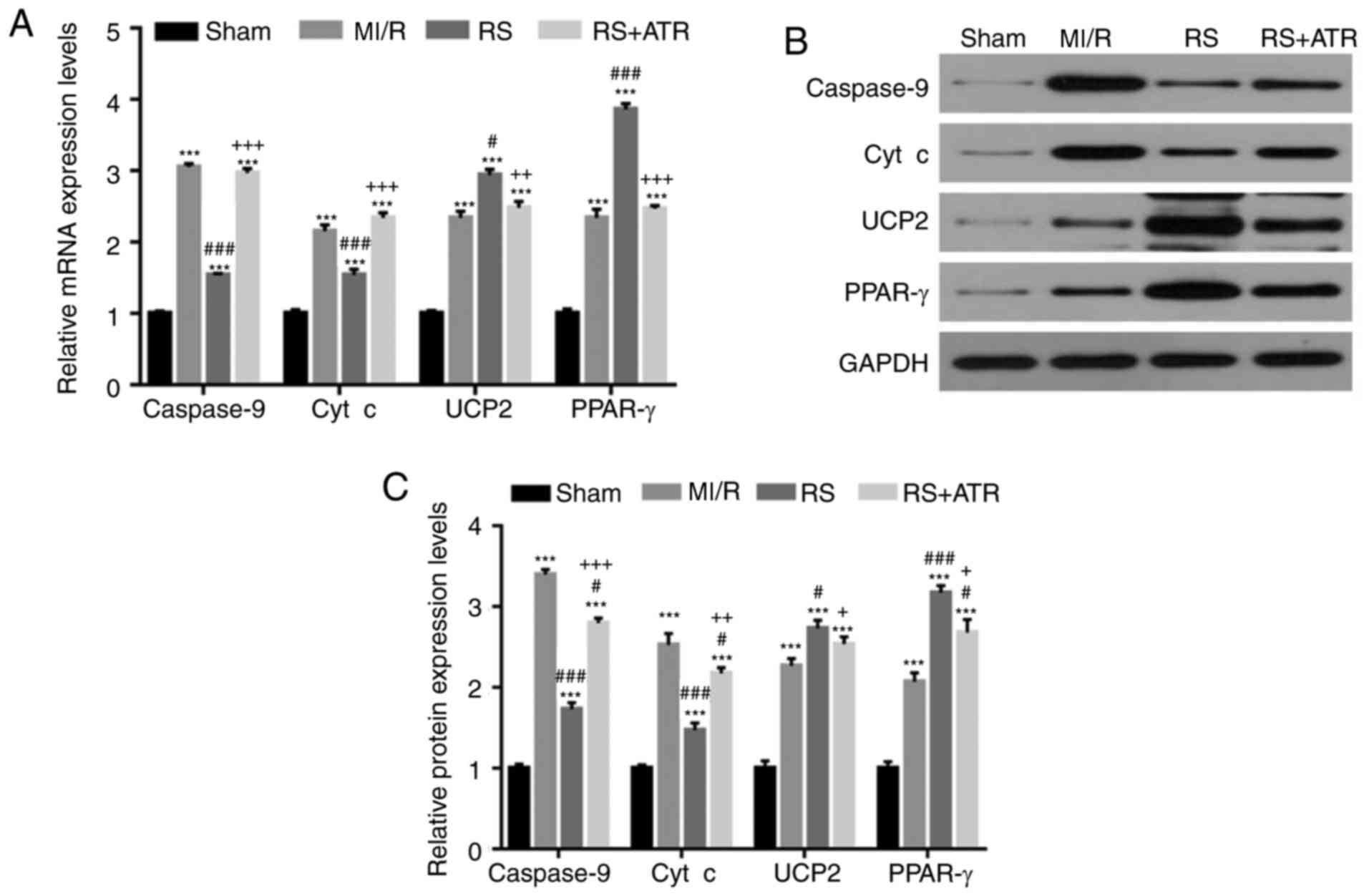
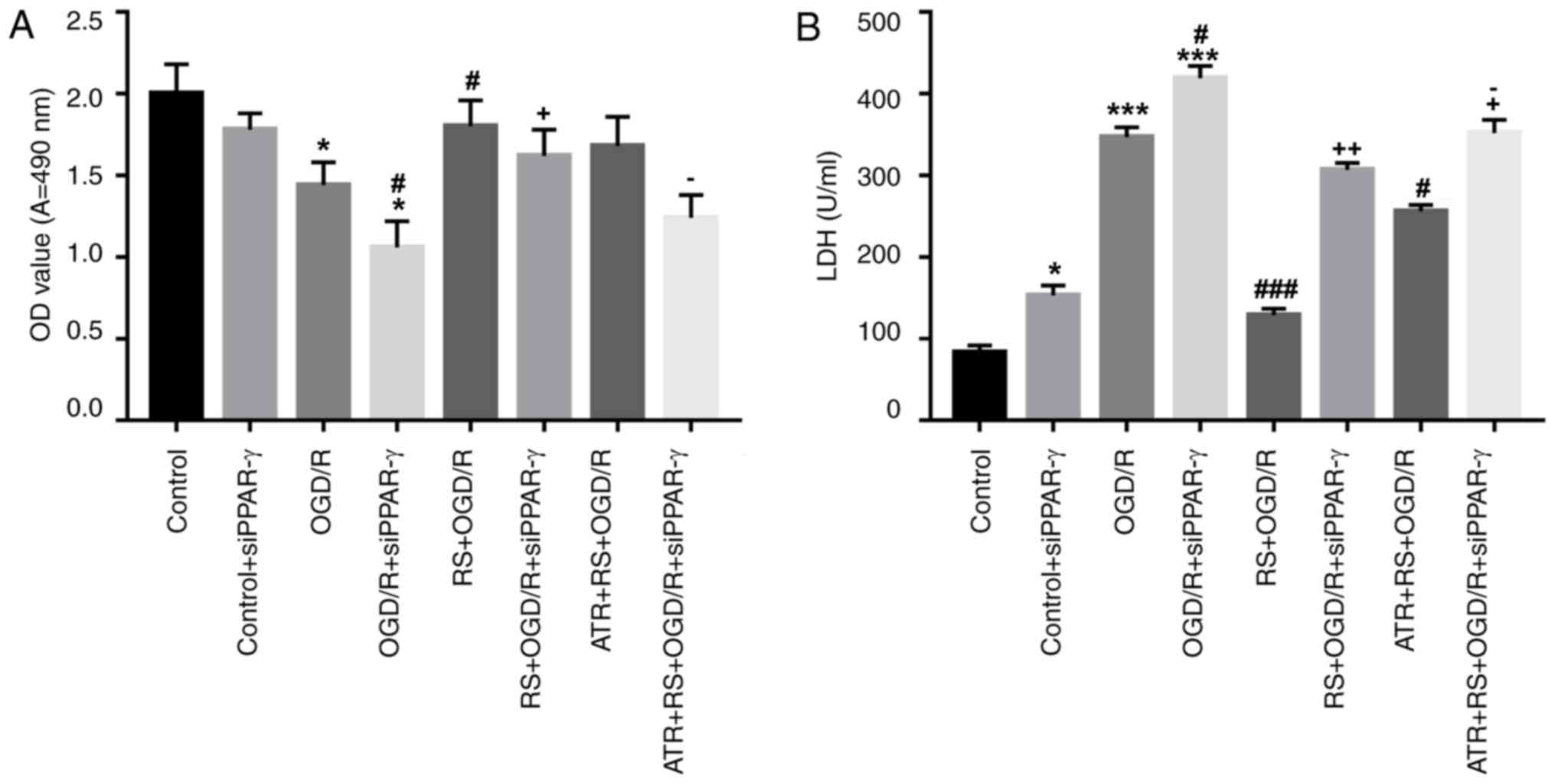
|
1
|
Cheng TO: Coronary arteriosclerotic
disease existed in China over 2,200 years ago. Methodist Debakey
Cardiovasc J. 8:47–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Libby P, Tabas I, Fredman G and Fisher EA:
Inflammation and its resolution as determinants of acute coronary
syndromes. Circ Res. 114:1867–1879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma P, Han L, Lv Z, Chen W, Hu H, Tu J,
Zhou X and Liu SM: In-hospital free fatty acids levels predict the
severity of myocardial ischemia of acute coronary syndrome. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 16:292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arnold JR, Karamitsos TD, van Gaal WJ,
Testa L, Francis JM, Bhamra-Ariza P, Ali A, Selvanayagam JB,
Westaby S, Sayeed R, et al: Residual ischemia after
revascularization in multivessel coronary artery disease: Insights
from measurement of absolute myocardial blood flow using magnetic
resonance imaging compared with angiographic assessment. Circ
Cardiovasc Interv. 6:237–245. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Torosoff MT, Sidhu MS and Boden WE: Impact
of myocardial ischemia on myocardial revascularization in stable
ischemic heart disease. Lessons from the COURAGE and FAME 2 trials.
Herz. 38:382–386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neto Frias CA, Koike MK, Saad KR, Saad PF
and Montero EF: Effects of ischemic preconditioning and cilostazol
on muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 29
Suppl 3:S17–S21. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Halladin NL: Oxidative and inflammatory
biomarkers of ischemia and reperfusion injuries. Dan Med J.
62:B50542015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hermida N and Balligand JL: Low-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol-induced endothelial dysfunction and
oxidative stress: The role of statins. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:1216–1237. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kosmas CE, Alkhawam H, El-Hunjul M, Wagman
G, Kahn MR, Grady KM and Vittorio TJ: Statin-mediated low-density
lipoprotein lowering in chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Med
Sci. 347:14–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barone E, Di Domenico F and Butterfield
DA: Statins more than cholesterol lowering agents in Alzheimer
disease: Their pleiotropic functions as potential therapeutic
targets. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:605–616. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gazzerro P, Proto MC, Gangemi G, Malfitano
AM, Ciaglia E, Pisanti S, Santoro A, Laezza C and Bifulco M:
Pharmacological actions of statins: A critical appraisal in the
management of cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 64:102–146. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kamada A, Yoshikawa Y, Domae E, Goda S,
Okazaki J, Kawamoto A, Komasa Y and Ikeo T: Effect of statin on
synthesis of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and extracellular matrix
in human osteosarcoma cells. J Osaka Odontolo Soc. 67:2004.
|
|
13
|
Adams SP, Sekhon SS and Wright JM:
Lipid-lowering efficacy of rosuvastatin. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev: CD010254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Robertsen I, Asberg A, Granseth T, Vethe
NT, Akhlaghi F, Ghareeb M, Molden E, Reier-Nilsen M, Holdaas H and
Midtvedt K: More potent lipid-lowering effect by rosuvastatin
compared with fluvastatin in everolimus-treated renal transplant
recipients. Transplantation. 97:1266–1271. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen K, Li D, Zhang X, Hermonat PL and
Mehta JL: Anoxia-reoxygenation stimulates collagen type-I and MMP-1
expression in cardiac fibroblasts: Modulation by the PPAR-gamma
ligand pioglitazone. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 44:682–687. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shao X, Wang M, Wei X, Deng S, Fu N, Peng
Q, Jiang Y, Ye L, Xie J and Lin Y: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ: Master regulator of adipogenesis
and obesity. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 11:282–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma T, Ma ZQ, Du XH, Yu QS, Wang R and Liu
L: Effect of valsartan on ACAT-1 and PPAR-γ expression in intima
with carotid artery endothelial balloon injury in rabbit. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:5527–5533. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Balaji Prathab S, Chand Vijay C, Justin A
and Ramanathan M: Telmisartan mediates anti-inflammatory and not
cognitive function through PPAR-γ agonism via SARM and MyD88
signaling. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 137:60–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jin H, Gebska MA, Blokhin IO, Wilson KM,
Ketsawatsomkron P, Chauhan AK, Keen HL, Sigmund CD and Lentz SR:
Endothelial PPAR-γ protects against vascular thrombosis by
downregulating P-selectin expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 35:838–844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boss O, Muzzin P and Giacobino JP: The
uncoupling proteins, a review. Eur J Endocrinol. 139:1–9. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Marchi U, Castelbou C and Demaurex N:
Uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3) modulates the activity of
Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) by decreasing
mitochondrial ATP production. J Biol Chem. 286:32533–32541. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ozcan C, Palmeri M, Horvath TL, Russell KS
and Russell RR III: Role of uncoupling protein 3 in
ischemia-reperfusion injury, arrhythmias and preconditioning. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1192–H1200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Gong J, Liu X, Zhan R, Kong R,
Zhao Y, Wan D, Leng X, Chen M and Qian L: Expression of uncoupling
protein 3 in mitochondria protects against stress-induced
myocardial injury: A proteomic study. Cell Stress Chaperones.
15:771–779. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoerter J, Gonzalez-Barroso MD, Couplan E,
Mateo P, Gelly C, Cassard-Doulcier AM, Diolez P and Bouillaud F:
Mitochondrial uncoupling protein 1 expressed in the heart of
transgenic mice protects against ischemic-reperfusion damage.
Circulation. 110:528–533. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen GG, Yan JB, Wang XM, Zheng MZ, Jiang
JP, Zhou XM, Cai B and Shen YL: Mechanism of uncoupling protein 2
mediated myocardial injury in hypothermic preserved rat hearts. Mol
Med Rep. 14:1857–1864. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ji XB, Li XR, Hao-Ding, Sun Q, Zhou Y, Wen
P, Dai CS and Yang JW: Inhibition of uncoupling protein 2
attenuates cardiac hypertrophy induced by transverse aortic
constriction in mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1688–1698. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Villarroya F, Iglesias R and Giralt M:
PPARs in the control of uncoupling proteins gene expression. PPAR
Res. 2007:743642007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oberkofler H, Klein K, Felder TK, Krempler
F and Patsch W: Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha in the transcriptional regulation
of the human uncoupling protein 2 gene in INS-1E cells.
Endocrinology. 147:966–976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sachdeva J, Dai W, Gerczuk PZ and Kloner
RA: Combined remote perconditioning and postconditioning failed to
attenuate infarct size and contractile dysfunction in a rat model
of coronary artery occlusion. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther.
19:567–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Yin J, Lu Z, Zhang G, Li J, Xing
T, Zhuang S and Wang N: Limb ischemic preconditioning protects
against contrast-induced nephropathy via renalase. EBioMedicine.
9:356–365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang F, Zhang G, Lu Z, Geurts AM, Usa K,
Jacob HJ, Cowley AW, Wang N and Liang M: Antithrombin III/SerpinC1
insufficiency exacerbates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney
Int. 88:796–803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rutering J, Ilmer M, Recio A, Coleman M,
Vykoukal J and Alt E: Improved method for isolation of neonatal rat
cardiomyocytes with increased Yield of C-Kit+ cardiac progenitor
cells. J Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:1–8. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tao L, Bei Y, Li Y and Xiao J: Neonatal
Rat Cardiomyocytes isolation, culture and determination of
MicroRNAs' effects in proliferation. Methods Mol Biol.
1733:203–213. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dalen JE, Alpert JS, Goldberg RJ and
Weinstein RS: The epidemic of the 20 (th) century: Coronary heart
disease. Am J Med. 127:807–812. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Faxon DP and Williams DO: Interventional
cardiology: Current status and future directions in coronary
disease and valvular heart disease. Circulation. 133:2697–2711.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Karu I, Tähepõld P, Ruusalepp A and
Starkopf J: Pretreatment by hyperoxia-a tool to reduce
ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the myocardium. Curr Clin
Pharmacol. 5:125–132. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ferdinandy P, Schulz R and Baxter GF:
Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning and postconditioning.
Pharmacol Rev. 59:418–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nissen SE, Tuzcu EM, Brewer HB, Sipahi I,
Nicholls SJ, Ganz P, Schoenhagen P, Waters DD, Pepine CJ, Crowe TD,
et al: Effect of ACAT inhibition on the progression of coronary
atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 354:1253–1263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao XJ, Liu XL, He GX and Xu HP: Effects
of single-dose atorvastatin on interleukin-6, interferon gamma and
myocardial no-reflow in a rabbit model of acute myocardial
infarction and reperfusion. Braz J Med Biol Res. 47:245–251. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao ZG, Tang ZZ, Zhang WK and Li JG:
Protective effects of embelin on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury following cardiac arrest in a rabbit model. Inflammation.
38:527–533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao ZQ: Oxidative stress-elicited
myocardial apoptosis during reperfusion. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
4:159–165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao K, Zhao GM, Wu D, Soong Y, Birk AV,
Schiller PW and Szeto HH: Cell-permeable peptide antioxidants
targeted to inner mitochondrial membrane inhibit mitochondrial
swelling, oxidative cell death and reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem.
279:34682–34690. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ding WX, Shen HM and Ong CN: Pivotal role
of mitochondrial Ca (2+) in microcystin-induced mitochondrial
permeability transition in rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 285:1155–1161. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A and Levi-Schaffer F:
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.
Apoptosis. 5:415–418. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Skemiene K, Rakauskaite G, Trumbeckaite S,
Liobikas J, Brown GC and Borutaite V: Anthocyanins block
ischemia-induced apoptosis in the perfused heart and support
mitochondrial respiration potentially by reducing cytosolic
cytochrome c. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:23–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu X, Zhang K, Wang Q, Chen S, Gou Y, Cui
Y and Li Q: Cisplatin-mediated c-myc overexpression and cytochrome
c (cyt release result in the up-regulation of the death receptors
DR4 and DR5 and the activation of caspase 3 and caspase 9, likely
responsible for the TRAIL-sensitizing effect of cisplatin. Med
Oncol. 32:1332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|