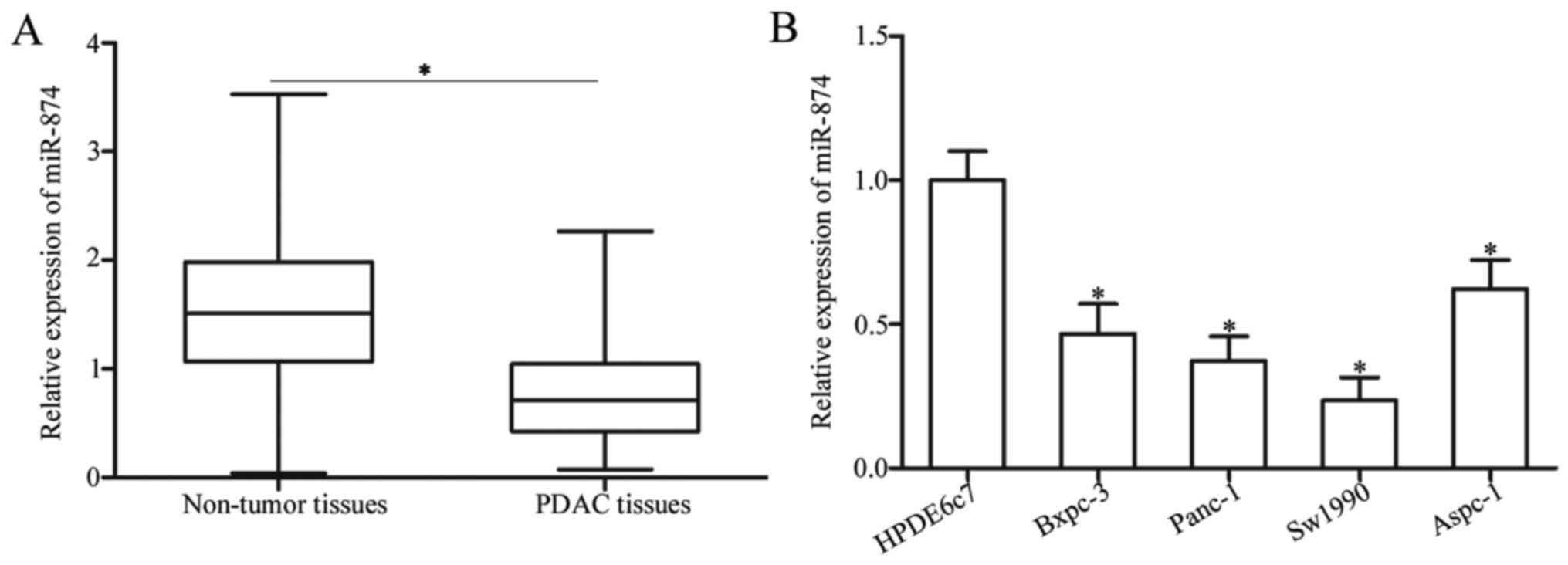
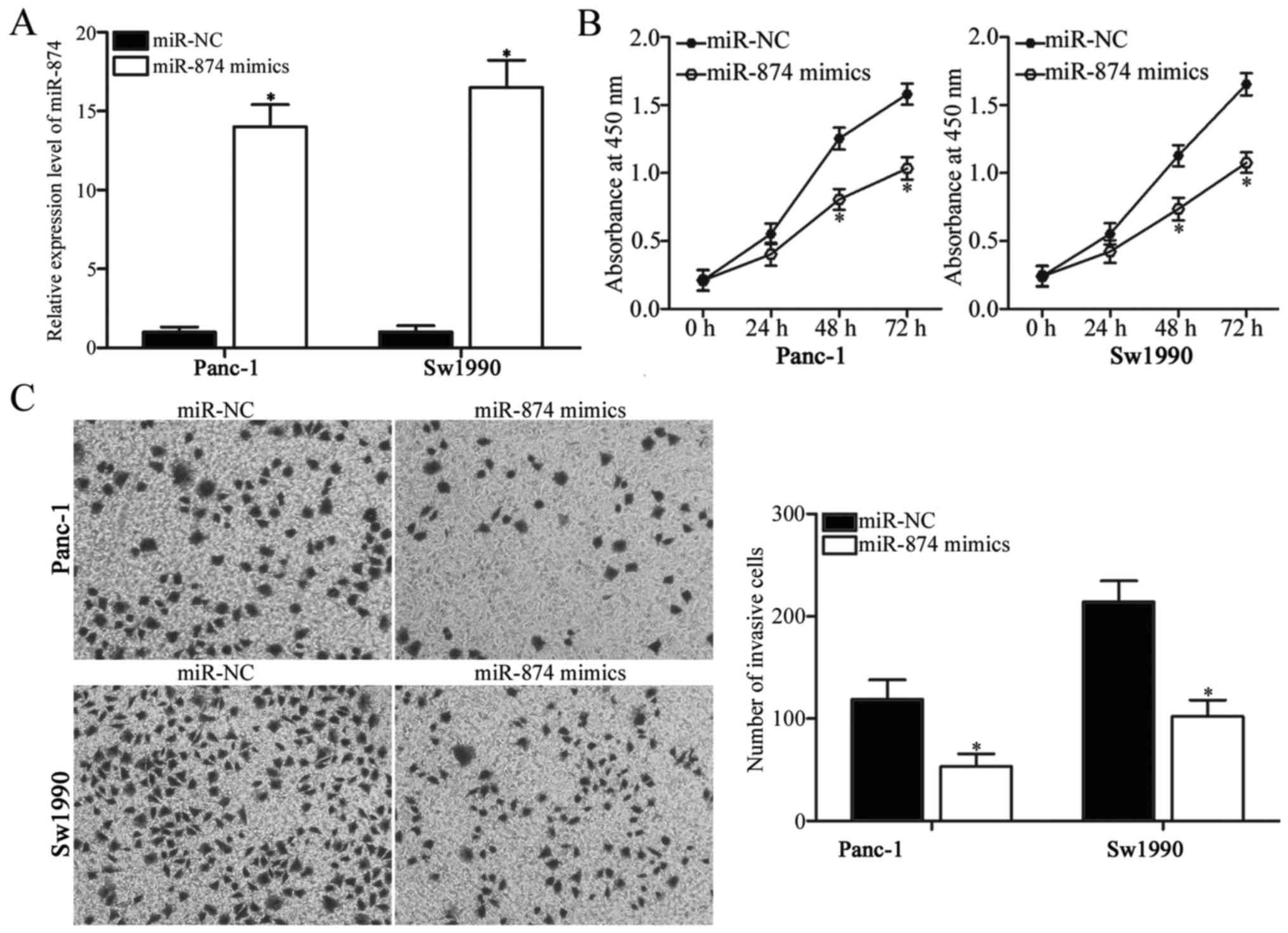
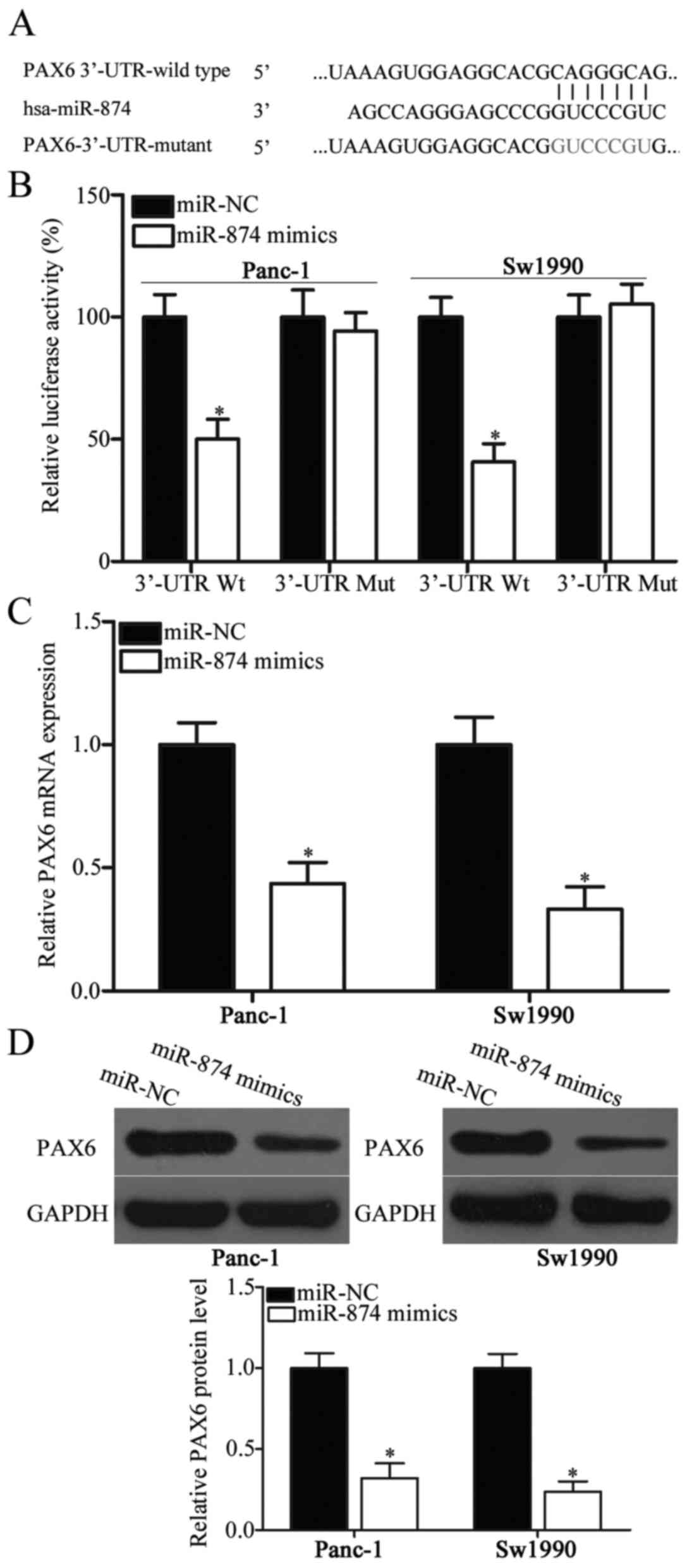
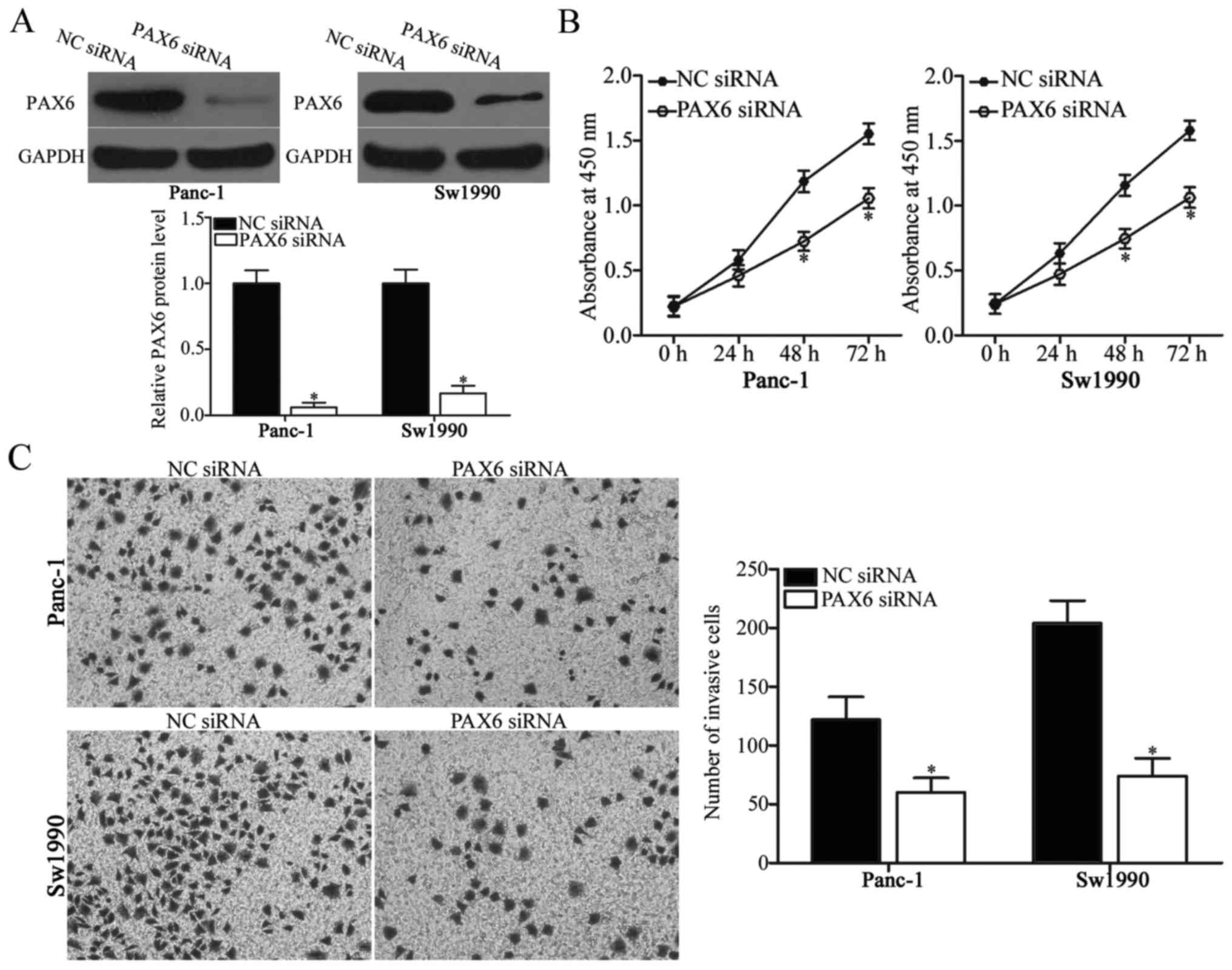
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moir J, White SA, French JJ, Littler P and
Manas DM: Systematic review of irreversible electroporation in the
treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol.
40:1598–1604. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burkey MD, Feirman S, Wang H, Choudhury
SR, Grover S and Johnston FM: The association between smokeless
tobacco use and pancreatic adenocarcinoma: A systematic review.
Cancer Epidemiol. 38:647–653. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li H, Wu Y and Li P: MicroRNA-452
suppresses pancreatic cancer migration and invasion by directly
targeting B-cell-specific Moloney murine leukemia virus insertion
site 1. Oncol Lett. 14:3235–3242. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Modolell I, Guarner L and Malagelada JR:
Vagaries of clinical presentation of pancreatic and biliary tract
cancer. Ann Oncol. 10 Suppl 4:S82–S84. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ryan DP, Hong TS and Bardeesy N:
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:1039–1049. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arslan C and Yalcin S: Current and future
systemic treatment options in metastatic pancreatic cancer. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 5:280–295. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lytle JR, Yario TA and Steitz JA: Target
mRNAs are repressed as efficiently by microRNA-binding sites in the
5′ UTR as in the 3′ UTR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9667–9672.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M
and Croce CM: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at
fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin S and Gregory RI: MicroRNA biogenesis
pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:321–333. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davis-Dusenbery BN and Hata A: MicroRNA in
cancer: The Involvement of Aberrant MicroRNA biogenesis regulatory
pathways. Genes Cancer. 1:1100–1114. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xia SS, Zhang GJ, Liu ZL, Tian HP, He Y,
Meng CY, Li LF, Wang ZW and Zhou T: MicroRNA-22 suppresses the
growth, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through a
Sp1 negative feedback loop. Oncotarget. 8:36266–36278. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gregory RI and Shiekhattar R: MicroRNA
biogenesis and cancer. Cancer Res. 65:3509–3512. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Babashah S and Soleimani M: The oncogenic
and tumour suppressive roles of microRNAs in cancer and apoptosis.
Eur J Cancer. 47:1127–1137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Gao W, Hu F, Xu Z and Wang F:
MicroRNA-874 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in
human breast cancer by targeting CDK9. FEBS Lett. 588:4527–4535.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Sakurai
D, Fujimura L, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, Yoshino H, Enokida H,
Nakagawa M, et al: Tumour suppressive microRNA-874 regulates novel
cancer networks in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 105:833–841. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T, Inamine
A, Kikkawa N, Itesako T, Yoshino H, Enokida H, Nakagawa M, Okamoto
Y and Seki N: Tumour-suppressive microRNA-874 contributes to cell
proliferation through targeting of histone deacetylase 1 in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 108:1648–1658. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kesanakurti D, Maddirela DR, Chittivelu S,
Rao JS and Chetty C: Suppression of tumor cell invasiveness and in
vivo tumor growth by microRNA-874 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 434:627–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mascarenhas JB, Young KP, Littlejohn EL,
Yoo BK, Salgia R and Lang D: PAX6 is expressed in pancreatic cancer
and actively participates in cancer progression through activation
of the MET tyrosine kinase receptor gene. J Biol Chem.
284:27524–27532. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yonemori K, Seki N, Idichi T, Kurahara H,
Osako Y, Koshizuka K, Arai T, Okato A, Kita Y, Arigami T, et al:
The microRNA expression signature of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma by RNA sequencing: Anti-tumour functions of the
microRNA-216 cluster. Oncotarget. 8:70097–70115. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Karamitopoulou E, Haemmig S, Baumgartner
U, Schlup C, Wartenberg M and Vassella E: MicroRNA dysregulation in
the tumor microenvironment influences the phenotype of pancreatic
cancer. Mod Pathol. 30:1116–1125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kanno S, Nosho K, Ishigami K, Yamamoto I,
Koide H, Kurihara H, Mitsuhashi K, Shitani M, Motoya M, Sasaki S,
et al: MicroRNA-196b is an independent prognostic biomarker in
patients with pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis. 38:425–431. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong D, Gong Y, Zhang D, Bao H and Gu G:
miR-874 suppresses the proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma
by targeting E2F3. Tumour Biol. 37:6447–6455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han J, Liu Z, Wang N and Pan W:
MicroRNA-874 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis and reverses
chemoresistance in colorectal cancer by targeting X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Oncol Rep. 36:542–550. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao B and Dong AS: MiR-874 inhibits cell
growth and induces apoptosis by targeting STAT3 in human colorectal
cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:269–277.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Que K, Tong Y, Que G, Li L, Lin H, Huang
S, Wang R and Tang L: Downregulation of miR-874-3p promotes
chemotherapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer via inactivation
of the Hippo signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 38:3376–3386.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leong KW, Cheng CW, Wong CM, Ng IO, Kwong
YL and Tse E: miR-874-3p is down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma and negatively regulates PIN1 expression. Oncotarget.
8:11343–11355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang T, Guan LY, Ye YS, Liu HY and Li R:
MiR-874 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SOX12. Am J Cancer Res.
7:1310–1321. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang B, Li Z, Zhang W, Wang H, Zhi X,
Feng J, Chen Z, Zhu Y, Yang L, Xu H and Xu Z: miR-874 Inhibits cell
proliferation, migration and invasion through targeting aquaporin-3
in gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 49:1011–1025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ghosh T, Varshney A, Kumar P, Kaur M,
Kumar V, Shekhar R, Devi R, Priyanka P, Khan MM and Saxena S:
MicroRNA-874 mediated inhibition of the major G1/S phase cyclin,
CCNE1 is lost in osteosarcomas. J Biol Chem. 292:21264–21281. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang X, Tang J, Zhi X, Xie K, Wang W, Li
Z, Zhu Y, Yang L, Xu H and Xu Z: miR-874 functions as a tumor
suppressor by inhibiting angiogenesis through STAT3/VEGF-A pathway
in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 6:1605–1617. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Georgala PA, Carr CB and Price DJ: The
role of Pax6 in forebrain development. Dev Neurobiol. 71:690–709.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hanson IM: PAX6 and congenital eye
malformations. Pediatr Res. 54:791–796. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Li Y, Liu Y, Xie P, Li F and Li G:
PAX6, a novel target of microRNA-7, promotes cellular proliferation
and invasion in human colorectal cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci.
59:598–606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li X, Yang L, Shuai T, Piao T and Wang R:
MiR-433 inhibits retinoblastoma malignancy by suppressing Notch1
and PAX6 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 82:247–255. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xia X, Yin W, Zhang X, Yu X, Wang C, Xu S,
Feng W and Yang H: PAX6 overexpression is associated with the poor
prognosis of invasive ductal breast cancer. Oncol Lett.
10:1501–1506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao X, Yue W, Zhang L, Ma L, Jia W, Qian
Z, Zhang C and Wang Y: Downregulation of PAX6 by shRNA inhibits
proliferation and cell cycle progression of human non-small cell
lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e857382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zou Q, Yi W, Huang J, Fu F, Chen G and
Zhong D: MicroRNA-375 targets PAX6 and inhibits the viability,
migration and invasion of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Exp Ther
Med. 14:1198–1204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|